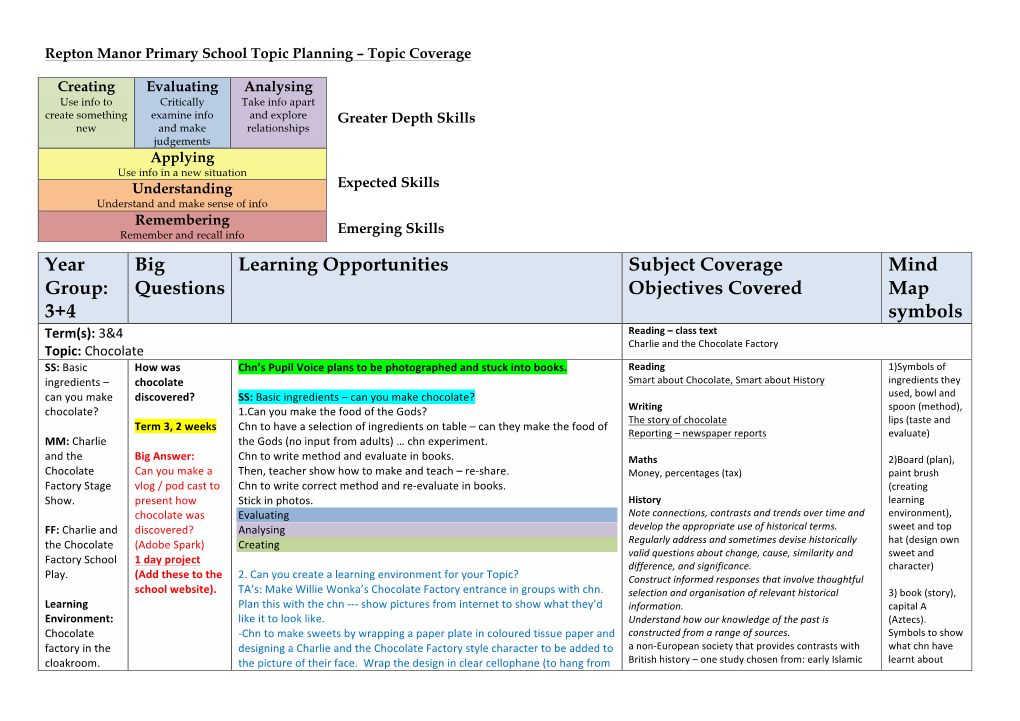
Chocolate Factory Topic: Chocolate SS: Basic How Was Chn’S Pupil Voice Plans to Be Photographed and Stuck Into Books
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

THE EVOLUTION of SCHOOL MATHEMATICS TEXTBOOKS Jeremy Kilpatrick University of Georgia [email protected]
International Conference on Mathematics Textbook Research and Development 2014 (ICMT-2014) 29-31 July 2014, University of Southampton, UK FROM CLAY TABLET TO COMPUTER TABLET: THE EVOLUTION OF SCHOOL MATHEMATICS TEXTBOOKS Jeremy Kilpatrick University of Georgia [email protected] Over the centuries and around the world, school mathematics textbooks have differed in many ways. In this idiosyncratic survey, I attempt to portray, across time and space, something of what researchers have learned about those textbooks: what they are, what they appear to be, how they are related, and how they have been used. In general, school mathematics textbooks have differed more in approach and form than in function or content. Their principal function has been to serve as repositories of authorized knowledge, although at times they have been enlisted as resources for creative problem solving or as material for self-instruction. In the past, as textbooks took different forms and appeared in different media—clay tablet, papyrus, parchment, bamboo, paper—they also began to take on a wider span of mathematical content and to vary extensively in pedagogical approach. Research on textbooks has examined many of their characteristics, looking at how they have changed over time and, less often, how they differ across communities. Today, school mathematics textbooks seem more similar in mathematical content than they are in appearance, pedagogical outlook, or assistance for the teacher. There does seem to be something of a virtual school mathematics curriculum worldwide, whereas there is little agreement on what features the textbooks enshrining that curriculum should have. Today’s textbooks vary along many dimensions. -

