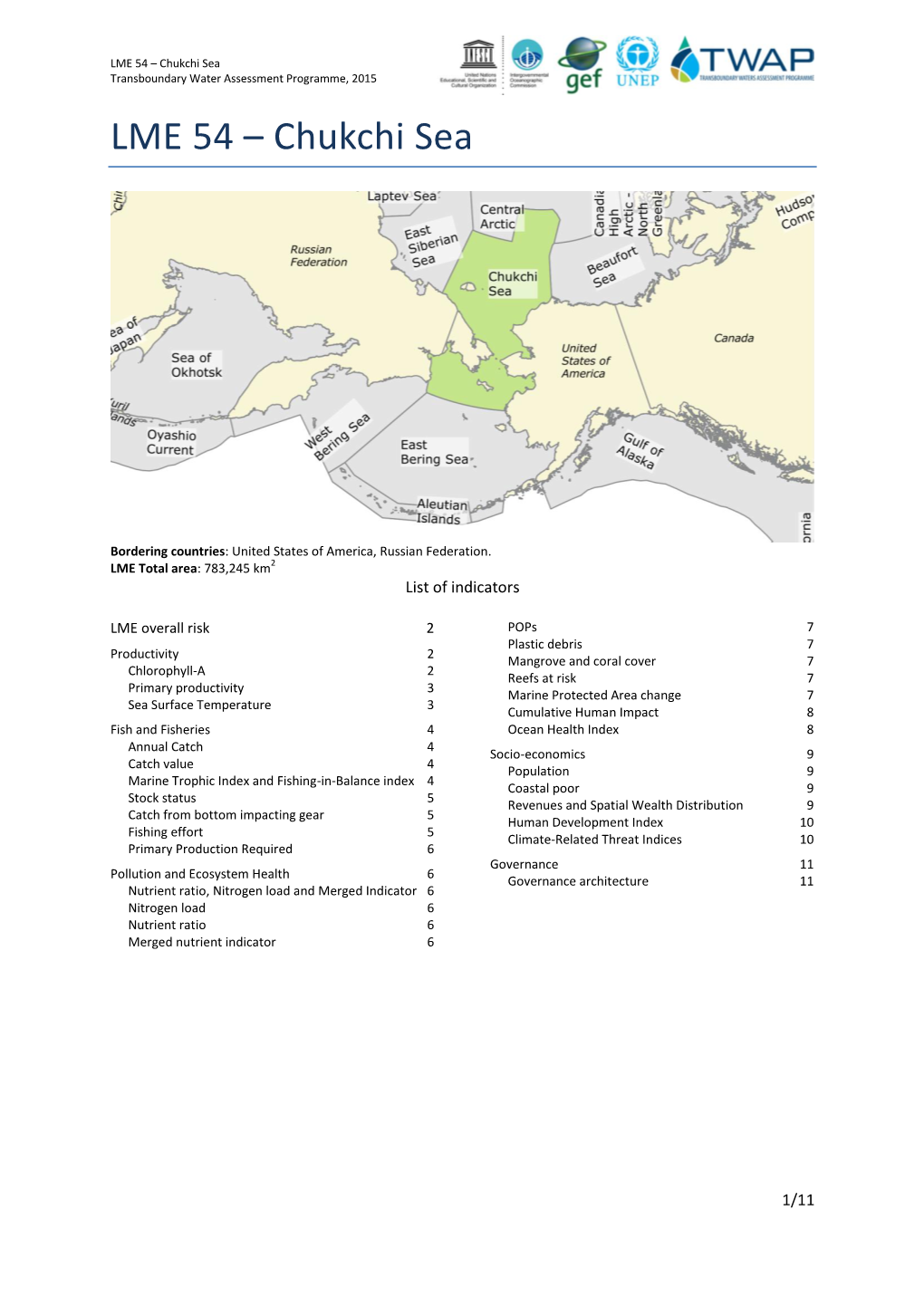
Chukchi Sea Transboundary Water Assessment Programme, 2015
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Introduction of Domestic Reindeer Into Alaska
M * Vice-President Stevenson. Mrs. Stevenson. Governor and Mrs. Sheakley. Teachers and Pupils, Presbyterian Mission School, Sitka, Alaska. 54th Congress, SENATE. f Document 1st Session. \ No. 111. IN THE SENATE OF THE UNITED STATES. REPO R T ON WITH MAPS AND ILLUSTRATIONS, MY SHELDON JACKSON, GENERAL AGENT OF EDUCATION IN ALASKA. WASHINGTON: GOVERNMENT PRINTING OFFICE. 1896. CONTENTS. Page. Action of the Senate of the United States. 5 Letter of the Secretary of the Interior to the President of the Senate. 7 Report of Dr. Sheldon Jackson, United States general agent of education in Alaska, to the Commissioner of Education, on the introduction of domestic reindeer i nto A1 aska for 1895. 9 Private benefactions. 11 Appropriations of Congress. 13 Importation of Lapps. 14 Distribution of reindeer. 15 Possibilities of the future. 16 Effect upon the development of Alaska. 16 Disbursements. 18 APPENDIXES. Report of William Hamilton on the itinerary of 1895. 21 Annual report of William A. Kjellmann. 42 Trip to Lapland. 43 Arrival at Teller Reindeer Station. 54 Statistics of the herd.. 55 Fining a reindeer thief. 57 Breaking in deer. 60 The birth of fawns. 61 Milking. 63 Eskimo dogs. 63 Herders and apprentices. 65 Rations. 72 Reindeer dogs. 73 Harness. 75 The Lapps. 77 Sealing. 78 Fishing. 79 Eskimo herd. 80 Sickness. 82 School. 82 Buildings. 83 Police. 84 Christmas. 85 Skees. 85 Physician. 88 Fuel. 89 Annual report of W. T. Lopp, Cape Prince of Wales, herd... 91 Letter of J. C. Widstead to Dr. Sheldon Jackson. 93 Letter of Dr. Sheldon Jackson to Hon. W. -

