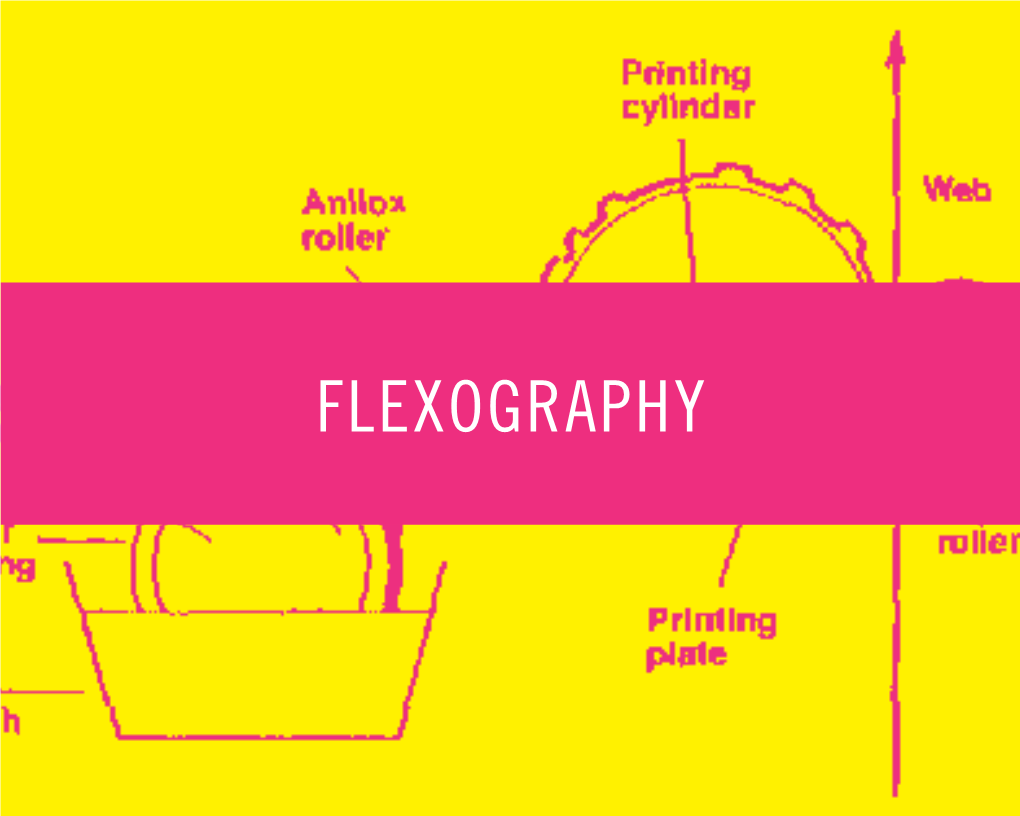
Flexography/Gravure
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Printing Technology (Offset, Flexo, Gravure, Screen, Digital, 3D Printing)
Printing Technology (Offset, Flexo, Gravure, Screen, Digital, 3D Printing) (Noncontact Printing ,Commercial Printing, Gravure Printing, Letterpress Printing, Offset Printing, Screen Printing, Offset Lithography, Lanography ,Flexography, Rotogravure, Digital Printing,3D Printing, 3D Printing Machinery, Blanket Cylinder, Plate Cylinder, Impression Cylinder, Web Offset Machines, printing press) Introduction Printing is a process of producing copies of text and pictures. Modern technology is radically changing the way publications are printed, inventoried and distributed. There are a wide variety of technologies that are used to print stuff. The main industrial printing processes are: Offset Lithography, Flexography, Digital Printing (Inkjet & Xerography), Gravure, Screen Printing. 3D printing which is also referred as additive printing technology that enables manufacturers to develop objects using a digital file and variety www.entrepreneurindia.co of printing materials. Global market for 3D printing material includes polymers, metals and ceramics. In addition, 3D printing offers a wide array of applications in various industries, namely consumer products, industrial products, defense & aerospace, automotive, healthcare, education & research and others. In India, the market for printing technology is at its nascent stage however offers huge growth opportunities in the coming years. Digital printing is now taking much more share, particularly in graphics (i.e. non- packaging applications). www.entrepreneurindia.co Digital's share of the whole market doubles in constant value terms from 9.5% to 19.7% and 3D printing market is estimated to garner $8.6 billion in coming years. The print technology in use is also changing. Digital printing is now taking much more share, particularly in graphics (i.e. non-packaging applications). Digital's share of the whole market doubles in constant value terms from 9.5% in 2008 to 19.7% by 2018, when packaging is excluded this share is 23.5% in 2012 to 38.1% by 2018. -

