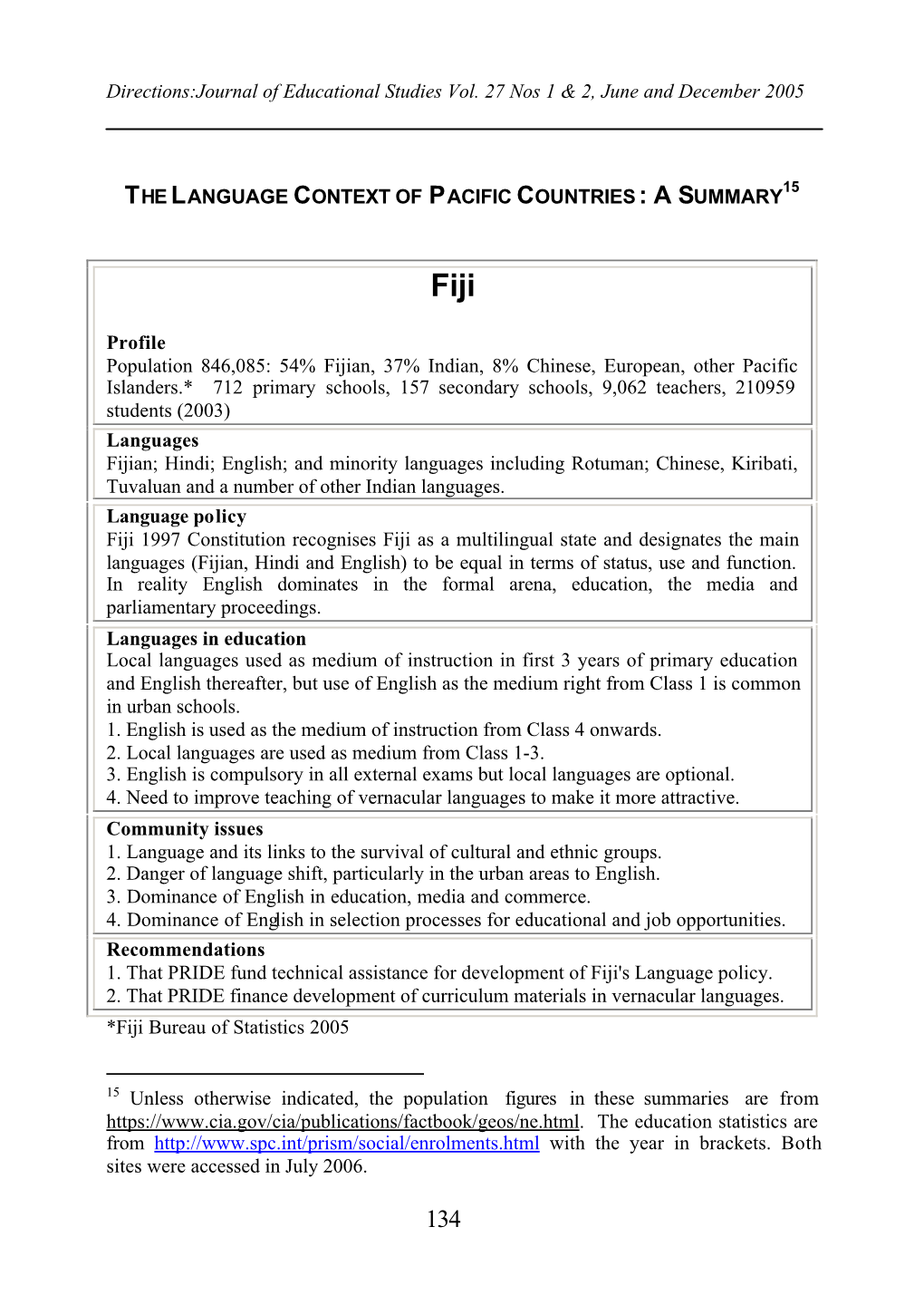
The Language Context of Pacific Countries : a Summary
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Palauan Language Report Carole Tiberius
Surrey Database of Agreement – Palauan Carole Tiberius Palauan Language Report Carole Tiberius 1 Introduction Palauan is a member of the Austronesian language family spoken in Palau. It has no close relatives within the Austronesian family. Palauan has about 17,000 speakers of whom about 80% live in the Republic of Palau. There is little dialectal variation (Georgopoulos 1991:21). This report draws heavily on Josephs’ (1975, 1997a, 1997b) Palauan grammar books. We are very grateful to him for his help and specialist advice. 2 Grammatical categories 2.1 T he Palauan words er, el, and a 2.1.1 The analysis of er Palauan has two words er (which are homonyms). Er can be a specifying word (indicated by SPEC in the glosses) or a relational word (indicated by REL in the glosses). The major function of the specifying word er is to distinguish specific objects from non-specific (general) ones. It marks a specific object noun phrase, but only when the verb is in the imperfective. For instance, (1a) A ngelek -ek a medakt a derumk PM child-1SG.POSS PM be.afraid PM thunder ‘My child is afraid of thunder.’ (1b) A ngelek -ek a medakt er a derumk PM child-1SG.POSS PM be.afraid SPEC PM thunder ‘My child is afraid of the thunder.’ (Josephs 1997a:74) As such, the presence of the specifying word er usually indicates a specific statement (as opposed to a general statement). In addition, er is sometimes used to distinguish between singular and plural with nonhuman object nouns, the presence of er marking the singular object as in the following example (Josephs 1997a:77): (2a) Ak ousbech er a ml-im el mo 1SG need SPEC PM car-2SG.POSS LINK go er a ocheraol SPEC PM money-raising.party ‘I need your car to go to the money-raising party.’ (2b) Ak ousbech a ml-im el mo 1.SG need PM car-2SG.POSS LINK go er a ocheraol SPEC PM money-raising.party ‘I need your cars to go to the money-raising party.’ 1 Surrey Database of Agreement – Palauan Carole Tiberius The relational word er, on the other hand, expresses certain types of relational phrases. -

