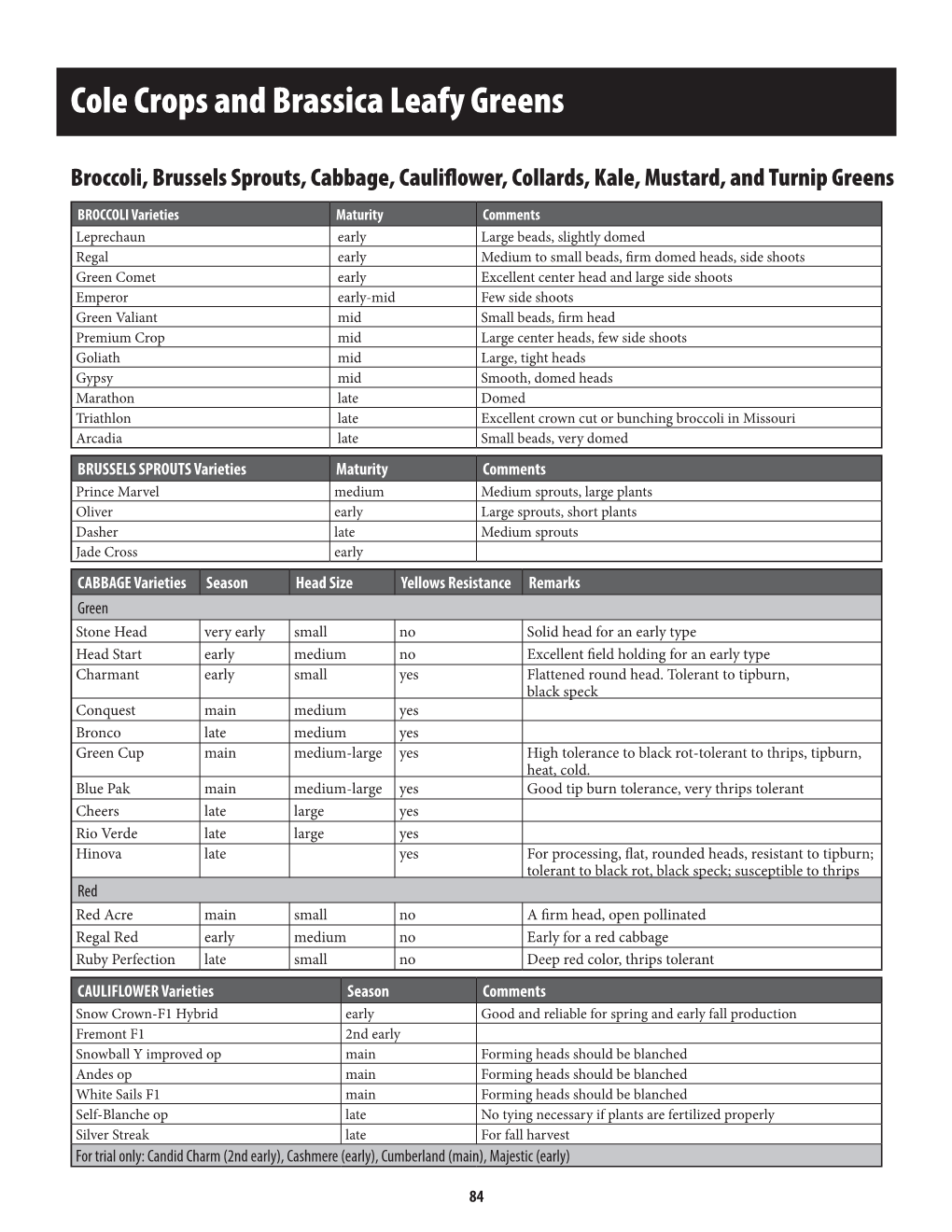
Cole Crops and Brassica Leafy Greens
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Hybridizing Collard and Cabbage May Provide a Means to Develop
HORTSCIENCE 40(6):1686–1689. 2005. of certain OP cultivars, for instance, a tendency of ‘Champion’ to resist bolting under winter conditions (Farnham and Garrett, 1996), have Hybridizing Collard and Cabbage May provided a reason for these older cultivars to persist in spite of the advantages commercial Provide a Means to Develop Collard hybrids provide. Today, the numbers of commercially avail- Cultivars able OP and hybrid collard cultivars are both limited. Nearly all cultivars tend to be sus- Mark W. Farnham1 ceptible to diseases such as fusarium yellows U.S. Department of Agriculture, Agricultural Research Service. U.S. Vegetable (Farnham et al. 2001), whereas most cabbage Laboratory, 2700 Savannah Highway, Charleston, SC 29414 cultivars are highly resistant (Dixon, 1981). Such disease susceptibility makes most collard Glen Ruttencutter2 cultivars vulnerable to severe damage when Seminis Vegetable Seed Co., 37437 State Highway 16, Woodland, CA 95695 grown in infested soil under warm conditions (Farnham et al., 2001). J. Powell Smith3 Previously, it was reported that heading of Clemson Edisto Research and Education Center, 64 Research Road, Blackville, cabbage is partially recessive to the nonheading nature expressed by collard (Dickson and Wal- SC 29817 lace, 1986). Thus, we hypothesized that hybrids Anthony P. Keinath4 between cabbage and collard would look more like collard than cabbage and that hybridizing Clemson Coastal Research and Education Center, 2700 Savannah Highway, between the crop groups might provide a Charleston, SC 29414 means to develop new collard cultivars. Such Additional index words. Brassica oleracea, cytoplasmic male sterility, Acephala Group hybrids could exploit the especially large pool of cabbage germplasm available in the United Abstract. -

