Aug. 17, 1971 J., F
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Peroxy Compounds Human Health and Ecological Draft Risk Assessment DP 455445, 455446
Peroxy Compounds Human Health and Ecological Draft Risk Assessment DP 455445, 455446 UNITED STATES ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY WASHINGTON, D.C. 20460 OFFICE OF CHEMICAL SAFETY AND POLLUTION PREVENTION MEMORANDUM Date: March 11, 2020 SUBJECT: Registration Review Draft Risk Assessment for the Peroxy Compounds PC Code: 000595, 063201, 063604, 063607, DP Barcode: 455445, 455446 063209, 128860 Decision No: 558073, 558074 Docket No: EPA-HQ-OPP-2009-0546 Regulatory Action: Registration Review Case No: 6059, 4072, 5081 Risk Assessment Type: DRA CAS No: 7722-84-1, 79-21-0, 33734-57-5, 15630-89-4, 10058-23-8, 70693-62-8 TO: Kendall Ziner, Chemical Review Manager Rick Fehir, Ph.D., Team Lead Rose Kyprianou, Branch Chief Regulatory Management Branch (RMB) II Antimicrobials Division (7510P) Office of Pesticide Programs FROM: Andrew Byro, Ph.D., Chemist Kathryn Korthauer, Biologist Timothy Dole, Industrial Hygienist Deborah Burgin, Ph.D., DABT, Toxicologist Risk Assessment and Science Support Branch Antimicrobials Division (7510P) Office of Pesticide Programs THROUGH: Judy Facey, Ph.D., Human Health Risk Assessment Process Leader MP for JF Diana Hsieh, Ecological Risk Assessment Process Leader MP for DH Timothy Leighton, Senior Science Advisor MP for TL Laura Parsons, Associate Branch Chief Melissa Panger, Ph.D., Branch Chief Risk Assessment and Science Support Branch Antimicrobials Division (7510P) This document provides the draft human health and ecological risk assessment conducted in support of the antimicrobial use sites of the following peroxy compounds: hydrogen peroxide, peracetic acid, peroxyoctanoic acid, and sodium percarbonate. Page 1 of 74 Peroxy Compounds Human Health and Ecological Draft Risk Assessment DP 455445, 455446 Although the peroxymonosulfate compounds were included in the peroxy compounds Final Work Plan (FWP), they will not be included in this risk assessment. -

Chemistry Inventory; Fall
CHEMISTRY FALL 2005 MSDS Mfg.'s Name Chemical Name Quantity Stored Storage Conditions (on file = 9) Aluminum 9 1.5 kg Aluminum chloride, anhydrous, 98.5% 9 0.2 kg Aluminum chloride · 6H2O 9 0.5 kg Aluminum hydroxide 9 0.5 kg Aluminum nitrate 9 0.5 kg Aluminum sulfate 9 0.5 kg Ammonia, concentrated 9 4.0 L Ammonium acetate 9 0.2 kg Ammonium chloride 9 Ammonium dihydrogen phosphate (monobasic) 9 0.4 kg J.T. Baker Ammonium hydrogen phosphate (dibasic) No 0.5 kg Ammonium nitrate 9 2.5 kg Ammonium oxalate 9 0.7 kg Ammonium peroxydisulfate 9 0.5 kg Ammonium