Festivals and Ceremonies of the Alaskan Eskimos: Historical and Ethnographic Sources, 1814-1940
Festivals and Ceremonies of the Alaskan Eskimos: Historical and Ethnographic Sources, 1814-1940 Jesús SALIUS GUMÀ Department of Prehistory, Universitat Autònoma de Barcelona AGREST Research Group [email protected] Recibido: 15 de octubre de 2012 Aceptado: 16 de enero de 2013 ABSTRACT The main objective of this article is to shed light on the festive and ceremonial events of some of the Eskimo cultures of Alaska through a review of the ethnohistorical documents at our disposal. The study centers on the ancient societies of the Alutiiq, Yup’ik and a part of the Inupiat, communities that share a series of com- mon features, and sees their festive and ceremonial activities as components of the strategies implemented to maintain control over social reproduction. This review of the historical and ethnographic sources identifies the authors and the studies that provide the most pertinent data on the subject. Key words: Ethnohistory, social reproduction, musical behaviors, Alaska Eskimo. Festivales y ceremonias de los esquimales de Alaska: fuentes históricas y etnográficas, 1814-1940 RESUMEN El objeto de este artículo es arrojar luz sobre las fiestas y ceremonias de algunas culturas esquimales de Alaska a través de la revisión de documentos etnohistóricos a nuestra disposición. La investigación se centra sobre las antiguas sociedades de los alutiiq, yup’ik y parte de los inupiat, comunidades que tienen una serie de rasgos comunes y contemplan sus actividades festivas y ceremoniales como parte de estrategias para mantener el control sobre la reproducción social. Esta revisión de fuentes históricas y etnográficas identifica a los autores y a los estudios que proporcionan los datos más significativos sobre el tema. -