Vegetables: Dark-Green Leafy, Deep Yellow, Dry Beans and Peas (Legumes), Starchy Vegetables and Other Vegetables1 Glenda L
Archival copy: for current recommendations see http://edis.ifas.ufl.edu or your local extension office. FCS 1055 Vegetables: Dark-Green Leafy, Deep Yellow, Dry Beans and Peas (legumes), Starchy Vegetables and Other Vegetables1 Glenda L. Warren2 • Deep yellow vegetables provide: Vitamin A. Eat 3 to 5 servings of vegetables each day. Examples: Carrots, pumpkins, sweet potatoes, Include all types of vegetables regularly. winter squash. What counts as one serving? • 1 cup of raw leafy vegetables (such as lettuce or spinach) • ½ cup of chopped raw vegetables • ½ cup of cooked vegetables • ¾ cup of vegetable juice Eat a variety of vegetables • Dry Beans and Peas (legumes) provide: It is important to eat many different vegetables. Thiamin, folic acid, iron, magnesium, All vegetables provide dietary fiber, some provide phosphorus, zinc, potassium, protein, starch, starch and protein, and they are also sources of fiber. Beans and peas can be used as meat many vitamins and minerals. alternatives since they are a source of protein. Examples: Black beans, black-eyed peas, • Dark-green vegetables provide: Vitamins A chickpeas (garbanzos), kidney beans, lentils, and C, riboflavin, folic acid, iron, calcium, lima beans (mature), mung beans, navy beans, magnesium, potassium. Examples: Beet pinto beans, split peas. greens, broccoli, collard greens, endive, • Starchy vegetables provide: Starch and escarole, kale, mustard greens, romaine varying amounts of certain vitamins and lettuce, spinach, turnip greens, watercress. minerals, such as niacin, vitamin B6, zinc, and 1. This document is FCS 1055, one of a series of the Department of Family, Youth and Community Sciences, Florida Cooperative Extension Service, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences, University of Florida. -

