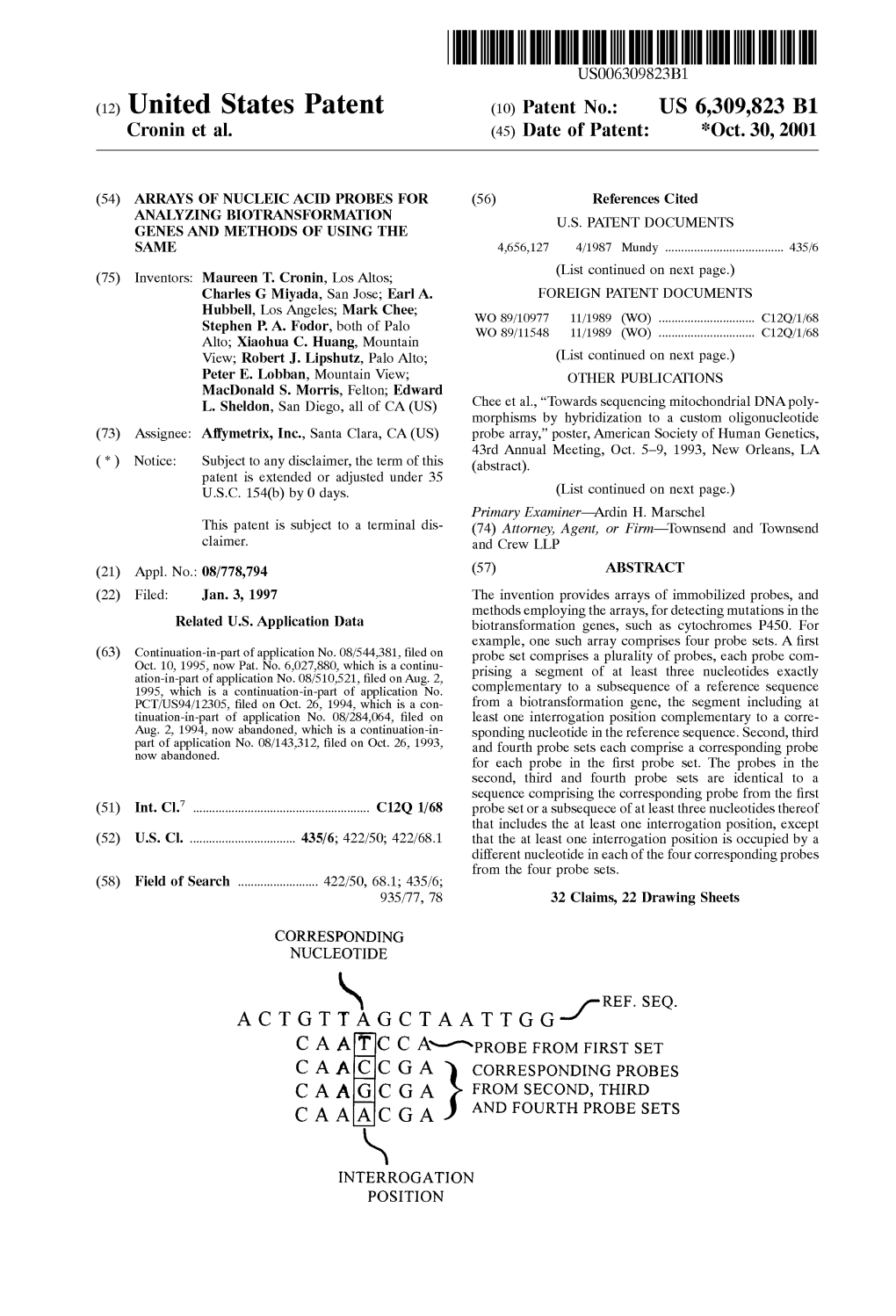
A C T G T Ta G Cta a Tt G G-1 Ref
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Ovid MEDLINE(R)
Supplementary material BMJ Open Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub Ahead of Print, In-Process & Other Non-Indexed Citations and Daily <1946 to September 16, 2019> # Searches Results 1 exp Hypertension/ 247434 2 hypertens*.tw,kf. 420857 3 ((high* or elevat* or greater* or control*) adj4 (blood or systolic or diastolic) adj4 68657 pressure*).tw,kf. 4 1 or 2 or 3 501365 5 Sex Characteristics/ 52287 6 Sex/ 7632 7 Sex ratio/ 9049 8 Sex Factors/ 254781 9 ((sex* or gender* or man or men or male* or woman or women or female*) adj3 336361 (difference* or different or characteristic* or ratio* or factor* or imbalanc* or issue* or specific* or disparit* or dependen* or dimorphism* or gap or gaps or influenc* or discrepan* or distribut* or composition*)).tw,kf. 10 or/5-9 559186 11 4 and 10 24653 12 exp Antihypertensive Agents/ 254343 13 (antihypertensiv* or anti-hypertensiv* or ((anti?hyperten* or anti-hyperten*) adj5 52111 (therap* or treat* or effective*))).tw,kf. 14 Calcium Channel Blockers/ 36287 15 (calcium adj2 (channel* or exogenous*) adj2 (block* or inhibitor* or 20534 antagonist*)).tw,kf. 16 (agatoxin or amlodipine or anipamil or aranidipine or atagabalin or azelnidipine or 86627 azidodiltiazem or azidopamil or azidopine or belfosdil or benidipine or bepridil or brinazarone or calciseptine or caroverine or cilnidipine or clentiazem or clevidipine or columbianadin or conotoxin or cronidipine or darodipine or deacetyl n nordiltiazem or deacetyl n o dinordiltiazem or deacetyl o nordiltiazem or deacetyldiltiazem or dealkylnorverapamil or dealkylverapamil -

Drug Delivery System for Use in the Treatment Or Diagnosis of Neurological Disorders
(19) TZZ __T (11) EP 2 774 991 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int Cl.: 10.09.2014 Bulletin 2014/37 C12N 15/86 (2006.01) A61K 48/00 (2006.01) (21) Application number: 13001491.3 (22) Date of filing: 22.03.2013 (84) Designated Contracting States: • Manninga, Heiko AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB 37073 Göttingen (DE) GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO •Götzke,Armin PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR 97070 Würzburg (DE) Designated Extension States: • Glassmann, Alexander BA ME 50999 Köln (DE) (30) Priority: 06.03.2013 PCT/EP2013/000656 (74) Representative: von Renesse, Dorothea et al König-Szynka-Tilmann-von Renesse (71) Applicant: Life Science Inkubator Betriebs GmbH Patentanwälte Partnerschaft mbB & Co. KG Postfach 11 09 46 53175 Bonn (DE) 40509 Düsseldorf (DE) (72) Inventors: • Demina, Victoria 53175 Bonn (DE) (54) Drug delivery system for use in the treatment or diagnosis of neurological disorders (57) The invention relates to VLP derived from poly- ment or diagnosis of a neurological disease, in particular oma virus