sulfate 9 0.2 kg Antimony 9 0.4 kg Barium chloride, anhydrous 9 2.5 kg Barium chloride · 2H2O 9 2.5 kg Barium nitrate 9 0.8 kg Bismuth 9 2.0 kg Boric Acid 9 0.4 kg Brass 9 Bromine 9 2.5 kg Cadmium 9 0.1 kg Cadmium nitrate 9 0.3 kg Calcium acetate · xH2O 9 0.5 kg Calcium carbide 9 1.0 kg Calcium carbonate 9 2.2 kg Calcium chloride 9 1.0 kg Calcium hydroxide 9 0.3 kg Calcium nitrate · 4H2O 9 1.0 kg Calcium oxide 9 0.3 kg Calcium sulfate · 2H2O 9 1.0 kg Carbon 9 0.1 kg Ceric ammonium nitrate 9 0.5 kg Cesium chloride 9 0.01 kg Chromium 9 0.01 kg Chromium chloride 9 0.5 kg Chromium nitrate 9 0.5 kg Cobalt 9 0.025 kg Cobalt chloride 9 0.7 kg Cobalt nitrate 9 0.6 kg Copper (assorted) 9 4.0 kg Copper acetate 9 0.05 kg Copper chloride 9 0.1 kg Copper nitrate 9 3.5 kg Copper oxide 9 0.4 kg Cupric sulfate, anhydrous 9 0.5 kg Cupric sulfate · 5H2O 9 2.75 kg EDTA 9 0.6 kg Iodine 9 2.0 kg Iron (assorted) 9 5.0 kg MSDS Mfg.'s Name Chemical Name Quantity Stored Storage Conditions (on file = 9) Ferric ammonium -

Flexaust Chemical Resistance Guide
Chemical Resistance Guide Rating Code: A=Excellent B=Good C=Fair D=Not Recommended ND=No Data HOSE MATERIAL Santoprene Polyethelene Buna-N Neoprene Hypalon Teflon Acrylic Silicone Polyurethane PVC Aluminum SS 304 SS 316 Polypropylene Chemical (TPR) (LLPE) Acetaldehyde D C D A ND A D ND C B B A A B Acetamide A C B A ND B D ND ND ND ND ND A A Acetate Solvents D D D A D ND ND ND C ND ND ND A D Acetic Acid, glacial C D C A D B D A ND B ND ND A B Acetic Acid, 5% B A A A A A D A A A ND A A A Acetic Acid, 10% B A B A B A D A A A A A A A Acetic Acid, 20% B A B A B A D A A A ND A A A Acetic Acid, 30% B C B A ND A D A A A ND A A A Acetic Acid, 50% B C C A ND B D A A A ND A A A Acetic Acid, 80% B C ND A ND ND ND A A A ND A A B Acetic Anhydride D C A A ND C D A C ND C A A A Acetone D C C A D B D A C B A A A B Acetone Cyanhydrin D B C A ND A D ND ND ND ND ND ND ND Acetonitrile C C B A ND ND ND ND ND ND A A A ND Acetophenone D D D A ND D D ND ND ND ND A A A Acetyl Acetone D D D A ND D C ND ND ND ND ND ND ND Acetyl Chloride D D D A ND C D ND C ND ND A A ND Acetylene B C C A ND B A A A ND A A A D Acetylene Dichloride D D D A ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND Acrolein B ND B A ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND Acrylonitrile D D C A ND D ND A C B ND ND ND B Adipic Acid B D ND A ND ND ND ND A ND ND ND ND ND Alcohol, Allyl A A A A ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND ND Alcohol, Amyl B A B A ND D D B C A ND ND A B Alcohol, Benzyl D C B A D ND D ND ND ND ND ND A A Alcohol, Butyl C A A A ND B D ND A A ND ND ND B Alcohol, Diacetone D C B A ND B C ND ND ND ND ND ND D Alcohol, -

