Phoenicians Spread Trade & Civilization
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

From Small States to Universalism in the Pre-Islamic Near East
REVOLUTIONIZING REVOLUTIONIZING Mark Altaweel and Andrea Squitieri and Andrea Mark Altaweel From Small States to Universalism in the Pre-Islamic Near East This book investigates the long-term continuity of large-scale states and empires, and its effect on the Near East’s social fabric, including the fundamental changes that occurred to major social institutions. Its geographical coverage spans, from east to west, modern- day Libya and Egypt to Central Asia, and from north to south, Anatolia to southern Arabia, incorporating modern-day Oman and Yemen. Its temporal coverage spans from the late eighth century BCE to the seventh century CE during the rise of Islam and collapse of the Sasanian Empire. The authors argue that the persistence of large states and empires starting in the eighth/ seventh centuries BCE, which continued for many centuries, led to new socio-political structures and institutions emerging in the Near East. The primary processes that enabled this emergence were large-scale and long-distance movements, or population migrations. These patterns of social developments are analysed under different aspects: settlement patterns, urban structure, material culture, trade, governance, language spread and religion, all pointing at population movement as the main catalyst for social change. This book’s argument Mark Altaweel is framed within a larger theoretical framework termed as ‘universalism’, a theory that explains WORLD A many of the social transformations that happened to societies in the Near East, starting from Andrea Squitieri the Neo-Assyrian period and continuing for centuries. Among other infl uences, the effects of these transformations are today manifested in modern languages, concepts of government, universal religions and monetized and globalized economies. -

Indo-Iranian Personal Names in Mitanni: a Source for Cultural Reconstruction DOI: 10.34158/ONOMA.54/2019/8
Onoma 54 Journal of the International Council of Onomastic Sciences ISSN: 0078-463X; e-ISSN: 1783-1644 Journal homepage: https://onomajournal.org/ Indo-Iranian personal names in Mitanni: A source for cultural reconstruction DOI: 10.34158/ONOMA.54/2019/8 Simone Gentile Università degli Studi di Roma Tre Dipartimento di Filosofia, Comunicazione e Spettacolo via Ostiense, 234˗236 00146 Roma (RM) Italy [email protected] To cite this article: Gentile, Simone. 2019. Indo-Iranian personal names in Mitanni: A source for cultural reconstruction. Onoma 54, 137–159. DOI: 10.34158/ONOMA.54/2019/8 To link to this article: https://doi.org/10.34158/ONOMA.54/2019/8 © Onoma and the author. Indo-Iranian personal names in Mitanni: A source for cultural reconstruction Abstract: As is known, some Indo˗Aryan (or Iranian) proper names and glosses are attested in documents from Egypt, Northern Mesopotamia, and Syria, related to the ancient kingdom of Mitanni (2nd millennium BC). The discovery of these Aryan archaic forms in Hittite and Hurrian sources was of particular interest for comparative philology. Indeed, some names can be readily compared to Indo˗Iranian anthroponyms and theonyms: for instance, Aššuzzana can likely be related with OPers. Aspačanā ‘delighting in horses’, probably of Median origin; Indaratti ‘having Indra as his guest’ clearly recalls Indra, a theonym which occurs both in R̥ gveda and Avesta. This paper aims at investigating the relationship between Aryan personal names preserved in Near Eastern documents and the Indo˗Iranian cultural milieu. After a thorough collection of these names, their 138 SIMONE GENTILE morphological and semantic structures are analysed in depth and the most relevant results are showed here. -

Quantitative Dynamics of Human Empires
Quantitative Dynamics of Human Empires Cesare Marchetti and Jesse H. Ausubel FOREWORD Humans are territorial animals, and most wars are squabbles over territory. become global. And, incidentally, once a month they have their top managers A basic territorial instinct is imprinted in the limbic brain—or our “snake meet somewhere to refresh the hierarchy, although the formal motives are brain” as it is sometimes dubbed. This basic instinct is central to our daily life. to coordinate business and exchange experiences. The political machinery is Only external constraints can limit the greedy desire to bring more territory more viscous, and we may have to wait a couple more generations to see a under control. With the encouragement of Andrew Marshall, we thought it global empire. might be instructive to dig into the mechanisms of territoriality and their role The fact that the growth of an empire follows a single logistic equation in human history and the future. for hundreds of years suggests that the whole process is under the control In this report, we analyze twenty extreme examples of territoriality, of automatic mechanisms, much more than the whims of Genghis Khan namely empires. The empires grow logistically with time constants of tens to or Napoleon. The intuitions of Menenius Agrippa in ancient Rome and of hundreds of years, following a single equation. We discovered that the size of Thomas Hobbes in his Leviathan may, after all, be scientifically true. empires corresponds to a couple of weeks of travel from the capital to the rim We are grateful to Prof. Brunetto Chiarelli for encouraging publication using the fastest transportation system available. -