Running Head: COFA PARENTS and EARLY CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT 1
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by ScholarSpace at University of Hawai'i at Manoa Running Head: COFA PARENTS AND EARLY CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT 1 CHUUKESE AND MARSHALLESE PARENT PERSPECTIVES OF EARLY CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE GRADUATE DIVISION OF THE UNIVERSITY OF HAWAI‘I AT MĀNOA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF EDUCATION IN EDUCATIONAL PSYCHOLOGY March 2018 By Victoria C. Timmerman Thesis Committee: Katherine T. Ratliffe, Chairperson Lois A. Yamauchi E. Brook Chapman de Sousa Keywords: Micronesia, Parents, Developmental Screening, Early Childhood Development, Early Childhood Milestones, Cultural Practices COFA PARENTS AND EARLY CHILDHOOD DEVELOPMENT 2 Abstract Recently there has been a significant increase in the number of COFA citizens emigrating to the US. Reasons for emigration include seeking employment and education opportunities, and improved healthcare. To advocate for early childhood health and well-being while optimizing cultural sensitivity, it is important to understand parenting perspectives of COFA citizens. Twenty adults (13 women, 7 men) from Chuuk and the Marshall Islands participated in five focus groups to discuss how parents care for and raise children between birth and five years old. Strategies emphasized by participants were maintaining nutrition, using local medicines, and observing children’s growth. Implications include how healthcare providers who work with Chuukese and Marshallese parents can link conversations about development with nutrition, and that these findings can help inform healthcare providers about local medicine practices. Additionally, educators can use these findings to further their understanding of the cultures and family backgrounds of Chuukese and Marshallese students. -

