Blackfoot High School Curriculum Map with Core and Content Standards for English / 11Th Grade
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Crown V. Susannah North Martin Court of the County of Essex, Colony of Massachusetts Salem, Year of Our Lord 1692
Crown v. Susannah North Martin Court of the County of Essex, Colony of Massachusetts Salem, Year of Our Lord 1692 Case Description and Brief Susannah Martin was born in Buckinghamshire, England in 1621. She was the fourth daughter, and youngest child, of Richard North and Joan (Bartram) North. Her mother died when she was a young child, and her father remarried a woman named Ursula Scott. In 1639, at the age of 18, Susannah and her family came to the United States, settling in Salisbury, Massachusetts. Richard North, a highly respected man, was listed as one of the first proprietors and founders of Salisbury On August 11, 1646, Susannah, now 24, married the widower George Martin, a blacksmith. Making their home in Salisbury, the couple had a loving marriage, that produced nine children, one of which died in infancy. Prosperous in business, George and Susannah became one of the largest landholders of the region. George died in 1686, leaving Susannah a widow. After her husband’s death she managed his estate and lands with acumen and talent. As a young woman she was known for her exceptional beauty. Descriptions of Susanna say that she was short, active, and of remarkable personal neatness. She was also said to be very outspoken, contemptuous of authority, and defiant in the face of challenge. Due to her attractiveness and family’s prosperity, she had been the target of jealous slander, which had followed her for years, all of which had been proven unfounded. In January 1692, a a group of young girls began to display bizarre behavior in nearby Salem, Massachusetts. -

Joint School District No. 2 English Language Arts Curriculum English 11 Revised 2012-13
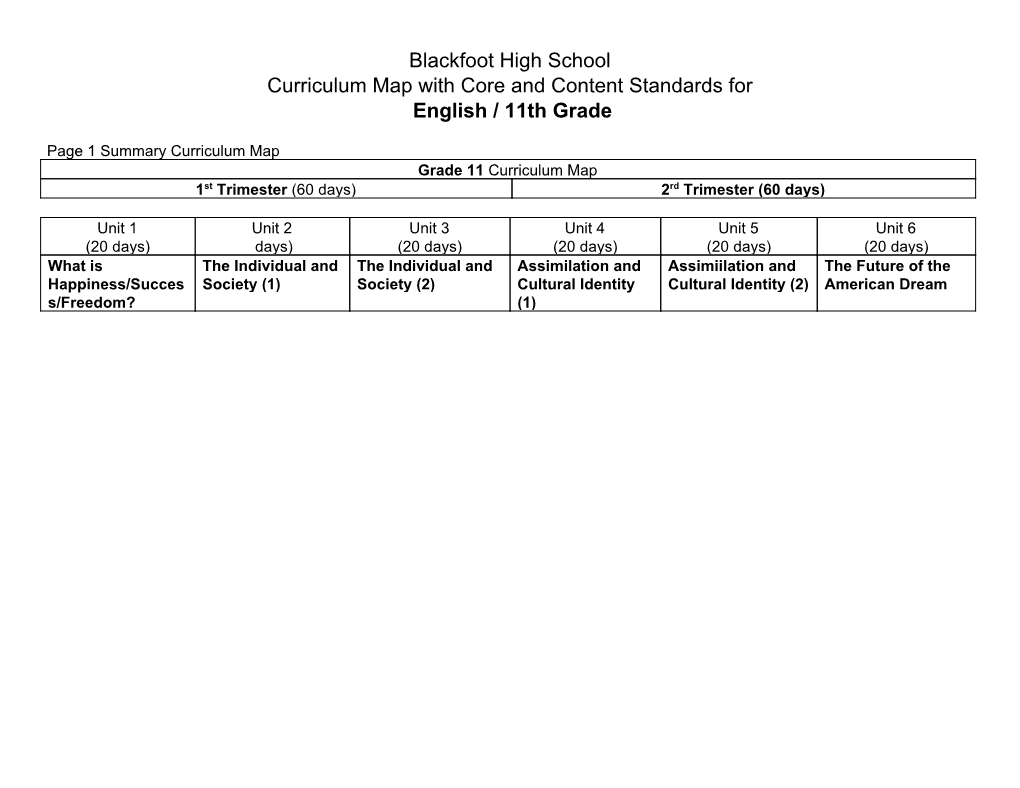
Joint School District No. 2 English Language Arts Curriculum English 11 Revised 2012-13 Curriculum Revision Committee: David Knife, Central Academy Kristina Haasakker, Centennial High School Josh McDonald, Eagle Academy Debra Smith, Meridian High School Kristin Galloway, Mountain View High School Nicole Thomas, Mountain View High School Justin Tharpe, Rocky Mountain High School Suzanne Mackelprang, Academic Coach Laura Gilchrist, English Language Arts Curriculum Coordinator Quarter 1 Quarter 2 Quarter 3 Quarter 4 What is The Individual and Assimilation and The Future of the Happiness/Success/ Society Cultural Identity American Dream Freedom? Table of Contents Page Scope and Sequence 2-4 Unit 1 5-12 Unit 2 13-23 Unit 3 24-33 Unit 4 34-44 1 |Revised April 2013, Hotlinks updated May, 2014 ELA Scope and Sequence Grade 11 F indicates that the standard is a focus standard and will be explicitly taught during the unit. X indicates that this standard will be met through throughout the year, but will not be explicitly taught; rather, teachers will need to ensure that students are meeting these standards as a result of explicit instruction through other standards. Standard Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Reading Literature 1 F F x F 2 F x x F 3 F x F 4 F x x 5 F x 6 F x x x 7 F x 8 n/a n/a n/a n/a 9 F F x 10 x x x x Standard Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Reading Informational Text 1 x x F F 2 F F F 3 x x F x 4 x F F x 5 F F F 6 x F x 7 x F x F 8 F x 9 F F 10 x x x x 2 |Revised April 2013, Hotlinks updated May, 2014 Standard Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit -

