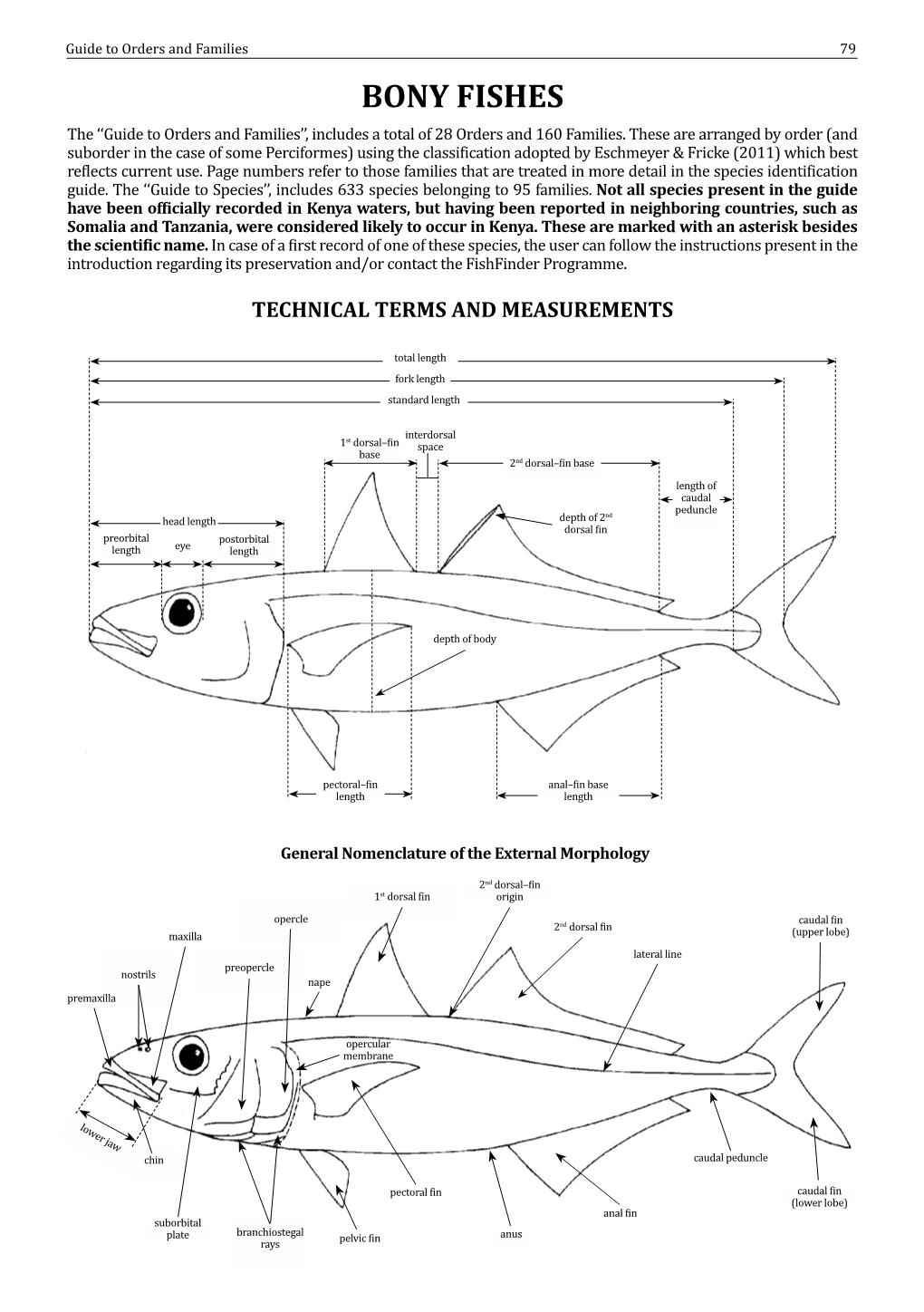
BONY FISHES the ‘‘Guide to Orders and Families’’, Includes a Total of 28 Orders and 160 Families
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Section 3.9 Fish
3.9 Fish MARIANA ISLANDS TRAINING AND TESTING FINAL EIS/OEIS MAY 2015 TABLE OF CONTENTS 3.9 FISH .................................................................................................................................. 3.9-1 3.9.1 INTRODUCTION .............................................................................................................................. 3.9-2 3.9.1.1 Endangered Species Act Species ................................................................................................ 3.9-2 3.9.1.2 Taxonomic Groups ..................................................................................................................... 3.9-3 3.9.1.3 Federally Managed Species ....................................................................................................... 3.9-5 3.9.2 AFFECTED ENVIRONMENT ................................................................................................................ 3.9-9 3.9.2.1 Hearing and Vocalization ......................................................................................................... 3.9-10 3.9.2.2 General Threats ....................................................................................................................... 3.9-12 3.9.2.3 Scalloped Hammerhead Shark (Sphyrna lewini) ...................................................................... 3.9-14 3.9.2.4 Jawless Fishes (Orders Myxiniformes and Petromyzontiformes) ............................................ 3.9-15 3.9.2.5 Sharks, Rays, and Chimaeras (Class Chondrichthyes) -