Brassica Rapa)Ssp
Li et al. Horticulture Research (2020) 7:212 Horticulture Research https://doi.org/10.1038/s41438-020-00449-z www.nature.com/hortres ARTICLE Open Access A chromosome-level reference genome of non- heading Chinese cabbage [Brassica campestris (syn. Brassica rapa)ssp. chinensis] Ying Li 1,Gao-FengLiu1,Li-MingMa2,Tong-KunLiu 1, Chang-Wei Zhang 1, Dong Xiao1, Hong-Kun Zheng2, Fei Chen1 and Xi-Lin Hou 1 Abstract Non-heading Chinese cabbage (NHCC) is an important leafy vegetable cultivated worldwide. Here, we report the first high-quality, chromosome-level genome of NHCC001 based on PacBio, Hi-C, and Illumina sequencing data. The assembled NHCC001 genome is 405.33 Mb in size with a contig N50 of 2.83 Mb and a scaffold N50 of 38.13 Mb. Approximately 53% of the assembled genome is composed of repetitive sequences, among which long terminal repeats (LTRs, 20.42% of the genome) are the most abundant. Using Hi-C data, 97.9% (396.83 Mb) of the sequences were assigned to 10 pseudochromosomes. Genome assessment showed that this B. rapa NHCC001 genome assembly is of better quality than other currently available B. rapa assemblies and that it contains 48,158 protein-coding genes, 99.56% of which are annotated in at least one functional database. Comparative genomic analysis confirmed that B. rapa NHCC001 underwent a whole-genome triplication (WGT) event shared with other Brassica species that occurred after the WGD events shared with Arabidopsis. Genes related to ascorbic acid metabolism showed little variation among the three B. rapa subspecies. The numbers of genes involved in glucosinolate biosynthesis and catabolism 1234567890():,; 1234567890():,; 1234567890():,; 1234567890():,; were higher in NHCC001 than in Chiifu and Z1, due primarily to tandem duplication. -

Produce Asian
RECIPIES Stir-Fried Spicy Chinese Your Chinese Greens Long Bean Salad Serves 4 to 6 • 1 pound Chinese long Guide 1 • 1 /2 pounds Chinese greens beans such as Chinese broccoli, rabe, • 1 quart water Garnish baby bok choy, baby Napa cabbage, • 1 teaspoons cooking oil • Black sesame seeds to Chinese long beans 1 • /4 teaspoon salt • Chopped jalapeno • 1 carrot, cut into matchstick stips Dressing pepper 1 • /4 pound fuzzy melon or diakon, peeled 1 ... • /4 cup sesame seeds 1 • 1 /2 to 2 tablespoons corn or peanut oil 1 • /4 cup hoisin sauce 1 • /4 cup rice wine or dry sherry 1 • /3 cup seasoned rice vinegar 1 • /4 cup plus 2 tablespoons unsalted chicken or • 1 teaspoon chili garlic sauce vegetable stock Place sesame seeds in a small frying pan over medium heat; cook, Trim the base of the Chinese broccoli only if woody; the stems shaking the pan frenquently until seeds are lightly browned, about are prized more than the leaves. Cut the stalks on the diagonal 3–4 minutes. Immediately remove from pan to cool. Place seeds into finger-lengths; leave the leaf and flower clusters attached to in blender and process until well-ground. the stem, or separate if large. Cut Chinese rabe in the same manner. Cut off the base of the baby cabbage; trim and reserve them. Leave Add remaining ingredients in blender and process until smooth. smaller leaves whole; cut larger leaves on the diagonal in half; Remove and discard ends of the long beans. Cut diagonally into leave intact the miniature cabbages at the core. -

SMOKY ROMESCO CAULIFLOWER Kale with Red Peppers, Dried Apricots & Feta, Roasted Potatoes
SMOKY ROMESCO CAULIFLOWER Kale with red peppers, dried apricots & feta, roasted potatoes COOK TIME SERVINGS CALORIES PER SERVING MENU 35 MIN 2 680 GLUTEN-FREE We love the smoky, tangy complexity of Spanish INGREDIENTS (11 ITEMS) WHAT YOU’LL NEED romesco sauce — a versatile condiment 1 oz Dried apricots medium & large sauté pans typically made with roasted red peppers, nuts, 9 ½ oz Red potatoes 2 baking sheets and vinegar. Inspired by the bold flavors of that 9 ¾ oz Cauliflower mixing bowls classic sauce, we seasoned roasted cauliflower ½ oz Hazelnuts T measuring cup & spoons florets with sweet and smoky paprika, 4 ¼ oz Green kale oven mitt then finished them in a vibrant red pepper ¼ oz Chives cooking oil vinaigrette. Sautéed kale (strewn with roasted 1 tsp Smoky Spanish-style seasoning salt & pepper peppers, dried apricots, and hazelnuts) forms 1 ¼ tsp Sweet & smoky paprika a nourishing base for the dish, while tender 1 oz Roasted red peppers ALLERGENS roasted potatoes make a savory side. 2 oz Feta cheese M T TREE NUTS (hazelnuts) 2 oz Roasted red pepper M MILK cider vinaigrette KING O FO O R C If you ordered the 4-serving version of this meal, 4 refer to the guidelines in Step 1. Certified gluten-free by the Gluten Intolerance Group’s Gluten-Free Safe Spot Program. GREEN CHEF IS PROUD to be a USDA Certified Organic company. Wash and dry fresh produce. Go to greenchef.com/faq for safe cooking guidelines and to learn more about food allergens. All produce and eggs are organic unless otherwise labeled. Questions? Contact us at (888) 236-7295. -