The Salem Witch Trials from a Legal Perspective: the Importance of Spectral Evidence Reconsidered
W&M ScholarWorks Dissertations, Theses, and Masters Projects Theses, Dissertations, & Master Projects 1984 The Salem Witch Trials from a Legal Perspective: The Importance of Spectral Evidence Reconsidered Susan Kay Ocksreider College of William & Mary - Arts & Sciences Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.wm.edu/etd Part of the Law Commons, and the United States History Commons Recommended Citation Ocksreider, Susan Kay, "The Salem Witch Trials from a Legal Perspective: The Importance of Spectral Evidence Reconsidered" (1984). Dissertations, Theses, and Masters Projects. Paper 1539625278. https://dx.doi.org/doi:10.21220/s2-7p31-h828 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Theses, Dissertations, & Master Projects at W&M ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dissertations, Theses, and Masters Projects by an authorized administrator of W&M ScholarWorks. For more information, please contact [email protected]. THE SALEM WITCH TRIALS FROM A LEGAL PERSPECTIVE; THE IMPORTANCE OF SPECTRAL EVIDENCE RECONSIDERED A Thesis Presented to The Faculty of the Department of History The College of Williams and Mary in Virginia In Partial Fulfillment Of the Requirements for the Degree of Master of Arts by Susan K. Ocksreider 1984 ProQuest Number: 10626505 All rights reserved INFORMATION TO ALL USERS The quality of this reproduction is dependent upon the quality of the copy submitted. In the unlikely event that the author did not send a com plete manuscript and there are missing pages, these will be noted. Also, if material had to be removed, a note will indicate the deletion. uest. ProQuest 10626505 Published by ProQuest LLC (2017). -

A Study of Salem Witch Trial: a Gender and Religion Based Discrimination
Annals of R.S.C.B., ISSN:1583-6258, Vol. 25, Issue 4, 2021, Pages. 9536 - 9552 Received 05 March 2021; Accepted 01 April 2021. A Study of Salem Witch Trial: A Gender and Religion Based Discrimination DeekshaKarunakar Law College Dehradun, Uttaranchal University, India Abstract: In the 16th century at the states of Massachusetts, in the United States of America, individuals were brutally tortured in the name of punishment under law and religion. This event showcased the effect of religion blindsiding a community. Salem witch trials have influenced many scholars and philosophers to put forward their study on different aspects of the case in the form of sociological, historical, demographic interpretations. Since then several regulations have been introduced worldwide for a fair and just trial. Furthermore, laws protecting women have also been introduced and in certain aspects Salem Witch Trial plays an important role for the same. The paper intends to focus on the global impact of Salem Witch Trial to the women in present along with the theories put forward on the basis of the case. Furthermore, the paper intends to recall the injustice served in this case for decades and how it impacted the faith of the justice system globally among the individuals. Keywords:-Witchcraft Trial, State, Criminal Justice, Salem, Injustice, Religion 1. HISTORY OF SALEM AND IDEOLOGY OF WITCHCRAFT The interpretation of the idea on witchcraft was heavily influenced by Hebrew’s Code and Bible. The practice of witchcraft was considered a sin, even centuries before the Salem Trials commenced. The ancient law of the Hebrews, Exodus 22:18[1] reads, “Thou shalt not suffer a witch to live.” This was later comprehended in the Bible 28:1[2] reads, “The Witch of Endor.” Both of these statements suggested that witchcraft is a sin and that God shall punish him and his sons with death and destruction of this practice. -