Amorphometric and Meristic Study of the Halfbeak, Hyporhamphus
W&M ScholarWorks Dissertations, Theses, and Masters Projects Theses, Dissertations, & Master Projects 1993 Amorphometric and Meristic Study of the Halfbeak, Hyporhamphus unifasciatus (Teleostei: Hemiramphidae) from the Western Atlantic, with the Description of a New Species Heidi M. Banford College of William and Mary - Virginia Institute of Marine Science Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.wm.edu/etd Part of the Marine Biology Commons, and the Oceanography Commons Recommended Citation Banford, Heidi M., "Amorphometric and Meristic Study of the Halfbeak, Hyporhamphus unifasciatus (Teleostei: Hemiramphidae) from the Western Atlantic, with the Description of a New Species" (1993). Dissertations, Theses, and Masters Projects. Paper 1539617658. https://dx.doi.org/doi:10.25773/v5-pbsc-sy52 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Theses, Dissertations, & Master Projects at W&M ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dissertations, Theses, and Masters Projects by an authorized administrator of W&M ScholarWorks. For more information, please contact [email protected]. A MORPHOMETRIC AND MERISTIC STUDY OF THE HALFBEAK, HYPORHAMPHUS UNIFASCIATUS (TELEOSTEI: HEMIRAMPHIDAE) FROM THE WESTERN ATLANTIC, WITH THE DESCRIPTION OF A NEW SPECIES A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the School of Marine Science The College of William and Mary in Virginia In Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Arts by Heidi M. Banford 1993 This thesis is submitted in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Master of Arts Heidi M. Banford Approved, July 1993 Jojm A. Musick,' Ph.D. flmittee Chairman/Advisor ~ t M . ^ Herbert M. Austin, Ph.D. -

MARKET FISHES of INDONESIA Market Fishes
MARKET FISHES OF INDONESIA market fishes Market fishes indonesiaof of Indonesia 3 This bilingual, full-colour identification William T. White guide is the result of a joint collaborative 3 Peter R. Last project between Indonesia and Australia 3 Dharmadi and is an essential reference for fish 3 Ria Faizah scientists, fisheries officers, fishers, 3 Umi Chodrijah consumers and enthusiasts. 3 Budi Iskandar Prisantoso This is the first detailed guide to the bony 3 John J. Pogonoski fish species that are caught and marketed 3 Melody Puckridge in Indonesia. The bilingual layout contains information on identifying features, size, 3 Stephen J.M. Blaber distribution and habitat of 873 bony fish species recorded during intensive surveys of fish landing sites and markets. 155 market fishes indonesiaof jenis-jenis ikan indonesiadi 3 William T. White 3 Peter R. Last 3 Dharmadi 3 Ria Faizah 3 Umi Chodrijah 3 Budi Iskandar Prisantoso 3 John J. Pogonoski 3 Melody Puckridge 3 Stephen J.M. Blaber The Australian Centre for International Agricultural Research (ACIAR) was established in June 1982 by an Act of the Australian Parliament. ACIAR operates as part of Australia’s international development cooperation program, with a mission to achieve more productive and sustainable agricultural systems, for the benefit of developing countries and Australia. It commissions collaborative research between Australian and developing-country researchers in areas where Australia has special research competence. It also administers Australia’s contribution to the International Agricultural Research Centres. Where trade names are used, this constitutes neither endorsement of nor discrimination against any product by ACIAR. ACIAR MONOGRAPH SERIES This series contains the results of original research supported by ACIAR, or material deemed relevant to ACIAR’s research and development objectives. -

