Species Present After Fire by Family
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Cambodian Journal of Natural History
Cambodian Journal of Natural History Artisanal Fisheries Tiger Beetles & Herpetofauna Coral Reefs & Seagrass Meadows June 2019 Vol. 2019 No. 1 Cambodian Journal of Natural History Editors Email: [email protected], [email protected] • Dr Neil M. Furey, Chief Editor, Fauna & Flora International, Cambodia. • Dr Jenny C. Daltry, Senior Conservation Biologist, Fauna & Flora International, UK. • Dr Nicholas J. Souter, Mekong Case Study Manager, Conservation International, Cambodia. • Dr Ith Saveng, Project Manager, University Capacity Building Project, Fauna & Flora International, Cambodia. International Editorial Board • Dr Alison Behie, Australia National University, • Dr Keo Omaliss, Forestry Administration, Cambodia. Australia. • Ms Meas Seanghun, Royal University of Phnom Penh, • Dr Stephen J. Browne, Fauna & Flora International, Cambodia. UK. • Dr Ou Chouly, Virginia Polytechnic Institute and State • Dr Chet Chealy, Royal University of Phnom Penh, University, USA. Cambodia. • Dr Nophea Sasaki, Asian Institute of Technology, • Mr Chhin Sophea, Ministry of Environment, Cambodia. Thailand. • Dr Martin Fisher, Editor of Oryx – The International • Dr Sok Serey, Royal University of Phnom Penh, Journal of Conservation, UK. Cambodia. • Dr Thomas N.E. Gray, Wildlife Alliance, Cambodia. • Dr Bryan L. Stuart, North Carolina Museum of Natural Sciences, USA. • Mr Khou Eang Hourt, National Authority for Preah Vihear, Cambodia. • Dr Sor Ratha, Ghent University, Belgium. Cover image: Chinese water dragon Physignathus cocincinus (© Jeremy Holden). The occurrence of this species and other herpetofauna in Phnom Kulen National Park is described in this issue by Geissler et al. (pages 40–63). News 1 News Save Cambodia’s Wildlife launches new project to New Master of Science in protect forest and biodiversity Sustainable Agriculture in Cambodia Agriculture forms the backbone of the Cambodian Between January 2019 and December 2022, Save Cambo- economy and is a priority sector in government policy. -

Hydrodictyon Reticulatum) in Lake Aniwhenua, New Zealand
WELLS, CLAYTON: IMPACTS OF WATER NET 55 Ecological impacts of water net (Hydrodictyon reticulatum) in Lake Aniwhenua, New Zealand Rohan D. S. Wells and John S. Clayton National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research, P.O. Box 11 115, Hamilton, New Zealand (E-mail: [email protected]) Abstract: The ecological impacts of Hydrodictyon reticulatum blooms (1989-94) were studied at Lake Aniwhenua (a constructed lake) in North Island, New Zealand by collating fish, invertebrate and macrophyte data collected towards the end of a four year bloom period and following its decline. Hydrodictyon reticulatum had some localised impacts on the biota of the lake. Some macrophyte beds were smothered to the extent that they collapsed and disappeared, and dense compacted accumulations of H. reticulatum caused localised anoxic conditions while it decayed. However, fish and some invertebrates in the lake benefited from the H. reticulatum blooms. High numbers of Ceriodaphnia sp. (maximum, 5.5 x 104 m-2) were recorded amongst H. reticulatum, and gastropods were exceptionally abundant, the most common being Potamopyrgus antipodarum (maximum, 1.8 x IOS m-2). Hydrodictyon reticulatum was consumed by three species of common gastropods in experimental trials, with Austropeplea tomentosa consuming up to 1.3 g dry weight H. reticulatum g-1,live weight of snail day-1. Gastropods comprised the major portion of the diet of Oncorhynchus mykiss in Lake Aniwhenua during and after the H. reticulatum bloom. A marked peak in sports fishing (with exceptional sizes and numbers of fish caught) coincided with the period of H. reticulatum blooms and the abundant invertebrate food source associated with the blooms. -