loaded with a drug (cargo) as a drug delivery multiple sclerosis, Parkinsons’s disease or Alzheimer’s system for transporting said drug into the CNS for treat- disease. EP 2 774 991 A1 Printed by Jouve, 75001 PARIS (FR) EP 2 774 991 A1 Description FIELD OF THE INVENTION 5 [0001] The invention relates to the use of virus like particles (VLP) of the type of human polyoma virus for use as drug delivery system for the treatment or diagnosis of neurological disorders. -

Composition Modulating Botulinum Neurotoxin Effect
(19) *EP003753568A1* (11) EP 3 753 568 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int Cl.: 23.12.2020 Bulletin 2020/52 A61K 38/17 (2006.01) A61K 31/205 (2006.01) A61K 31/4178 (2006.01) A61K 38/48 (2006.01) (2006.01) (2006.01) (21) Application number: 19181635.4 A61P 9/00 A61P 21/00 A61P 29/00 (2006.01) (22) Date of filing: 21.06.2019 (84) Designated Contracting States: •Cros, Cécile AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB 74580 Viry (FR) GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO • Hulo, Nicolas PL PT RO RS SE SI SK SM TR 1252 Meinier (CH) Designated Extension States: • Machicoane, Mickaël BA ME 1290 Versoix (CH) Designated Validation States: KH MA MD TN (74) Representative: Barbot, Willy Simodoro-ip (71) Applicant: Fastox Pharma SA 82, rue Sylvabelle 1003 Lausanne (CH) 13006 Marseille (FR) (72) Inventors: • Le Doussal, Jean-Marc 1007 Lausanne (CH) (54) COMPOSITION MODULATING BOTULINUM NEUROTOXIN EFFECT (57) The present invention relates to a method for cholinergic neuronal transmission to the botulinum neu- modulating the effect of a botulinum neurotoxin compo- rotoxin composition. The invention also relates to com- sition, that is accelerating the onset of action and /or ex- positions comprising at least one postsynaptic inhibitor tending the duration of action and/or enhancing the in- of cholinergic neuronal transmission and a botulinum tensity of action of a botulinum neurotoxin composition, neurotoxin, and their uses for treating aesthetic or ther- comprising adding at least one postsynaptic inhibitor of apeutic conditions. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub
US 2002006 1835A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2002/0061835A1 Kensey (43) Pub. Date: May 23, 2002 (54) IN VIVO DELIVERY METHODS AND which is a continuation-in-part of application No. COMPOSITIONS 08/919,906, filed on Aug. 28, 1997, now patented. (76) Inventor: Kenneth R. Kensey, Malvern, PA (US) Publication Classification Correspondence Address: (51) Int. Cl. ............................. A61K 31/00; A61 B 5/00 CAESAR, RIVISE, BERNSTEIN, (52) U.S. Cl. ................................................. 