Radioactive Waste Management Programmes in Oecd/Nea Member Countries
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

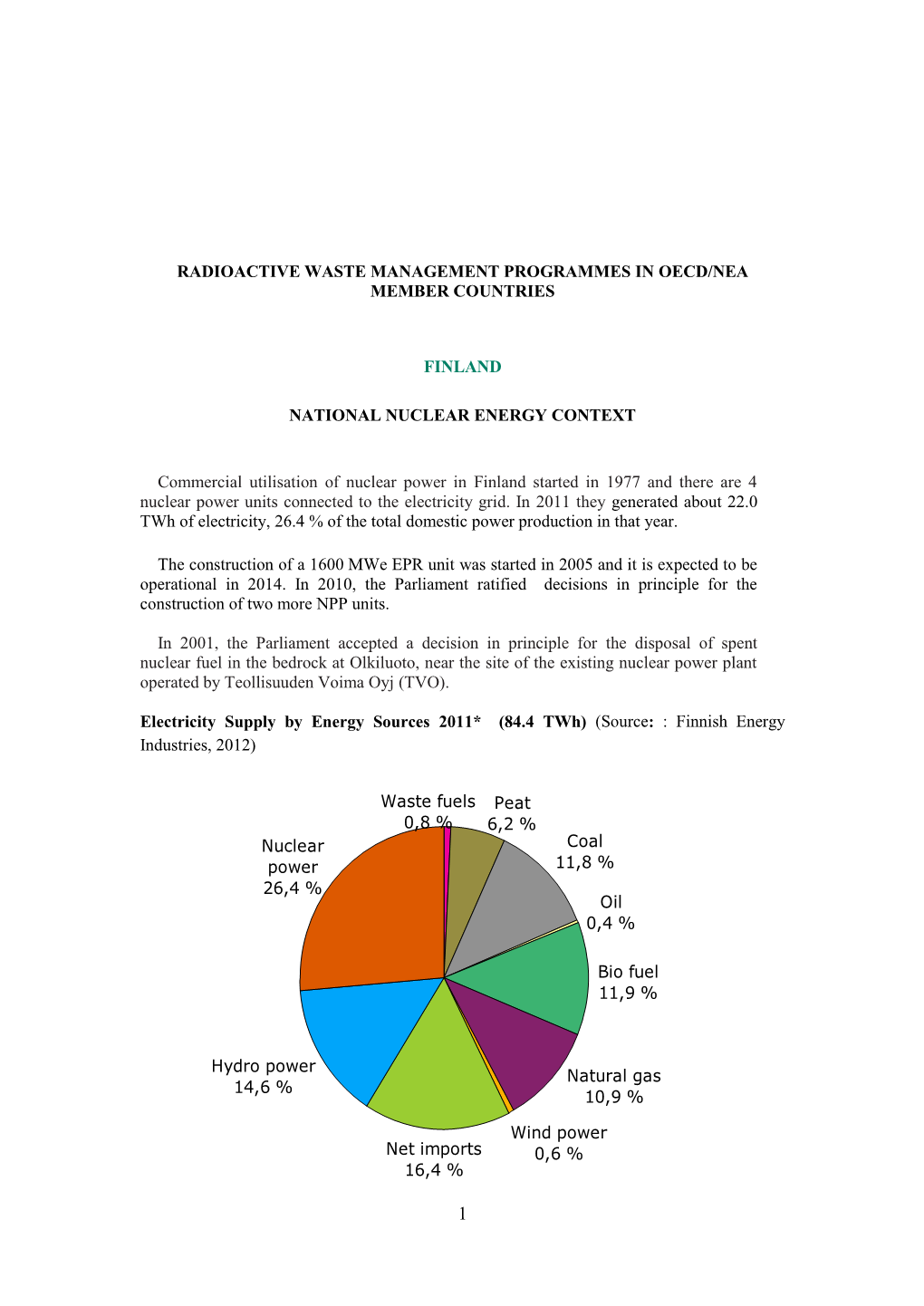
Finland 242 Finland Finland
FINLAND 242 FINLAND FINLAND 1. GENERAL INFORMATION 1.1. General Overview Finland (in Finnish Suomi) is a republic in northern Europe, bounded on the north by Norway, on the east by Russia, on the south by the Gulf of Finland and Estonia, on the south-west by the Baltic Sea and on the west by the Gulf of Bothnia and Sweden. Nearly one third of the country lies north of 2 2 the Arctic Circle. The area of Finland, including 31 557 km of inland water, totals 338 000 km . The terrain is generally level, hilly areas are more prominent in the north and mountains are found only in the extreme north-west. The average July temperature in the capital Helsinki on the southern coast is 17 °C. The February average in Helsinki is about -5.7 °C. The corresponding figures at Sodankylä (Lapland) in the northern Finland are 14.1 °C and -13.6 °C. Precipitation (snow and rain) averages about 460 mm in the north and 710 mm in the south. Snow covers the ground for four to five months a year in the south, and about seven months in the north. Finland has a population of 5.16 million (1998) and average population density of 17 per km2 of land. Historical population data is shown in Table 1. The predicted annual population growth rate between the years 1998 and 2010 is 0.21 %. More than two thirds of the population reside in the southern third of the country. In Finland the total primary energy consumption1 per capita was about 60 % higher than the European Union average (according to 1996 statistics) and about 35 % higher than the OECD average. -