Study Guide #16 the Rise of Macedonia and Alexander the Great
Name_____________________________ Global Studies Study Guide #16 The Rise of Macedonia and Alexander the Great The Rise of Macedonia. Macedonia was strategically located on a trade route between Greece and Asia. The Macedonians suffered near constant raids from their neighbors and became skilled in horseback riding and cavalry fighting. Although the Greeks considered the Macedonians to be semibarbaric because they lived in villages instead of cities, Greek culture had a strong influence in Macedonia, particularly after a new Macedonian king, Philip II, took the throne in 359 B.C. As a child, Philip II had been a hostage in the Greek city of Thebes. While there, he studied Greek military strategies and learned the uses of the Greek infantry formation, the phalanx. After he left Thebes and became king of Macedonia, Philip used his knowledge to set up a professional army consisting of cavalry, the phalanx, and archers, making the Macedonian army one of the strongest in the world at that time. Philip’s ambitions led him to conquer Thrace, to the east of Macedonia. Then he moved to the trade routes between the Aegean Sea and the Black Sea. Soon Philip turned his attention to the Greek citystates. Although some Greek leaders tried to get the city-states to unite, they were unable to forge a common defense, which made them vulnerable to the Macedonian threat. Eventually, Philip conquered all the city-states, including Athens and Thebes, which he defeated at the battle of Chaeronea in 338 B.C. This battle finally ended the independence of the Greek city-states. -

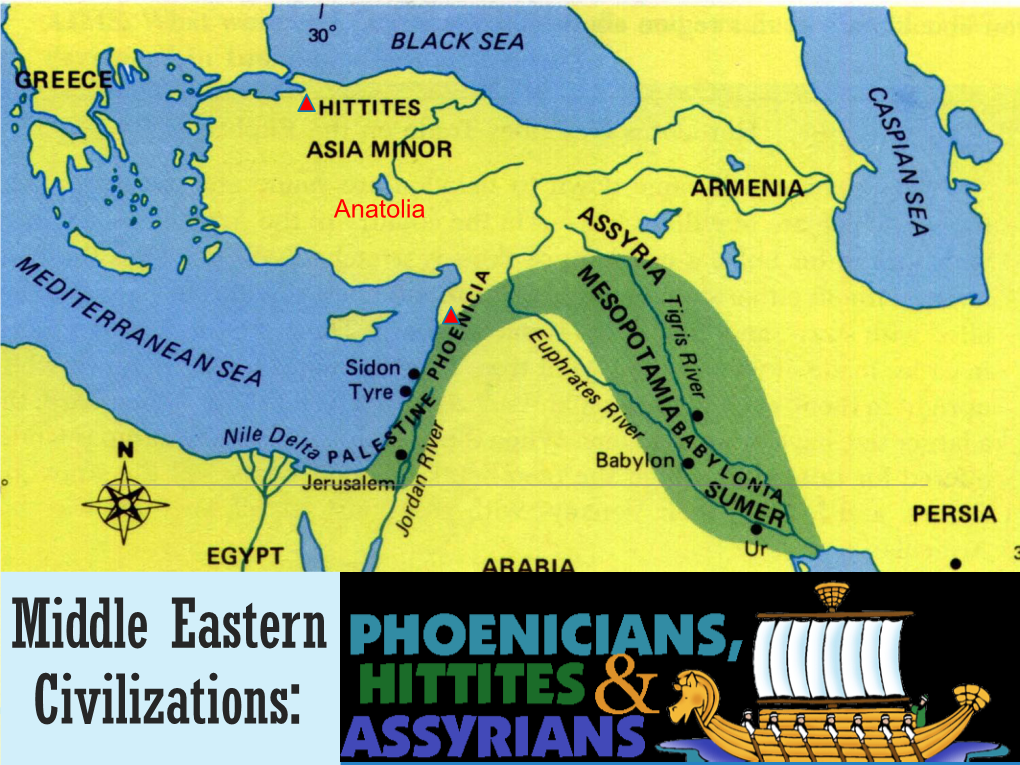
Anatolian Civilizations.Pdf
P a g e | 1 ANATOLIAN CIVILIZATIONS: “From Hittites to the Persian Domination” Text written by Erdal Yavuz Anatolia, also called Asia Minor, at the Their center was Hattusas (in Boğazköy near crossroads of Asia and Europe, has been the home Yozgat) which will also be the capital city of the of numerous peoples during the prehistoric ages, Hittite kingdoms. with well-known Neolithic settlements such as Hattians spoke a language related to the Çatalhöyük , Çayönü, Hacılar to name a few. Northwest Caucasian language group eventually The settlement of legendary Troy also starts merged with the Hittites, who spoke the Indo- in the Neolithic period and continues forward into European Hittite language. the Iron Age. In the east and south east Anatolia, one of Anatolia offered a mild climate with reliable the earliest state builders were the Hurrians, and regular rainfall necessary for a regular entering the scene toward the end of the 3rd agricultural production. Besides the timber and millennium BC stone essential for construction but deficient in Hurrians occupied large sections of eastern Mesopotamia, Anatolia had rich mines, which Anatolia and later the Cilicia region (From Alanya to provided copper, silver, iron, and gold. Mersin including the Taurus Mountains) and had a Since the peninsula is a land bridge between strong influence on the Hittite culture, language and Asia and Europe as well as the Mediterranean and mythology. the Black Sea, trade to and from the region also had However the Hurrians lost all political and been important since the prehistoric times. All the cultural identity by the last part of the 2nd above particularities made Anatolia very attractive millennium BC. -