Practical Marshallese
Practical Marshallese Peter Rudiak-Gould 1 Dedication To the people of Ujae Atoll for teaching me their language Gan ri-Ujae ro kcn aer kar katakin ec kajin eo aer Contact the author Please email the author at [email protected] with any questions or comments. Copyright Statement This book was originally written for the WorldTeach Marshall islands program for use by its volunteers. It can be freely distributed to anyone in any form. However, it is also © Peter Rudiak-Gould 2004.and thus cannot be sold or used for financial gain. 2 Table of Contents Introduction 5 Lessons 6 Lesson 1: The Letters and Sounds of Marshallese 6 Lesson 2: Hello, How are you, Thank you (Beginning Phrases) 9 Lesson 3: One, two, three, four (Numbers, time, age, and price) 11 Lesson 4: Monday, Tuesday, January, February (Words from English) 13 Lesson 5: I am happy, you are happy (Subject pronouns) 15 Lesson 6: I know, you know (Verbs that work like adjectives) 17 Lesson 7: I am running, you are running (The present tense) 19 Lesson 8: I ate, you ate (The past tense) 21 Lesson 9: I will run, you will run (The future tense) 23 Lesson 10: I am about to go, you are about to go (Near future tense) 25 Lesson 11: I am in Majuro, you are in Ebeye (Location) 27 Lesson 12: Me, you, him, her (Object pronouns) 29 Lesson 13: Me, you, him, her (again?) (The emphatic pronouns) 31 Lesson 14: I am not playing, you are not playing (Negatives) 33 Lesson 15: Wrapping up pronouns and tenses 35 Lesson 16: Are you eating? Are you happy? (Yes/No questions) 37 Lesson 17: Do you know?, Yes -

Maori & Pasifika Infants and Toddlers
Tangata Pasifika: Sustaining cultural knowledge and language competency for Pacific peoples. Presentation at the Victoria University Autumn Research Seminar, May 2018. Ali Glasgow Faculty of Education Language, culture, identity • A leai se gagana, ona leai lea o sa ta aganu’u, a leai la ta aganu’u ona po lea o le nu’u (Samoan proverb) • If there is no language, then there is no culture, • If there is no culture, then all of the village will be in darkness Presentation outline • My background • Pacific context • Aoteroa New Zealand context – culture, language • Research findings – Vuw Summer Scholarship (2015), TLRI ( Teaching and Learning Research Initiative, 2017). Ali – Kuki Airani – Tongareva Atoll Pacific perspectives • Pacific region located historically, contextually and geographically within Oceania, more particularly in the region of the Southern Pacific referred to as the Polynesian triangle (Ritchie & Ritchie, 1970) • ‘Our sea of islands ( Hau’ofa, 1993) Reclaiming & Reconceptualising Pacific Education • Pacific Education (currently) prioritises the voice and worldview of the outside which amputates our capacity for human agency. Within the Pacific the bulk of what we teach and learn in our schools and at our universities and colleges in the Pacific is what has been conceptualised and developed in and for the Western world (Koya-Vakauta,2016). • The indigenous peoples of the Pacific need to create their own pedagogy... rooted in Pacific values, assumptions, processes and practices ( Glasgow, 2010; Mara, Foliaki & Coxon, 1994; Tangatapoto,1984 & Taufe’ulungake, 2001). Aspiration Statement ( MOE, 2017, p.5) • Competent and confident learners and communicators, healthy in mind, body and spirit, secure in their sense of belonging and in the knowledge that they make a valued contribution to society. -

Laulōtaha; Tongan Perspectives of 'Quality' in Early Childhood Education Dorothy Lorraine Pau'uvale a Thesis Submitted To
Laulōtaha; Tongan Perspectives of ‘Quality’ in Early Childhood Education Dorothy Lorraine Pau’uvale A thesis submitted to Auckland University of Technology in partial fulfillment of the requirements for a degree of Master of Education (MEd) 2011 School of Education i Table of Contents List of Tables ..................................................................................................................... vi Attestation of Authorship .................................................................................................. vii Fakamālō/ Acknowledgements ........................................................................................ viii Ethical Approval .............................................................................................................. xiii Abstract ............................................................................................................................... 1 Chapter 1: Talateu/ Introduction ......................................................................................... 2 1.1 Introduction .......................................................................................................... 2 1.2 Purpose of the study .................................................................................................. 2 1.3 Context of the study .................................................................................................. 3 1.4 Importance of the study ........................................................................................... -