ANALISIS ASPEK BIOLOGI IKAN TERBANG Cheilopogon Katoptron Bleeker, 1865, DI PERAIRAN PEMUTERAN, BALI BARAT TESIS DONY ARMA
UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANALISIS ASPEK BIOLOGI IKAN TERBANG Cheilopogon katoptron Bleeker, 1865, DI PERAIRAN PEMUTERAN, BALI BARAT TESIS DONY ARMANTO 0906577034 FAKULTAS MATEMATIKA DAN ILMU PENGETAHUAN ALAM PROGRAM MAGISTER ILMU KELAUTAN DEPOK JANUARI 2012 Analisis aspek..., Dony Armanto, FMIPA UI, 2012 2 UNIVERSITAS INDONESIA ANALISIS ASPEK BIOLOGI IKAN TERBANG Cheilopogon katoptron Bleeker, 1865, DI PERAIRAN PEMUTERAN, BALI BARAT TESIS Diajukan sebagai salah satu syarat untuk memperoleh gelar Magister Sains DONY ARMANTO 0906577034 FAKULTAS MATEMATIKA DAN ILMU PENGETAHUAN ALAM PROGRAM MAGISTER ILMU KELAUTAN DEPOK JANUARI 2012 ii Universitas Indonesia Analisis aspek..., Dony Armanto, FMIPA UI, 2012 3 HALAMAN PERNYATAAN ORISINALITAS Tesis ini adalah hasil karya sendiri, dan semua sumber baik yang dikutip maupun yang dirujuk telah saya nyatakan dengan benar. Nama : Dony Armanto NPM : 0906577034 Tanda Tangan : .............................. Tanggal : 3 Januari 2012 iii Universitas Indonesia Analisis aspek..., Dony Armanto, FMIPA UI, 2012 4 HALAMAN PENGESAHAN Tesis ini diajukan oleh: Nama : Dony Armanto NPM : 0906577034 Program Studi : Magister Ilmu Kelautan Judul Tesis : Analisis Aspek Biologi Ikan Terbang Cheilopogon katoptron Bleeker, 1865, di Perairan Pemuteran, Bali Barat Telah berhasil dipertahankan di hadapan Dewan Penguji dan diterima sebagai bagian persyaratan yang diperlukan untuk memperoleh gelar Magister Sains (M.Si) pada Program Studi Ilmu Kelautan, Fakultas Matematika dan Ilmu Pengetahuan Alam, Universitas Indonesia. DEWAN PENGUJI -

Ambush Predator’ Guild – Are There Developmental Rules Underlying Body Shape Evolution in Ray-Finned Fishes? Erin E Maxwell1* and Laura AB Wilson2
Maxwell and Wilson BMC Evolutionary Biology 2013, 13:265 http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2148/13/265 RESEARCH ARTICLE Open Access Regionalization of the axial skeleton in the ‘ambush predator’ guild – are there developmental rules underlying body shape evolution in ray-finned fishes? Erin E Maxwell1* and Laura AB Wilson2 Abstract Background: A long, slender body plan characterized by an elongate antorbital region and posterior displacement of the unpaired fins has evolved multiple times within ray-finned fishes, and is associated with ambush predation. The axial skeleton of ray-finned fishes is divided into abdominal and caudal regions, considered to be evolutionary modules. In this study, we test whether the convergent evolution of the ambush predator body plan is associated with predictable, regional changes in the axial skeleton, specifically whether the abdominal region is preferentially lengthened relative to the caudal region through the addition of vertebrae. We test this hypothesis in seven clades showing convergent evolution of this body plan, examining abdominal and caudal vertebral counts in over 300 living and fossil species. In four of these clades, we also examined the relationship between the fineness ratio and vertebral regionalization using phylogenetic independent contrasts. Results: We report that in five of the clades surveyed, Lepisosteidae, Esocidae, Belonidae, Sphyraenidae and Fistulariidae, vertebrae are added preferentially to the abdominal region. In Lepisosteidae, Esocidae, and Belonidae, increasing abdominal vertebral count was also significantly related to increasing fineness ratio, a measure of elongation. Two clades did not preferentially add abdominal vertebrae: Saurichthyidae and Aulostomidae. Both of these groups show the development of a novel caudal region anterior to the insertion of the anal fin, morphologically differentiated from more posterior caudal vertebrae. -