Nuclear Options in Electricity Production-Finnish Experience
6th International Conference on Nuclear Option in Countries with Small • Dubr°Vr HR0600024 Nuclear Option in Electricity Production - Finnish Experience Antti Piirto TVO Nuclear Services Ltd 27160 Olkiluoto, Finland [email protected] Nuclear energy has played a key role in Finnish electricity production since the beginning of the 1980s. The load factors of nuclear power plants have been high, radioactive emissions low and the price of nuclear electricity competitive. In addition, detailed plans exist for the final disposal of nuclear waste as well as for the financing of final disposal, and the implementation of final disposal has already been started with the authorities regulating nuclear waste management arrangements at all levels. Deregulation of the electricity market has meant increasing trade and co-operation, with both the other Nordic countries and the other EU Member States. In May 2002, the Finnish Parliament approved the application for a decision in principle on the construction of the fifth nuclear power plant unit in Finland. In December 2003, Teollisuuden Voima Oy concluded an agreement for the supply of the new nuclear power plant unit with a consortium formed by the French- German Framatome ANP and the German Siemens. The new unit, which will be built at Olkiluoto, is a pressurised water reactor having a net electrical output of about 1600 MW. The total value of the project is ca. 3 billion Euros, including investments connected with the development of infrastructure and waste management. The objective is to connect the new unit to the national grid in 2009. When in operation, the unit will increase the share of nuclear energy of Finnish electricity consumption, currently some 26%, to a little more than one third, and decrease Finnish carbon dioxide emissions by more than 10%. -

Waiting for the Nuclear Renaissance: Exploring the Nexus of Expansion and Disposal in Europe
Risk, Hazards & Crisis in Public Policy www.psocommons.org/rhcpp Vol. 1: Iss. 4, Article 3 (2010) Waiting for the Nuclear Renaissance: Exploring the Nexus of Expansion and Disposal in Europe Robert Darst, University of Massachusetts-Dartmouth Jane I. Dawson, Connecticut College Abstract This article focuses on the growing prospects for a nuclear power renaissance in Europe. While accepting the conventional wisdom that the incipient renaissance is being driven by climate change and energy security concerns, we argue that it would not be possible without the pioneering work of Sweden and Finland in providing a technological and sociopolitical solution to the industry’s longstanding “Achilles’ heel”: the safe, permanent, and locally acceptable disposal of high-level radioactive waste. In this article, we track the long decline and sudden resurgence of nuclear power in Europe, examining the correlation between the fortunes of the industry and the emergence of the Swedish model for addressing the nuclear waste problem. Through an in-depth exploration of the evolution of the siting model initiated in Sweden and adopted and successfully implemented in Finland, we emphasize the importance of transparency, trust, volunteerism, and “nuclear oases”: locations already host to substantial nuclear facilities. Climate change and concerns about energy independence and security have all opened the door for a revival of nuclear power in Europe and elsewhere, but we argue that without the solution to the nuclear waste quandary pioneered by Sweden and Finland, the industry would still be waiting for the nuclear renaissance. Keywords: high-level radioactive waste, permanent nuclear waste disposal, nuclear power in Europe, nuclear politics in Finland and Sweden © 2010 Policy Studies Organization Published by Berkeley Electronic Press - 49 - Risk, Hazards & Crisis in Public Policy, Vol. -