Other Printing Methods
FLEXO vs. OTHER PRINTING METHODS Web: www.luminite.com Phone: 888-545-2270 As the printing industry moves forward into 2020 and beyond, let’s take a fresh look at the technology available, how flexo has changed to meet consumer demand, and how 5 other popular printing methods compare. CONTENTS ● A History of Flexo Printing ● How Flexo Printing Works ● How Litho Printing Works ● How Digital Printing Works ● How Gravure Printing Works ● How Offset Printing Works ● What is Screen Printing? ● Corrugated Printing Considerations ● Flexo Hybrid Presses ● Ready to Get Started with Flexo? 2 A History of Flexo Printing The basic process of flexography dates back to the late 19th century. It was not nearly as refined, precise, or versatile as the flexo process today -- and can be best described as a high-tech method of rubber stamping. Printing capabilities were limited to very basic materials and designs, with other printing methods greatly outshining flexo. Over the past few decades flexo technology has continuously evolved. This is largely thanks to the integration of Direct Laser Engraving technology, advancements in image carrier materials, and in press technologies. These innovations, among others, have led to increased quality and precision in flexo products. These technological improvements have positioned flexography at the helm of consumer product and flexible packaging printing. Flexo is growing in popularity in a variety of other industries, too, including medical and pharmaceutical; school, home, and office products; and even publishing. How Flexo Printing Works Flexo typically utilizes an elastomer or polymer image carrier such as sleeves, cylinders, and plates. The image carrier is engraved or imaged to create the design for the final desired product. -

Aspects of Flexographic Print Quality and Relationship to Some Printing Parameters
Faculty of Technology and Science Chemical Engineering Johanna Johnson Aspects of Flexographic Print Quality and Relationship to some Printing Parameters DISSERTATION Karlstad University Studies 2008:28 Johanna Johnson Aspects of Flexographic Print Quality and Relationship to some Printing Parameters Karlstad University Studies 2008:28 Johanna Johnson. Aspects of Flexographic Print Quality and Relationship to some Printing Parameters DISSERTATION Karlstad University Studies 2008:28 ISSN 1403-8099 ISBN 978-91-7063-187-0 © The Author Distribution: Faculty of Technology and Science Chemical Engineering 651 88 Karlstad 054-700 10 00 www.kau.se Printed at: Universitetstryckeriet, Karlstad 2008 Abstract Flexographic printing is a common printing method in the packaging field. The printing method is characterized primarily by the flexible printing plate and the low viscosity inks which make it suitable for use on almost any substrate. The object of this study was to obtain further knowledge of some important mechanisms of flexographic printing and how they influence the print quality. The thesis deals with printing primarily on board and liner but also on newsprint with water-borne ink using a full- scale flexographic central impression (CI) printing press. Several printing trials have been performed with a focus on the chemical interaction between the ink and substrate and the physical contact between the ink- covered printing plate and the substrate. Multicolour printing exposes the substrate to water from the water- containing ink. The emphasis was to investigate the relation between print quality and water-uptake of the paper surface with heat and water. Printing trials was carried out on substrates possessing a hydrophobic, and also a rather hydrophilic surface using a regular commercial water-borne ink. -