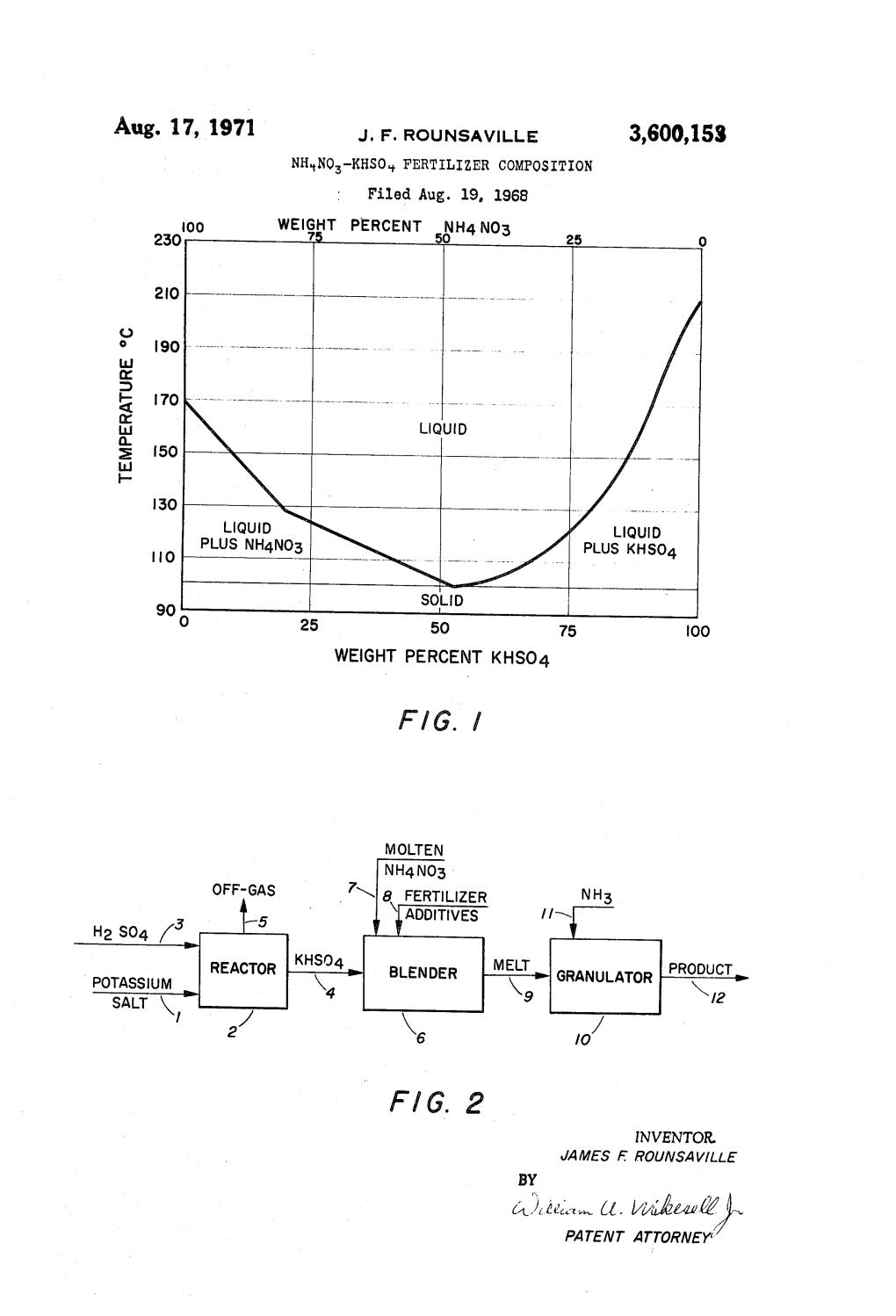
Are U-1 || | | | | | | 1 \ | | | | | | 7 KH SO -7 T /I\ | | | | Z 52 5.I
United States Patent to (11) 3,998,935 Adams et al. 45 Dec. 21, 1976 54 MANUFACTURE OF POTASSIUM SULFATE 1,145,390 3/1969 United Kingdom ............... 4231482 75 Inventors: Ben E. Adams, Hanford, Calif.; John OTHER PUBLICATIONS B. Sardisco, Shreveport, La., Erhart Seidell, A., Solubilities of Inorganic and Metal Organic K. Drechsel, Houston, Tex. Compounds, American Chemical Society, Washington, 73) Assignee: Pennzoil Company, Shreveport, La. DC, 1965, 4th Edition, vol. II, pp. 1 16, 133-135, 297-299, 301,982–984. 22 Filed: Jan. 30, 1975 Handbook of Chemistry & Physics, Hodigins Editor, 43 (21) Appl. No. 545,554 edition, 1961, Chemical Rubber Publishing Company, 52 U.S. Cl. ............................. 4231552; 23/302 R; Cleveland, Ohio, pp. 626-627,636-637. 4231482 (51) Int. Cl.’....................... C01D 5/02; C01B 7/08 Primary Examiner-Oscar R. Vertiz (58) Field of Search .......... 423.1552, 481,482, 199, Assistant Examiner-Gary P. Straub " . 423/202; 23/296, 302 Attorney, Agent, or Firm-Lowe, King, Price & Markva (56) References Cited 57 ABSTRACT UNITED STATES PATENTS Potassium sulfate (KSO) is prepared by contacting 995,105 6/1911 Thompson ..................... 4231552 X potassium chloride with an aqueous solution containing 2,816,820 12/1957 Pernert .......................... 4231482 X potassium bisulfate at a temperature of about 65-10 2,902,341 9/1959 Baniel et al. .................. 423.1552 X C., cooling the solution and permitting the potassium 3,687,639 8/1972 Barlow et al. ................. 4231552 X sulfate to crystallize from solution. FOREIGN PATENTS OR APPLICATIONS 1,100,258 9/1955 France ............................... 423.1552 12 Claims, 3 Drawing Figures loss-to-coll" Il-1 || || || are U-1 || | | | | | | 1 \ | | | | | | 7 KH SO -7 t /I\ | | | | Z 52 5.I U.S. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0168472 A1 Bogan, JR
US 20100168472A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2010/0168472 A1 Bogan, JR. et al. (43) Pub. Date: Jul. 1, 2010 (54) PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF ACROLEN Publication Classification FROM GLYCEROL (51) Int. Cl. (76) Inventors: Leonard Edward Bogan, JR., CD7C5L/6 (2006.01) Lansdale, PA (US); Mark Anthony C07C 45/29 (2006.01) Silvano, New Hope, PA (US) (52) U.S. Cl. ......................................... 