Report-VIC-Croajingolong National Park-Appendix A
Croajingolong National Park, Victoria, 2016 Appendix A: Fauna species lists Family Species Common name Mammals Acrobatidae Acrobates pygmaeus Feathertail Glider Balaenopteriae Megaptera novaeangliae # ~ Humpback Whale Burramyidae Cercartetus nanus ~ Eastern Pygmy Possum Canidae Vulpes vulpes ^ Fox Cervidae Cervus unicolor ^ Sambar Deer Dasyuridae Antechinus agilis Agile Antechinus Dasyuridae Antechinus mimetes Dusky Antechinus Dasyuridae Sminthopsis leucopus White-footed Dunnart Felidae Felis catus ^ Cat Leporidae Oryctolagus cuniculus ^ Rabbit Macropodidae Macropus giganteus Eastern Grey Kangaroo Macropodidae Macropus rufogriseus Red Necked Wallaby Macropodidae Wallabia bicolor Swamp Wallaby Miniopteridae Miniopterus schreibersii oceanensis ~ Eastern Bent-wing Bat Muridae Hydromys chrysogaster Water Rat Muridae Mus musculus ^ House Mouse Muridae Rattus fuscipes Bush Rat Muridae Rattus lutreolus Swamp Rat Otariidae Arctocephalus pusillus doriferus ~ Australian Fur-seal Otariidae Arctocephalus forsteri ~ New Zealand Fur Seal Peramelidae Isoodon obesulus Southern Brown Bandicoot Peramelidae Perameles nasuta Long-nosed Bandicoot Petauridae Petaurus australis Yellow Bellied Glider Petauridae Petaurus breviceps Sugar Glider Phalangeridae Trichosurus cunninghami Mountain Brushtail Possum Phalangeridae Trichosurus vulpecula Common Brushtail Possum Phascolarctidae Phascolarctos cinereus Koala Potoroidae Potorous sp. # ~ Long-nosed or Long-footed Potoroo Pseudocheiridae Petauroides volans Greater Glider Pseudocheiridae Pseudocheirus peregrinus -

Assessing the Invertebrate Fauna Trajectories in Remediation Sites of Winstone Aggregates Hunua Quarry in Auckland
ISSN: 1179-7738 ISBN: 978-0-86476-417-1 Lincoln University Wildlife Management Report No. 59 Assessing the invertebrate fauna trajectories in remediation sites of Winstone Aggregates Hunua quarry in Auckland by Kate Curtis1, Mike Bowie1, Keith Barber2, Stephane Boyer3 , John Marris4 & Brian Patrick5 1Department of Ecology, Lincoln University, PO Box 85084, Lincoln 7647 2Winstone Aggregates, Hunua Gorge Road, Red Hill 2110, Auckland 3Department of Nature Sciences, Unitec Institute of Technology, PO Box 92025, Auckland 1142. 4Bio-Protection Research Centre, Lincoln University, PO Box 85084, Lincoln 7647. 5Consultant Ecologist, Wildlands, PO Box 33499, Christchurch. Prepared for: Winstone Aggregates April 2016 Table of Contents Abstract……………………………………………………………………………………....................... 2 Introduction…………………………………………………………………………………………………… 2 Methodology…………………………………………………………………………………………………. 4 Results…………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 8 Discussion……………………………………………………………………………………………………. 31 Conclusion…………………………………………………………………………………………………… 37 Recommendations………………………………………………………………………………………. 38 Acknowlegdements……………………………………………………………………………………… 38 References…………………………………………………………………………………………………… 39 Appendix……………………………………………………………………………………………………… 43 1 Abstract This study monitored the invertebrates in restoration plantings in the Winstone Aggregates Hunua Quarry. This was to assess the re-establishment of invertebrates in the restoration planting sites and compare them with unplanted control and mature sites. This study follows on from -

ARTHROPODA Subphylum Hexapoda Protura, Springtails, Diplura, and Insects