Toimintakertomus Ja Tilinpäätös 2019
HALLITUKSEN TOIMINTAKERTOMUS JA TILINPÄÄTÖS HALLITUKSEN TOIMINTAKERTOMUS KESKEISET TUNNUSLUVUT KONSERNIN TILINPÄÄTÖS EMOYHTIÖN TILINPÄÄTÖS TALOUDELLISET TIEDOTTEET Sisältö 3 Teollisuuden Voima Oyj:n hallituksen 11 Vireillä olevat oikeudenkäynnit ja riita-asiat 20 Olennaiset tapahtumat tilikauden päättymisen jälkeen toimintakertomus 2019 12 Ydinvoima 21 Arvio tulevasta kehityksestä 3 Vuoden 2019 keskeiset tapahtumat 12 Olkiluoto 1 ja Olkiluoto 2 21 Ehdotukset yhtiökokoukselle 5 Toimintaympäristö 13 Vuosihuollot 5 TVO yhtiönä 13 Olkiluoto 3 EPR 22 Tilinpäätös 2019 6 Liiketoiminnan tulos 13 Ydinpolttoaine 22 Konsernin keskeisiä tietoja ja tunnuslukuja 6 Rahoitus ja maksuvalmius 13 Ydinjätehuolto 23 Emoyhtiön keskeisiä tietoja ja tunnuslukuja 7 Osakepääoma 15 Hiilivoima 24 Konsernin tilinpäätös 7 Hallinnointiperiaatteet 15 Meri-Pori 71 Emoyhtiön tilinpäätös 7 Hallintoelimet 15 Tutkimus- ja kehitystoiminta 89 Ehdotukset yhtiökokoukselle 8 Sääntely-ympäristö 15 Investoinnit käyttöomaisuuteen ja osakkeisiin 89 Toimintakertomuksen ja tilinpäätöksen allekirjoitukset 9 Riskienhallinta, merkittävimmät riskit ja 16 Vastuullisuus 90 Tilintarkastuskertomus epävarmuustekijät 17 Turvallisuus ja työturvallisuus 96 Taloudelliset tiedotteet vuonna 2020 9 Riskienhallinta 18 Ympäristö 9 Riskienhallintaprosessi 18 Henkilöstö ja henkilöstön koulutus 9 Merkittävimmät riskit ja epävarmuustekijät 20 Tytäryhtiöt ja yhteisyritykset 2 Hallituksen toimintakertomus ja tilinpäätös 2019 HALLITUKSEN TOIMINTAKERTOMUS KESKEISET TUNNUSLUVUT KONSERNIN TILINPÄÄTÖS EMOYHTIÖN -

POHJOLAN VOIMA Annual Report 1999 CONTENTS
POHJOLAN VOIMA Annual Report 1999 CONTENTS Key figures for the Group 1999 4 Company Structure, 1 April 2000 5 Production and services 6 Review by the President of Pohjolan Voima Oy 8 Review by the President of PVO-Palvelut Oy 10 Strategy outline 12 Pohjolan Voima, environment and society 14 Events in 1999 17 Production 18 Services 25 Environmental year 1999 32 Administration 34 Accounts for 1999 Review by the Board of Directors 36 Consolidated Profit and Loss Account 39 Consolidated Balance Sheet 40 Consolidated Cash Flow Statement 41 Profit and Loss Account of Parent Company 42 Parent Company Balance Sheet 43 Parent Company Cash Flow Statement 44 Accounting Policies 45 Notes to the Accounts 46 Notes to the Balance Sheet 48 Report of the Auditors 58 Information on Shares 59 Management 60 Adresses 62 The Annual General Meeting The Annual General Meeting of Pohjolan Voima Oy will be held on Thursday, 27 April 2000 at 10 am in Mikonkatu 15A, 00100 Helsinki. P o h j o l a n V o i m a 2 CHANGE IS AN OPPORTUNITY. CHANGING IS ESSENTIAL. OPERATING IDEA Ability and long-term commitment are re- As a whole, Pohjolan Voima will be de- The Pohjolan Voima Group is a privately- quired to ensure future operating conditions veloped into an international operator, able owned group of energy sector companies, in the energy field. to offer its shareholders and other customers which generates and purchases power In 1999, Pohjolan Voima’s energy gen- competitive energy solutions, through a wide and heat for the shareholders. -

