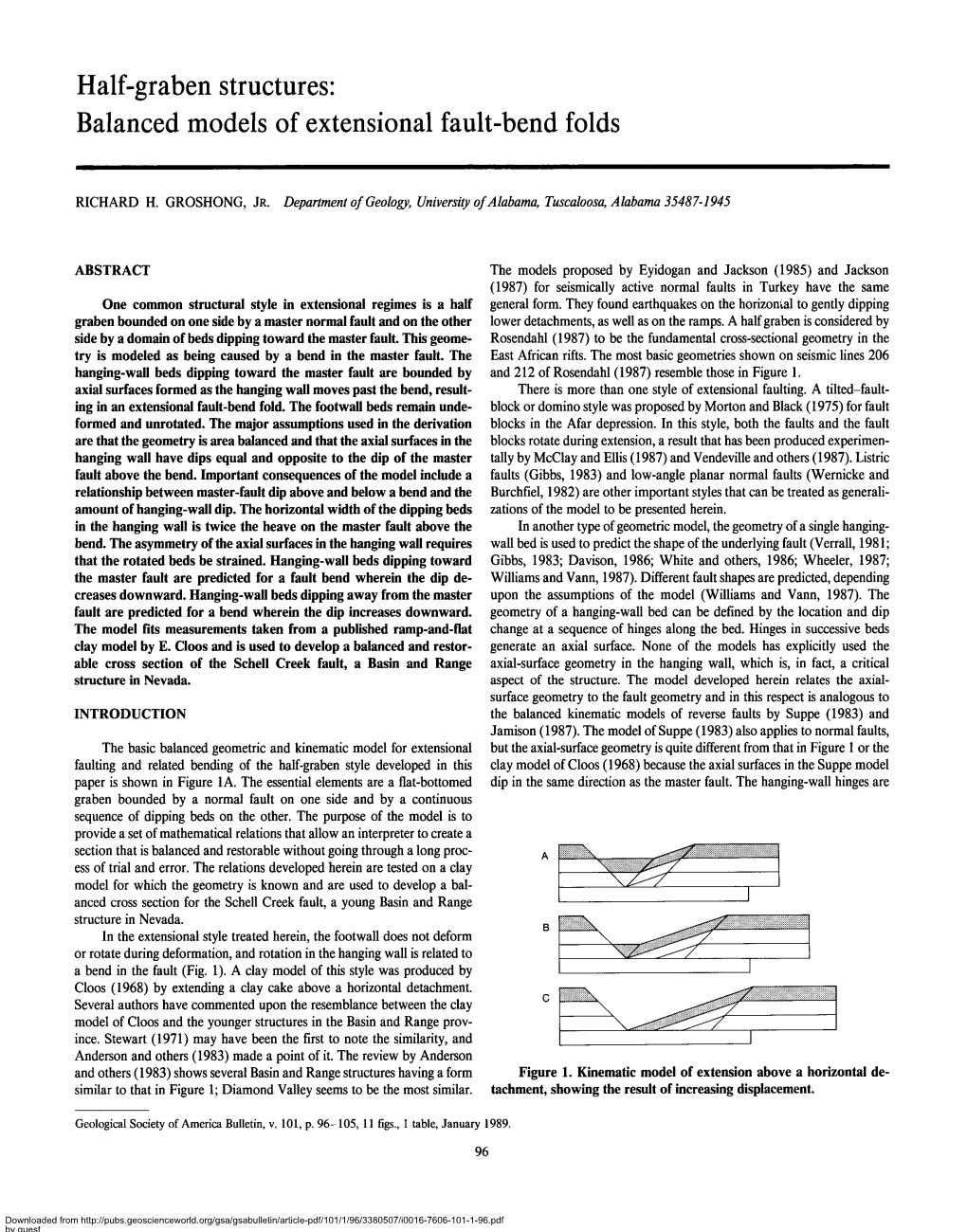
Half-Graben Structures: Balanced Models of Extensional Fault-Bend Folds
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