Local Study Into Local Compost Production
Local study into local compost production Live & Learn Environmental Education Tuvalu | 2020 Tuvalu Food Futures is supported by the Australian Government and Implemented by Live & Learn Tuvalu Live & Learn Environmental Education – Tuvalu Ekalesia Kelisiano Tuvalu (EKT) Women’s Centre Senala, Funafuti Tuvalu T +688 20 206 E. [email protected] Country Manager: Teuleala Manuella Copyright Live & Learn Environmental Education Author: Alex McClean, Arid Edge Environmental Services (a trading name of the Arid Lands Environment Centre Inc). Citation: McClean, A. (2020) Tuvalu Compost Feasibility Study, Live & Learn Environmental Education. Disclaimer This publication has been funded by the Australian Government through the Department of Foreign Affairs and Trade. The views expressed in this publication are the author's alone and are not necessarily the views of the Australian Government. Table of Contents 1. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 4 5.3. Current compost supply and production 24 5.3.1. Summary of compost producers 24 2. INTRODUCTION 7 5.3.2. Limits and barriers to increased on supply and quality 29 3. METHODOLOGY 8 5.3.3. Opportunities for improved supply (quality, quantity, 3.1. Approach 8 consistency) of compost products. 30 3.2. Data collection and analysis 9 3.3. Compost specific terminology 9 6. RECOMMENDATIONS 33 6.1. Integrated National 4. CONTEXT 11 Level Compost Strategy 33 4.1. Country context 11 6.2. Upgrade the DoW Compost Production 4.1.1. General Context 11 Site – Funafuti 34 4.1.2. Environmental and 6.3. Outer Island Local Government Level Climate Change Context 12 Production 37 4.1.3. National Food Security Strategy 13 6.4. -

Celebration of the Niuean Language and Culture Ko E Tau Fakafiafiaaga
Celebration of the #pacificstars Niuean Language and Culture Ko e tau Fakafiafiaaga he Vagahau Niue mo e tau Aga Fakamotu Facts on Niue | Folafolaaga hagaaoia Population | Puke tagata ke he motu ko Niue In 2013 Niue peoples were the fourth largest Pacific • Niue is one of the world's largest coral islands. ethnic group in New Zealand making up 8.1% or 23,883 • Niue (pronounced “New-e (‘e’ as in ‘end’ – which means of New Zealand’s Pacific peoples’ population. 'behold the coconut') may be the world’s smallest The most common region this group lived in was the independent nation. Auckland Region (77.7 percent or 18,555 people), followed • The island is commonly referred to as "The Rock", by the Wellington Region (6.6 percent or 1,575 people), a reference to Niue being one of the biggest raised and the Waikato Region (4.3 percent or 1,038 people). coral islands in the world. The median age was 20.4 years. • The capital of Niuē is the village of Alofi. • Niueans are citizens of New Zealand. 78.9 percent (18,465 people) were born in New Zealand. • Niue is an elevated coral atoll with fringing coral reefs encircling steep limestone cliffs. It has a landmass of 259km and its highest point is about 60 metres In 2013 Niue peoples made up above sea level. • Niue lies 2400 km northeast of New Zealand 23,883 between Tonga, Samoa and the Cook Islands. of New Zealand's Pacific peoples' population History | Tau Tala Tu Fakaholo Polynesians from Samoa settled Niue around 900 AD. -

Gender & Interaction in a Globalizing World: Negotiating the Gendered
Chapter 13 Gender and interaction in a globalizing world: Negotiating the gendered self in Tonga* Niko Besnier 1. Gender and language in microscopic and macroscopic perspectives One of the more important developments in our understanding of the rela- tionship between language and gender in the last couple of decades is the recognition that the gendering of language is semiotically complex. Indeed, linguistic forms and practices do not define “women’s language” and “men’s language”, as earlier researchers argued (e.g., Lakoff 1975), but articulate with a host of social categories and processes that surround gen- der and help construct it. The clearest articulation of this position is Ochs’ (1992) demonstration that gendered linguistic practices are both indexical and indirect. Indexicality captures the insight that features of language (phonological, syntactic, discursive, etc.) “point to”, or suggest, gendered identities, and do not refer to gender in an unequivocal fashion, as linguistic symbols would. In this respect, the relationship between language and gen- der is no different from the relationship between language and any other aspect of socio-cultural identity, as we have known since the early days of sociolinguistics (Labov 1966a). However, the indexical linking of language and gender presents another layer of complexity: linguistic resources are semiotically connected to gender through the mediation of other aspects of the socio-cultural world. For example, features of language and interaction invoke social roles (e.g., mother, CEO, construction work), demeanors (e.g., politeness, authority, or the lack thereof), and activities (e.g., forms of work and play), all of which are in turn indexically associated with gender (see Figure 1). -