Annual Report Noaa Ocseap Ecological Studies Of
ANNUAL REPORT NOAA OCSEAP Contract No. 03-6-022-35210 Research Unit No. 460 ECOLOGICAL STUDIES OF COLONIAL SEABIRDS AT CAPE THOMPSON AND CAPE LISBURNE, ALASKA Principal Investigators Alan M. Springer David G. Roseneau Renewable Resources Consulting Services, Ltd. 3529 College Road Fairbanks, Alaska 99701 839 i CONTENTS I. Summary of objectives, conclusions and implications with respect to OCS oil and gas development 1 II. Introduction -> A. General nature and scope of study 3 B. Specific objectives 3 c. Relevance to problems of petroleum development 3 III. Current state of knowledge 9 Iv. Study area 9 v. Sources, methods and rationale of data collection A. Census 16 B. Phenology of breedirrgacttvities 18 c. Food habits 18 VI. Results A. Murres 19 B. Black-legged Kittiwakes 66 c. Horned Puffins 84 D. Glaucous Gulls 89 E. Pelagic Cormorants 94 F. Tufted Puffins 94 G. Guillemots 96 H. Raptors and Ravens 98 I. Cape Lewis 99 J. Other areas utilized by seabirds 101 K. Other observations 104 840 ii VII and VIII. Discussion and Conclusions 105 Ix. Summary of 4th quarter operations 111 x. Acknowledgements 113 XI. Literature cited 114 841 LIST OF TABLES TABLE PAGE 1. Murre census summary, Cape Thompson. 19 2. Murre census, Colony 1; Cape Thompson, 1977. 20 3. Murre census, Colony 2; Cape Thompson, 1977. 21 4. Murre census, Colony 3; Cape Thompson, 1977, 22 5. Murre census, Colony 4; Cape Thompson, 1977. 23 6. Murre census, Colony 5; Cape Thompson, 1977. 24 7. Score totals, Colonies 1-4. 25 8. Compensation counts of murres; Cape Thompson, 1977. -

HEAVY MINERAL CONCENTRATION in a MARINE SEDIMENT TRANSPORT CONDUIT, BERING STRAIT, ALASKA by James C
Alaska Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys PRELIMINARY INTERPRETIVE REPORT 2016-4 HEAVY MINERAL CONCENTRATION IN A MARINE SEDIMENT TRANSPORT CONDUIT, BERING STRAIT, ALASKA by James C. Barker, John J. Kelley, and Sathy Naidu June 2016 Released by STATE OF ALASKA DEPARTMENT OF NATURAL RESOURCES Division of Geological & Geophysical Surveys 3354 College Rd., Fairbanks, Alaska 99709-3707 Phone: (907) 451-5010 Fax (907) 451-5050 [email protected] www.dggs.alaska.gov $3.00 Contents INTRODUCTION .................................................................................................................................................. 1 REGIONAL SETTING ............................................................................................................................................ 2 MATERIALS AND METHODS ................................................................................................................................ 3 RESULTS .............................................................................................................................................................. 5 Heavy Mineral Deposition in the Bering Strait Area .................................................................................... 5 Heavy Mineral Composition ......................................................................................................................... 8 Mineralogy .................................................................................................................................................. -

The Alaska Eskimos
THEALASKA ESKIMOS A SELECTED, AN NOTATED BIBLIOGRAPHY Arthur E. Hippler and John R. Wood Institute of Social and Economic Research University of Alaska Standard Book Number: 0-88353-022-8 Library of Congress Catalog Card Number: 77-620070 Published by Institute of Social and Economic Research University of Alaska Fairbanks, Alaska 99701 1977 Printed in the United States of America PREFACE This Report is one in a series of selected, annotated bibliographies on Alaska Native groups that is being published by the Institute of Social and Economic Research. It comprises annotated references on Eskimos in Alaska. A forthcoming bibliography in this series will collect and evaluate the existing literature on Southeast Alaska Tlingit and Haida groups. ISER bibliographies are compiled and written by institute members who specialize in ethnographic and social research. They are designed both to support current work at the institute and to provide research tools for others interested in Alaska ethnography. Although not exhaustive, these bibliographies indicate the best references on Alaska Native groups and describe the general nature of the works. Lee Gorsuch Director, ISER December 1977 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS A number of people are always involved in such an undertaking as this. Particularly, we wish to thank Carol Berg, Librarian at the Elmer E. Rasmussen Library, University of Alaska, whose assistance was invaluable in obtaining through interlibrary loans, many of the articles and books annotated in this bibliography. Peggy Raybeck and Ronald Crowe had general responsibility for editing and preparing the manuscript for publication, with editorial and production assistance provided by Susan Woods and Kandy Crowe. The cover photograph was taken from the Henry Boos Collection, Archives and Manuscripts, Elmer E. -