Environmental and Genetic Variation in Essential Mineral Nutrients and Nutritional Value Among Brassica Vegetables
Journal of Agricultural Science; Vol. 10, No. 7; 2018 ISSN 1916-9752 E-ISSN 1916-9760 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education Environmental and Genetic Variation in Essential Mineral Nutrients and Nutritional Value Among Brassica Vegetables Moo Jung Kim1, Tyler J. Simpson1, Yu-Chun Chiu1, Talon M. Becker2, John A. Juvik3 & Kang-Mo Ku1 1 Division of Plant and Soil Sciences, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV, USA 2 Extension-Commercial Agriculture, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Benton, IL, USA 3 Department of Crop Sciences, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Urbana, IL, USA Correspondence: Kang-Mo Ku, Division of Plant and Soil Sciences, West Virginia University, Morgantown, WV 26505, USA. Tel: 1-304-293-2549. E-mail: [email protected] Received: March 20, 2018 Accepted: April 28, 2018 Online Published: June 15, 2018 doi:10.5539/jas.v10n7p1 URL: https://doi.org/10.5539/jas.v10n7p1 Abstract Dietary minerals play an important role in human nutrition and proper metabolism. We grew various Brassica crops under field conditions in 2012 and 2013 and analyzed 8 essential minerals from edible tissues of those crops. Among the investigated crops, pak choi (Brassica rapa), mustard greens (B. juncea; B. nigra), and komatsuna (B. rapa) were generally high in most minerals, according to dry weight-based concentrations. The percentage recommended daily intake (RDA) or adequate intake (AI) values, calculated using fresh weight-based concentrations, suggest that Brassica vegetables are a good source of iron, calcium, and manganese, providing > 20% of %RDA/AI depending on crop. Kale (B. oleracea; B. napus) was generally higher in %RDA/AI, in particular for calcium (Ca), phosphorous (P), magnesium (Mg), and manganese (Mn). -

Companion Plants for Better Yields
Companion Plants for Better Yields PLANT COMPATIBLE INCOMPATIBLE Angelica Dill Anise Coriander Carrot Black Walnut Tree, Apple Hawthorn Basil, Carrot, Parsley, Asparagus Tomato Azalea Black Walnut Tree Barberry Rye Barley Lettuce Beans, Broccoli, Brussels Sprouts, Cabbage, Basil Cauliflower, Collard, Kale, Rue Marigold, Pepper, Tomato Borage, Broccoli, Cabbage, Carrot, Celery, Chinese Cabbage, Corn, Collard, Cucumber, Eggplant, Irish Potato, Beet, Chive, Garlic, Onion, Beans, Bush Larkspur, Lettuce, Pepper Marigold, Mint, Pea, Radish, Rosemary, Savory, Strawberry, Sunflower, Tansy Basil, Borage, Broccoli, Carrot, Chinese Cabbage, Corn, Collard, Cucumber, Eggplant, Beet, Garlic, Onion, Beans, Pole Lettuce, Marigold, Mint, Kohlrabi Pea, Radish, Rosemary, Savory, Strawberry, Sunflower, Tansy Bush Beans, Cabbage, Beets Delphinium, Onion, Pole Beans Larkspur, Lettuce, Sage PLANT COMPATIBLE INCOMPATIBLE Beans, Squash, Borage Strawberry, Tomato Blackberry Tansy Basil, Beans, Cucumber, Dill, Garlic, Hyssop, Lettuce, Marigold, Mint, Broccoli Nasturtium, Onion, Grapes, Lettuce, Rue Potato, Radish, Rosemary, Sage, Thyme, Tomato Basil, Beans, Dill, Garlic, Hyssop, Lettuce, Mint, Brussels Sprouts Grapes, Rue Onion, Rosemary, Sage, Thyme Basil, Beets, Bush Beans, Chamomile, Celery, Chard, Dill, Garlic, Grapes, Hyssop, Larkspur, Lettuce, Cabbage Grapes, Rue Marigold, Mint, Nasturtium, Onion, Rosemary, Rue, Sage, Southernwood, Spinach, Thyme, Tomato Plant throughout garden Caraway Carrot, Dill to loosen soil Beans, Chive, Delphinium, Pea, Larkspur, Lettuce, -