Finland's Legal Preparedness for International Disaster Response
HOST NATION SUPPORT GUIDELINES Finland’s legal preparedness for international disaster response – Host Nation Support Guidelines Finnish Red Cross 2014 Report on the regulation of the reception of international aid in Finland ECHO/SUB/2012/638451 The report is part of the project titled ”Implementation of the EU Host Nation Support Guidelines”, (ECHO/SUB/2012/638451) The project is funded by the Civil Protection Financial Instrument of the European Union for 2013– 2014, provided by the European Community Humanitarian Office (ECHO) Author: Maarit Pimiä, Bachelor of Laws Mandators: The Finnish Red Cross, National Preparedness Unit The Department of Rescue Services of the Ministry of the Interior Translated by: Semantix Finland Oy Date: 14.3.2014 © Finnish Red Cross The European Commission is not responsible for the content of this report or the views expressed in this report. The authors are responsible for the content. 2 Report on the regulation of the reception of international aid in Finland ECHO/SUB/2012/638451 Contents Abbreviations ........................................................................................................................ 6 Definitions ............................................................................................................................. 8 1. Introduction .................................................................................................................... 11 1.1 Background of the report ..................................................................................... -

Recent Developments of Nuclear Power in Finland: Olkiluoto 3, and More…
RECENT DEVELOPMENTS OF NUCLEAR POWER IN FINLAND: OLKILUOTO 3, AND MORE… Jarmo Vehmas 15th REFORM Group meeting Schloss Leopoldskron, Salzburg, 10.9.2010 CONTENT 1. Olkiluoto 3: Basics 2. Olkiluoto 3: About TVO 3. Olkiluoto 3: Delays 4. Olkiluoto 3: Financing and increasing costs 5. Olkiluoto 3. Conclusions 6. Government decision-in-principle, June/July 2010 7. Fennovoima: Shareholders 8. Fennovoima: Site alternatives 9. Olkiluoto 4 and Fennovoima: Conclusions OLKILUOTO 3: BASICS • Fifth nuclear reactor in Finland, ordered by TVO, a private power company • TVO already has two units, taken into use in 1978 (OL 1) and 1982 (OL 2). State-owned Fortum has two units in Loviisa, taken into use in 1977 and 1981 • Attemps for a fifth unit were made ijointly by Fortum and TVO in mid-1980s (cancelled after Chernobyl), in early 1990s (rejected in 1993 by the Parliament), • TVO submitted the OL 3 application in 2000 and it was accepted by the Government and ratified by the Parliament in 2002. • OL 3 is a new plant design, European pressurized reactor (EPR) by AREVA, 4300/1600 MW • The construction license was granted and construction started in 2005. • Original scedule and budget: In commercial operation in 2009, turnkey contract of €3.2 bn 2. OLKILUOTO 3: ABOUT TVO • Teollisuuden Voima Oy (TVO), is a Finnish power company which produces electricity to its shareholders only. • According to its articles of association, TVO shareholders pay fixed costs in relation to their shares of the stock, and receive corresponding right to the produced electricity. • TVO Shareholders pay the moving cost in relation to their use of the produced electricity. -

Application for a Decision- In-Principle Concerning the Construction of a Nuclear Power Plant Unit – Olkiluoto 4
Application for a Decision- in-Principle concerning the Construction of a Nuclear Power Plant Unit – Olkiluoto 4 Teollisuuden Voima Oyj 2008 OOL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.inddL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.indd 1 55/30/08/30/08 2:11:562:11:56 PPMM OOL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.inddL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.indd 2 55/30/08/30/08 2:11:592:11:59 PPMM Application for a Decision- in-Principle concerning the Construction of a Nuclear Power Plant Unit – Olkiluoto 4 Th is publication does not include the following documents enclosed with the actual decision-in-principle application: - Extract from the Trade Register, Teollisuuden Voima Oyj (Appendix 1) - Copy of the company’s Articles of Association and Register of Shareholders (Appendix 2) - Annual Report 2007, Teollisuuden Voima Oyj (Appendix 5.1) - Environmental Impact Assessment Report, Extension of the Olkiluoto Nuclear Power Plant by a fourth Unit (Appendix 12.1) More information: Teollisuuden Voima Oyj Olkiluoto FI-27160 EURAJOKI Tel. +358 2 83 811 www.tvo.fi OOL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.inddL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.indd 3 55/30/08/30/08 2:11:592:11:59 PPMM OOL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.inddL4_PAP_eng_FINAL.indd 4 55/30/08/30/08 2:11:592:11:59 PPMM TEOLLISUUDEN VOIMA OYJ APPLICATION FOR DECISION-IN-PRINCIPLE 1(7) OLKILUOTO 4 TO THE COUNCIL OF STATE APPLICATION FOR A DECISION-IN-PRINCIPLE CONCERNING THE CONSTRUCTION OF A NUCLEAR POWER PLANT UNIT APPLICANT Teollisuuden Voima Oyj, hereinaft er “TVO”. APPLICATION Th e applicant requests for the Council of State’s decision-in-principle re- ferred to in Section 11 of the Nuclear Energy Act confi rming that the con- struction of the new nuclear power plant unit described in the ‘Scope of the application’ section is in line with the overall good of society. -