562/532:568/.486 (57) ABSTRACT Correspondence Address: The present invention relates to a process for producing ROHMAND HAAS COMPANY acrolein by liquid phase dehydration of glycerol by preparing PATENT DEPARTMENT a mixture of a catalyst Suspended in an organic solvent com 1OONDEPENDENCE MALL WEST prising one or more vinyl polymers and glycerol; and then PHILADELPHIA, PA 19106-2399 (US) mixing and heating the mixture to between 150° C. and 350° C. to dehydrate the glycerol and form acrolein. The vinyl (21) Appl. No.: 12/592, 182 polymers are selected from the group consisting of polyole fins, polystyrene, and mixtures thereof. The polyolefins may (22) Filed: Nov. 20, 2009 be polyethylene, polypropylene, polybutylene, polyisobuty lene, polyisoprene, polypentene, or mixtures thereof. The Related U.S. Application Data acrolein may be subjected to vapor phase oxidation in the (60) Provisional application No. 61/203.554, filed on Dec. presence of a catalyst, Such as a mixed metal oxide, to pro 24, 2008. duce acrylic acid. US 2010/01 68472 A1 Jul. 1, 2010 PROCESS FOR PRODUCTION OF ACROLEN erol, the selectivity of the reaction to acrolein and the service FROM GLYCEROL life of the catalyst are appreciably reduced at higher concen trations, and a glycerol concentration of between 10 and 25% by weight glycerol is recommended. -

HASA OXIDIZER Safety Data Sheet (SDS No
Safety Data Sheet (SDS No. 214) HASA OXIDIZER HASA OXIDIZER Safety Data Sheet Emergency 24 Hour Telephone: CHEMTREC 800.424.9300 Corporate Headquarters: Hasa Inc. P. O. Box 802736 Santa Clarita, CA 91355 Telephone 661.259.5848 Fax 661.259.1538 SECTION 1: CHEMICAL PRODUCT AND COMPANY IDENTIFICATION 1.1 Product Identification : 1.1.1 Product Name : Hasa Oxidizer 1.1.2 CAS # : (Chemical Abstracts This product is a mixture of Oxone® and other Service) ingredients. The active ingredient of Oxone® is potassium peroxymonosulfate, KHSO 5 [CAS 10058-23- 8], commonly known as potassium monopersulfate, which is present as a component of a triple salt with the formula 2KHSO 5·KHSO 4·K 2SO 4 (potassium hydrogen peroxymonsulfate sulfate (5:3:2:2), [CAS 70693-62-8]). 1.1.3 RTECS : (Registry of Toxic Not available. Effects of Chemical Substances) 1.1.4 EINECS : (European Inventory Not available. of Existing Chemical Substances) 1.1.5 Synonym : Oxone® (DuPont™), Potassium Monopersulfate (MPS), Potassium Peroxymonosulfate. 1.1.6 Chemical Name : Potassium Peroxymonosulfate Sulfate 1.1.7 Chemical Formula : 2KHSO 5·KHSO 4·K 2SO 4 1.2 Recommended Use : Pool and spa shock oxidizer. 1.3 Company Identification : Hasa Inc. P. O. Box 802736 Santa Clarita, CA 91355 1.4 Emergency Telephone Number : CHEMTREC : 1-800-424-9300 (24 hour) 1.5 Non -Emer gency Assistance : 661-259-5848 (8 AM – 5 PM PST / PDT) Revision Date: 06/01/2015 (Supersedes previous revisions) Page 1 of 10 SECTION 2: HAZARD(S) IDENTIFICATION Safety Data Sheet (SDS No. 214) HASA Health Hazard Skin Corrosion/Irritation Category 1 Acute Toxicity (oral) Category 4 Symbol OXIDIZER Signal Word WARNING Causes severe skin burn and eye damage. -