NINE Phylum ARTHROPODA SUBPHYLUM HEXAPODA Protura, springtails, Diplura, and insects ROD P. MACFARLANE, PETER A. MADDISON, IAN G. ANDREW, JOCELYN A. BERRY, PETER M. JOHNS, ROBERT J. B. HOARE, MARIE-CLAUDE LARIVIÈRE, PENELOPE GREENSLADE, ROSA C. HENDERSON, COURTenaY N. SMITHERS, RicarDO L. PALMA, JOHN B. WARD, ROBERT L. C. PILGRIM, DaVID R. TOWNS, IAN McLELLAN, DAVID A. J. TEULON, TERRY R. HITCHINGS, VICTOR F. EASTOP, NICHOLAS A. MARTIN, MURRAY J. FLETCHER, MARLON A. W. STUFKENS, PAMELA J. DALE, Daniel BURCKHARDT, THOMAS R. BUCKLEY, STEVEN A. TREWICK defining feature of the Hexapoda, as the name suggests, is six legs. Also, the body comprises a head, thorax, and abdomen. The number A of abdominal segments varies, however; there are only six in the Collembola (springtails), 9–12 in the Protura, and 10 in the Diplura, whereas in all other hexapods there are strictly 11. Insects are now regarded as comprising only those hexapods with 11 abdominal segments. Whereas crustaceans are the dominant group of arthropods in the sea, hexapods prevail on land, in numbers and biomass. Altogether, the Hexapoda constitutes the most diverse group of animals – the estimated number of described species worldwide is just over 900,000, with the beetles (order Coleoptera) comprising more than a third of these. Today, the Hexapoda is considered to contain four classes – the Insecta, and the Protura, Collembola, and Diplura. The latter three classes were formerly allied with the insect orders Archaeognatha (jumping bristletails) and Thysanura (silverfish) as the insect subclass Apterygota (‘wingless’). The Apterygota is now regarded as an artificial assemblage (Bitsch & Bitsch 2000). -

Journal of Hymenoptera Research
c 3 Journal of Hymenoptera Research . .IV 6«** Volume 15, Number 2 October 2006 ISSN #1070-9428 CONTENTS BELOKOBYLSKIJ, S. A. and K. MAETO. A new species of the genus Parachremylus Granger (Hymenoptera: Braconidae), a parasitoid of Conopomorpha lychee pests (Lepidoptera: Gracillariidae) in Thailand 181 GIBSON, G. A. P., M. W. GATES, and G. D. BUNTIN. Parasitoids (Hymenoptera: Chalcidoidea) of the cabbage seedpod weevil (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) in Georgia, USA 187 V. Forest GILES, and J. S. ASCHER. A survey of the bees of the Black Rock Preserve, New York (Hymenoptera: Apoidea) 208 GUMOVSKY, A. V. The biology and morphology of Entedon sylvestris (Hymenoptera: Eulophidae), a larval endoparasitoid of Ceutorhynchus sisymbrii (Coleoptera: Curculionidae) 232 of KULA, R. R., G. ZOLNEROWICH, and C. J. FERGUSON. Phylogenetic analysis Chaenusa sensu lato (Hymenoptera: Braconidae) using mitochondrial NADH 1 dehydrogenase gene sequences 251 QUINTERO A., D. and R. A. CAMBRA T The genus Allotilla Schuster (Hymenoptera: Mutilli- dae): phylogenetic analysis of its relationships, first description of the female and new distribution records 270 RIZZO, M. C. and B. MASSA. Parasitism and sex ratio of the bedeguar gall wasp Diplolqjis 277 rosae (L.) (Hymenoptera: Cynipidae) in Sicily (Italy) VILHELMSEN, L. and L. KROGMANN. Skeletal anatomy of the mesosoma of Palaeomymar anomalum (Blood & Kryger, 1922) (Hymenoptera: Mymarommatidae) 290 WHARTON, R. A. The species of Stenmulopius Fischer (Hymenoptera: Braconidae, Opiinae) and the braconid sternaulus 316 (Continued on back cover) INTERNATIONAL SOCIETY OF HYMENOPTERISTS Organized 1982; Incorporated 1991 OFFICERS FOR 2006 Michael E. Schauff, President James Woolley, President-Elect Michael W. Gates, Secretary Justin O. Schmidt, Treasurer Gavin R. -

Occasional Papers