THE JOURNAL of GEOLOGY March 1990
VOLUME 98 NUMBER 2 THE JOURNAL OF GEOLOGY March 1990 QUANTITATIVE FILLING MODEL FOR CONTINENTAL EXTENSIONAL BASINS WITH APPLICATIONS TO EARLY MESOZOIC RIFTS OF EASTERN NORTH AMERICA' ROY W. SCHLISCHE AND PAUL E. OLSEN Department of Geological Sciences and Lamont-Doherty Geological Observatory of Columbia University, Palisades, New York 10964 ABSTRACT In many half-graben, strata progressively onlap the hanging wall block of the basins, indicating that both the basins and their depositional surface areas were growing in size through time. Based on these con- straints, we have constructed a quantitative model for the stratigraphic evolution of extensional basins with the simplifying assumptions of constant volume input of sediments and water per unit time, as well as a uniform subsidence rate and a fixed outlet level. The model predicts (1) a transition from fluvial to lacustrine deposition, (2) systematically decreasing accumulation rates in lacustrine strata, and (3) a rapid increase in lake depth after the onset of lacustrine deposition, followed by a systematic decrease. When parameterized for the early Mesozoic basins of eastern North America, the model's predictions match trends observed in late Triassic-age rocks. Significant deviations from the model's predictions occur in Early Jurassic-age strata, in which markedly higher accumulation rates and greater lake depths point to an increased extension rate that led to increased asymmetry in these half-graben. The model makes it possible to extract from the sedimentary record those events in the history of an extensional basin that are due solely to the filling of a basin growing in size through time and those that are due to changes in tectonics, climate, or sediment and water budgets. -

Geotectonic Model of the Alpine Development of Lakavica Graben in the Eastern Part of the Vardar Zone in the Republic of Macedonia
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by UGD Academic Repository Geologica Macedonica, Vol. 27, No. 1, pp. 87–93 (2013) GEOME 2 ISSN 0352 – 1206 Manuscript received: May 17, 2013 UDC: 551.245.03(497.71/.73) Accepted: October 25, 2013 Original scientific paper GEOTECTONIC MODEL OF THE ALPINE DEVELOPMENT OF LAKAVICA GRABEN IN THE EASTERN PART OF THE VARDAR ZONE IN THE REPUBLIC OF MACEDONIA Goše Petrov, Violeta Stojanova, Gorgi Dimov Faculty of Natural and Technical Sciences, “Goce Delčev” University, P.O.Box 201, MK 2000 Štip, Republic of Macedonia [email protected]//[email protected] A b s t r a c t: Lakavica graben is located in the eastern subzone of the Vardar zone, which during the Alpine orogenesis was covered with very complex processes of tectogenesis. On the area of about 200 km2, in the Lakavica graben, are present geological units from the oldest geological periods (Precam- brian) to the youngest (Neogene and Quaternary). Tectonic structure, or rupture tectonic, is very intense developed and gives possibility for analysis of the geotectonic processes in the Alpine orogen phase. This paper presents the possible model for geotectonic processes in the Lakavica graben, according to which can be generalized geotectonic processes in the Vardar zone during the Alpine orogeny. Key words: Lakavica graben; geotectonic model; Alpine orogeny; Vardar zone INTRODUCTION Vardar zone as a tectonic unit, for the first niki Gulf (Greece), than bent eastward and crosses time, is separated and showed on the "Geological- the ophiolite zone Izmir–Ankara (Turkey). -