River Valley Civilizations: Mesopotamia (3500 BCE-1600 BCE)
FCPS World I SOL Standards: WHI 3a, 3b, 3c and 3e River Valley Civilizations: Mesopotamia (3500 B.C.E.-1600 B.C.E.) You Mean the Wheel Was Invented in the Middle East? Geography of the Fertile Crescent Mesopotamia is a Greek word that means “land between two rivers.” The Tigris is the river which sits on “top” and Euphrates which is “under.” Mesopotamia is located in a region called the Fertile Crescent because of the land’s curved shape consisting of rich soil. This region is located between the Persian Gulf and the Mediterranean Sea in Southwest Asia. The Tigris and Euphrates rivers flooded Mesopotamia at least once a year leaving behind a fertile mud called silt. Farmers planted crops in the rich soil and used these rivers for irrigation. Early civilizations developed in river valleys because the rivers helped with trade, gave these early city- Map of Mesopotamia states protection, and provided fertile soil. Source: http://www.marshallcavendishdigital.com/articledisplay/17/4505/46435/#img_11691 The Sumerians (3000 B.C.E.) Sumer is believed to be one of the first civilizations located in Mesopotamia. The Sumerians built many cities that shared the same culture yet they had their own government with their own rulers. This began the development of a city-state. At the center of every Sumerian city was a walled temple called a ziggurat. Religion played an important role in Sumer and the Sumerians believed in many gods. The belief in more than one god is called polytheism. Early Sumerian governments were controlled by temple priests but after 2500 B.C.E. -

Happy Presidents
VOL. 117 - NO. 7 BOSTON, MASSACHUSETTS, FEBRUARY 15, 2013 $.30 A COPY IT’S WINTER, Happy It Can Snow and Sometimes too Much Presidents Day by Sal Giarratani FEBRUARY 18, 2013 News Briefs by Sal Giarratani The Paul Revere Mall (a/k/a The Prado) on Hanover Street in Boston’s North End was a winter wonderland. (Photo by Rosario Scabin, Ross Photography) What Happened to the Days of As someone who is a sur- old storm when I lived in on the street, you become so Cronkite, Huntley & Brinkley and vivor of the Blizzard of ’78, I Charlestown, I can say that very grateful as I when you Howard K. Smith? wasn’t that excited over the this storm was really bad and have off-street parking. I hype leading up to this lat- in the top five storms in his- couldn’t live in crowded Once long before the major networks had stiff est Blizzard of ’13. I stopped tory but nothing will ever be neighborhoods without it. competition from 24/7 cable news outlets, the watching all the weather worse than the impact that My street, like many big three networks gave us the news and let us reports because they be- the 1978 storm had on the across the city’s neighbor- digest it for ourselves. Real newsmen like Walter came so silly. I wasn’t going entire seacoast of Massa- hoods, is barely wide enough Cronkite, Chet Huntley, David Brinkley and to go into a panic over snow chusetts. Everything was for cars to use. -

Blockchain As an Anti- Corruption Tool Case Examples and Introduction to the Technology
U4 Issue 2020:7 Blockchain as an anti- corruption tool Case examples and introduction to the technology By Per Aarvik Series editor: Arne Strand Disclaimer All views in this text are the author(s)’, and may differ from the U4 partner agencies’ policies. Partner agencies Australian Government – Department for Foreign Affairs and Trade – DFAT German Corporation for International Cooperation – GIZ German Federal Ministry for Economic Cooperation and Development – BMZ Global Affairs Canada Ministry for Foreign Affairs of Finland Ministry of Foreign Affairs of Denmark / Danish International Development Assistance – Danida Swedish International Development Cooperation Agency – Sida Swiss Agency for Development and Cooperation – SDC The Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation – Norad UK Aid – Department for International Development About U4 U4 is a team of anti-corruption advisers working to share research and evidence to help international development actors get sustainable results. The work involves dialogue, publications, online training, workshops, helpdesk, and innovation. U4 is a permanent centre at the Chr. Michelsen Institute (CMI) in Norway. CMI is a non-profit, multi-disciplinary research institute with social scientists specialising in development studies. www.U4.no [email protected] Cover photo Clifford Photography on Unsplash (CC cc0) https://unsplash.com/photos/TekPZz1YP3A Keywords blockchain - corruption - development - e-government - illicit financial flows - money laundering - sustainable development goals - transparency Publication type U4 Issue Creative commons This work is licenced under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International licence (CC BY-NC-ND 4.0) The technology behind bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies was supposed to end poverty, eliminate corruption, and provide financial inclusion for all. -