514/1; 600/309 COHEN & POKOTILOW, LTD. 12TH FLOOR, SEVEN PENN CENTER (57) ABSTRACT 1635 MARKET STREET Various methods are provided for determining and utilizing PHILADELPHIA, PA 19103-2212 (US) the Viscosity of the circulating blood of a living being over Appl. No.: 09/828,761 a range of Shear rates for diagnostics and treatment, Such as (21) detecting/reducing blood Viscosity, work of the heart, con (22) Filed: Apr. 9, 2001 tractility of the heart, for detecting/reducing the Surface tension of the blood, for detecting plasma Viscosity, for Related U.S. Application Data explaining/countering endothelial cell dysfunction, for pro Viding high and low blood vessel wall Shear StreSS data, red (63) Continuation-in-part of application No. 09/727,950, blood cell deformability data, lubricity of blood, and for filed on Dec. 1, 2000, which is a continuation-in-part treating different ailments Such as peripheral arterial disease of application No. 09/628,401, filed on Aug. 1, 2000, in combination with administering to a living being at least which is a continuation-in-part of application No. one pharmaceutically acceptable agent. -

Federal Register / Vol. 60, No. 80 / Wednesday, April 26, 1995 / Notices DIX to the HTSUS—Continued
20558 Federal Register / Vol. 60, No. 80 / Wednesday, April 26, 1995 / Notices DEPARMENT OF THE TREASURY Services, U.S. Customs Service, 1301 TABLE 1.ÐPHARMACEUTICAL APPEN- Constitution Avenue NW, Washington, DIX TO THE HTSUSÐContinued Customs Service D.C. 20229 at (202) 927±1060. CAS No. Pharmaceutical [T.D. 95±33] Dated: April 14, 1995. 52±78±8 ..................... NORETHANDROLONE. A. W. Tennant, 52±86±8 ..................... HALOPERIDOL. Pharmaceutical Tables 1 and 3 of the Director, Office of Laboratories and Scientific 52±88±0 ..................... ATROPINE METHONITRATE. HTSUS 52±90±4 ..................... CYSTEINE. Services. 53±03±2 ..................... PREDNISONE. 53±06±5 ..................... CORTISONE. AGENCY: Customs Service, Department TABLE 1.ÐPHARMACEUTICAL 53±10±1 ..................... HYDROXYDIONE SODIUM SUCCI- of the Treasury. NATE. APPENDIX TO THE HTSUS 53±16±7 ..................... ESTRONE. ACTION: Listing of the products found in 53±18±9 ..................... BIETASERPINE. Table 1 and Table 3 of the CAS No. Pharmaceutical 53±19±0 ..................... MITOTANE. 53±31±6 ..................... MEDIBAZINE. Pharmaceutical Appendix to the N/A ............................. ACTAGARDIN. 53±33±8 ..................... PARAMETHASONE. Harmonized Tariff Schedule of the N/A ............................. ARDACIN. 53±34±9 ..................... FLUPREDNISOLONE. N/A ............................. BICIROMAB. 53±39±4 ..................... OXANDROLONE. United States of America in Chemical N/A ............................. CELUCLORAL. 53±43±0 -

Permanently Charged Sodium and Calcium Channel Blockers As Anti-Inflammatory Agents