Full Circle Market List of 104 Ingredients
Full Circle Market List of 104 Ingredients 1. ACESULFAME-K (ACESULFAME POTASSIUM) 36. DISODIUM CALCIUM EDTA 71. POTASSIUM BISULFATE 2. ACETYLATED ESTER OF MONO-AND 37. DISODIUM DIHYDROGEN EDTA 72. POTASSIUM BROMATE DIGLYCERIDES 3. AMMONIUM CHLORIDE 38. DISODIUM GUANYLATE 73. POTASSIUM HYDROXIDE 4. ANTIBIOTICS 39. DISODIUM SUCCINATE 74. POTASSIUM METABISULFITE 5. ARTIFICIAL FLAVORS 40. EDTA (ETHYLENEDIAMINE TETRAACETIC 75. POTASSIUM NITRATE OR NITRITE ACID) 6. ASPARTAME 41. ERYTHORBIC ACID 76. POTASSIUM SORBATE (ACCEPTABLE IN SUPPLEMENTS ONLY) 7. ASTAXANTHIN (ACCEPTABLE IN 42. ESTER GUMS 77. PROPIONATES (CALCIUM AND SODIUM) SUPPLEMENTS, IF NATURAL) 8. AZODICARBONAMIDE 43. ETHYL VANILLIN 78. PROPYL GALLATE 9. BENTONITE (ACCEPTABLE IN 44. ETHYLENE OXIDE 79. PROPYLENE OXIDE SUPPLEMENTS) 10. BENZOATES IN FOOD 45. ETHOXYQUIN 80. PROPYLPARABEN 11. BENZOYL PEROXIDE 46. FD&C BLUE NO. 1 81. SACCHARIN 12. BENZYL ALCOHOL 47. FD&C BLUE NO. 2 82. SIMPLESSE 13. BHA (BUTYLATED HYDROXYANISOLE) 48. FD&C GREEN NO. 3 83. SODIUM ALUMINUM PHOSPHATE 14. BHT (BUTYLATED HYDROXYTOLUENE) 49. FD&C RED NO. 3 84. SODIUM ALUMINUN SULFATE 15. BISULFITES 50. FD&C RED NO. 40 85. SODIUM BENZOATE 16. BLEACHED FLOUR 51. FD&C YELLOW NO. 5 86. SODIUM BISULFATE 17. BROMATED FLOUR 52. FD&C YELLOW NO. 6 87. SODIUM DIACETATE 18. BROMINATED VEGETABLE OIL (BVO) 53. GLYCEROL ESTER OF WOOD ROSIN 88. SODIUM FERROCYANIDE 19. CALCIUM BROMATE 54. HEXA-, HEPTA- AND OCTA-ESTERS OF 89. SODIUM GLUTAMATE SUCROSE 20. CALCIUM DISODIUM EDTA 55. HIGH FRUCTOSE CORN SYRUP 90. SODIUM METABISULFITE 21. CALCIUM PEROXIDE 56. HYDROGENATED OIL 91. SODIUM NITRATE/NITRITE 22. CALCIUM PROPIONATE 57. HYDROXYPROPYL GUAR GUM 92. -

SDS Contains All of the Information Required by the HPR
SAFETY DATA SHEET Preparation Date: 4/4/2018 Revision Date: 4/4/2018 Revision Number: G1 1. IDENTIFICATION Product identifier Product code: P1195 Product Name: POTASSIUM BISULFATE, CRYSTAL, REAGENT Other means of identification Synonyms: Acid potassium sulfate Potassium acid sulfate Monopotassium sulfate Potassium bisulphate Sulfuric acid, monopotassium salt CAS #: 7646-93-7 RTECS # TS7200000 CI#: Not available Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use Recommended use: No information available. Uses advised against No information available Supplier: Spectrum Chemical Mfg. Corp 14422 South San Pedro St. Gardena, CA 90248 (310) 516-8000 Order Online At: