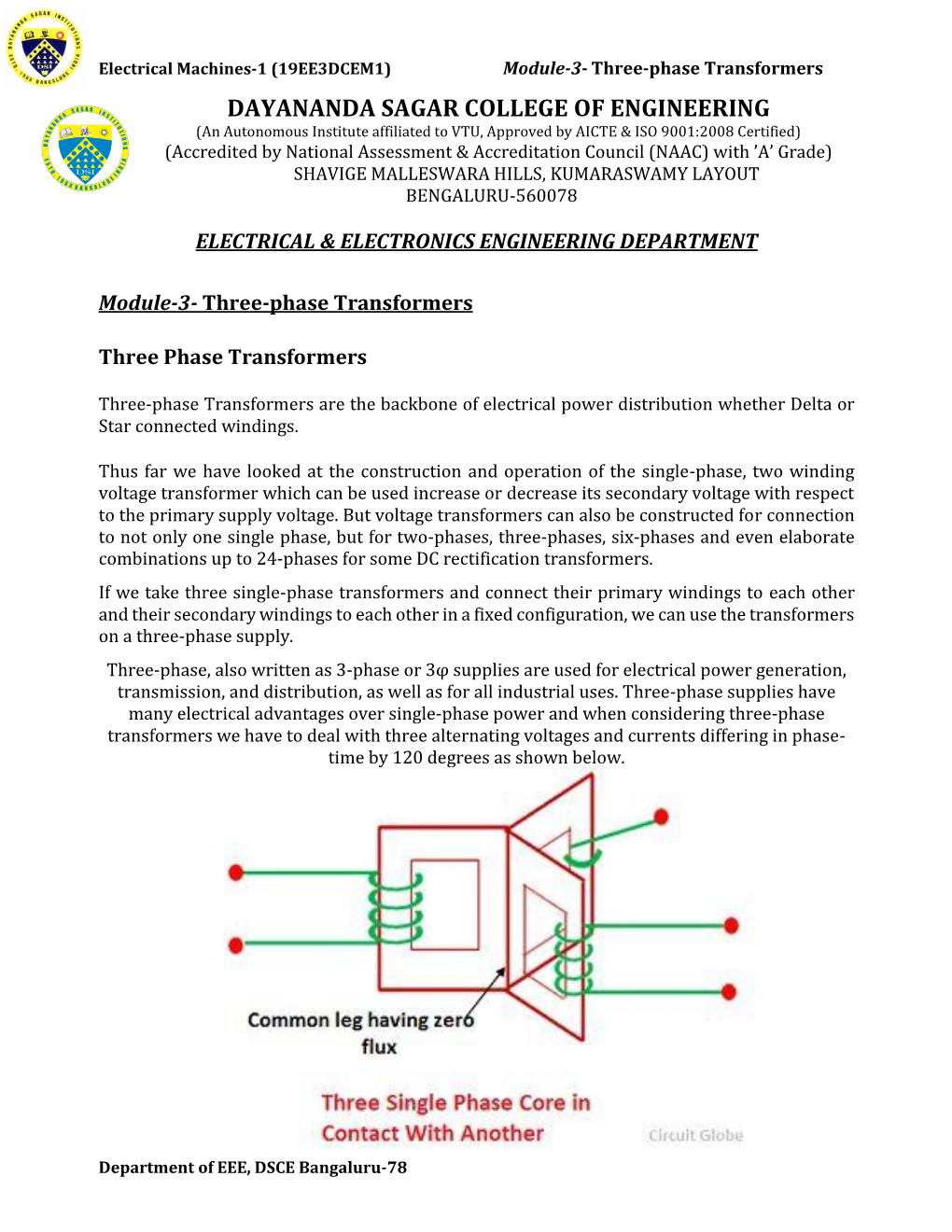
Module-3-Three-Phase Transformers
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