(19) TZZ ¥Z¥_T (11) EP 2 995 303 A1 (12) EUROPEAN PATENT APPLICATION (43) Date of publication: (51) Int Cl.: 16.03.2016 Bulletin 2016/11 A61K 31/165 (2006.01) A61K 31/277 (2006.01) A61K 45/06 (2006.01) A61P 25/00 (2006.01) (2006.01) (2006.01) (21) Application number: 15002768.8 A61P 11/00 A61P 13/00 A61P 17/00 (2006.01) A61P 1/00 (2006.01) (2006.01) (2006.01) (22) Date of filing: 09.07.2010 A61P 27/02 A61P 29/00 A61P 37/08 (2006.01) (84) Designated Contracting States: (72) Inventors: AL AT BE BG CH CY CZ DE DK EE ES FI FR GB • WOOLF, Clifford, J. GR HR HU IE IS IT LI LT LU LV MC MK MT NL NO Newton, MA 02458 (US) PL PT RO SE SI SK SM TR • BEAN, Bruce, P. Waban, MA 02468 (US) (30) Priority: 10.07.2009 US 224512 P (74) Representative: Lahrtz, Fritz (62) Document number(s) of the earlier application(s) in Isenbruck Bösl Hörschler LLP accordance with Art. 76 EPC: Patentanwälte 10797919.7 / 2 451 944 Prinzregentenstrasse 68 81675 München (DE) (71) Applicants: • President and Fellows of Harvard College Remarks: Cambridge, MA 02138 (US) This application was filed on 25-09-2015 as a • THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORPORATION divisional application to the application mentioned Boston, MA 02114 (US) under INID code 62. • CHILDREN’S MEDICAL CENTER CORPORATION Boston, Massachusetts 02115 (US) (54) PERMANENTLY CHARGED SODIUM AND CALCIUM CHANNEL BLOCKERS AS ANTI-INFLAMMATORY AGENTS (57) The present invention relates to a composition or a kit comprising N-methyl etidocaine for use in a method for treating neurogenic inflammation in a patient, wherein the kit further comprises instructions for use. -

US5478848.Pdf
||||||||||| US005478848A United States Patent (19) 11 Patent Number: 5,478,848 Aune 45) Date of Patent: Dec. 26, 1995 54) INHIBITION OF ARTHRITIS BYL-TYPE Kong et al., Second Messenger Phosphoproteins 13, CALCIUM CHANNEL ANTAGONSTS 117-130 (1991). NIMODIPINE, NISOLDIPINE AND Olsen et al., Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 162,448-455 NFEDIPINE (1989). Dayer and Demczuk, Cytokines and Other Mediators in 75) Inventor: Thomas M. Aune, Hamden, Conn. Rheumatoid Arthritis, Springer Seminars in Immunopathol ogy, pp. 1-27 (Springer-Verlag 1984). 73) Assignee: Bayer Corporation, Pittsburgh, Pa. Gay and Koopman, Current Opinion in Rheumatology 1, 8-14 (1989). (21) Appl. No.: 188464 Brennan et al., The Lancet Jul. 29, 224-247 (1989). Taurog et al., Meth. Enzymol. 162, 339-355 (1988). (22 Filed: Jan. 26, 1994 Otterness and Bliven et al., Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory (51 Int. Cl. .................. A61K 31/44 Drugs, pp. 111-252 (1985). 52 U.S. Cl. ............ 514/356; 514/355 Ward, Am. J. Med., pp. 3-9 (1984). Triggle and Janis, Structure and Physiology if the Slow (58) Field of Search ...................................... 514/355, 356 Inward Calcium Channel, pp. 51-70 (1987). (56) References Cited Godfraind et al., Pharmacol. Rev. 38, 321-416 (1986). Janis and Triggle, Drug Dev. Res. 4, 257-274 (1984). U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Schramm et al., Nature 303, 535-537 (1983). Re. 33,963 6/1992 Hegasy ......... ... 424/78.24 Scriabine, Rational Drug Therapy 21, 1-17 (1987). 3,932,645 1/1976 Meyer et al. ........................... 424/266 Chen et al., Science 239, 1024 (1988). 4,154,839 5/1979 Wehinger et al. -