https://www.spectrumchemical.com Emergency telephone number Chemtrec 1-800-424-9300 Contact Person: Martin LaBenz (West Coast) Contact Person: Ibad Tirmiz (East Coast) 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION Classification This chemical is considered hazardous according to the 2012 OSHA Hazard Communication Standard (29 CFR 1910.1200) Considered a dangerous substance or mixture according to the Globally Harmonized System (GHS) Skin corrosion/irritation Category 1 Sub-category B Serious eye damage/eye irritation Category 1 Specific target organ toxicity (single exposure) Category 3 Label elements Danger Hazard statements Causes severe skin burns and eye damage Product code: P1195 Product name: POTASSIUM 1 / 12 BISULFATE, CRYSTAL, REAGENT May cause respiratory irritation Hazards not otherwise classified (HNOC) Not Applicable Other hazards May be harmful if swallowed Precautionary Statements - Prevention Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray Wash face, hands and any exposed skin thoroughly after handling Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area Precautionary Statements - Response Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician Specific treatment (see .? on this label) IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. -

Chemical Capabilities Listing Laboratory, R&D, Industrial and Manufacturing Applications
Page 1 of 3 Chemical Capabilities Listing Laboratory, R&D, Industrial and Manufacturing Applications Acacia, Gum Arabic Barium Oxide Chromium Trioxide Acetaldehyde Bentonite, White Citric Acid, Anhydrous Acetamide Benzaldehyde Citric Acid, Monohydrate Acetanilide Benzoic Acid Cobalt Oxide Acetic Acid Benzoyl Chloride Cobaltous Acetate Acetic Anhydride Benzyl Alcohol Cobaltous Carbonate Acetone Bismuth Chloride Cobaltous Chloride Acetonitrile Bismuth Nitrate Cobaltous Nitrate Acetyl Chloride Bismuth Trioxide Cobaltous Sulfate Aluminium Ammonium Sulfate Boric Acid Cottonseed Oil Aluminon Boric Anhydride Cupferron Aluminum Chloride, Anhydrous Brucine Sulfate Cupric Acetate Aluminum Chloride, Hexahydrate n-Butyl Acetate Cupric Bromide Aluminum Fluoride n-Butyl Alcohol Cupric Carbonate, Basic Aluminum Hydroxide tert-Butyl Alcohol Cupric Chloride Aluminum Nitrate Butyric Acid Cupric Nitrate Aluminum Oxide Cadmium Acetate Cupric Oxide Aluminum Potassium Sulfate Cadmium Carbonate Cupric Sulfate, Anhydrous Aluminum Sulfate Cadmium Chloride, Anhydrous Cupric Sulfate, Pentahydrate 1-Amino-2-Naphthol-4-Sulfonic Acid Cadmium Chloride, Hemipentahydrate Cuprous Chloride Ammonium Acetate Cadmium Iodide Cuprous Oxide, Red Ammonium Bicarbonate Cadmium Nitrate Cyclohexane Ammonium Bifluoride Cadmium Oxide Cyclohexanol Ammonium Bisulfate Cadmium Sulfate, Anhydrous Cyclohexanone Ammonium Bromide Cadmium Sulfate, Hydrate Devarda's Alloy Ammonium Carbonate Calcium Acetate Dextrose, Anhydrous Ammonium Chloride Calcium Carbide Diacetone Alcohol Ammonium Citrate -