People on Both Sides of the Aegean Sea. Did the Achaeans And
BULLETIN OF THE MIDDLE EASTERN CULTURE CENTER IN JAPAN General Editor: H. I. H. Prince Takahito Mikasa Vol. IV 1991 OTTO HARRASSOWITZ • WIESBADEN ESSAYS ON ANCIENT ANATOLIAN AND SYRIAN STUDIES IN THE 2ND AND IST MILLENNIUM B.C. Edited by H. I. H. Prince Takahito Mikasa 1991 OTTO HARRASSOWITZ • WIESBADEN The Bulletin of the Middle Eastern Culture Center in Japan is published by Otto Harrassowitz on behalf of the Middle Eastern Culture Center in Japan. Editorial Board General Editor: H.I.H. Prince Takahito Mikasa Associate Editors: Prof. Tsugio Mikami Prof. Masao Mori Prof. Morio Ohno Assistant Editors: Yukiya Onodera (Northwest Semitic Studies) Mutsuo Kawatoko (Islamic Studies) Sachihiro Omura (Anatolian Studies) Die Deutsche Bibliothek - CIP-Einheitsaufnahme Essays on Ancient Anatolian and Syrian studies in the 2nd and Ist millennium B.C. / ed. by Prince Takahito Mikasa. - Wiesbaden : Harrassowitz, 1991 (Bulletin of the Middle Eastern Culture Center in Japan ; Vol. 4) ISBN 3-447-03138-7 NE: Mikasa, Takahito <Prinz> [Hrsg.]; Chükintö-bunka-sentä <Tökyö>: Bulletin of the . © 1991 Otto Harrassowitz, Wiesbaden This work, including all of its parts, is protected by Copyright. Any use beyond the limits of Copyright law without the permission of the publisher is forbidden and subject to penalty. This applies particularly to reproductions, translations, microfilms and storage and processing in electronic Systems. Printed on acidfree paper. Manufactured by MZ-Verlagsdruckerei GmbH, 8940 Memmingen Printed in Germany ISSN 0177-1647 CONTENTS PREFACE -