Marrakesh Agreement Establishing the World Trade Organization
No. 31874 Multilateral Marrakesh Agreement establishing the World Trade Organ ization (with final act, annexes and protocol). Concluded at Marrakesh on 15 April 1994 Authentic texts: English, French and Spanish. Registered by the Director-General of the World Trade Organization, acting on behalf of the Parties, on 1 June 1995. Multilat ral Accord de Marrakech instituant l©Organisation mondiale du commerce (avec acte final, annexes et protocole). Conclu Marrakech le 15 avril 1994 Textes authentiques : anglais, français et espagnol. Enregistré par le Directeur général de l'Organisation mondiale du com merce, agissant au nom des Parties, le 1er juin 1995. Vol. 1867, 1-31874 4_________United Nations — Treaty Series • Nations Unies — Recueil des Traités 1995 Table of contents Table des matières Indice [Volume 1867] FINAL ACT EMBODYING THE RESULTS OF THE URUGUAY ROUND OF MULTILATERAL TRADE NEGOTIATIONS ACTE FINAL REPRENANT LES RESULTATS DES NEGOCIATIONS COMMERCIALES MULTILATERALES DU CYCLE D©URUGUAY ACTA FINAL EN QUE SE INCORPOR N LOS RESULTADOS DE LA RONDA URUGUAY DE NEGOCIACIONES COMERCIALES MULTILATERALES SIGNATURES - SIGNATURES - FIRMAS MINISTERIAL DECISIONS, DECLARATIONS AND UNDERSTANDING DECISIONS, DECLARATIONS ET MEMORANDUM D©ACCORD MINISTERIELS DECISIONES, DECLARACIONES Y ENTEND MIENTO MINISTERIALES MARRAKESH AGREEMENT ESTABLISHING THE WORLD TRADE ORGANIZATION ACCORD DE MARRAKECH INSTITUANT L©ORGANISATION MONDIALE DU COMMERCE ACUERDO DE MARRAKECH POR EL QUE SE ESTABLECE LA ORGANIZACI N MUND1AL DEL COMERCIO ANNEX 1 ANNEXE 1 ANEXO 1 ANNEX -
Chemical Structure-Related Drug-Like Criteria of Global Approved Drugs
Molecules 2016, 21, 75; doi:10.3390/molecules21010075 S1 of S110 Supplementary Materials: Chemical Structure-Related Drug-Like Criteria of Global Approved Drugs Fei Mao 1, Wei Ni 1, Xiang Xu 1, Hui Wang 1, Jing Wang 1, Min Ji 1 and Jian Li * Table S1. Common names, indications, CAS Registry Numbers and molecular formulas of 6891 approved drugs. Common Name Indication CAS Number Oral Molecular Formula Abacavir Antiviral 136470-78-5 Y C14H18N6O Abafungin Antifungal 129639-79-8 C21H22N4OS Abamectin Component B1a Anthelminithic 65195-55-3 C48H72O14 Abamectin Component B1b Anthelminithic 65195-56-4 C47H70O14 Abanoquil Adrenergic 90402-40-7 C22H25N3O4 Abaperidone Antipsychotic 183849-43-6 C25H25FN2O5 Abecarnil Anxiolytic 111841-85-1 Y C24H24N2O4 Abiraterone Antineoplastic 154229-19-3 Y C24H31NO Abitesartan Antihypertensive 137882-98-5 C26H31N5O3 Ablukast Bronchodilator 96566-25-5 C28H34O8 Abunidazole Antifungal 91017-58-2 C15H19N3O4 Acadesine Cardiotonic 2627-69-2 Y C9H14N4O5 Acamprosate Alcohol Deterrant 77337-76-9 Y C5H11NO4S Acaprazine Nootropic 55485-20-6 Y C15H21Cl2N3O Acarbose Antidiabetic 56180-94-0 Y C25H43NO18 Acebrochol Steroid 514-50-1 C29H48Br2O2 Acebutolol Antihypertensive 37517-30-9 Y C18H28N2O4 Acecainide Antiarrhythmic 32795-44-1 Y C15H23N3O2 Acecarbromal Sedative 77-66-7 Y C9H15BrN2O3 Aceclidine Cholinergic 827-61-2 C9H15NO2 Aceclofenac Antiinflammatory 89796-99-6 Y C16H13Cl2NO4 Acedapsone Antibiotic 77-46-3 C16H16N2O4S Acediasulfone Sodium Antibiotic 80-03-5 C14H14N2O4S Acedoben Nootropic 556-08-1 C9H9NO3 Acefluranol Steroid -