Chemical Resistance
Chemical Resistance 1 = excellent resistance 3 = medium resistance 2 = good resistance x = none-resistant PUR- PUR- Silicone Hypalon® Viton® PVC PE PTFE Neopren® Kapton® TPV PE-EL Ester Ether accumulator acid (sulfuric acid 30%) x 2 x 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 1 acetaldehyde 3 2 2 3 2 x 2 to 3 1 3 1 1 1 acetamide x x 2 2 1 to 2 x 1 1 1 1 1 acetic acid 10% 322123111 111 acetic acid 100% (conc.) x x 2 to 3 3 x x x 1 x 1 1 1 acetic acid 25% x 3 2 to 3 1 to 2 2 x 1 1 1 to 2 1 1 1 acetic acid 3% 211121111 111 acetic acid 50% x x 2 to 3 2 2 x 3 1 2 to 3 1 1 1 acetic acid anhydride 50% xx11xx312 11 acetic acid ethyl ester (ethyl acetate) xx2xxx213 111 acetone 3 x 2 2 to 3 x 3 1 to 2 1 3 1 1 1 acetyl salicylic acid (aspirin) 1 1 1 1 acetylacetone 3xx xxx1 11x acetylene gas 2-3 2-3 2 2 1 1 3 1 2 1 1 1 acids s. spec. designation, aplicable in general x 3 2 2-3 1-2 1-2 2 1 3 1 1-2 acrylic acid ethyl ester (ethyl acrylate) xx21xxx1x 11x acrylonitrile xx232x113 111 adipic acid (hexane diacid) 3 1 to 3 x 1 1 1 1 1 2 1 adipic acid diethyl ester 1 x x 1 1 1 adipose (animal grease) 1 1 3 1 to 2 1 2 2 to 3 1 3 1 2 1 air, atmospheric, oil-free, to +°C 85 80 175 120 200 70 90 200 200 125 1 air, oil-saturated, to +°C 85 80 175 120 200 70 90 200 200 125 1 alcohols s. -

SAFETY DATA SHEET Issuing Date 10-Sep-2020 Revision Date 14-Oct-2020 Revision Number 4
SAFETY DATA SHEET Issuing Date 10-Sep-2020 Revision Date 14-Oct-2020 Revision Number 4 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND OF THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING Product Identifier Product Name POTASSIUM MONO PERSULFATE Other means of identification Product Code 3326700 CAS Number MIXTURE Formula Not available Synonyms Not available UN-No UN3260 Recommended use of the chemical and restrictions on use Recommended Use Corrosion Inhibitor Uses advised against Do not use where contact with food or drinking water is possible. Avoid prolonged contact with eyes, skin, and clothing. Details of the supplier of the safety data sheet Supplier Address ACETO US, LLC 4 Tri Harbor Court Port Washington, NY 11050-4661 Phone: (516) 627-6000 Fax: (516) 627-6093 Email: [email protected] Emergency Telephone Number(s) ChemTrec: 1-800-424-9300 Outside of the United States: 1-703-527-3887 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION Classification Skin