Deformation Pattern During Normal Faulting: a Sequential Limit Analysis
Originally published as: Yuan, X., Maillot, B., Leroy, Y. M. (2017): Deformation pattern during normal faulting: A sequential limit analysis. ‐ Journal of Geophysical Research, 122, 2, pp. 1496—1516. DOI: http://doi.org/10.1002/2016JB013430 Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth RESEARCH ARTICLE Deformation pattern during normal faulting: 10.1002/2016JB013430 A sequential limit analysis Key Points: • New 2-D mechanically balanced X. P. Yuan1,2 , B. Maillot3, and Y. M. Leroy1,4 model of formation and evolution of half-grabens above low-angle normal 1Laboratoire de Géologie, CNRS UMR, École Normale Supérieure, Paris, France, 2Now at Helmholtz Centre Potsdam, detachment 3 • Tectonic extensional and gravitational German Research Center for Geosciences (GFZ), Potsdam, Germany, Laboratoire Géosciences et Environnement Cergy, 4 modes of deformation in frictional Université de Cergy-Pontoise, Cergy-Pontoise, France, Now at Total, CSTJF, Pau, France wedges are well captured • Fault weakening and sedimentation control number of fault-bounded Abstract We model in 2-D the formation and development of half-graben faults above a low-angle blocks in hanging wall normal detachment fault. The model, based on a “sequential limit analysis” accounting for mechanical equilibrium and energy dissipation, simulates the incremental deformation of a frictional, cohesive, and Supporting Information: fluid-saturated rock wedge above the detachment. Two modes of deformation, gravitational collapse and • Supporting Information S1 tectonic collapse, are revealed which compare well with the results of the critical Coulomb wedge theory. •MovieS1 •MovieS2 We additionally show that the fault and the axial surface of the half-graben rotate as topographic •MovieS3 subsidence increases. This progressive rotation makes some of the footwall material being sheared and •MovieS4 entering into the hanging wall, creating a specific region called foot-to-hanging wall (FHW). -

GEOLOGIC MAP of the CHELAN 30-MINUTE by 60-MINUTE QUADRANGLE, WASHINGTON by R
DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR TO ACCOMPANY MAP I-1661 U.S. GEOLOGICAL SURVEY GEOLOGIC MAP OF THE CHELAN 30-MINUTE BY 60-MINUTE QUADRANGLE, WASHINGTON By R. W. Tabor, V. A. Frizzell, Jr., J. T. Whetten, R. B. Waitt, D. A. Swanson, G. R. Byerly, D. B. Booth, M. J. Hetherington, and R. E. Zartman INTRODUCTION Bedrock of the Chelan 1:100,000 quadrangle displays a long and varied geologic history (fig. 1). Pioneer geologic work in the quadrangle began with Bailey Willis (1887, 1903) and I. C. Russell (1893, 1900). A. C. Waters (1930, 1932, 1938) made the first definitive geologic studies in the area (fig. 2). He mapped and described the metamorphic rocks and the lavas of the Columbia River Basalt Group in the vicinity of Chelan as well as the arkoses within the Chiwaukum graben (fig. 1). B. M. Page (1939a, b) detailed much of the structure and petrology of the metamorphic and igneous rocks in the Chiwaukum Mountains, further described the arkoses, and, for the first time, defined the alpine glacial stages in the area. C. L. Willis (1950, 1953) was the first to recognize the Chiwaukum graben, one of the more significant structural features of the region. The pre-Tertiary schists and gneisses are continuous with rocks to the north included in the Skagit Metamorphic Suite of Misch (1966, p. 102-103). Peter Misch and his students established a framework of North Cascade metamorphic geology which underlies much of our construct, especially in the western part of the quadrangle. Our work began in 1975 and was essentially completed in 1980. -

Constraining the Tectonic Evolution of Extensional Fault Systems in the Cyclades (Greece) Using Low-Temperature Thermochronology Stephanie Brichau
Constraining the tectonic evolution of extensional fault systems in the Cyclades (Greece) using low-temperature thermochronology Stephanie Brichau To cite this version: Stephanie Brichau. Constraining the tectonic evolution of extensional fault systems in the Cyclades (Greece) using low-temperature thermochronology. Applied geology. Université Montpellier II - Sciences et Techniques du Languedoc; Johannes Gutenberg Universität Mainz, 2004. English. tel- 00006814 HAL Id: tel-00006814 https://tel.archives-ouvertes.fr/tel-00006814 Submitted on 3 Sep 2004 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Universität Mainz “Johannes Gutenberg” and Université de Montpellier II “Sciences et techniques du Languedoc” Dissertation zur Erlangung des Grades “DOKTOR DER NATURWISSENSCHAFTEN” am Fachbereich Geowissenschaften der Johannes Gutenberg-Universität Mainz THESE Pour obtenir le grade de “DOCTEUR DE L’UNIVERSITÉ MONTPELLIER II” Discipline: Terre solide, géodynamique Formation Doctorale: Structure et Evolution de la Lithosphère Ecole Doctorale: Science de la Terre et de l’Eau Presented and publicly defended at Mainz by Stéphanie Brichau June 29th, 2004 Title: Constraining the tectonic evolution of extensional fault systems in the Cyclades (Greece) using low-temperature thermochronology JURY M. Stephen Foley GP, Mainz President M. Michel Faure IST, Orléans Reviewer M. -