Hotspots, Extinction Risk and Conservation Priorities of Greater Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico Marine Bony Shorefishes
Old Dominion University ODU Digital Commons Biological Sciences Theses & Dissertations Biological Sciences Summer 2016 Hotspots, Extinction Risk and Conservation Priorities of Greater Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico Marine Bony Shorefishes Christi Linardich Old Dominion University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.odu.edu/biology_etds Part of the Biodiversity Commons, Biology Commons, Environmental Health and Protection Commons, and the Marine Biology Commons Recommended Citation Linardich, Christi. "Hotspots, Extinction Risk and Conservation Priorities of Greater Caribbean and Gulf of Mexico Marine Bony Shorefishes" (2016). Master of Science (MS), Thesis, Biological Sciences, Old Dominion University, DOI: 10.25777/hydh-jp82 https://digitalcommons.odu.edu/biology_etds/13 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Biological Sciences at ODU Digital Commons. It has been accepted for inclusion in Biological Sciences Theses & Dissertations by an authorized administrator of ODU Digital Commons. For more information, please contact [email protected]. HOTSPOTS, EXTINCTION RISK AND CONSERVATION PRIORITIES OF GREATER CARIBBEAN AND GULF OF MEXICO MARINE BONY SHOREFISHES by Christi Linardich B.A. December 2006, Florida Gulf Coast University A Thesis Submitted to the Faculty of Old Dominion University in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE BIOLOGY OLD DOMINION UNIVERSITY August 2016 Approved by: Kent E. Carpenter (Advisor) Beth Polidoro (Member) Holly Gaff (Member) ABSTRACT HOTSPOTS, EXTINCTION RISK AND CONSERVATION PRIORITIES OF GREATER CARIBBEAN AND GULF OF MEXICO MARINE BONY SHOREFISHES Christi Linardich Old Dominion University, 2016 Advisor: Dr. Kent E. Carpenter Understanding the status of species is important for allocation of resources to redress biodiversity loss. -

First Record of Mothocya Arrosor Bruce, 1986 Parasitizing Euleptorhamphus Viridis (Van Hasselt, 1823) from India
Zoology and Ecology, 2021, Volume 31, Number 1 Online ISSN: 2165-8013 https://doi.org/10.35513/21658005.2021.1.2 FIRST RECORD OF MOTHOCYA ARROSOR BRUCE, 1986 PARASITIZING EULEPTORHAMPHUS VIRIDIS (VAN HASSELT, 1823) FROM INDIA P. Vigneshwarana* and S. Ravichandrana, b aCentre of Advanced Study in Marine Biology, Annamalai University, Parangipettai – 608 502, India bGovernment Thirumagal Mills College, Gudiyatham – 632 602, Tamil Nadu, India *Corresponding author. Email: [email protected] Article history Abstract. The first record of Mothocya arrosor Bruce, 1986 parasitizing ribbon halfbeak fish 14 September 2020; Euleptorhamphus viridis is here reported from the southeast coast of India. The important characters accepted 15 February 2021 distinguishing M. arrosor from other species in the genus include the body slightly twisted to one side, dorsum weakly convex, coxae of pereonites 6 and 7 distinctly rounded, pleon more completely Keywords: overlapped by pereonite 7, pleonite 1 scarcely visible in dorsal view, uropod peduncle longer than cymothoid; Mothocya; fish rami, lacking strongly convex medial and lateral margins. The damage of gill rakers and erosion of parasites; first report; India gill lamellae were the acute gross lesions observed as a result of isopod infestation. Cymothoids are one of the most recognisable groups of tifiable asMothocya arrosor Bruce, 1986 was collected isopods and represent obligate ectoparasites of various in Parangipettai, Tamilnadu, south-eastern coast of India marine, brackish and freshwater fish species (Smit et al. (11°29' N 70°64' E). This collection constitutes the first 2014). These large (> 6 mm) aquatic parasites are com- Indian record of M. arrosor from the host fish ribbon monly found attached to the host surface (exterior body), halfbeak Euleptorhamphus viridis (van Hasselt, 1823) inside the buccal cavity, or inside the branchial cavity of (Beloniformes: Hemiramphidae) and the sixth species the host. -