A Botanical Survey of the Goodnews Bay Region, Alaska
A BOTANICAL SURVEY OF THE GOODNEWS BAY REGION, ALASKA Robert Lipkin Alaska Natural Heritage Program ENVIRONMENT AND NATURAL RESOURCES INSTITUTE UNIVERSITY OF ALASKA ANCHORAGE 707 A Street, Anchorage, AK 99501 In cooperation with the U.S. Bureau of Land Management Anchorage District 6881 Abbott Loop Road, Anchorage, AK 99507 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS This report is a continuation of a cooperative relationship begun in 1990 between the Bureau of Land Management (BLM) and the Alaska Natural Heritage Program (AKNHP). We would like to thank Jeff Denton of the Anchorage District, BLM, who was instrumental in initiating this particular project and who has evinced continual interest in the rare plants of the District. Jeff Denton and the Anchorage District provided transportation and all other logistical support of the field work, without which this survey would not have been possible. I would also like to acknowledge and thank the other members of the field team including: Julie Michaelson (AKNHP), Alan Batten (University of Alaska Museum), Virginia Moran (U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Western Alaska Ecological Service), and Debbie Blank of the BLM State Office. Debbie Blank not only participated in the field work, but also in the thankless tasks of specimen sorting and data entry. Alan Batten identified or verified the aquatic collections. Thanks also go to David Murray, Curator Emeritus of the Herbarium of the University of Alaska Museum, for his assistance with identifications of several critical taxa. The collections and literature files at the Herbarium provided invaluable help in completing the plant identifications and in evaluating their significance. June Mcatee of Calista Corporation provided valuable background information on the geology of the region. -

On the Water Exchange Through Bering Strait1
ON THE WATER EXCHANGE THROUGH BERING STRAIT1 L. K. Coachman and K. Aagawd Department of Oceanography, University of Washington, Seattle 98105 ABSTRACT A critique of current observations from Bering Strait through 1960 elucidates the gross features of the flow. There is no substantiating evidence for a net southerly flow ever occurring through Bering Strait into the Bering Sea in summer, although the current may on occasion be southerly near Cape Dezhneva and Cape Prince of Wales. During 5-7 August 1964, the most intensive survey to date of the oceanographic condi- tions and currents was made from the USCGC Northwind. Hydrographic conditions and currents in 1964 were typical of Bering Strait in summer. In the eastern channel of the strait, there was a pycnocline at lo-15 m, which was also a region of velocity shear; the surface water layer speeds were typically 50-100 cm/set, ancl the lower layer speeds less than 50 cm/set. While speeds in the western channel were more uniform, they varied widely with time (20-70 cm/set). The northward transport calculated from the Northwind data was 1.4 x 10’ m’/scc, with about one-half flowing through each channel. At least three types of speed fluctuations may be observed in Bering Strait: 1) short-term irregular fluctuations of lo-15 cm/set, probably related to turbulence; 2) regular fluctua- tions of as much as 50% of the mean speed, occurring at all depths and having a period of 12-13 hr (tidal or inertial); and 3) long-term fluctuations of as much as 1000/o, probably associated with major changes in the wind regime, the atmospheric pressure distribution over the Bering or Chukchi seas, or both. -