"Extension Layer-Parallel Shear and Normal Faulting."
* * A/H6 Extensional layer-parallel shear and normal faulting DAVID A. FERRILL Center for Nuclear Waste Regulatory Analyses, Southwest Research Institute, 6220 Culebra Road, San Antonio, Texas 78238 ALAN P. MORRIS Division of Earth and Physical Sciences, University of Texas at San Antonio, San Antonio, Texas 78249 SIDNEY M. JONES and JOHN A. STAMATAKOS Center for Nuclear Waste Regulatory Analyses, Southwest Research Institute, 6220 Culebra Road, San Antonio, Texas 78238 Abstract-An extensional fault system in Bare Mountain, Nevada, contains abundant evidence of layer-parallel shear deformation contemporaneous with faulting. Layer-parallel shear is manifest by deformation of pre-existing fabrics such as teeth on bedding-parallel stylolites and shape fabrics in fossiliferous and oolitic limestone that all indicate shear in the down-dip direction, perpendicular to fault-bedding intersections. Cleavage at a low angle to bedding has the same vergence, indicating development and/or modification during shear parallel to bedding with a down-dip sense. Localized layer-parallel shear along discrete bedding planes has locally offset normal faults, and shear distributed within layers has reoriented block-bounding normal faults. These observations of internal deformation within fault blocks indicate that layer-parallel shear contributes to fault block deformation. In simple rigid-block models of extension accommodated by normal faults above a low-angle detachment or decollement zone, extension causes faults to rotate to progressively lower dips, while originally horizontal beds rotate to steeper dips. These rotations reorient faults away from originally optimum conditions for slip 2 into orientations of a lower slip tendency, whereas bedding rotates to steeper dips with progressively higher slip tendency. -

The Shumagin Seismic Gap Structure and Associated Tsunami Hazards, Alaska Convergent Margin GEOSPHERE, V
Research Paper THEMED ISSUE: Subduction Top to Bottom 2 GEOSPHERE The Shumagin seismic gap structure and associated tsunami hazards, Alaska convergent margin GEOSPHERE, v. 15, no. 2 Roland von Huene1,*,†, John J. Miller2,*,†, and Anne Krabbenhoeft3 https://doi.org/10.1130/GES01657.1 1U.S. Geological Survey, 800 Blossom Hill Road, Los Gatos, California 95032, USA 2U.S. Geological Survey, Denver Federal Center, Denver, Colorado 80225, USA 3 14 figures; 1 set of supplemental files GEOMAR Helmholz Centre for Ocean Research, D-24148, Kiel, Germany CORRESPONDENCE: rhuene@ mindspring .com ABSTRACT ruptured in the 1964 great earthquake, the Semidi segment that broke in a CITATION: von Huene, R., Miller, J.J., and Krabben‑ 1938 earthquake, and the Unimak segment that ruptured in 1946. In contrast, hoeft, A., 2019, The Shumagin seismic gap structure and associated tsunami hazards, Alaska convergent The potential for a major earthquake in the Shumagin seismic gap, and the the Shumagin segment has no historic great earthquake and is constrained by margin: Geosphere, v. 15, no. 2, p. 324–341, https:// tsunami it could generate, was reported in 1971. However, while potentially its neighboring segments rather than its own aftershocks. Since Sykes (1971) doi .org /10 .1130 /GES01657.1. tsunamigenic splay faults in the adjacent Unimak and Semidi earthquake seg- first drew attention to the Shumagin segment, it has been a proposed seismic ments are known, such features along the Shumagin segment were undoc- gap. Earthquakes in the adjacent segments have produced tsunamis. To the Science Editor: Shanaka de Silva umented until recently. To investigate margin structure and search for splay southwest, during the 1946 M8.6 earthquake, the Unimak segment generated Associate Editor: Laura M. -