Samoan Research Methodology
VolumePacific-Asian 23 | Number Education 21 | 2011 Pacific-Asian Education The Journal of the Pacific Circle Consortium for Education Volume 23, Number 2, 2011 SPECIAL ISSUE Inside (and around) the Pacific Circle: Educational Places, Spaces and Relationships SPECIAL ISSUE EDITORS Eve Coxon The University of Auckland, New Zealand Airini The University of Auckland, New Zealand SPECIAL ISSUE EDITORIAL COMMITTEE Elizabeth Rata The University of Auckland, New Zealand Diane Mara The University of Auckland, New Zealand Carol Mutch The University of Auckland, New Zealand EDITOR Elizabeth Rata, School of Critical Studies in Education, Faculty of Education, The University of Auckland, New Zealand. Email: [email protected] EXECUTIVE EDITORS Airini, The University of Auckland, New Zealand Alexis Siteine, The University of Auckland, New Zealand CONSULTING EDITOR Michael Young, Institute of Education, University of London EDITORIAL BOARD Kerry Kennedy, The Hong Kong Institute of Education, Hong Kong Meesook Kim, Korean Educational Development Institute, South Korea Carol Mutch, Education Review Office, New Zealand Gerald Fry, University of Minnesota, USA Christine Halse, University of Western Sydney, Australia Gary McLean, Texas A & M University, USA Leesa Wheelahan, University of Melbourne, Australia Rob Strathdee, Victoria University of Wellington, New Zealand Xiaoyu Chen, Peking University, P. R. China Saya Shiraishi, The University of Tokyo, Japan Richard Tinning, University of Queensland, Australia ISSN 1019-8725 Pacific Circle Consortium for Education Publication design and layout: Halcyon Design Ltd, www.halcyondesign.co.nz Published by Pacific Circle Consortium for Education http://pacificcircleconsortium.org/PAEJournal.html Pacific-Asian Education Volume 23, Number 2, 2011 CONTENTS Editorial Eve Coxon 5 Articles Tala Mai Fafo: (Re)Learning from the voices of Pacific women 11 Tanya Wendt Samu Professional development in the Cook Islands: Confronting and challenging 23 Cook Islands early childhood teachers’ understandings of play. -

Threatened Endemic Plants of Palau
THREA TENED ENDEMIC PLANTS OF PALAU BIODI VERSITY CONSERVATION LESSONS LEARNED TECHNICAL SERIES 19 BIODIVERSITY CONSERVATION LESSONS LEARNED TECHNICAL SERIES 19 Threatened Endemic Plants of Palau Biodiversity Conservation Lessons Learned Technical Series is published by: Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund (CEPF) and Conservation International Pacific Islands Program (CI-Pacific) PO Box 2035, Apia, Samoa T: + 685 21593 E: [email protected] W: www.conservation.org The Critical Ecosystem Partnership Fund is a joint initiative of l’Agence Française de Développement, Conservation International, the Global Environment Facility, the Government of Japan, the MacArthur Foundation and the World Bank. A fundamental goal is to ensure civil society is engaged in biodiversity conservation. Conservation International Pacific Islands Program. 2013. Biodiversity Conservation Lessons Learned Technical Series 19: Threatened Endemic Plants of Palau. Conservation International, Apia, Samoa Authors: Craig Costion, James Cook University, Australia Design/Production: Joanne Aitken, The Little Design Company, www.thelittledesigncompany.com Photo credits: Craig Costion (unless cited otherwise) Cover photograph: Parkia flowers. © Craig Costion Series Editors: Leilani Duffy, Conservation International Pacific Islands Program Conservation International is a private, non-profit organization exempt from federal income tax under section 501c(3) of the Internal Revenue Code. OUR MISSION Building upon a strong foundation of science, partnership and field demonstration, -