Manali Project Prospectus
Manali Project Prospectus Brief Overview and Areas for Further Research (April, 2017) Contents A. Description of Manali Project B. Overview of Story (as currently envisioned) C. Effort to Highlight Ways of Creating Unprecedented Culture Change, Cultivating Spiritual Wisdom D. Areas for Further Research A. Description of Project The Manali Project is a fictionalized account of three story lines taking place in a time period of from maybe 2080-2150. Hopefully, the story lines would highlight—through both dramatic and everyday circumstances-- 1) the positive possibilities associated with permaculture, appropriate technology 2) the humor associated with salvaging material culture from the previous “advanced” civilization --and share much about ways to create unprecedented culture change, and arrive at communities which integrate spiritual wisdom into the everyday circumstances of daily life. Note: (the name Manali is taken from the name of a town in India)…“Manali is named after the Sanatan Hindu lawgiver Manu. The name Manali is regarded as the derivative of 'Manu-Alaya' which literally means 'the abode of Manu'. Legend has it that sage Manu stepped off his ark in Manali to recreate human life after a great flood had deluged the world.” (Wikipedia) Questions which this fictional account seeks to explore include “what is wisdom?”, and “how does cultural transmission of wisdom take place?”. There will also be an effort to be realistic about what kind of material culture each of the three story lines have. Included below are some sources which I have identified as starting points for giving the three story lines authentic material cultures. However, this kind of writing involves more research than what I’ve done before, and so I’m looking for ideas about how to develop the material culture piece of it. -

Armenia and the Pontus
A r me n ia an d t he p on t u s BY E I R AM ARC D . S The Stat e of A rm e nia that is to be crea ted by th e Peace Co nference wi ll nat ura lly i nclude wi t hi nit s co n fi nes th e dis nd— l A t riet of Trebiz o the B lack Sea litt ora of rmenia . Ther e d in n n l i s t o be foun this regio a co siderab e Greek populat ion . V n l n . d l M r e iz e os , in the mem ora um on the t erri toria claims w S u d of Greece , hich he bmit te t o the Peace Conferenc e , advoca t ed that said district be incl uded in the pr opose d A — A n S tat e of Armenia . Greek rmenian com mi ssi o which held it s sessio ns in Pa ris has already agre ed upon a p lan which will insure the Greeks of Trebi zond full cu lt ural n \V e t n n and aut o om y . rej oice tha Arme ia Gre ek l eaders have thus laid t he foundation of an Arme no - Greek rap roch ement ld n and n p , which shou devel op i t o a clos e e during n friendshi p between the two ki dr ed races . Thi s paper has two purposes " (a ) To examine and det er t h e n and mine geographical , e th ographical , his torical eco nomic st atus of Po ntus and (b ) t o show tha t Pontus is an A n i nt egral part of rme ia . -

Egyptians Hittites Assyrians Babylonians Persians Seleukids
Egyptians Hittites Assyrians Babylonians Persians Seleukids Romans Language Cuneiform on clay Hittite cuneiform on Cuneiform Assyrian Aramaic, except to Royal Greek on papyri or Originals of high tablets. Int’l clay or wooden and Babylonian on temples, for which inscriptions in stone inscriptions, officials do not correspondence found tablets for state clay tablets. correspondence was Elamite, and some literary survive, but c. in Babylonian, letters. (Some on Aramaic on in Babylonian Babylonian, Old sources. Cities 9,000 copies Assyrian, Hurrian, and wooden tablets in parchment cuneiform Persian, & Egypt. could choose to survive of papyri Hittite, but mostly hieroglyphics.) discouraged, but hieroglyphs (cf. inscribe royal or inscriptions. Peripheral Akkadian. maybe used; none Esth 3:12). letters on stone. Greek and Latin extant. Admin. used for state Aramaic. correspondence. Records Armarna letters were Administrative “[N]othing much Unknown; Aramaic Depository room Archives of Little known, but Location? all (but one) found at rooms in Tapikka, can be said about letters on for Persepolis officials at different the commentarii, Tell el-Amarna and Hattusa (some in the original storage parchment no Treasury Texts. levels and of cities which had copies were likely kept in a temples), and royal and archival longer extant. Local archives and of associations. of hearings, records office. citadel Büyükkale. organization of the Cuneiform tablets kept by satraps. The kind had his official state found in temples Cf. Ezra 5:17- own royal archive. correspondence, & correspondence” Ebabbar of Sippar 6:2. imperial acts. (81). Most letters and Eanna of Uruk. found at Nineveh, not Assyria’s admin center. Authors Scribes trained in Trained scribes; Scribes trained by Trained scribes. -