Review of Billfish Biology from Indian Fishery 1Bishnupadasethi and 2Ansy Mathew, N
IOTC–2014–WPB12–11 Rev_2 Review of Billfish biology from Indian fishery 1BishnupadaSethi and 2Ansy Mathew, N. P. 1Secretary & Commissioner (Fisheries), Government of Odisha, Bhubaneswar-751 001, Odisha, India. Email:[email protected] 2Fisheries Research and Investigation Officer, Department of Animal Husbandry, Dairying & Fisheries, Ministry of Agriculture, Government of India, KrishiBhawan, New Delhi-110114. E- mail: [email protected] Abstract In India, billfish fishery is contributed by Indo-pacific sailfish, blue marlin, black marlin, striped marlin and swordfish. The landings of the billfishes along the Indian coast are showing an increasing trend since the 1990s and the estimated landing during 2012 was 11613 t. Drift gillnets-cum-longline, handlines and longlines operated from mechanized and motorized craft contributed maximum to the catches. Along the east coast, peak catches occur during July- September and along the west coast during October-March. Length-weight structure and biology of the dominant species are presented and discussed. Keywords: Billfish, sailfish, drift gillnet, longline, by-catch Introduction In India, targeted fishery for billfishes does not exist, but this group constitute one of the most important components of bycatch in the longline, troll and oceanic drift gillnet fishery of Indian waters. Three species of marlins – stripped (Tetrapturus audax), blue (Makaira mazara) and black (M. Indica); Indo-Pacific sailfish (Istiophorus platypterus) and swordfish (Xiphias gladius) are the billfish species reported in the Indian fishery. The landings of the billfishes along the Indian coast are showing an increasing trend since the 1990s and the estimated landing during 2012 was 11613 t. Drift gillnets-cum-longline, handlines and longlines operated from mechanized and motorized craft contributed maximum to the catches. -

Ontogenetic and Seasonal Variations in the Feeding Ecology of Indo-Pacific Sailfish, Istiophorus Platypterus (Shaw, 1792), of the Eastern Arabian Sea
Indian Journal of Geo-Marine Sciences Vol. 42(5), September 2013, pp. 593-605 Ontogenetic and seasonal variations in the feeding ecology of Indo-Pacific sailfish, Istiophorus platypterus (Shaw, 1792), of the eastern Arabian Sea 1Sijo P. Varghese, 2V. S. Somvanshi & Deepak K. Gulati3 Cochin Base of Fishery Survey of India, PB No. 853, XIII/488, Kochangadi, Kochi 682005, India 2A - 1 Tower, Flat No. 701, Riddhi Gardens, Film City Road, Goregaon (East), Mumbai 400097, India Fishery Survey of India, Botawala Chambers, Sir P. M. Road, Mumbai 400001, India [Email: [email protected]] Received 21 May 2012; revised 21 August 2012 Present study consists the studies on the stomach contents of Indo-Pacific sailfish, Istiophorus platypterus (Shaw, 1792), caught during tuna longline survey conducted in the western Indian EEZ (eastern Arabian Sea) between 2006 and 2009 to investigate the sexual, ontogenetic and seasonal effects in the diet. Stomachs of 290 specimens in the forklength range of 101-261 cm were examined, of which 38 (13.10%) were empty. Prey composition was assessed in terms of occurrence by number, frequency of occurrence, weight and Index of Relative Importance. Quantile regression techniques were used to determine the mean and upper and lower bounds of the relation between prey size and sailfish length. Diet was dominated by teleost fishes, followed by cephalopods while crustaceans were represented in limited instances. Purpleback flying squid, Sthenoteuthis oualaniensis, was the most preferred prey species. Other important prey species identified were Euthynnus affinis, Cubiceps pauciradiatus, Gempylus serpens and Onychoteuthis banksii. Diet did not varied by sex, but the ontogenetic and seasonal variations in diet were significant. -