6 · Cartography in the Ancient Near East
6 · Cartography in the Ancient Near East A. R. MILLARD Under the term "ancient Near East" fall the modern amples of these lists have been unearthed in Babylonia, states of Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Jordan, and Israel. Tur at Abu Salabikh near Nippur, and at the northern Syrian key, Saudi Arabia, the Gulf States, Yemen, and Iran may settlement of Ebla, the scene of important discoveries also be included. The eras embraced begin with the first by Italian archaeologists, lying fifty-five kilometers south urban settlements (ca. 5000 B.C.) and continue until the of Aleppo. The scribes who wrote these tablets were defeat of Darius III by Alexander the Great, who offi working between 2500 and 2200 B.C., but their lists cially introduced Hellenism to the area (330 B.C.). There were drawn from earlier sources that reached back as are few examples of maps as they have been defined in far as the beginning of the third millennium. Besides the the literature of the history of cartography, but those names of places in Babylonia, names of Syrian towns that remain are important in helping to build a picture appear in the lists from Ebla, including Ugarit (Ra's of the geographical knowledge available, and of related Shamrah) on the Mediterranean coast.1 This is one in achievements. dication of the level Babylonian geographical knowledge had reached at an early date. In support of that may be BABYLONIAN GEOGRAPHICAL KNOWLEDGE cited historical sources, contemporary and traditional, for military campaigns by King Sargon of Akkad and Babylonia was open to travelers from all directions. -

Successor to Token Accounting Richard Mattessich
Accounting Historians Journal Volume 25 Article 2 Issue 1 June 1998 1998 Recent insights into Mesopotamian accounting of the 3rd millennium B.C. -- Successor to token accounting Richard Mattessich Follow this and additional works at: https://egrove.olemiss.edu/aah_journal Part of the Accounting Commons, and the Taxation Commons Recommended Citation Mattessich, Richard (1998) "Recent insights into Mesopotamian accounting of the 3rd millennium B.C. -- Successor to token accounting," Accounting Historians Journal: Vol. 25 : Iss. 1 , Article 2. Available at: https://egrove.olemiss.edu/aah_journal/vol25/iss1/2 This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Archival Digital Accounting Collection at eGrove. It has been accepted for inclusion in Accounting Historians Journal by an authorized editor of eGrove. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Mattessich: Recent insights into Mesopotamian accounting of the 3rd millennium B.C. -- Successor to token accounting Accounting Historians Journal Vol. 25, No. 1 June 1998 Richard Mattessich UNIVERSITY OF BRITISH COLUMBIA RECENT INSIGHTS INTO MESOPOTAMIAN ACCOUNTING OF THE 3RD MILLENNIUM B.C. — SUCCESSOR TO TOKEN ACCOUNTING Abstract: This paper examines from an accounting perspective re cent work by Nissen et al. [1993], here regarded as an extension of the archaeological research of Schmandt-Besserat [1977, 1992] and its analysis by Mattessich [1987, 1994]. The transition from the 4th millennium B.C. to the 3rd millennium B.C. featured the use of proto- cuneiform and cuneiform accounting techniques to replace the older token accounting. This research reinforces the previously made hypothesis [Mattessich, 1987] that the inserting of tokens into a clay container during the last phase of token accounting corre sponded to debit entries, while the impressing of tokens on the sur face of the container was meant to convey the credit total of an equity. -

The Discovery of a Sumerian Clay Tablet with Cuneiform Writing, Showing the Solar System from the Third Millennium B.C
The discovery of a Sumerian clay tablet with cuneiform writing, showing the solar system from the third millennium B.C. During my visit earlier last year to the Iraqi Museum in Baghdad, at the Sumerian wing, I observed among the numerous historical items there, three clay tablets with cuneiform writing and drawings dating back to around 3000 BC. One tablet depicted the drawing of Geometric-Algebraic equations and shapes such as angled triangles, Euclid Theorem similar to it (Photos 1, 1a, 1b); the second is a mathematical tablet and the Pythagorean Theorem resembles it (Photo 2) and the third tablet is of the heliocentric drawings of the solar system (Photo 3). Photo 1, Sumarian Photo 1a. Photo 1b. Photo 2, Sumerian Photo 3, Sumerian Clay Tablet showing Clay Tablet (2) of the Clay Tablet (3) Geometric -Algabric Geometric -Algabric the Solar system Euclid theory about Pythagoras theory About 3000 BC About 3000 BC About 3000 BC In Medieval Science and during the middle Ages, Europeans learned the theory of geocentrism: the Earth was motionless in the centre of the universe with all the stars revolving around it. This concept was adopted in Europe for over 1,400 years and anyone who believed otherwise was deemed "foolish and absurd in philosophy, and formally heretical since it explicitly contradicts in many places the sense of Holy Scripture”. Nicolas Copernicus (Polish, 1473- 1543) secretly developed and defended the theory of heliocentricm, which claimed that the Earth revolves around the Sun, which was supposedly at the centre of the Universe. At the date of his death, his book titled: De Revolutionibus Orbium Coelestium (From the Revolutions of the Celestial Spheres) was published. -