IEEE/PES Transformers Committee Fall 2017 Meeting Minutes
Transformers Committee Chair: Stephen Antosz Vice Chair: Sue McNelly Secretary: Bruce Forsyth Treasurer: Greg Anderson Awards Chair/Past Chair: Don Platts Standards Coordinator: Jim Graham IEEE/PES Transformers Committee Fall 2017 Meeting Minutes Louisville, KY October 30 – November 2, 2017 Unapproved (These minutes are on the agenda to be approved at the next meeting in Spring 2018) TABLE OF CONTENTS GENERAL ADMINISTRATIVE ITEMS 1.0 Agenda 2.0 Attendance OPENING SESSION – MONDAY OCTOBER 30, 2017 3.0 Approval of Agenda and Previous Minutes – Stephen Antosz 4.0 Chair’s Remarks & Report – Stephen Antosz 5.0 Vice Chair’s Report – Susan McNelly 6.0 Secretary’s Report – Bruce Forsyth 7.0 Treasurer’s Report – Gregory Anderson 8.0 Awards Report – Don Platts 9.0 Administrative SC Meeting Report – Stephen Antosz 10.0 Standards Report – Jim Graham 11.0 Liaison Reports 11.1. CIGRE – Raj Ahuja 11.2. IEC TC14 – Phil Hopkinson 11.3. Standards Coordinating Committee, SCC No. 18 (NFPA/NEC) – David Brender 11.4. Standards Coordinating Committee, SCC No. 4 (Electrical Insulation) – Paulette Payne Powell 12.0 Hot Topics for the Upcoming – Subcommittee Chairs 13.0 Opening Session Adjournment CLOSING SESSION – THURSDAY NOVEMBER 2, 2017 14.0 Chair’s Remarks and Announcements – Stephen Antosz 15.0 Meetings Planning SC Minutes & Report – Gregory Anderson 16.0 Reports from Technical Subcommittees (decisions made during the week) 17.0 Report from Standards Subcommittee (issues from the week) 18.0 New Business 19.0 Closing Session Adjournment APPENDIXES – ADDITIONAL DOCUMENTATION Appendix 1 – Meeting Schedule Appendix 2 – Semi-Annual Standards Report Appendix 3 – IEC TC14 Liaison Report Appendix 4 – CIGRE Report Page 2 of 55 ANNEXES – UNAPPROVED MINUTES OF TECHNICAL SUBCOMMITTEES NOTE: The Annexes included in these minutes are unapproved by the respective subcommittees and are accurate as of the date the Transformers Committee meeting minutes were published. -

IEEE Grounding Transformers
Grounding Transformers John S. Levine, P.E. Levine Lectronics and Lectric, Inc. [email protected] 1 • It is used to provide a ground path on either an ungrounded Wye or a Delta connected system • The relatively low impedance path to ground maintains the system neutral at ground potential • On Ungrounded systems you can have overvoltages of 6 to 8 times normal with arcing faults Arcing Ground Faults Intermittent or Re-strike •Plot of transient over-voltage for an arcing ground fault Arcing Ground Faults Intermittent or Re-strike •Intermittent ground fault: A re-striking ground fault can create a high frequency oscillator (RLC circuit), independent of L and C values, causing high transient over- voltages. – i.e. re-striking due to ac voltage waveform or loose wire caused by vibration 480V Delta Source 3Ø Load Rfe V V Cb Cb S fa THE HIGH RESISTANCE GROUNDED POWER SYSTEM CONTROL OF TRANSIENT OVERVOLTAGE • It supports the voltage on a faulted phase – If a single line-to-ground fault occurs on an ungrounded or isolated system, no return path exists and no current flows – The system will continue to operate but the other two un- faulted lines will rise in in voltage by the square root of 3, possibly overstressing the transformer insulation, and other components, by 173% UNGROUNDED SYSTEM NORMAL CONDITIONS UNGROUNDED SYSTEM GROUND FAULT ON PHASE A • Provides a metering point to measure faults A typical example is a Wind Farm. They utilize grounding transformers for fault protection on ungrounded lines When a ground fault occurs on a collector cable causes the substation circuit breaker to open, the wind turbine string becomes isolated Turbines do not always detect the fault and the generators continue to energize the cable. -

Neutral Current Problem and Mitigation Techniques: an Overview
IOSR Journal of Engineering (IOSR JEN) www.iosrjen.org ISSN (e): 2250-3021, ISSN (p): 2278-8719 PP 62-68 Neutral Current Problem and Mitigation Techniques: An Overview Karuna Nikum1, Rakesh Saxena2, Abhay Wagh3 1(Department of Electrical Engineering, ACE, Mumbai University, India) 2(SGSITS, RGPV University, Indore, India) 3(Directorate of Technical Education, Mumbai, India ) Abstract: In this paper, an attempt to overview a various number of mitigation techniques and power quality problems associated with neutral current for commercial loads are discussed. The load connected to three phase four wire system are generally single-phase loads and generate triplen harmonic currents due to unbalancing in phases at neutral. There are various neutral current mitigation techniques including active and passive has been discussed. The existing approach and a framework of references for researchers in this field are provided. I. ‘Introduction The ample use of electronic devices in all types of loads i.e. residential, commercial and industrial is adversely affecting the power quality (PQ) of the system[1]-[10]. When three-phase four-wire distribution (3P4W) systems are used to supply single-phase low voltage loads such as lighting ballasts (electronic type), light emitting diodes (LED), compact fluorescent lighting (CFL), personal computers, monitors, laser printers, variable speed drives, adjustable speeds drives (ASD) in air conditioner, UPS systems and other electronic equipment. These loads produces harmonics especially 3rd harmonics in the neutral. In general, the distribution systems designed for linear load type and no longer suitable for delivering large number of non-linear and harmonic generating loads [11]-[15]. The concern PQ issues are high reactive power requirement, harmonic current, low power factor and increased losses[16], [17]. -