The Crucible
October 4 – October 21, 2017 By Arthur Miller Directed by Jonathan Berry The Crucible When does Index a lie become 2 Welcome Letter 4 Cold, Hard, Wicked Facts: 10 Things You May Not Know About The Crucible the truth? 6 The Crucible Play Synopsis 8 The Crucible Character Descriptions 10 Inside the Mind of Abigail Williams: An Actor Creates Backstory 12 A Loss of Agency, A Loss of Control: The Young Women of The Crucible (Classroom Activity) 14 The World of The Crucible: A Conversation with Director Jonathan Berry 18 What Makes a Witch Hunt?: Mapping the History of the Salem Witch Trials 20 An Allegorical Response: The Crucible and Communism 22 The Truth in Our Actions (Classroom Activity) Dear teachers: story, is able to manipulate the fear of her neighbors, Continuing the Conversation: The Burn fed by a series of distrustful and escalating 26 Thank you for joining Steppenwolf Education for accusations, into a source of individual agency. our 2017/2018 Steppenwolf for Young Adults season In our theater, and in your classrooms, we hope that 28 Additional Resources featuring two plays in conversation: When does a lie this story will spur conversations and encourage a become the truth? careful examination of the ease in which a lie might Common Core State Standards become accepted as reality. 30 For our first show of the season, we are excited to present a fresh take on a familiar entry to the canon. This season, we are also excited to announce the Acknowledgements 31 STUDY GUIDE CURATED BY Written in response to the spread of McCarthyism, creation of Steppenwolf Education, a new Jared Bellot Arthur Miller’s classic work The Crucible explores a department under which Steppenwolf for Young paranoid witch hunt and its very real consequences Adults will be housed and continue its tradition of ARTICLES BY Jared Bellot, Sindy Isabel Castro, in the town of Salem, Massachusetts. -

Mercy Lewis Mercy Lewis Born in Falmouth, Maine in 1675, Mercy Lewis Lost Both Her Parents to Indian Attacks and Became an Orphan at a Young Age
Mercy Lewis Mercy Lewis Born in Falmouth, Maine in 1675, Mercy Lewis lost both her parents to Indian attacks and became an orphan at a young age. Dislocated from her family, like many of the accusing girls in Salem Village, she resided first as a servant with Reverend George Burroughs and then later with the family of Thomas Putnam to whom she was distantly related. As a friend of Ann Putnam and the other girls involved in the witchcraft accusations, Mercy herself became one of the most consistent and vocal accusers during the 1692 witchcraft trials in Salem. Mercy Lewis Written By Meghan Carroll, 2001 and Jenny Stone, 2002 Salem Witch Trials in History and Literature An Undergraduate Course, UV Spring Semester 2002 "I veryly believe in my heart," began 19 -year-old Mercy Lewis on April 19, 1692, "that Giles Corey is a dreadful wizzard." Lewis's confidence in herself was not unique to her accusation of Corey during the Salem Witchcraft Trials. Throughout the months plagued by chaos and confusion in Salem Village, Mercy Lewis acted as a member of the core group of accusing young women in the Village, blatantly accusing several persons of afflicting herself and her friends. Besides Giles Cory, Mercy Lewis accused Bridget Bishop, Mary Lacey, Sr., Susannah Martin, John Willard, Nehemiah Abbot, Jr., Sarah Wilds, and her former guardian, George Burroughs. Mercy Lewis was born in Falmouth, Maine in 1675. The Lewis family lived in Maine until an Indian attack killed all of Mercy's extended family. In the Devil's Snare historian Mary Beth Norton suspects that Mercy's parents were killed in a later attack witnessed by Mercy herself. -