Styles of Positive Inversion Tectonics in the Central Apennines and in the Adriatic Foreland: Implications for the Evolution of the Apennine Chain (Italy)
ARTICLE IN PRESS Journal of Structural Geology xxx (2009) 1–19 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Journal of Structural Geology journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/jsg Styles of positive inversion tectonics in the Central Apennines and in the Adriatic foreland: Implications for the evolution of the Apennine chain (Italy) Vittorio Scisciani* Dipartimento di Scienze della Terra, Universita` ‘‘G. D’Annunzio’’ Chieti-Pescara, Campus Universitario Madonna delle Piane, Via dei Vesini, 30, 68013 Chieti Scalo (CH), Italy article info abstract Article history: Integration of new field structural and geophysical data with existing information from the Apennines Received 22 February 2008 chain in Italy and its adjacent Adriatic foreland indicates that the styles of positive inversion tectonics Received in revised form and the modes of interaction between the extensional and the subsequent compressive structures vary. 19 February 2009 Starting from the Cretaceous, the contractional deformation induced by the mainly north-directed Accepted 27 February 2009 convergence of Africa/Adria with respect to the European plate promoted the closure of various arms of Available online xxx the Atlantic and the Neo-Tethys oceans, which opened in different times and with distinct orientations. The mosaic of continental blocks, carbonate platforms, rift basins and oceanic domains with several Keywords: Positive inversion tectonics geometries and orientations with respect to the axis of the subsequent compression, and the resulting Extensional and contractional deformation heterogeneities within the shallow sedimentary cover and the overall lithosphere, strongly influenced Thick-skinned tectonics both the structural evolution of the Apennine orogenic belt and the intra-continental deformation within Fault reactivation the Adriatic foreland. -

Characteristics of Earthquake Ruptures and Dynamic Off-Fault Deformation on Propagating Faults
Solid Earth, 11, 1333–1360, 2020 https://doi.org/10.5194/se-11-1333-2020 © Author(s) 2020. This work is distributed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License. Characteristics of earthquake ruptures and dynamic off-fault deformation on propagating faults Simon Preuss1, Jean Paul Ampuero2, Taras Gerya1, and Ylona van Dinther3 1Geophysical Fluid Dynamics, Institute of Geophysics, Department of Earth sciences, ETH Zürich, 8092 Zürich, Switzerland 2Géoazur Laboratory, Institut de Recherche pour le Développement – Université Côte d’Azur, Campus Azur du CNRS, 06560 Valbonne, France 3Tectonics, Department of Earth Sciences, Utrecht University, Princetonlaan 4, 3584 CB, Utrecht, the Netherlands Correspondence: Simon Preuss ([email protected]) Received: 8 February 2020 – Discussion started: 25 February 2020 Revised: 16 June 2020 – Accepted: 26 June 2020 – Published: 22 July 2020 Abstract. Natural fault networks are geometrically complex tures range from fan-shaped distributed deformation to local- systems that evolve through time. The evolution of faults ized splay faults. We observe that the fault-normal width of and their off-fault damage patterns are influenced by both the outer damage zone saturates with increasing fault length dynamic earthquake ruptures and aseismic deformation in due to the finite depth of the seismogenic zone. We also ob- the interseismic period. To better understand each of their serve that dynamically and statically evolving stress fields contributions to faulting we simulate both earthquake rup- from neighboring fault strands affect primary and secondary ture dynamics and long-term deformation in a visco-elasto- fault growth and thus that normal stress variations affect plastic crust subjected to rate- and state-dependent friction. -

EPS 116 – Laboratory Structural Geology Lab Exercise #1 Spring 2016
EPS 116 – Laboratory Structural Geology LAB #1 – Orientation of Structures in Space Familiarize yourself with the following terms. Sketch each feature and include relevant details, e.g., footwall, hanging wall, motion arrows, etc. Also always include at least 3 horizontal layers and an up arrow in the cross sections and a north arrow in each map view. Stress vs. Strain Feature Cross Section Map View compression tension Horst and contraction/shortening Graben extension (Label hanging /foot wall and slip Brittle Deformation direction) joint fault earthquake Thrust Fault thrust/reverse fault (Label hanging / normal fault footwall and slip footwall direction) hanging wall strike-slip fault right lateral or dextral Anticline left lateral (Label hinge axis, or sinistral force direction, dip-slip contact topo lines in map view) oblique-slip Ductile Deformation fold Normal Fault anticline (Label hanging / footwall and slip syncline direction) Map View longitude latitude geographic vs. magnetic north Syncline topography (Label hinge axis, scale force direction, profile contact topo lines in map view) Strike-Slip fault (Label hanging / footwall and slip direction) Lab Exercise #1 Spring 2016 Page 1 of 9 EPS 116 – Laboratory Structural Geology Strike & Dip Strike and dip describe the orientation of a plane in space. Example: the peaked roof of a house: Strike Line Dip Direction Strike is the orientation of the intersection line of the plane in question (roof of a house) with the horizontal plane. If you were to look down on the house from directly above, it would look like this: North Strike Line Strike The angle between the strike line and north is used to describe the strike. -