Austronesian Diaspora a New Perspective
AUSTRONESIAN DIASPORA A NEW PERSPECTIVE Proceedings the International Symposium on Austronesian Diaspora AUSTRONESIAN DIASPORA A NEW PERSPECTIVE Proceedings the International Symposium on Austronesian Diaspora PERSPECTIVE 978-602-386-202-3 Gadjah Mada University Press Jl. Grafika No. 1 Bulaksumur Yogyakarta 55281 Telp./Fax.: (0274) 561037 [email protected] | ugmpress.ugm.ac.id Austronesian Diaspora PREFACE OF PUBLISHER This book is a proceeding from a number of papers presented in The International Symposium on Austronesian Diaspora on 18th to 23rd July 2016 at Nusa Dua, Bali, which was held by The National Research Centre of Archaeology in cooperation with The Directorate of Cultural Heritage and Museums. The symposium is the second event with regard to the Austronesian studies since the first symposium held eleven years ago by the Indonesian Institute of Sciences in cooperation with the International Centre for Prehistoric and Austronesia Study (ICPAS) in Solo on 28th June to 1st July 2005 with a theme of “the Dispersal of the Austronesian and the Ethno-geneses of People in the Indonesia Archipelago’’ that was attended by experts from eleven countries. The studies on Austronesia are very interesting to discuss because Austronesia is a language family, which covers about 1200 languages spoken by populations that inhabit more than half the globe, from Madagascar in the west to Easter Island (Pacific Area) in the east and from Taiwan-Micronesia in the north to New Zealand in the south. Austronesia is a language family, which dispersed before the Western colonization in many places in the world. The Austronesian dispersal in very vast islands area is a huge phenomenon in the history of humankind. -

A Beginning Reading Program in Marshallese
Central Washington University ScholarWorks@CWU All Master's Theses Master's Theses 1969 A Beginning Reading Program in Marshallese Charles E. Eko Central Washington University Follow this and additional works at: https://digitalcommons.cwu.edu/etd Part of the Curriculum and Instruction Commons, Educational Methods Commons, and the Teacher Education and Professional Development Commons Recommended Citation Eko, Charles E., "A Beginning Reading Program in Marshallese" (1969). All Master's Theses. 1088. https://digitalcommons.cwu.edu/etd/1088 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Master's Theses at ScholarWorks@CWU. It has been accepted for inclusion in All Master's Theses by an authorized administrator of ScholarWorks@CWU. For more information, please contact [email protected]. A BEGINNING READING PROGRAM IN MARSHALLESE A Thesis / Presented to the Graduate Faculty Central Washington State College In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Education by Charles E. Eko July, 1969 uo1.8U'!lf" A\ 'lbnqsua1ra ;)8~no 1 •qlllS UC!}Jill''.f'"ll :t/. J~~!{UJJ If.~"'-~}~,'. q?.1 No11~:n10~ 7V1::i.1c1s 'F,;? I'€" ·1 L l.._s ct7 APPROVED FOR THE GRADUATE FACULTY ________________________________ John E. Davis, COMMITTEE CHAIRMAN _________________________________ Azella Taylor _________________________________ Doris Jakubek Nan Rikaki Ro Im Rijikul Ro Ilo Ailin In Majel Kin Menin Joij Im Jiban Ko Ami · Kaj oj o Nan Na Kom Emol. TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER PAGE I. INTRODUCTION • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 1 STATEMENT OF PROBLEM • • • • • • • • • • • • 2 NEED FOR THE STUDY • • • • • • • • • • • • • 2 LIMITATION OF THE STUDY • • • • • • • • • • 5 No Standard Orthography • • • • • • • • • 6 Extremely Limited Materials in Marshallese • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 6 Untrained Teachers • • • • • • • • • • • • 6 Geography • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 7 Culture • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • • 8 II.