Phase Shifting with Transformers – New Approaches for Harmonic Mitigation & Power Factor Correction
Phase Shifting with Transformers – New Approaches for Harmonic Mitigation & Power Factor Correction Abstract Improved designs for electrically powered equipment such as solid-state motor drives, electronic lighting ballasts, DC power supplies and computers offer the promise of dramatically improving energy efficiency. These new technologies can have power quality side effects, which must be considered along with the energy benefits. Current demand characteristics, harmonic production and power susceptibility requirements create new issues of compatibility with other devices in the electrical environment. Contrary to this new energy saving product design, the dry type transformer efficiency in the last 20 years has been decreasing to meet market price competition. Under these modern loads, the standard distribution transformer became much less efficient and in some cases obsolete. In view of the increasing cost of energy we are seeing improvements in the design of distribution transformers. C802.2 and TP1 became legislation in the U.S. on January 1st, 2007 and became law in Canada on January 1st, 2005. We will review the reasons and the new style of transformers being designed for these applications. The positive side is that the new energy saving designs are converging with the power quality needs for the new electronic rich environments of our modern facilities. Introduction At the turn of the century, electricity invaded homes all over North America. The power grid that evolved from the beginning has remained essentially the same to this day. Important power transmission over long distances has led to the use of alternating current technology to simplify power transfer. This has served us well for the needs of namely light bulbs and motors. -

MO-201 Electric Power Distribution Systems
______________________________________________________________________ http://waterheatertimer.org/How-to-wire-3-phase-electric.html http://waterheatertimer.org/What-is-3-phase-electric.html Naval Facilities Engineering Command 200 Stovall Street Alexandria, Virginia 22332-2300 Electric Power Distribution Systems Operations NAVFAC MO-201 April 1990 SN 0525-LP-320-1900 FOREWORD This manual on electric power distribution systems is one of a series developed to aid utility supervisory personnel at shore establishments in the performance of their duties. It includes information obtained from extensive research of current literature on the subject and preferred practices based on practical experience. The principles and procedures described are in accordance with national professional society, association, and institute codes. Additional information concerning procedures, suggestions, recommendations or modifications that will improve this manual are invited and should be submitted through appropriate channels to the Commander, Naval Facilities Engineering Command, (Attention: Code 165), 200 Stovall Street, Alexandria, VA 22332-2300. This publication has been reviewed and approved in accordance with the Secretary of the Navy Instruction 5600.16A and is certified as an official publication of the Naval Facilities Engineering Command. It cancels and supersedes Operation of Electric Power Distribution Systems, NAVFAC MO-201, November 1963, in its entirety. D. B. CAMPBELL Assistant Commander for Public Works Centers and Departments ABSTRACT Application principles and procedures for the operation of electric power distribution systems and associated major apparatus are presented. The contents include principles of power systems, cabling systems, electrical equipment, power system protection and coordination, instruments and meters, operational procedures, and electrical utilization systems. i CONTENTS PAGE CHAPTER 1 PRINCIPLES OF POWER SYSTEMS 1-1 1.1 Typical Power Network........................................................................... -

Applications of Zigzag Transformers to Reduce Harmonics in Distribution System
Applications of Zigzag Transformers to Reduce Harmonics in Distribution System Abstract. This paper presents a scheme of the zigzag transformer for system neutral [3]. If the neutral is grounded, the connection is reducing the neutral current and investigates by means of simulations referred to as a grounded-neutral connection. If the primary is the performance of a zigzag transformer on a three-phase diode not an effectively grounded system, the permissible bridge rectifier in order to reduce line current harmonics. This connections are delta-star grounded, delta-zigzag grounded application is carried out in a 23 kV-220/127 distribution system. The first scheme is based on the installation of a zigzag transformer and star-zigzag grounded. The star grounded- star grounded between the transformer-secondary lines and the neutral of the same should not be used except on 4-wire effectively grounded transformer. For the second scheme the zigzag transformer is primaries. installed between the transformer secondary lines and the diode bridge. For the first scheme, the research considers two connections c d m g for the transformer, delta-star grounded, and star-star grounded. Both schemes are very effective reducing the current harmonics. In the last 3V part we analyze the third harmonic in the delta winding of transformers. h n b Keywords: harmonics, neutral conductor, zigzag transformer, V distribution system, three-phase diode bridge rectifier 3 V 1. Introduction. The zigzag transformer has been used some f years ago for creating a neutral, thereby converting a three- p wire distribution system to a four-wire system [1]. -