Ifnec Finance Workshop
IFNEC FINANCE WORKSHOP London 9 May 2012 Lauri Piekkari SVP, Treasury © Teollisuuden Voima Oyj CONTENT • TVO in general • Financing of commercial nuclear investments • risk allocation? • financing model? • TVO’s financing model 2 TEOLLISUUDEN VOIMA OYJ (TVO) IN A NUTSHELL Company • Electricity generator owned mainly by leading Finnish utility companies • Sells electricity to its shareholders at cost • Produced 16% of electricity consumed in Finland in 2011 Existing Nuclear Power Plant Units (Olkiluoto 1 and 2) • 2 x 880 MW, BWR, Westinghouse Atom • Among the world’s best in terms of availability and stability Nuclear Power Plant Unit (OL3) under construction • 1 x 1,600 MW, PWR, under construction by Areva-Siemens consortium • According to turnkey plant supplier, commercial operation is expected to start in 2014 OL4 under planning Coal Condensing Power Plant Unit (Meri-Pori) • 257 MW stake in 565 MW coal condensing unit Posiva, a joint venture company with TVO (60%) and Fortum (40%) • responsible for the final disposal of spent fuel and nuclear waste © Teollisuuden Voima Oyj 33 TVO’S UNDERLYING OWNERS (ABOUT 60 OFF-TAKERS) Fortum 26% Industry 44% Municip. 30% © Teollisuuden Voima Oyj 4 RISK ALLOCATION • Risk/return profile for equity and debt investors • Pure debt holders do not generally like risks • However, there are financial instruments between debt and equity that may change risk/return profile • Who is best positioned to carry various risks? • Who will get the benefits? • How are risks shared in construction phase vs. operational -

Financing Nuclear Power
NUKLEARMALAYSIA / P /2013/1 Financing Nuclear Power By: Sheriffah Noor Khamseah Al-Idid bt Dato’ Syed Ahmad Idid Malaysia @ Nuclear Power Asia 2013 15-16 January 2013 Shangri-La Hotel, Kuala Lumpur 2013 BANGI, 43000, KAJANG, MALAYSIA AGENSI NUKLEAR MALAYSIA (NUKLEAR MALAYSIA) BANGI, 43000, KAJANG, MALAYSIA Acc. No :2862 Financing Nuclear Power @ Nuclear Power Asia 2013 15-16 January 2013 Shangri-La Hotel, Kuala Lumpur By: Sheriffah Noor Khamseah Al-Idid bt Dato’ Syed Ahmad Idid Malaysia CONTENTS 1 Cost Components for Financing Nuclear Power Plants- An Overview 2 Cost Estimates of Nuclear Power Plants 3 Key Challenges for Financing Nuclear Power 4 Financing Structures and Its Changing Dynamics 5 Sources for Financing Nuclear Power 6 Banks financing Nuclear Power 7 Export Credit Agencies (ECA 8 Financing of Nuclear Power Plants by Government 9 Financing of Nuclear Power Plants by Private Companies – The Finnish Experience (OKILUOTO 3) 10 New Financing Models – Loan Guarantees –USA 11 New Financing Models – Foreign equity Participation – Taishan ( CGNPC & EDF ) 12 Recommendations 1. Cost Components for a Nuclear Power Project - An Overview 2. Cost Estimates of Nuclear Power Plants Cost of Nuclear Power Plants $ 2 $ 4 Overnight costs: the cost of a construction project if no interest was incurred during construction, as if the project was completed "overnight Cost of Nuclear Power Plants Figure III shows the overnight costs for both the completed plants and the projections for future plants. The estimates are roughly equally divided between government consultants, utilities, government entities, utilities, and Wall Street/independent analysts, plus a small number of academic institutions. The "great bandwagon market" for By 2008,projected costs nuclear reactors comprised were three to four times Construction delays and cost overruns, higher than the initial cost as well as regulatory changes which projections in 2001-2004. -