Coming to Terms with the Salem Witch Trials
Coming to Terms with the Salem Witch Trials JOHN M. MURRIN OR SEVERAL YEARS I have been approaching the Salem witch trials from two different directions.' Breaking out in F1692, they became the last major upheaval that afflicted the English Atlantic world between the third Anglo-Dutch War of 1672-74 and the 1690s. The Dutch reconquest of New York for fifteen months in 1673-74 reconfigured the politics ofthat colony and established patterns of partisanship that would prevail until after 1700. In 1675-76, King Philip's War devastated New Eng- land, generated massacres on both sides, and led to the enslave- ment of hundreds of Indians. While all of the New England gov- ernments survived the crisis intact and were finally able to win the war, it was only with significant support from the praying Indians, the Mohegans, and the Pequots. New England's victory inflicted civil war upon the Indians within the recognized boundaries of Plymouth, Massachusetts, Connecticut, and Rhode Island. By contrast, when an Indian war erupted at almost the same time in 1.1 wish to thank the Erasmus Institute at the University of Notre Dame, the National Endowment for the Humanities, and the American Antiquarian Society for their financial support in the academic year 2001-2. An earlier version of this essay, entitled 'How Close Are We to Understanding the Salem Witch Trials?' was delivered as a paper at the Colum- bia University Seminar in Early American History, November 9, 1999. A revised version became a New England Regional Seminar at the American Antiquarian Society on May 7, 2002.1 wish to thank the participants at both events for their many thoughtful suggestions. -

Teaching History to Deaf Students
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses 9-14-2005 Teaching history to deaf students Brooke Erickson Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.rit.edu/theses Recommended Citation Erickson, Brooke, "Teaching history to deaf students" (2005). Thesis. Rochester Institute of Technology. Accessed from This Master's Project is brought to you for free and open access by RIT Scholar Works. It has been accepted for inclusion in Theses by an authorized administrator of RIT Scholar Works. For more information, please contact [email protected]. MSSE Master's Proiect Submitted to the Faculty Of the Master of Science Program in Secondary Education Of Students who are Deaf or Hard of Hearing National Technical Institute for the Deaf ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY By Brooke J. Erickson (Student Signature) ,. In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements For the Degree of Master of Science Rochester. New York ~ (Date) Approved: Project ABSTRACT I have developed a cuniculum based on the Salem Witch Trials incorporating the usage of "The Crucible" play written by Arthur Miller. Along with that concept, the topic of communism and Senator Joseph McCarthy will be discussed. Within this curriculum,studentswill be exposedto activities such as participatingin class discussions, role-playing, designing a newspaper,conducting research, and writing a final paperby followingthe compare/contrastconcept. This curriculum is expected to take a month to conduct and the students will be able to learn about how two time periods are similar to one another but yet different. PROJECT OVERVIEW This curriculum will consist of a detailed unit plan describing the events that will take place throughout a one-month period. -

Women's History Month
The Office of Senate President Karen E. Spilka Women’s History Month There are so many women who have shaped Massachusetts, here are 88 from past and present whose work, advocacy, and legacy live on. Zipporah Potter Atkins 1645-1705 An accurate Atkins was the first African-American landowner in Boston. illustration of Zipporah Potter Atkins does not exist. Weetamoo 1676 As Sachem of Wampanoags in Plymouth, she led forces to drive out European settlers, and was eventually killed by English colonists. Victims of the Salem Witch Trials and Sarah Clayes 1638-1703 Fourteen women were tried, sentenced, and executed in the Salem Witch Trials in 1692. They are: Bridget Bishop, Martha Carrier, Martha Corey, Mary Eastey, Sarah Good, Elizabeth Howe, Susannah Martin, Rebecca Nurse, Mary & Alice Parker, Ann Pudeator, Wilmot Redd, Margaret Scott, and Sarah Wildes. Sarah Clayes fled the Salem Witch Trials to establish a safe haven in Framingham for other accused women. Elizabeth Freeman 1742-1829 Also known as Mum Bett, she was the first enslaved woman to file and win a freedom suit in Massachusetts. The Massachsuetts Supreme Judicial Court ruling in Freeman’s favor found slavery to be unconstitu- tional, according to the 1780 Massachusetts State Constitution. Abigail Adams 1744-1818 Along with being the second First Lady of the United States, Adams was an abolitionist and advocate for women’s rights. She is from Weymouth and moved to Quincy, MA. Phillis Wheatley 1753-1784 Wheatley was an enslaved poet from Senegal or Gambia working in Boston who corresponded with George Washington. Deborah Sampson 1760-1827 Injured in battle in the Revolutionary War, and disguised as a man, she suffered injuries that she managed to heal herself so that doctors would not discover her gender. -