The History of Early Materials
Western Oregon University Digital Commons@WOU History of the Book: Disrupting Society from Student Scholarship Tablet to Tablet 6-2015 Chapter 01 - The iH story of Early Materials Alyssa Adams Western Oregon University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.wou.edu/history_of_book Part of the Cultural History Commons, and the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine Commons Recommended Citation Adams, Alyssa. "The iH story of Early Materials." Disrupting Society from Tablet to Tablet. 2015. CC BY-NC This is brought to you for free and open access by the Student Scholarship at Digital Commons@WOU. It has been accepted for inclusion in History of the Book: Disrupting Society from Tablet to Tablet by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons@WOU. For more information, please contact [email protected]. 1 The History of Early Materials -Alyssa Adams- From the time that man discovered how to draw on cave walls, human interest in recording information and events flourished. Cities were built, societies and civilizations were born, and the world as we know it was forever changed. While writing began as symbols and drawings, it soon blossomed into multiple languages with a variety of mediums such as clay tablets, papyrus, silk and paper on which to record information. Clay Tablets In Mesopotamia circa 3500 B.C. an ancient tribe known as the Such writings Sumerians found a source of wonder. Clay was found in the nearby rivers as The Epic of Gilgamesh which could be molded into pots, urns, and also into writing tablets. While still were written on clay tablets wet, these tablets were drawn on in the first form of writing called cuneiform1. -

Bart Preneel.Pdf
A Perspective on Bitcoin and Blockchain BART PRENEEL IMEC-COSIC KU LEUVEN BART.PRENEEL(AT)ESAT.KULEUVEN.BE 6 JUNE 2017 1 Currencies = maintaining memory “Envelope and contents from Susa, Iran, circa 3300 BCE.” “Each lenticular disc stands for “a flock” (perhaps 10 animals). The large cone represents a very large measure of grain; the small cones designate small measures of grain.” Tensions between centralized and de-centralized ways to remember value exchanges, debts, and what is due •Centralization (clay tablet): economies of scale, high-integrity, vulnerable •Decentralized (coins): high-availability, difficult to destroy as a system, forgery Image provided courtesy of Denise Schmandt-Besseratand Musée du Louvre, Département des Antiquités Orientales Slide credit: George Danezis 2 Hash functions (1975): one-way easy to compute but hard to invert RIPEMD-160 SHA-256 SHA-512 This is an input to a crypto- graphic hash function. The SHA-3 input is a very long string, that is reduced by the hash function to a string of fixed length. There are additional f 1A3FD4128A198FB3CA345932 security conditions: it should be very hard to find an input hashing to a given value (a preimage) or to find two colliding inputs (a collision). 3 Digital signatures (1975): “equivalent” to manual signature Donald agrees to Public key pay to Hillary 100 Bitcoins on Feb. 22 2017 Private key 4 Timestamping (1990) Collect documents and hash them with a Merkle tree Chain these trees together with a hash chain Publish intermediate values on a regular basis hash f f f 0 -