New Species and New Records of Fishes from Bermuda 1
II B RAR.Y OF THE U N IVER.SITY Of ILLINOIS 580.5 PI v.3L cop. 3 NATURAL HISTORY SURm NATURAL HISTORY SURVEY LIPP*f?Y Si 3 FIELDIANA ZOOLOGY Published by CHICAGO NATURAL HISTORY MUSEUM Volume 31 September 14, 1951 No. 53 NEW SPECIES AND NEW RECORDS OF FISHES FROM BERMUDA 1 Loren P. Woods Curator, Division of Fishes AND Robert H. Kanazawa Formerly Assistant, Division of Fishes In spite of the extensive collecting of shore fishes in Bermuda by the New York Zoological Society and earlier workers the fish fauna of these isolated islands is still far from completely known. During the summer of 1948 the members of the Bermuda Deep Sea Expedi- tion of Chicago Natural History Museum, operating from the Bermuda Biological Station for Research, were able to engage in only a limited amount of shore fishing. The principal collecting of this expedition was by means of the Woods Hole Oceanographic Institution's vessel, the 98-foot ketch, Caryn. Five poison stations in shoal waters were worked, four sweeps were made with a 75-foot otter trawl in 60 feet of water in the lagoon, and at odd times some additional specimens were gathered in traps and seines; a few pelagic fishes and young of shore fishes were taken in the deep sea nets at the surface, in sargassum, swimming to our light at night, or on a feather trolled behind the Caryn. By far the greater number of new records and species of Bermuda fishes have been found during the course of cataloguing a large col- lection made during the past forty years by Mr. -

Training Manual Series No.15/2018
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by CMFRI Digital Repository DBTR-H D Indian Council of Agricultural Research Ministry of Science and Technology Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute Department of Biotechnology CMFRI Training Manual Series No.15/2018 Training Manual In the frame work of the project: DBT sponsored Three Months National Training in Molecular Biology and Biotechnology for Fisheries Professionals 2015-18 Training Manual In the frame work of the project: DBT sponsored Three Months National Training in Molecular Biology and Biotechnology for Fisheries Professionals 2015-18 Training Manual This is a limited edition of the CMFRI Training Manual provided to participants of the “DBT sponsored Three Months National Training in Molecular Biology and Biotechnology for Fisheries Professionals” organized by the Marine Biotechnology Division of Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), from 2nd February 2015 - 31st March 2018. Principal Investigator Dr. P. Vijayagopal Compiled & Edited by Dr. P. Vijayagopal Dr. Reynold Peter Assisted by Aditya Prabhakar Swetha Dhamodharan P V ISBN 978-93-82263-24-1 CMFRI Training Manual Series No.15/2018 Published by Dr A Gopalakrishnan Director, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (ICAR-CMFRI) Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute PB.No:1603, Ernakulam North P.O, Kochi-682018, India. 2 Foreword Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute (CMFRI), Kochi along with CIFE, Mumbai and CIFA, Bhubaneswar within the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) and Department of Biotechnology of Government of India organized a series of training programs entitled “DBT sponsored Three Months National Training in Molecular Biology and Biotechnology for Fisheries Professionals”. -

NEPA-EA-Acls-Coral-R
U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration NATIONAL MARINE FISHERIES SERVICE Pacific Islands Regional Office 1845 Wasp Blvd. Bldg.176 Honolulu, Hawaii 96818 (808) 725-5000 • Fax (808) 725-5215 Environmental Assessment Specification of Annual Catch Limits and Accountability Measures for Pacific Island Coral Reef Ecosystem Fisheries in Fishing Years 2015 through 2018 (RIN 0648-XD558) August 12, 2015 Responsible Agency: National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) National Marine Fisheries Service (NMFS) Pacific Islands Regional Office (PIRO) Responsible Official: Michael D. Tosatto Regional Administrator, PIRO 1845 Wasp Blvd., Bldg 176 Honolulu, HI 96818 Tel (808)725-5000 Fax (808)725-5215 Responsible Council: Western Pacific Fishery Management Council 1164 Bishop St. Suite 1400 Honolulu, HI 96813 Tel (808)522-8220 Fax (808)522-8226 Abstract: The Western Pacific Fishery Management Council (Council) recommended NMFS specify multi-year annual catch limits (ACL) and accountability measures (AM) effective in fishing years 2015-2018, the environmental effects of which are analyzed in this document. NMFS proposes to implement the specifications for fishing year 2015, 2016, 2017, and 2018 separately prior to each fishing year. The specifications pertain to ACLs for coral reef ecosystem fisheries in the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ or federal waters; generally 3-200 nautical miles or nm) around American Samoa, the Commonwealth of the Northern Mariana Islands (CNMI), Guam, and Hawaii, and a post-season AM to correct the overage of an ACL if it occurs. Because of the large number of individual coral reef ecosystem management unit species (CREMUS) in each island area, individual species were aggregated into higher taxonomic groups, generally at the family level.