Construction and Maintenance of High Voltage Power Transformers
STAMATIOS VLACHOS CONSTRUCTION AND MAINTENANCE OF HIGH VOLTAGE POWER TRANSFORMERS CENTRAL OSTROBOTHNIA UNIVERSITY OF APPLIED SCIENCES Abstract This paper is produced by student Stamatios Vlachos and professor Jari Halme. The main purpose of this research is to gather in one paper information about construction and maintenance of high voltage power transformers. There are included informations about condition monitoring techniques, maintenance techniques and also information about the degradation processes that happened in oil paper insulated transformers. TABLE OF CONTENTS CHAPTER 1 Introduction in power transformers 1.1 What is a transformer? 1.2 Historical models of transformers 1.3 Basic principles 1.4 Energy losses 1.5 Types 1.6 Applications CHAPTER 2 Construction and design of power transformers 2.1 Construction 2.1.1 Cores 2.1.2 Windings 2.1.3 Coolant 2.2 Design and cooling methods 2.3 Tappings and tapchangers 2.4 Transformer tanks CHAPTER 3 Degradation processes in oil-paper insulated transformers 3.1 Insulation 3.2 Transformer oils 3.3 Chemical stability 3.4 Theory of gas evolution 3.5 Origin of furanic compounds in thermal degradation of cellulosic insulating paper CHAPTER 4 Condition monitoring techniques 4.1 On-line monitoring of liquid-immersed transformers 4.2 Direct benefits 4.3 Strategic benefits 4.4 On-line monitoring systems 4.5 Diagnostics techniques for assessing insulation condition in aged transformers CHAPTER 5 Maintenance and testing of power transformers 5.1 Test procedures 5.2 Vacuum oil filling 5.3 Maintenance of spare transformers 5.4 Preventative maintenance versus predictive maintenance 5.5 Factory tests 5.6 Ratio test 5.7 Other factory tests 5.8 Field tests 1. -

Fundamentals of Electric Motors and Transformers
Short Course on Energy Efficiency ISBN : 984-32-1803-6 15 Fundamentals of Electric Motors and Transformers Rajib Mikail Lecturer Department of Electrical and Electronic Engineering Bangladesh University of Engineering and Technology Dhaka e-mail: [email protected] Introduction Motors and transformers are the key driving force for industrial and residential appliances. We can’t even imagine an industry without motors and transformers. In industry all types of linear or rotational force, movement, torque, etc are applied by motors. Industries are getting automated day by day, hence the use of motors are increasing with the same pace. The power supply to any medium or large scale industry comes through transformer as the utilities prefer to supply at higher grid voltage. Maximum portion of power that is consumed in any industry is by motors. So the efficiency is a great issue for an industry owner to think about. The efficiency of the major consumer, the motor must be of as high as possible. The efficiency of the transformer, through which all the power is consumed, must also be near 100 percent. So every personnel related to the decision making in industry must have the knowledge regarding the energy efficiency issue for motors and transformers. Operation To discuss about the operation of motors and transformers we must know the basic principles of Faraday’s Law of Electromagnetic induction. According to Faraday if there is any rate of change of flux incorporated inside a conducting loop then there will be an EMF, hence voltage induced in the loop. If the loop is shorted or connected end to end, then a current will flow through the conductor. -

Chapter One Introduction
CHAPTER ONE INTRODUCTION 1.1 General Concepts The practice of grounding of electrical systems is almost as old as the development and widespread use of electric power itself, Poor grounding not only contributes to unnecessary downtime, but a lack of good grounding is also dangerous and increases the risk of equipment failure. Without an effective grounding system, we could be exposed to the risk of electric shock, not to mention instrumentation errors, harmonic distortion issues, power factor problems and a host of possible intermittent dilemmas. If fault currents have no path to the ground through a properly designed and maintained grounding system, they will find unintended paths that could include people. However, good grounding isn‟t only for safety; it is also used to prevent damage to industrial plants and equipment. A good grounding system will improve the reliability of equipment and reduce the likelihood of damage due to lightning or fault currents. Billions are lost each year in the workplace due to electrical fires. This does not account for related litigation costs and loss of personal and corporate productivity.(" Practical Grounding, Bonding, Shielding and Surge Protection") 1.2 Problem Statement This research aims to study the effect of earthing resistance on the service voltage of distribution transformers. 1.3 Objectives This research aims to study the effect of earthing resistance on the service voltage of distribution transformers, decrease of the earthing resistance of distribution transformers, and also balance of distribution of loads to face transformers faults. 1 1.4 Methodology Earth resistance readings obtained by using a device named (Earth/Ground tester 1625). -