The Effects of Ink and Media Parameters on Offset Solid Ink and Xerographic Halftoned Image View Quality
IS&T's 1998 PICS Conference IS&T's 1998 PICS Conference Copyright 1998, IS&T The Effects of Ink and Media Parameters on Offset Solid Ink and Xerographic Halftoned Image View Quality Steve Korol Tektronix Color Printing and Imaging Division Wilsonville, Oregon Abstract meet these goals, the successful device must have the ability to print acceptable quality images on a wide variety of Xerographic and offset solid ink technologies are currently substrates reliably. Although both technologies under study dominant in the networked office color printer market. Here, generally render text acceptably, each possesses a set of speed, reliability, ease-of-use, cost-per-copy, and image limitations when grayscale images are considered. quality are all important factors to the office customer who In the case of offset solid ink technology, material is often on a tight budget. Both xerography and solid ink properties of the ink and the print processing steps within have been able to deliver acceptable text output on a wide the printer do indeed afford great media flexibility; however, variety of inexpensive papers; however, such is not always in current implementations of the technology, images may the case for halftoned images. Interestingly, when halftoned appear grainy to the customer, especially in areas of light image quality fails, it is often for widely different reasons optical density (in the range 0.1 to 0.3). The primary reason depending on the technology employed. for this perceived granularity is the minimum diameter and While offset solid ink exhibits excellent receiver media optical density of the smallest achievable mark. -

Printing Industry Is the Large Proportion of Very Small Firms
The printing sector is a diversified industry sector composed of firms who perform printing as well as firms who render services for the printing trade, such as platemaking and bookbinding. One of the most significant characteristics of the printing industry is the large proportion of very small firms. The Census Bureau reported that in 2002 nearly half of the 37,538 printing companies had fewer than five employees; approximately 80 percent employed fewer than 20 workers. Processes used in printing include a variety of methods used to transfer an image from a plate, screen, film, or computer file to some medium, such as paper, plastics, metal, textile articles, or wood. The most prominent of these methods is to transfer the image from a plate or screen to the medium (lithographic, gravure, screen, and flexographic printing). A rapidly growing new technology uses a computer file to directly "drive" the printing mechanism to create the image and new electrostatic and other types of equipment (digital or nonimpact printing). Four Main Segments The printing industry can be separated into four main segments: Lithography Flexography Gravure Screen printing Lithography Lithography is a planographic printing system where the image and non-image areas are chemically differentiated with the image area being oil receptive and non-image area water receptive. Ink film from the lithographic plate is transferred to an intermediary surface called a blanket, which, in turn, transfers the ink film to the substrate. Fountain solution is applied to maintain the hydrophilic properties of the non-image area. Ink drying is divided into heatset and non- heatset. -

Introduction to Printing Technologies
Edited with the trial version of Foxit Advanced PDF Editor To remove this notice, visit: www.foxitsoftware.com/shopping Introduction to Printing Technologies Study Material for Students : Introduction to Printing Technologies CAREER OPPORTUNITIES IN MEDIA WORLD Mass communication and Journalism is institutionalized and source specific. Itfunctions through well-organized professionals and has an ever increasing interlace. Mass media has a global availability and it has converted the whole world in to a global village. A qualified journalism professional can take up a job of educating, entertaining, informing, persuading, interpreting, and guiding. Working in print media offers the opportunities to be a news reporter, news presenter, an editor, a feature writer, a photojournalist, etc. Electronic media offers great opportunities of being a news reporter, news editor, newsreader, programme host, interviewer, cameraman,Edited with theproducer, trial version of Foxit Advanced PDF Editor director, etc. To remove this notice, visit: www.foxitsoftware.com/shopping Other titles of Mass Communication and Journalism professionals are script writer, production assistant, technical director, floor manager, lighting director, scenic director, coordinator, creative director, advertiser, media planner, media consultant, public relation officer, counselor, front office executive, event manager and others. 2 : Introduction to Printing Technologies INTRODUCTION The book introduces the students to fundamentals of printing. Today printing technology is a part of our everyday life. It is all around us. T h e history and origin of printing technology are also discussed in the book. Students of mass communication will also learn about t h e different types of printing and typography in this book. The book will also make a comparison between Traditional Printing Vs Modern Typography. -