Broccoli; the Green Beauty: a Review
A. I. Owis /J. Pharm. Sci. & Res. Vol. 7(9), 2015, 696-703 Broccoli; The Green Beauty: A Review A. I. Owis Department of Pharmacognosy, Beni-Suef University, Beni-Suef,Egypt Telephone: +202-01202500017 Abstract Context: Plants are nature′s blessing to mankind to make malady free sound life, and assume an essential part to protect our wellbeing. Broccoli - Brassica oleracea L.var. italica Plenk (Brassicaceae) - is considered as a nutritional powerhouse. The present review comprises the phytochemical and therapeutic potential of broccoli. Objective: This aim of this review to collect results obtained from various studies in order to spot more light towards the surprising green world of broccoli. In addition to, a number of recommendations that will help to secure a more sound „proof- of-concept‟ to complete the whole picture providing significant information could be used as a dietary guideline that encourage broccoli consumption for the management of various diseases. Methods: This review has been compiled using references from major databases such as Chemical Abstracts, ScienceDirect, SciFinder, PubMed, Henriette′s Herbal Homepage and Google scholars Databases. Results: An extensive survey of literature revealed that broccoli is a good source of health promoting compounds such as glucosinolates, flavonoids, hydroxycinnamic acids and vitamins. Moreover, broccoli is the kind of nutrient that has so many wonderful applications including gastroprotective, antimicrobial, antioxidant, anticancer, hepatoprotective, cardioprotective, anti-obesity, anti-diabetic, anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities. Conclusion: There are still missing areas need further in-depth investigation such as effect of broccoli on central nervous system. Keywords: biological activities, Brassica oleracea, Brassicaceae, phytochemistry. INTRODUCTION leaves. -

KC Refrigerated Product List 10.1.19.Indd
Created 3.11.09 One Color White REFRIGERATEDWhite: 0C 0M 0Y 0K COLLECTION Albondigas (Mexican Meatball Soup) Black Bean Soup Butternut Squash & Apple Soup 700856 700820 VN VG DF GF 700056 GF Savory meatballs, white rice and vibrant Slow-cooked black beans, red peppers, A blend of puréed butternut squash, onions tomatoes in a handcrafted chicken stock roasted sweet corn and diced green chilies and handcrafted stock with caramelized infused with traditional Mexican aromatics in a purée of vine-ripened tomatoes with a Granny Smith apples and a pinch of fresh and a touch of fresh lime juice. splash of fresh-squeezed orange juice. nutmeg. Angus Steak Chili with Beans Black Lentil & Roasted Garlic Dahl* Caribbean Jerk Chicken Soup 700095 DF GF 701762 VG GF 700708 DF GF Tender strips of seared Angus beef, green Black beluga lentils, sautéed onions, roasted Tender chicken, sweet potatoes, carrots peppers and red beans in slow-simmered garlic and ginger slow-simmered in a rich and tomatoes in a handcrafted chicken tomatoes with Southwestern spices. tomato broth, infused with warming spices, stock with white rice, red beans, traditional finished with butter and heavy cream. jerk seasoning and a hint of molasses. Beef Barley & Vegetable Soup Broccoli Cheddar Soup Carrot Ginger Soup 700023 700063 VG GF 700071 VN VG DF GF Seared strips of lean beef and pearl barley Delicately puréed broccoli and sautéed Sweet carrots puréed with fresh-squeezed with red peppers, mushrooms, peas, onions in a rich blend of extra sharp orange juice, hand-peeled ginger and tomatoes and green beans in a rich cheddar cheese and light cream with a sautéed onions with a touch of toasted beef stock. -