The Siege of Tyre
The Siege of Tyre 1 Contents Past Questions! 2 Arrian’s Account Of The Siege! 4 Key Points! 14 Past Questions 1985 Give Alexander's reasons for besieging Tyre and describe the siege. What does the siege tell us about Alexander's character? (50) 1991 "Alexander had no difficulty in persuading his officers that the attempt on Tyre must be made". (Arrian, Book 2. Ch. 18) What arguments did Alexander use to persuade his officers? What factors made the siege of Tyre “a tremendous undertaking"? (50) 1995 2 What particular skills did Alexander show in his sieges of Halicarnassus and Tyre? (50) 2004 (ii) The siege and capture of Tyre has been described as Perhaps the hardest task that Alexander’s military genius ever encountered. (Bury and Meiggs) (a) What were the main challenges presented by Tyre and its defenders, and how did Alexander’s genius overcome those challenges? (40) (b) What is your opinion of Alexander’s treatment of the survivors after the capture of Tyre? (10) 2012 (ii) (a) Explain why the city of Tyre was so difficult to capture. (15) (b) How did Alexander overcome the difficulties presented by Tyre and its defenders? (25) (c) What do you learn about Alexander’s character from Arrian’s account of the siege and capture of Tyre? (10) 3 Arrian’s Account Of The Siege • Alexander easily persuaded his men to make an attack on Tyre. An omen helped to convince him, because that very night during a dream he seemed to be approaching the walls of Tyre, and Heracles was stretching out his right hand towards him and leading him to the city. -

Standing the Test of Time: Impact of the Sea Peoples on Phoenician Cultural Development
Standing the Test of Time: Impact of the Sea Peoples on Phoenician Cultural Development. By Marc Groenewald 26273706 Submitted in fulfilment of the requirements for the degree MA Ancient Languages and Cultures Faculty Humanities University of Pretoria Supervisor: Prof G. Prinsloo Co-supervisor: Prof W. Boshoff Submission Date: 08 November 2013 1 © University of Pretoria TABLE OF CONTENTS I. ABSTRACT ........................................................................................................................................ 8 CHAPTER 1 ........................................................................................................................................ 10 INTRODUCTION ................................................................................................................................ 10 CHAPTER 2 ........................................................................................................................................ 16 EGYPT AND THE HITTITES............................................................................................................ 16 2.1 INTRODUCTION ..................................................................................................................... 16 2.2 THE EGYPTIANS .................................................................................................................... 17 2.2.1 Start of a Structured Society ........................................................................................... 18 2.2.2 Historical Sources on Egypt........................................................................................... -

I. Phoenicia (1200 – 500 BCE)
I. Phoenicia (1200 – 500 BCE) Settlers from ancient Syria, Lebanon, and Israel area. City-states: commerce Ex. Byblos, Berytus, Sidon, Tyre First Alphabetical Writing System: most important contribution Phoenicians wrote on poor papyrus: a lot of records disintegrated Expansion to Cyprus, African Coast, Spanish Coast, Sardinia, Sicily, Malta State and private help for expansion: trade and manufacturing (textiles: used purple dye) Reasons: Assyrian Expansion and shortage of agriculture (in Tyre) Trade opportunities Led to Greek Conflict: violent struggle for Sicily (3rd century BCE): Phoenicia upper- hand Carthage: founded by migrating Phoenicians (modern-day Tunis) 814 BCE Walled city Leaders = 2 judges (upperclass families decide) Senate (Merchant families decide) -Allowed successful people to gain political influence Foreign Policy: Protect sea trade NAVY Fast warships Citizen rowers and navigators Trade: Commercial monopoly (explorer Hanno): West African Coast Mediterranean – Sub-Sahara Africa – Spanish and French Coasts and Cornwall Empire of trade routes and ports (not territorial empire) Civilian government Military Religion: Capricious Gods – appeased by sacrifice (children) Greeks and Romans felt Cathagians treated subjects hard and gloomy Conquests of Assyrian Conquest: Destruction of Israel Deportation of Jewish people Pressure on Judah Pressure on Phoenicians: Led to Phoenician Colonization Occupied Egypt and Babylonia and western Iran Empire too big to control: expensive campaigns and arms race. Left empire vulnerable Subjects began to hate Assyrians Kingdom of Medes in Iran: Medes captured Assyrian homeland in Mesopotamia and eastern Anatolia Neo-Babylonian Dynasty took other territory from the Assyrians .