NUMBER 136, 37 pages 28 August 2020 BISHOP MUSEUM OCCASIONAL PAPERS TAXONOMIC REVISION AND BIOGEOGRAPHY OF PHASSODES BETHUNE -B AKER , 1905 (L EPIDOPTERA : H EPIALIDAE ), GHOST MOTH DESCENDANTS OF A SUBDUCTION ZONE WEED IN THE SOUTH -WEST PACIFIC JOHN R. G REHAN & C ARLOS G.C. M IELKE BISHOP MUSEUM PRESS HONOLULU Cover illustration: Selection of scales from central forewing of Phassodes spp. (see page 14). Photos by James Boone, Miho Maeda, and Agnes Stubblefield. Bishop Museum Press has been publishing scholarly books on the natu - ESEARCH ral and cultural history of Hawai‘i and the Pacific since 1892. The R Bishop Museum Occasional Papers (eISSN 2376-3191) is a series of UBLICATIONS OF short papers describing original research in the natural and cultural sci - P ences. BISHOP MUSEUM The Bishop Museum Press also published the Bishop Museum Bulletin series. It was begun in 1922 as a series of monographs presenting the results of research in many scientific fields throughout the Pacific. In 1987, the Bulletin series was superceded by the Museum’s five current monographic series, issued irregularly: Bishop Museum Bulletins in Anthropology (eISSN 2376-3132) Bishop Museum Bulletins in Botany (eISSN 2376-3078) Bishop Museum Bulletins in Entomology (eISSN 2376-3124) Bishop Museum Bulletins in Zoology (eISSN 2376-3213) Bishop Museum Bulletins in Cultural and Environmental Studies (eISSN 2376-3159) To subscribe to any of the above series, or to purchase individual publi - cations, please write to: Bishop Museum Press, 1525 Bernice Street, Honolulu, Hawai‘i 96817-2704, USA. Phone: (808) 848-4135. Email: [email protected]. BERNICE PAUAHI BISHOP MUSEUM The State Museum of Natural and Cultural History eISSN 2376-3191 1525 Bernice Street Copyright © by Bishop Museum Honolulu, Hawai‘i 96817-2704, USA Published online: 28 August 2020 ISSN (online) 2376-3191 Taxonomic revision and biogeography of Phassodes Bethune-Baker, 1905 (Lepidoptera: Hepialidae), ghost moth descendants of a subduc - tion zone weed in the south-west Pacific. -

The Little Things That Run the City How Do Melbourne’S Green Spaces Support Insect Biodiversity and Promote Ecosystem Health?
The Little Things that Run the City How do Melbourne’s green spaces support insect biodiversity and promote ecosystem health? Luis Mata, Christopher D. Ives, Georgia E. Garrard, Ascelin Gordon, Anna Backstrom, Kate Cranney, Tessa R. Smith, Laura Stark, Daniel J. Bickel, Saul Cunningham, Amy K. Hahs, Dieter Hochuli, Mallik Malipatil, Melinda L Moir, Michaela Plein, Nick Porch, Linda Semeraro, Rachel Standish, Ken Walker, Peter A. Vesk, Kirsten Parris and Sarah A. Bekessy The Little Things that Run the City – How do Melbourne’s green spaces support insect biodiversity and promote ecosystem health? Report prepared for the City of Melbourne, November 2015 Coordinating authors Luis Mata Christopher D. Ives Georgia E. Garrard Ascelin Gordon Sarah Bekessy Interdisciplinary Conservation Science Research Group Centre for Urban Research School of Global, Urban and Social Studies RMIT University 124 La Trobe Street Melbourne 3000 Contributing authors Anna Backstrom, Kate Cranney, Tessa R. Smith, Laura Stark, Daniel J. Bickel, Saul Cunningham, Amy K. Hahs, Dieter Hochuli, Mallik Malipatil, Melinda L Moir, Michaela Plein, Nick Porch, Linda Semeraro, Rachel Standish, Ken Walker, Peter A. Vesk and Kirsten Parris. Cover artwork by Kate Cranney ‘Melbourne in a Minute Scavenger’ (Ink and paper on paper, 2015) This artwork is a little tribute to a minute beetle. We found the brown minute scavenger beetle (Corticaria sp.) at so many survey plots for the Little Things that Run the City project that we dubbed the species ‘Old Faithful’. I’ve recreated the map of the City of Melbourne within the beetle’s body. Can you trace the outline of Port Phillip Bay? Can you recognise the shape of your suburb? Next time you’re walking in a park or garden in the City of Melbourne, keep a keen eye out for this ubiquitous little beetle. -