Application Note 102 Stabiliti™ and Sundial™ 30Kw Series PCS
Application Note 102 Stabiliti™ and SunDial™ 30kW Series PCS PURPOSE AND SCOPE Ideal Power Conversion Systems (PCS) are designed to operate in North America at a nominal 480 Vac and 60 Hz on the 3-wire, 3-phase AC power port. Applications that require different AC voltages or applications involving grid-forming capabilities are accommodated by use of a transformer. This application note details considerations and requirements for successful interconnection of the PCS to a facility electrical power system. PCS ELECTRICAL BACKGROUND The Stabiliti™ and SunDial™ series PCS both have a 3-wire, 3-phase AC electrical connection interface and power is made phase-to-phase at 480 Vac, 60 Hz in North America. The PCS does not accommodate a neutral wire connection and therefore does not directly produce power at 277 Vac. This configuration is referred to as a delta connected circuit. Refer to the section on zigzag transformers for information on supporting 277 Vac phase-to-neutral loads. Figure 1: PCS AC electrical connection interface showing 3 phase power connectors. DOC-00033 REV A Page 1 of 12 As with all electrical equipment, an Ideal Power PCS includes components with certain voltage withstand limits and internal overvoltage surge protection. As a result, the AC input voltages must be anchored relative to ground to ensure proper protection of the system. Input circuits which are not constrained and not grounded are referred to as floating and in this case, while the input phases may remain constant phase-to-phase, during power flow they may easily rise in voltage relative to ground by hundreds of volts. -

C-100EA NGR Application Guide.Indd
NEUTRAL GROUNDING RESISTORS APPLICATIONNGR GUIDE Application Guide, September 2014 ABOUT I-GARD I-Gard’s commitment to electrical safety provides both industrial and commercial customers with the products needed to protect their electrical equipment and the people that operate them. As the only electrical-safety focused company whose product portfolio includes neutral grounding resistors, high-resistance grounding systems and optical arc mitigation, we take pride in our technologies that reduce the frequency and impact of electrical hazards, such as arc flash and ground faults. For those customers who have purchased from us over the last 30 years, you know us for the quality and robustness of our products, our focus on customer service and technical leadership. We build on this foundation by investing in developing new products in electrical safety education - including EFC scholarship program - by actively participating in the IEEE community programs on technical and electrical safety standard, and working with local universities at discovering new technologies. We remain unrelenting in our goal of improving electrical safety in the workplace. Our commitment to excellence is validated by long-standing relationships with industry leaders in fields as diverse as oil and gas, hospitals, automotive, data centers, food processing, aerospace, water and waste water plants, and telecommunications. We provide them with the product and application support required to ensure that their electrical distribution system is safe and reliable. TABLE OF -
Lecture Notes on Electrical Machines-Ii
LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II PCEL-4302 ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II 5TH SEMESTER B.TECH IN ELECTRICAL ENGINEERING LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II SYLLABUS LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II Disclaimer This document does not claim any originality and cannot be used as a substitute for prescribed textbooks. The information presented here is merely a collection by the committee faculty members for their respective teaching assignments as an additional tool for the teaching-learning process. Various sources as mentioned at the reference of the document as well as freely available material from internet were consulted for preparing this document. The ownership of the information lies with the respective authors or institutions. Further, this document is not intended to be used for commercial purpose and the committee faculty members are not accountable for any issues, legal or otherwise, arising out of use of this document. The committee faculty members make no representations or warranties with respect to the accuracy or completeness of the contents of this document and specifically disclaim any implied warranties of merchantability or fitness for a particular purpose. LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II MODULE-I CHAPTER-3 Salient Pole type Three Phase Synchronous Generators LECTURE NOTES ON ELECTRICAL MACHINES-II Introduction: The simple cylindrical theory of a synchronous generator ignores the effect of the reluctance torque on the generator. Fig.3.1 shows a salient-pole rotor with no windings inside a three-phase stator. The stator magnetic field produced in the air gap of the generator induces a magnetic field in the rotor.