Glossary of Flexographic Printing Terms
GLOSSARY OF FLEXOGRAPHIC PRINTING TERMS AA: Authors Alterations, changes other than corrections, made by a client after the proofing process has begun. AA's are usually charged to a client as billable time. Abrasion: Process of wearing away the surface of a material by friction. Abrasion marks: Marks on a photographic print or film appearing as streaks or scratches, caused by the condition of the developer. Can be partially removed by swabbing with alcohol. Abrasion resistance: Ability to withstand the effects of repeated rubbing and scuffing. Also called scuff or rub resistance. Abrasion test: A test designed to determine the ability to withstand the effects of rubbing and scuffing. Abrasiveness: That property of a substance that causes it to wear or scratch other surfaces. Absorption: In paper, the property which causes it to take up liquids or vapors in contact with it. In optics, the partial suppression of light through a transparent or translucent material. Acceptance sampling or inspection: The evaluation of a definite lot of material or product that is already in existence to determine its acceptability within quality standards. Accelerate: In flexographic printing, as by the addition of a faster drying solvent or by increasing the temperature or volume of hot air applied to the printed surface. Electrical - To speed rewind shafts during flying splices, and in taking up web slackness. Accordion Fold: Bindery term, two or more parallel folds which open like an accordion. Acetone: A very active solvent used in packaging gravure inks; the fastest drying solvent in the ketone family. Activator: A chemistry used on exposed photographic paper or film emulsion to develop the image. -

Relationship of Solid Ink Density and Dot Gain in Digital Printing
International Journal of Engineering and Technical Research (IJETR) ISSN: 2321-0869, Volume-2, Issue-7, July 2014 Relationship of Solid Ink Density and Dot Gain in Digital Printing Vikas Jangra, Abhishek Saini, Anil Kundu gain while meeting density requirements. As discussed Abstract— Ours is the generation which is living in the age of above Dot gain is the measurement of the increase in tone science and technology. The latest scientific inventions have value from original file to the printed sheet. given rise to various technologies in every aspect of our life. Newer technologies have entered the field of printing also. II. MATERIALS AND METHODS Digital printing is one of these latest technologies which have further revolutionized entire modern printing industry in many Densitometer is used for measuring density of ink ways. It also facilitates working on large variety of surfaces, on the paper. Densitometer can be classified according to besides these factors digital printing have grown widely and type of materials they are designed to measure i.e. opaque made a special impact in print market. The presented analysis and transparent. Density of opaque materials is measured by system is used for study of print quality in Digital Printing. reflected light with a device called reflection type densitometer. Density of transparent materials is measured Index Terms— Digital Printing, Dot Gain, Solid ink density, by transmitted light with a device called transmission type Coated Paper and Uncoated Paper. densitometer. In order to measure the print quality i.e. solid ink density (SID) and dot gain (DG) on coated and uncoated I. -

The Art of the Cigar Label
The Art of the Cigar Label A.AMO&CO. LA BVA TAMPA.FLA. An exhibition by the Ybor City Museum Society with assistance from the University of South Florida Libraries' Special Collections Curated by: Emanuel Leto "True, our pictures are many of them for the soap manufacturer, the insurance com panies, and the patent medicine man; but we try in our way to be educators of the people , and to give them good drawings and harmonious coloring. These business operators of ours who use pictures for advertising purposes know that the public have become fastidious; hence, they will only accept good designs. It is not so very long ago that advertising pictures invariably had hard, glaring backgrounds and crude, contrasting colors ... but that type of work would find no sale now except in the back woods." - Anonymous lithographer, New York, 1894 1 At first glance, the images on cigar labels seem simple; they are beautifully em bossed and the illustration- whether an attractive woman or a famous writer- jumps out at the viewer. However, cigar labels of the late 19th and early 20th centuries are also rich in allegory and symbolism, subtly illustrating themes like commerce, trade, or U.S. foreign relations. Label themes "reflect the tobacco industry's important influence on the economic, social, and political climate of Cuba and Florida cities like Key West and Tampa," 2 becoming "windows to the past," depicting contemporary events, political leaders, celebrities, and so cial life. A look at cigar labels also reveals quite a bit about America in the Gilded Age, from roughly 1870 to 1920. -