Deciphering Mechanisms of Diapause Entry and Exit in the Annual Killifish Austrofundulus Limnaeus
Portland State University PDXScholar Dissertations and Theses Dissertations and Theses 4-15-2021 Connecting Environment and Phenotype: Deciphering Mechanisms of Diapause Entry and Exit in the Annual Killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus Erin Monica Davis Portland State University Follow this and additional works at: https://pdxscholar.library.pdx.edu/open_access_etds Part of the Animal Sciences Commons, and the Biology Commons Let us know how access to this document benefits ou.y Recommended Citation Davis, Erin Monica, "Connecting Environment and Phenotype: Deciphering Mechanisms of Diapause Entry and Exit in the Annual Killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus" (2021). Dissertations and Theses. Paper 5680. https://doi.org/10.15760/etd.7552 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dissertations and Theses by an authorized administrator of PDXScholar. Please contact us if we can make this document more accessible: [email protected]. Connecting Environment and Phenotype: Deciphering Mechanisms of Diapause Entry and Exit in the Annual Killifish Austrofundulus limnaeus by Erin Monica Davis A thesis submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Science in Biology Thesis Committee: Jason Podrabsky, Chair Deborah Duffield Annie Lindgren Portland State University 2021 ©2021 Erin Monica Davis ABSTRACT Embryonic development is complex, dynamic, and dependent on environmental factors. Mechanisms of sensing and integrating environmental stimuli are diverse, and understanding these mechanisms in extant species can elucidate how complex phenotypes emerge from genomic information expressed in an environmental context. In Austrofundulus limnaeus, an annual killifish with alternative developmental trajectories, light and temperature are vital factors that determine if an embryo will enter a state of diapause. -

Anicdotes • ISSUE 1 AUGUST 2012
1 ISSUE 9 • OCTOBER 2016 The official newsletter of the Australian National Insect Collection CSIRO NATIONAL FACILITIES AND COLLECTIONS www.csiro.au Welcome to our second issue of 2016 INSIDE THIS ISSUE David Yeates, Director Welcome to our second issue of 2016 ....................1 This issue has been delayed because many ANIC staff attended Coleoptera reports on a recent trip to Welcome Juanita, our new hymenopterist ............2 the International Congress of Entomology during the last week Sun Yat-sen University in Guangzhou. of September, and we wanted to include a report from the Her visit strengthens the links between Welcome Thomas, our new DAWR Liaison Officer 3 conference in this issue. Most importantly, Adam Ślipiński was the ANIC and China. Andreas Zwick was awarded the Westwood Medal in a ceremony at the Congress. invited to instruct overseas at workshops Our Chinese Students .............................................3 ANIC staff have received two of the five Westwood medals in China and Ecuador. You Ning Su A welcome to ANIC for Michael Braby and his A awarded so far, which is an incredible achievement reports on his June visit to increase Field Guide to Australian Butterflies ......................4 digital imaging capabilities in Lao PRD This issue also includes introductions for two new members and Thailand. Adam Ślipiński and Cate of staff, our new hymenopterist Dr Juanita Rodriguez, and a The International Congress of Entomology and the also hosted three Australians and one David Yeates biosecurity entomologist Thomas Wallenius. Juanita is a native Westwood Medal ...................................................5 New Zealand Entomologist for a two- of Colombia, but comes to us via PhD and postdoctoral studies week intensive training course in longicorn ANIC contributions to the International Congress in the USA. -