Methods of Clay Tablet Reconstruction in Virtual and Real
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Repository@Nottingham Observed Methods of Cuneiform Tablet Reconstruction in Virtual and Real World Environments. Authors Andrew Lewis, Sandra Woolley, Eugene Ch'ng, Erlend Gehlken Affiliations Andrew Lewis & Sandra Woolley: University of Birmingham, UK Eugene Ch'ng: University of Nottingham Ningbo, China Erlend Gehlken: Universität Frankfurt/Main, Germany Correspondence: Andrew Lewis {[email protected], Digital Humanities Hub, University of Birmingham, Edgbaston, Birmingham, B15 2TT} Abstract The reconstruction of fragmented artefacts is a tedious process that consumes many valuable work hours of scholars' time. We believe that such work can be made more efficient via new techniques in interactive virtual environments. The purpose of this research is to explore approaches to the reconstruction of cuneiform tablets in the real and virtual environment, and to address the potential barriers to virtual reconstruction of fragments. In this paper we present the results of an experiment exploring the reconstruction strategies employed by individual users working with tablet fragments in real and virtual environments. Our findings have identified physical factors that users find important to the reconstruction process and further explored the subjective usefulness of stereoscopic 3D in the reconstruction process. Our results, presented as dynamic graphs of interaction, compare the precise order of movement and rotation interactions, and the frequency of interaction achieved by successful and unsuccessful participants with some surprising insights. We present evidence that certain interaction styles and behaviours characterise success in the reconstruction process. Keywords Collaboration, 3D Visualization, Virtual Environments, Fragment Reassembly, Artefact Reconstruction, Cuneiform. -

Cuneiform.” the Signs Are Grouped Into Boxes And, at This Early Date, Are Usually Read from Top to Bottom and Right to Left
The earliest writing we know of dates back to around 3,000 B.C.E. and was probably invented by the Sumerians, living in major cities with centralized economies in what is now southern Iraq. The earliest tablets with written inscriptions represent the work of administrators, perhaps of large temple institutions, recording the allocation of rations or the movement and storage of goods. Temple officials needed to keep records of the grain, sheep and cattle entering or leaving their stores and farms and it became impossible to rely on memory. So, an alternative method was required and the very earliest texts were pictures of the items scribes needed to record (known as pictographs). Writing, the recording of a spoken language, emerged from earlier recording systems at the end of the fourth millennium. The first written language in Mesopotamia is called Sumerian. Most of the early tablets come from the site of Uruk, in southern Mesopotamia, and it may have been here that this form of writing was invented. These texts were drawn on damp clay tablets using a pointed tool. It seems the scribes realized it was quicker and easier to produce representations of such things as animals, rather than naturalistic impressions of them. They began to draw marks in the clay to make up signs, which were standardized so they could be recognized by many people. Early writing tablet recording the allocation of beer, probably from southern Iraq, Late Prehistoric period, clay, 3100-3000 B.C.E. (The British Museum) Early Writing Tablet recording the allocation of beer, 3100-3000 B.C.E, Late Prehistoric period, clay, probably from southern Iraq. -

Correlated Walks Down the Babylonian Markets (Pdf)
OFFPRINT Correlated walks down the Babylonian markets N. E. Romero, Q. D. Y. Ma, L. S. Liebovitch, C. T. Brown and P. Ch. Ivanov EPL, 90 (2010) 18004 Please visit the new website www.epljournal.org TARGET YOUR RESEARCH WITH EPL Sign up to receive the free EPL table of contents alert. www.epljournal.org/alerts April 2010 EPL, 90 (2010) 18004 www.epljournal.org doi: 10.1209/0295-5075/90/18004 Correlated walks down the Babylonian markets N. E. Romero1(a),Q.D.Y.Ma2,3(a),L.S.Liebovitch4,C.T.Brown5 and P. Ch. Ivanov2,6,7(b) 1 Physics Department, Florida Atlantic University - Boca Raton, FL 33431, USA 2 Harvard Medical School and Division of Sleep Medicine, Brigham and Women’s Hospital - Boston, MA 02115, USA 3 College of Geography and Biological Information, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications Nanjing 210003, China 4 Center for Complex Systems and Brain Sciences, Florida Atlantic University - Boca Raton, FL 33431, USA 5 Anthropology Department, Florida Atlantic University - Boca Raton, FL 33431, USA 6 Center for Polymer Studies and Department of Physics, Boston University - Boston, MA 02215, USA 7 Departamento de F´ısica Aplicada II, Universidad de M´alaga - 29071 M´alaga, Spain, EU received 27 January 2010; accepted in final form 29 March 2010 published online 5 May 2010 PACS 89.65.Gh – Economics; econophysics, financial markets, business and management PACS 02.50.-r – Probability theory, stochastic processes, and statistics PACS 89.65.Ef – Social organizations; anthropology Abstract – To investigate the evolution of market dynamics in different stages of historical development, we analyze commodity prices from two distinct periods —ancient Babylon, and medieval and early modern England.