Extensional Tectonics and Gravitational Collapse in an Ordovician Passive Margin: the Western Argentine Precordillera ⁎ J.L
Available online at www.sciencedirect.com Gondwana Research 13 (2008) 204–215 www.elsevier.com/locate/gr Extensional tectonics and gravitational collapse in an Ordovician passive margin: The Western Argentine Precordillera ⁎ J.L. Alonso a, , J. Gallastegui a, J. García-Sansegundo a, P. Farias a, L.R. Rodríguez Fernández b, V.A. Ramos c a Department of Geology, University of Oviedo, c/ Arias de Velasco s/n, 33005 Oviedo, Spain b Instituto Geológico y Minero de España, c/ La Calera, 1, 28740, Tres Cantos, Madrid, Spain c Laboratorio de Tectónica Andina, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad de Buenos Aires 1428, Buenos Aires, Argentina Received 29 September 2006; accepted 28 May 2007 Available online 7 June 2007 Abstract The paper describes ubiquitous extensional structures developed in a passive margin of Ordovician age in the Argentine Precordillera. These extensional structures include normal faults and boudinaged sequences. In some places the boudinage reaches very high extension values, giving rise to block-in-matrix formations. Most of these extensional structures developed when sediments were not well lithified, as recorded by hydroplastic fractures, slump folds and pinch-and-swell structures. The presence of slump folds coeval with the extensional deformation, the variable extension directions obtained from the kinematic analysis and a weak cleavage recording layer-perpendicular shortening support the interpretation that gravitational collapse related to submarine sliding was the cause for extensional deformation. Well-consolidated rocks, located at the lower part of the stratigraphic sequence, also display scarce extensional faults. These extensional faults predate folding because they were breached by flexural-slip faults and, as a result of their passive rotation in fold limbs, these initial normal faults may now appear as reverse faults, particularly in steep and overturned limbs. -

RESEARCH Topographic Expressions of Lunar Graben
RESEARCH Topographic expressions of lunar graben Melanie B. Callihan* and Christian Klimczak STRUCTURAL GEOLOGY AND GEOMECHANICS GROUP, DEPARTMENT OF GEOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF GEORGIA, ATHENS, GEORGIA 30602, USA ABSTRACT Graben, defined as landforms produced by normal faulting, have long been recognized on the Moon, but their map patterns, as well as topographic expressions, have not been studied systematically. The topography across graben and its along-strike variations reveal details about the growth of the normal faults forming the graben. Individual normal faults grow in length by the propagation of fault tips during slip events, which can also enlarge the displacement along the fault plane. Displacement and length accumulate and grow larger over time with more slip events, fault interaction, and linkage. We measured fault lengths and vertical offsets and then calculated the displacement for lunar graben using data from the camera and laser altimeter onboard the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter. Our study systematically investigated 14 graben systems across the lunar surface. Graben lengths were found to range from ~43 to 453 km, and displacements ranged from ~127 to 1115 m. These displacements were plotted against graben fault length to produce slip distributions, which revealed growth patterns involving mechanical interaction and fault linkage. Displacement-to-length scaling was used to further study the evolu- tion of graben-bounding normal faults. We observed a sublinear growth pattern for lunar graben-bounding normal faults, consistent with growth of faults via segment linkage, where different stages of linkage are present on the lunar surface. Lunar graben-bounding faults show higher scaling ratios than previously estimated, likely due to variations in host-rock properties and mechanical stratigraphy.