REPORT on APPLES – Fruit Pathway and Alert List
EU project number 613678 Strategies to develop effective, innovative and practical approaches to protect major European fruit crops from pests and pathogens Work package 1. Pathways of introduction of fruit pests and pathogens Deliverable 1.3. PART 5 - REPORT on APPLES – Fruit pathway and Alert List Partners involved: EPPO (Grousset F, Petter F, Suffert M) and JKI (Steffen K, Wilstermann A, Schrader G). This document should be cited as ‘Wistermann A, Steffen K, Grousset F, Petter F, Schrader G, Suffert M (2016) DROPSA Deliverable 1.3 Report for Apples – Fruit pathway and Alert List’. An Excel file containing supporting information is available at https://upload.eppo.int/download/107o25ccc1b2c DROPSA is funded by the European Union’s Seventh Framework Programme for research, technological development and demonstration (grant agreement no. 613678). www.dropsaproject.eu [email protected] DROPSA DELIVERABLE REPORT on Apples – Fruit pathway and Alert List 1. Introduction ................................................................................................................................................... 3 1.1 Background on apple .................................................................................................................................... 3 1.2 Data on production and trade of apple fruit ................................................................................................... 3 1.3 Pathway ‘apple fruit’ ..................................................................................................................................... -
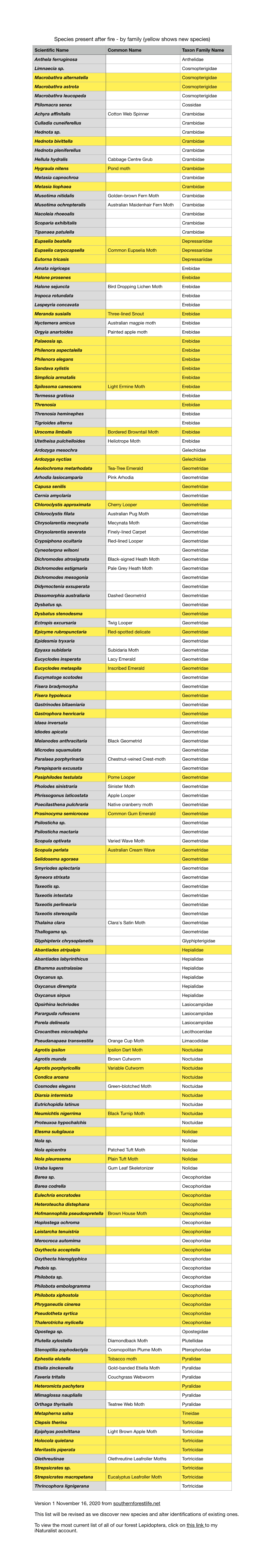
Moths Postfire to Feb16 2021 by Family
Species present after fire - by family Scientific Name Common Name Taxon Family Name Anthela acuta Common Anthelid Moth Anthelidae Anthela ferruginosa Anthelidae Anthela ocellata Eyespot Anthelid Moth Anthelidae Labdia chryselectra Cosmopterigidae Limnaecia sp. Cosmopterigidae Limnaecia camptosema Cosmopterigidae Macrobathra alternatella Cosmopterigidae Macrobathra astrota Cosmopterigidae Macrobathra leucopeda Cosmopterigidae Ptilomacra senex Cossidae Achyra affinitalis Cotton Web Spinner Crambidae Culladia cuneiferellus Crambidae Eudonia aphrodes Crambidae Hednota sp. Crambidae Hednota bivittella Crambidae Hednota pleniferellus Crambidae Heliothela ophideresana Crambidae Hellula hydralis cabbage centre grub Crambidae Hygraula nitens Pond moth Crambidae Metasia capnochroa Crambidae Metasia dicealis Crambidae Metasia liophaea Crambidae Musotima nitidalis Golden-brown Fern Moth Crambidae Musotima ochropteralis Australian maidenhair fern moth Crambidae Nacoleia oncophragma Crambidae Nacoleia rhoeoalis Crambidae Scoparia chiasta Crambidae Scoparia emmetropis Crambidae Scoparia exhibitalis Crambidae Scopariinae Moss-eating Crambid Snout Moths Crambidae Tipanaea patulella White Rush Moth Crambidae Agriophara confertella Depressariidae Eupselia beatella Depressariidae Eupselia carpocapsella Common Eupselia Moth Depressariidae Eutorna tricasis Depressariidae Peritropha oligodrachma Depressariidae Phylomictis sp. Depressariidae Amata nigriceps Erebidae Cyme structa Erebidae Dasypodia cymatodes Northern wattle moth Erebidae Dasypodia selenophora Southern