Alaska Press
University of Alaska Press Fall 2008 Spring 2009 University of Alaska Press Nonprofit Organization PO Box 756240 U.S. Postage Fairbanks AK 99775-6240 PAID Permit No. 2 Fairbanks, AK FALL 2008 Living With Wildness Bill Sherwonit Bill Sherwonit has added a fine new volume to the literature of place, a literature that may be the most vital and venture- some of any kind being written in America today. Tracing “the intelligence of nature” from the streets of Anchorage to the mountains of Alaska’s Brooks Range, he marvels over chickadees and grizzlies, wood frogs and sandhill cranes, moose and mice and countless other creatures, along with snow and stars and shimmering northern lights. In prose as clear as an unsullied stream, he tells about his search for the Born in Bridgeport, Connecticut, wildness in the depths of mind that answers to the wildness nature writer BILL SHERWONIT in the world. has called Alaska home since —Scott Russell Sanders, author of A Private History of Awe 1982. He worked a dozen years at newspapers, including a Like one of his winter days in Anchorage, Sherwonit’s book is decade at the Anchorage Times. bright and calm. Its gifts are a wild landscape of delight and Sherwonit has contributed essays a lesson in attentiveness. and articles to a wide variety of —Kathleen Dean Moore, author of The Pine Island Paradox newspapers, magazines, journals, and anthologies; his essay “In Bill Sherwonit writes, “I never imagined myself becoming the Company of Bears” (now a a resident of America’s ‘last frontier.’” But in 1974, at age chapter in Living with Wildness) twenty-four, he arrived in Alaska, wide open to the experi- was selected for the Best American ence. -

S Denver Museum of Nature & Science Reports
DENVER MUSEUM OF NATURE & SCIENCE REPORTS DENVER MUSEUM OF NATURE & SCIENCE REPORTS THE FORTUNATE LIFE OF A MUSEUM NATURALIST: ALFRED M. BAILEY BAILEY ALFRED M. NATURALIST: LIFE OF A MUSEUM THE FORTUNATE NUMBER 13, MARCH 10, 2019 WWW.DMNS.ORG/SCIENCE/MUSEUM-PUBLICATIONS Denver Museum of Nature & Science Reports 2001 Colorado Boulevard (Print) ISSN 2374-7730 Denver, CO 80205, U.S.A. Denver Museum of Nature & Science Reports (Online) ISSN 2374-7749 Frank Krell, PhD, Editor and Production VOL. 2 VOL. DENVER MUSEUM OF NATURE & SCIENCE & SCIENCE OF NATURE DENVER MUSEUM Cover photo: Russell W. Hendee and A.M. Bailey in Wainwright, Alaska, 1921. Photographer unknown. DMNS No. IV.BA21-007. The Denver Museum of Nature & Science Reports (ISSN 2374-7730 [print], ISSN 2374-7749 [online]) is an open- access, non peer-reviewed scientifi c journal publishing papers about DMNS research, collections, or other Museum related topics, generally authored or co-authored The Fortunate Life of a Museum Naturalist: by Museum staff or associates. Peer review will only be arranged on request of the authors. REPORTS Alfred M. Bailey The journal is available online at science.dmns.org/ 10, 2019 • NUMBER 13 MARCH Volume 2—Alaska, 1919–1922 museum-publications free of charge. Paper copies are exchanged via the DMNS Library exchange program ([email protected]) or are available for purchase from our print-on-demand publisher Lulu (www.lulu.com). Kristine A. Haglund, Elizabeth H. Clancy DMNS owns the copyright of the works published in the & Katherine B. Gully (Eds) Reports, which are published under the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial license. -

Annotated Checklists of Bryophytes and Lichens Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, U.S.A
Annotated Checklists of Bryophytes and Lichens Cape Prince of Wales, Alaska, U.S.A. by JoAnn W. Flock, Museum Associate, University of Colorado Herbarium Version 1, May 10, 2011 Cape Prince of Wales, from Cape Mountain Photo by Tass Kelso Location of the study area on the tip of the Seward Peninsula on the west coast of Alaska. CONTENTS INTRODUCTION .......................................................................................................................... 2 DESCRIPTION OF THE STUDY AREA ..................................................................................... 3 ANNOTATED CHECKLIST OF BRYOPHYTES ....................................................................... 4 MOSSES ..................................................................................................................................... 4 LIVERWORTS ......................................................................................................................... 14 ANNOTATED CHECKLIST OF LICHENS ............................................................................... 16 REFERENCES TO LICHEN COLLECTIONS AND EXPEDITIONS IN ALASKA- CANADA ................................................................................................................................. 29 ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS .......................................................................................................... 30 INTRODUCTION In June 1978, I had the good fortune to spend two weeks at Cape Prince of Wales on the western tip of Alaska's Seward Peninsula -