Final Disposal of Spent Nuclear Fuel in Finnish Bedrock - Olkiluoto Site Report
FI9900144 POSIVA 99-10 Final disposal of spent nuclear fuel in Finnish bedrock - Olkiluoto site report Pekka Anttila, Fortum Engineering Oy Henry Ahokas, Fintact Oy Kai Front, VTT Communities and Infrastructure Heikki Hinkkanen, Posiva Oy Erik Johansson, Saanio & Riekkola Oy Seppo Paulamaki, Geological Survey of Finland Reijo Riekkola, Saanio & Riekkola Oy Jouni Saari, Fortum Engineering Oy Pauli Saksa, Fintact Oy Margit Snellman, Posiva Oy Liisa Wikstrom. Posiva Oy Antti Ohberg, Saanio & Riekkola Oy 30-42 June 1 999 Maps: ©Maanmittauslaitos permission 41/MYY/99 POSIVA OY Mikonkatu 15 A. FIN-OO1OO HELSINKI. FINLAND Phone (09) 2280 3O (nat.), ( + 358-9-) 2280 30 (int.) Fax (O9) 2280 3719 (nat.). ( + 358-9-) 228O 3719 (int.) ISBN 951-652-065-0 ISSN 1239-3096 Posiva-raportti - Posiva Report Raportin tunnus -Report code POSIVA 99-10 Posiva Oy . Mikonkatu 15 A, FIN-00100 HELSINKI, FINLAND JuiKaisuaika uate Puh. (09) 2280 30 - Int. Tel. +358 9 2280 30 June 1999 Tekijä(t) - Author(s) Toimeksiantaja(t) - Commissioned by Pekka Anttila, Henry Ahokas, Kai Front, Heikki Hinkkanen, Erik Johansson, Seppo Paulamäki, Reijo Riekkola, Jouni Saari, Posiva Oy Pauli Saksa, Margit Snellman, Liisa Wikström, Antti Öhberg Nimeke - Title FINAL DISPOSAL OF SPENT NUCLEAR FUEL IN FINNISH BEDROCK OLKILUOTO SITE REPORT Tiivistelmä - Abstract Posiva Oy is studying the Finnish bedrock for the geological disposal of spent nuclear fuel. The study is based on the site selection research programme started originally in 1983. The programme is in accordance with the decision in principle by the Council of State in 1983 and aims at the selection of one site in 2000. -

Finland's Dependence on Russian Energy—Mutually Beneficial Trade
sustainability Article Finland’s Dependence on Russian Energy—Mutually Beneficial Trade Relations or an Energy Security Threat? Jaakko J. Jääskeläinen 1, Sakari Höysniemi 2,* , Sanna Syri 1 and Veli-Pekka Tynkkynen 2 1 Department of Mechanical Engineering, School of Engineering, Aalto University, P.O. Box 14100, FI-00076 Aalto, Finland; jaakko.j.jaaskelainen@aalto.fi (J.J.J.); sanna.syri@aalto.fi (S.S.) 2 Aleksanteri Institute, Faculty of Arts, University of Helsinki, P.O. Box 24, FI-00014 University of Helsinki, Finland; veli-pekka.tynkkynen@helsinki.fi * Correspondence: sakari.hoysniemi@helsinki.fi; Tel.: +358-50-3148944 Received: 31 August 2018; Accepted: 25 September 2018; Published: 27 September 2018 Abstract: Studies on energy security in the context of relations between European Union (EU) and Russia tend to focus on cases, with an open conflict related to supply, such as “hard” energy weapons, or on only one fuel, often natural gas. However, there is a need to understand the long-term impacts that energy relations have politically, economically and physically, and their linkages between resilience, sustainability and security. We analyse the Finnish-Russian energy relations as a case study, as they are characterised by a non-conflictual relationship. To assess this complex relationship, we apply the interdependence framework to analyse both the energy systems and energy strategies of Finland and Russia, and the energy security issues related to the notable import dependence on one supplier. Moreover, we analyse the plausible development of the energy trade between the countries in three different energy policy scenarios until 2040. The findings of the article shed light on how the trends in energy markets, climate change mitigation and broader societal and political trends could influence Russia’s energy trade relations with countries, such as Finland.