(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.263,125 B2 Vaya Et Al
US008263125B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 8.263,125 B2 Vaya et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Sep. 11, 2012 (54) DOSAGE FORM FOR HIGH DOSE-HIGH (52) U.S. Cl. ......... 424/469: 424/464; 424/465; 424/468 SOLUBLITY ACTIVE INGREDIENTS THAT (58) Field of Classification Search ........................ None PROVIDES FOR MIMEDIATE RELEASE AND See application file for complete search history. MODIFIED RELEASE OF THE ACTIVE INGREDIENTS (56) References Cited (75) Inventors: Navin Vaya, Gujarat (IN); Rajesh Singh Karan, Gujarat (IN); Sunil Sadanand U.S. PATENT DOCUMENTS Nadkarni, Gujarat (IN); Vinod Kumar 3,048,526 A * 8, 1962 Boswell ........................ 424,472 3,336,200 A 8, 1967 Krause et al. Gupta, Gujarat (IN) 4,139,589 A * 2/1979 Beringer et al. ... ... 264/250 4,503,031 A * 3/1985 Glassman ...... ... 424/467 (73) Assignee: Torrent Pharmaceuticals Limited, 4,996,061 A * 2/1991 Webb et al. ... ... 424/475 Ahmedabad (IN) 5,445,829 A * 8/1995 Paradissis et al. ... 424/480 5,738,874. A * 4/1998 Conte et al. ........ ... 424/472 (*) Notice: Subject to any disclaimer, the term of this 5,840,332 A * 1 1/1998 Lerner et al. .................. 424/464 5,985,843. A 1 1/1999 Higo et al. patent is extended or adjusted under 35 6,001,391 A 12/1999 Zeidler et al. U.S.C. 154(b) by 0 days. 6,238,699 B1 5, 2001 Rubin 6,372.254 B1 * 4/2002 Ting et al. ...... ... 424/473 This patent is Subject to a terminal dis 6,660,300 B1* 12/2003 Timmins et al. -
Redalyc.Mechanism of the Negative Inotropic Effect of Naringin in Mouse
Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacognosy Research E-ISSN: 0719-4250 [email protected] Asociación de Académicos de Ciencias Farmacéuticas de Antofagasta Chile Alvarez -Collazo, Julio; López -Medina, Ana I.; Rodríguez, Armando A.; Alvarez, Julio L. Mechanism of the negative inotropic effect of naringin in mouse heart Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacognosy Research, vol. 2, núm. 5, septiembre-octubre, 2014, pp. 148-157 Asociación de Académicos de Ciencias Farmacéuticas de Antofagasta Antofagasta, Chile Available in: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=496050270005 How to cite Complete issue Scientific Information System More information about this article Network of Scientific Journals from Latin America, the Caribbean, Spain and Portugal Journal's homepage in redalyc.org Non-profit academic project, developed under the open