Dr. James Taylor White's 1898 Manuscript on Tobacco
1 INTRODUCTION TO “THEY ARE INVETERATE USERS OF TOBACCO”: DR. JAMES TAYLOR WHITE’S 1898 MANUSCRIPT ON TOBACCO USE AND PIPE CONSTRUCTION AMONG ALASKA NATIVES Gary C. Stein 6300 Montgomery Blvd. NE, Albuquerque, NM 87109; [email protected] I met James T. White in 1980, while I was researching in the Alaska and Polar Regions Collections and Archives at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. We instantly became fast friends. He had been dead for 68 years, but he let me pry into his life through his diaries, correspondence, scrapbooks, photographs, and natural history and ethnological collections located in various archives, museums, and cemeteries in Alaska, Washington State, California, and Washington, DC. We are friends still—I’ve even smoked a pipe with him at his grave—and there is more of his life to share. This is just one small part. BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH OF JAMES T. WHITE, MD James Taylor White (Fig. 1) was born on December 13, Bear, participating in the third year of Sheldon Jackson’s 1866, in Port Townsend, Washington Territory. Not project to transport domestic reindeer from Siberia to the many years later, his father, a captain in the United States Teller Reindeer Station on the Seward Peninsula. From Revenue-Cutter Service (a predecessor of the U.S. Coast 1900 to 1902, White served on the Revenue Steamer Guard), moved his family to San Francisco, where White Nunivak, patrolling the Yukon River in the wake of the attended high school and, in 1888, graduated from the Klondike and Nome gold rushes. While on the Nunivak, University of California Medical College (University of he treated Natives who were victims of the combined flu California 1889:41). -

Orders Affecting Public Lands in Alaska
Orders Affecting Public Lands In Alaska Reference Date Order No Serial No Action Acres X‐Reference Numbers Fed Reg/Stat 1A 12/1/1867 Letter Land Reserved for Government Purposes at Kodiak by Ref: 1C, 9 Order of General Jeff Davis (Custom House Site) 1B 12/1/1867 General Orders All islands in Harbor of Sitka; Reserve in City (Sitka), Ref: 2, 9 No 6 Hospital Reserve (Sitka), Set Aside for Government republished as Purposes by General Orders No. 6, Headquarters General Orders Military District of Alaska (New Archangel), Alaska No 8 Territory NOTE: Re‐published as General Orders No. 8, Headquarters Department of the Columbia, Portland, Oregon on 3‐18‐1875 1C 04/15/1868 Special Orders Establishment of Military Reservation ‐ Fort Kodiak Ref: 1C‐1, 1D No 59 1C‐1 06/6/1868 Orders No 1 Appointment of Post Adjutant and Post Treasurer of Ref: 1C Fort Kodiak 1C‐2 10/15/1897 Special Orders Regarding Disposition of Various Military Posts and No 99 Personnel in Alaska, 1D 04/12/1874 General Orders Customhouse Site at Fort Kodiak Transferred to Ref: 1C No 13 Treasure Dept. by General Orders No. 13, Headquarters Department of the Columbia 1E 07/5/1884 ACT To Provide for Disposal of Abandoned & Useless 23Stat.103 Military Reservations (AMR) 2 06/21/1890 EO School Site (Juneau), Block 23 except Lots 5 & 6 as 0.80 Ref: 44A shown on TS Plat by Hanus. 200' x 200' Douglas School Site (Douglas City) 0.92 Ref: 1436 Coaling Station (Juneau Island) Ref: 900 Fort Wrangell Government Buildings (USS 125) (see 4.00 Ref: 3017 AA‐50617) Wharf (Sitka) (USS 1276, shown on USS 1473) (QCD 0.16 from U.S.