Lithography Aluminum Plate Lithography
Kevin Haas | http://kevinhaas.com/printmaking/ Lithography Aluminum Plate Lithography Preparing Your Plate The Five Main Steps in Cutting Your Plate to Size Lithography: The 25.5” x 36” aluminum litho plates can be cut either in half (18” x 25.5”), 1. Preparing Your Plate thirds (25.5” x 12”), or quarters (12.75” x 18”), but shouldn’t be any smaller than this. Plates should be handled by the edges only and with clean hands. 2. Drawing Your Image Lay the plate face down on a protective sheet of paper on a cutting board. Mark 3. First Etch and score the back of the plate about 10 times while firmly holding the straight 4. Roll-up and Second edge. Flip the plate over and fold the plate up and down. The plate will split at Etch the score. 5. Printing Round the corners of your plate with scissors and lightly file any rough edges. De-Oxidizing Before drawing on your plate, it is necessary to remove oxides that build up on the aluminum so the drawing material will attach well to your plate. To deoxidize your plate, rinse it with hot water. Wipe the entire surface in vertical and horizontal strokes for about two minutes to remove the oxides from your plate. Use a completely clean cotton rag or Webril Wipe that will not scratch or abrade your plate. If there are noticeable fingerprints or marks on the plate, use the Aluminum Plate Counter-Etch which contains phosphoric and hydrochloric acids. Wear gloves while applying in the same manner as above. -

Commercial Nineteenth-Century American Lithography: an Economic History
Commercial Nineteenth-Century American Lithography: An Economic History Georgia B. Barnhill American Antiquarian Society Presented at “Representations of Economy: Lithography in America from 1820 to 1860” The Ninth Annual Conference of the Program in Early American Economy and Society Co-Sponsored with the Visual Culture Program and “Philadelphia on Stone” At the Library Company of Philadelphia 1314 Locust Street, Philadelphia, PA Friday, October 15, 2010 1 Writers on American prints generally have ignored the speculative and entrepreneurial aspect of printing and publishing. We tend to focus on individual prints and the stories that they present, either through their publication and distribution or through the subject matter of the image. When Cathy Matson invited me to participate in this conference, I suggested a look at some of the economic aspects of the lithographic industry as a whole. This is a story that is difficult to construct because so little primary material has survived. I have tried to stitch together information gathered from a variety of sources with the understanding that this is not a definitive study. Others will have to build on this fragile patchwork. As in so many manufacturing enterprises, success is not guaranteed and seldom is there a straight line moving towards economic stability. There are many lithographic companies that lasted just a year or two, suggesting that being successful required a variety of skills. Other companies struggled at times and managed to survive. And, just as in book publishing, not all printers were publishers. Separating the two roles is important as we look at the business of lithographic printing and publishing. -

Mechanization of the Printing Press Robin Roemer Western Oregon University, [email protected]
Western Oregon University Digital Commons@WOU History of the Book: Disrupting Society from Student Scholarship Tablet to Tablet 6-2015 Chapter 08 - Mechanization of the Printing Press Robin Roemer Western Oregon University, [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.wou.edu/history_of_book Part of the Critical and Cultural Studies Commons, Cultural History Commons, and the History of Science, Technology, and Medicine Commons Recommended Citation Roemer, Robin. "Mechanization of the Printing Press." Disrupting Society from Tablet to Tablet. 2015. CC BY-NC. This is brought to you for free and open access by the Student Scholarship at Digital Commons@WOU. It has been accepted for inclusion in History of the Book: Disrupting Society from Tablet to Tablet by an authorized administrator of Digital Commons@WOU. For more information, please contact [email protected]. 8 Mechanization of the Printing Press - Robin Roemer - One of the important leaps in the technology of copying text was the mechanization of printing. The speed and efficiency of printing was greatly improved through mechanization. This took several forms including: replacing wooden parts with metal ones, cylindrical printing, and stereotyping. The innovations of printing during the 19th century affected the way images were reproduced for illustrations as well as for type. These innovations were so influential on society because they greatly increased the ability to produce large quantities of work quickly. This was very significant for printers of newspapers, who were limited by the amount their press could produce in a short amount of time. Iron Printing Press One major step in improving the printing press was changing the parts from wood to metal.