AGENTS of the DEVIL?: WOMEN, WITCHCRAFT, and MEDICINE in EARLY AMERICA a Thesis by JEWEL CARRIE PARKER Submitted to the Graduate
AGENTS OF THE DEVIL?: WOMEN, WITCHCRAFT, AND MEDICINE IN EARLY AMERICA A Thesis by JEWEL CARRIE PARKER Submitted to the Graduate School at Appalachian State University in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of MASTER OF ARTS May 2018 Department of History AGENTS OF THE DEVIL?: WOMEN, WITCHCRAFT, AND MEDICINE IN EARLY AMERICA A Thesis by JEWEL CARRIE PARKER May 2018 APPROVED BY: Lucinda M. McCray Chairperson, Thesis Committee Sheila R. Phipps Member, Thesis Committee Antonio T. Bly Member, Thesis Committee James Goff Chairperson, Department of History Max C. Poole, Ph.D. Dean, Cratis D. Williams School of Graduate Studies Copyright by Jewel Carrie Parker 2018 All Rights Reserved Abstract AGENTS OF THE DEVIL?: WOMEN, WITCHCRAFT, AND MEDICINE IN EARLY AMERICA Jewel Carrie Parker: B.A., Appalachian State University M.A., Appalachian State University Chairperson: Lucinda M. McCray This thesis argues that early American women healers were especially vulnerable to witchcraft accusations because their positions of power threatened patriarchal society and their colonial communities. Colonial society already viewed early American women as more susceptible to witchcraft than men because they believed women were more vulnerable to temptations by the devil. In particular, women healers faced accusations of witchcraft because they had it within their power to cure or to hurt. Women healers were involved in early American witchcraft trials as character witnesses and inspectors for witches’ marks. However, their abilities to recognize witchcraft-induced illness, injuries, and deaths contributed to the fears of their neighbors who did not possess such skills. Because of their power and influence, women healers represent a prime example of revolutionary women who acted as agents of change within their own lives. -

The Anatomy of Correction: Additions
KU ScholarWorks | http://kuscholarworks.ku.edu Please share your stories about how Open Access to this article benefits you. The Anatomy of Correction: Additions, Cancellations, and Changes in the Documents of the Salem Witchcraft Trials by Peter Grund 2007 This is the author’s accepted manuscript, post peer-review. The original published version can be found at the link below. Peter Grund. 2007. “The Anatomy of Correction: Additions, Cancellations, and Changes in the Documents of the Salem Witchcraft Trials.” Studia Neophilologica 79(1): 3–24. Published version: http://dx.doi.org/10.1080/00393270701287439 Terms of Use: http://www2.ku.edu/~scholar/docs/license.shtml This work has been made available by the University of Kansas Libraries’ Office of Scholarly Communication and Copyright. Peter Grund. 2007. “The Anatomy of Correction: Additions, Cancellations, and Changes in the Documents of the Salem Witchcraft Trials.” Studia Neophilologica 79(1): 3–24. (accepted manuscript version, post-peer review) The Anatomy of Correction: Additions, Cancellations, and Changes in the Documents of the Salem Witchcraft Trials1 Peter Grund, Uppsala University 1. Introduction The Salem witchcraft trials of 1692 hold a special place in early American history. Though limited in comparison with many European witch persecutions, the Salem trials have reached mythical proportions, particularly in the United States. The some 1,000 extant documents from the trials and, in particular, the pre-trial hearings have been analyzed from various perspectives by (social) historians, anthropologists, biologists, medical doctors, literary scholars, and linguists (see e.g. Rosenthal 1993: 33–36; Mappen 1996; Grund, Kytö and Rissanen 2004: 146). But despite this intense interest in the trials, very little research has been carried out on the actual manuscript documents that have survived from the trials. -

3.2 Hartford Witch-Hunt
Table of Contents 1 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................ 1 2 BACKGROUND .................................................................................. 3 2.1 Witch .............................................................................................. 3 2.2 Sabbat ........................................................................................... 3 2.3 To reveal a witch ........................................................................... 4 2.4 Causes .......................................................................................... 5 2.5 Hammer of Witches ....................................................................... 7 2.6 Testing a witch ............................................................................... 8 2.7 Witchcraft acts ............................................................................... 9 3 TRIALS IN CONNECTICUT ............................................................. 10 3.1 Period between 1648 and 1662................................................... 11 3.2 Hartford witch-hunt ...................................................................... 11 3.3 Last trial in Connecticut ............................................................... 12 4 TRIALS IN MASSACHUSETTS ....................................................... 14 4.1 Possession of the Goodwin Children .......................................... 15 4.2 Salem .........................................................................................