Crispy Brussels Sprout & Saffron Risotto
Crispy Brussels Sprout & Saffron blueapron.com Risotto with Parmesan Cheese 2 SERVINGS | 25–35 MINS R IS P Ingredients C & Serve with Blue Apron M wine that has this symbol Y I N L L blueapron.com/wine 1/2 lb Brussels E R A 1 cup Carnaroli Rice 2 cloves Garlic Sprouts 1 Lemon 1 Shallot 2 Tbsps Butter 2 Tbsps Mascarpone 1/4 cup Grated 1 pinch Saffron Cheese Parmesan Cheese 1/4 tsp Crushed Red Pepper Flakes 1 Prepare the ingredients 3 Make the risotto • Place an oven rack in the center • To the pot of cooked shallot, of the oven; preheat to 450°F. add the rice, saffron, and 3 cups • Wash dry the fresh produce. of water (carefully, as the liquid may splatter); season with salt • Peel and finely chop the shallot. and pepper. Heat to boiling • Peel and roughly chop 2 cloves on high. of garlic. • Once boiling, reduce the heat • Combine the chopped shallot to medium-high. Cook, stirring and chopped garlic in a bowl. occasionally, 15 to 17 minutes, or • Quarter and deseed the lemon. until most of the liquid has been absorbed and the rice is al dente (still slightly firm to the bite). • Cut off and discard the stem ends of the brussels sprouts; quarter lengthwise. • Turn off the heat. Add the butter, mascarpone, and the juice of 2 lemon wedges; stir until thoroughly combined and the butter 2 Cook the shallot is melted. • In a medium pot, heat • Taste, then season with salt and pepper if desired. 2 teaspoons of olive oil on medium-high until hot. -

Brussels Sprout
Brussels Sprout Introduction: At this club in October 2011 Dick Turvey told us that he believed that growing Brussels Sprouts was an easier way for two people to eat cabbage greens than growing cabbages. He planted seedlings in the first week of October, November and December for succession and claimed “Maxim” was the best variety. My own experience has been that they are at least as easy to grow as cabbages and provide a more continuous yield. We can pick what we need for a meal rather than picking a whole cabbage and a brussels sprout crops over a longer period than a cabbage. Growing: You can have Brussels Sprouts virtually all year round in Dunedin (apart for the hungry gap between October and December). Plant seedlings as soon as growth starts in the spring (September-October) for the summer and autumn and again in January for winter and early spring. They should be 30cm apart in rows that are 60 cm apart. We grow six plants in Spring and six in January. Like all the cabbage family they grow fastest if you have lots of nitrogen in the soil. They grow in temperatures of 7 – 24 ⁰ C with highest yields at 15 – 18 ⁰ C and home gardeners have an advantage over commercial growers in that you can harvest them over many weeks and they are not affected by freezing temperatures – some say it even enhances the flavour. They are part of the cabbage family and so put them in the same plot as Broccoli, cabbage & Chinese cabbage, cauliflower, radish, swede, kale, kohlrabi, mustard, radish and rocket. -

Vegetables Discover Our Varieties 2 3
VEGETABLES DISCOVER OUR VARIETIES 2 3 CONTENTS INTRODUCTION ..........................................................................4-5 MEET THE TEAM .........................................................................6-7 CLUBROOT SOLUTIONS ............................................................8-9 BROCCOLI ..............................................................................10-13 BRUSSELS SPROUTS .............................................................14-19 CABBAGE ...............................................................................20-27 CAULIFLOWER .......................................................................28-37 COURGETTE ...........................................................................38-41 WHOLEHEAD LETTUCE ..........................................................42-47 BABYLEAF ..............................................................................48-53 ENDIVE ...................................................................................54-55 ROOTS & BULBS ....................................................................56-59 LEVELS OF RESISITANCE ............................................................ 60 TABLE OF ABBREVIATIONS ......................................................... 61 4 INTRODUCTION In 2017, Syngenta celebrated 150 years as leading pioneers of vegetable seed breeding, with the commemoration of the creation of Sluis & Groot (S&G) by two Dutch farmers from Andijk in the Netherlands, in July 1867. From those origins as cabbage seed exporters,