Corrosion/Irritation Category 1 Sub-category B Serious eye damage/eye irritation Category 1 Specific target organ toxicity (single exposure) Category 3 Label elements Emergency Overview Signal Word DANGER Hazard statements Causes severe skin burns and eye damage May cause respiratory irritation _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Page 1 / 10 3326700 POTASSIUM MONO PERSULFATE Revision Date 14-Oct-2020 _____________________________________________________________________________________________ Appearance Physical State Odor White Crystalline Solid No information available Precautionary Statements - Prevention Do not breathe dust/fume/gas/mist/vapors/spray Wash face, hands and any exposed skin thoroughly after handling Wear protective gloves/protective clothing/eye protection/face protection Use only outdoors or in a well-ventilated area Precautionary Statements - Response Immediately call a POISON CENTER or doctor/physician Specific treatment (see supplemental first aid instructions on this label) IF IN EYES: Rinse cautiously with water for several minutes. -
10-Chemical Resistance
CHEMICAL RESISTANCE GUIDE Tyler Pipe/Soil Pipe Division • 11910 CR 492 • Tyler, TX 75706 • (800) 527-8478 RESISTANCE RATING KEY: E = Excellent G = Good C = Conditional U = Unsatisfactory - = Test Data Not Available AGENT NITRILE NEOPRENE EPOXY STAINLESS STEELDUCTILE/CASTBRONZE IRON ALUMINUM AGENT NITRILE NEOPRENE EPOXY STAINLESS STEELDUCTILE/CASTBRONZE IRON ALUMINUM AGENT NITRILE NEOPRENE EPOXY STAINLESS STEELDUCTILE/CASTBRONZE IRON ALUMINUM AGENT NITRILE NEOPRENE EPOXY STAINLESS STEELDUCTILE/CASTBRONZE IRON ALUMINUM Acetaldehyde U C E E C G G Ammonium Phosphate, Mono-Di-Tri E E E E C C G Acetamide E G E E U U - Ammonium Sulfate E E E G C G G Acetic Acid (Up to 10%, Ammonium Sulfide E E - E U U C 100°F Max.) G E C E U C G Ammonium Thiocyanate E E - G - - - Acetic Acid (10-50%, 100°F Max.) G G G E U C G Amyl Acetate U U E E C C G Acetic Acid, Glacial (100°F Max.) U U G E U C G Amyl Alcohol G G U E C E G Acetic Anhydride U G E E G C G Amyl Borate E E - - - - - Acetone U U U E E E E Amyl Chloride U U E G - E U Acetonitrile G - - - - - - Amyl Chloronaphthalene U U - - - - - Acetaphenone U U - - - - - Amyl Naphthalene U U - - - - - Acrolein, (40%, 120°F) - - - G G G E Aniline U U C E C C C Acrolein, (100%, 200°F) - - - G G G G Aniline Dyes U G - E C C C Acrylic Resin - G - - - - - Aniline Hydrochloride G U - - - - - Acrylonite U U - E C E G Aniline Oil U U E E E E C Acrylonitrile U U E E E E G Animal Fats E G E E E - - Adipic Acid E - - G - - G Animal Oil, (Lard Oil) E G E E E E E Allyl Alcohol, (up to 96%) E E - E E G C Anthraquinone U U