access initiative © 2014 Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacognosy Research, 2 (5), 148-157 ISSN 0719-4250 http://jppres.com/jppres Original Article | Artículo Original Mechanism of the negative inotropic effect of naringin in mouse heart [Mecanismo del efecto inotrópico negativo de la naringina en el corazón de ratón] Julio Alvarez-Collazoa, Ana I. López-Medinaa, Armando A. Rodríguezb, Julio L. Alvareza* aLaboratorio de Electrofisiología. Instituto de Cardiología y Cirugía Cardiovascular. 17 N° 702, Vedado, La Habana, Cuba. bResearch Group for Experimental and Clinical Peptide Chemistry. Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany. * E-mail: [email protected] Abstract Resumen Context: Naringin (NRG) is the major flavonoid (flavanone glycoside) in Contexto: La naringina (NRG) es el principal flavonoide (glicósido de grapefruit juice. Its biological activity has been only partially flavanona) en el jugo de toronja. Su actividad biológica ha sido solo characterized and little is known about the mechanism of the negative parcialmente caracterizada y poco se conoce acerca del mecanismo de la inotropic action of this flavonoid. -

Downloaded for Personal Non-Commercial Research Or Study, Without Prior Permission Or Charge
https://theses.gla.ac.uk/ Theses Digitisation: https://www.gla.ac.uk/myglasgow/research/enlighten/theses/digitisation/ This is a digitised version of the original print thesis. Copyright and moral rights for this work are retained by the author A copy can be downloaded for personal non-commercial research or study, without prior permission or charge This work cannot be reproduced or quoted extensively from without first obtaining permission in writing from the author The content must not be changed in any way or sold commercially in any format or medium without the formal permission of the author When referring to this work, full bibliographic details including the author, title, awarding institution and date of the thesis must be given Enlighten: Theses https://theses.gla.ac.uk/ [email protected] The contractility of the portal vein: role of oxygen and calcium. A thesis presented for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. BY OLUFUNMILAYO ABOSEDE FASEHUN INSTITUTE OF PHYSIOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF GLASGOW. OCTOBER 1987 ProQuest Number: 10997347 All rights reserved INFORMATION TO ALL USERS The quality of this reproduction is dependent upon the quality of the copy submitted. In the unlikely event that the author did not send a com plete manuscript and there are missing pages, these will be noted. Also, if material had to be removed, a note will indicate the deletion. uest ProQuest 10997347 Published by ProQuest LLC(2018). Copyright of the Dissertation is held by the Author. All rights reserved. This work is protected against unauthorized copying under Title 17, United States C ode Microform Edition © ProQuest LLC.