Basic Cell Biology
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Glossary - Cellbiology
1 Glossary - Cellbiology Blotting: (Blot Analysis) Widely used biochemical technique for detecting the presence of specific macromolecules (proteins, mRNAs, or DNA sequences) in a mixture. A sample first is separated on an agarose or polyacrylamide gel usually under denaturing conditions; the separated components are transferred (blotting) to a nitrocellulose sheet, which is exposed to a radiolabeled molecule that specifically binds to the macromolecule of interest, and then subjected to autoradiography. Northern B.: mRNAs are detected with a complementary DNA; Southern B.: DNA restriction fragments are detected with complementary nucleotide sequences; Western B.: Proteins are detected by specific antibodies. Cell: The fundamental unit of living organisms. Cells are bounded by a lipid-containing plasma membrane, containing the central nucleus, and the cytoplasm. Cells are generally capable of independent reproduction. More complex cells like Eukaryotes have various compartments (organelles) where special tasks essential for the survival of the cell take place. Cytoplasm: Viscous contents of a cell that are contained within the plasma membrane but, in eukaryotic cells, outside the nucleus. The part of the cytoplasm not contained in any organelle is called the Cytosol. Cytoskeleton: (Gk. ) Three dimensional network of fibrous elements, allowing precisely regulated movements of cell parts, transport organelles, and help to maintain a cell’s shape. • Actin filament: (Microfilaments) Ubiquitous eukaryotic cytoskeletal proteins (one end is attached to the cell-cortex) of two “twisted“ actin monomers; are important in the structural support and movement of cells. Each actin filament (F-actin) consists of two strands of globular subunits (G-Actin) wrapped around each other to form a polarized unit (high ionic cytoplasm lead to the formation of AF, whereas low ion-concentration disassembles AF). -

Bacterial Cell Membrane
BACTERIAL CELL MEMBRANE Dr. Rakesh Sharda Department of Veterinary Microbiology NDVSU College of Veterinary Sc. & A.H., MHOW CYTOPLASMIC MEMBRANE ➢The cytoplasmic membrane, also called a cell membrane or plasma membrane, is about 7 nanometers (nm; 1/1,000,000,000 m) thick. ➢It lies internal to the cell wall and encloses the cytoplasm of the bacterium. ➢It is the most dynamic structure of a prokaryotic cell. Structure of cell membrane ➢The structure of bacterial plasma membrane is that of unit membrane, i.e., a fluid phospholipid bilayer, composed of phospholipids (40%) and peripheral and integral proteins (60%) molecules. ➢The phospholipids of bacterial cell membranes do not contain sterols as in eukaryotes, but instead consist of saturated or monounsaturated fatty acids (rarely, polyunsaturated fatty acids). ➢Many bacteria contain sterol-like molecules called hopanoids. ➢The hopanoids most likely stabilize the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. ➢The phospholipids are amphoteric molecules with a polar hydrophilic glycerol "head" attached via an ester bond to two non-polar hydrophobic fatty acid tails. ➢The phospholipid bilayer is arranged such that the polar ends of the molecules form the outermost and innermost surface of the membrane while the non-polar ends form the center of the membrane Fluid mosaic model ➢The plasma membrane contains proteins, sugars, and other lipids in addition to the phospholipids. ➢The model that describes the arrangement of these substances in lipid bilayer is called the fluid mosaic model ➢Dispersed within the bilayer are various structural and enzymatic proteins, which carry out most membrane functions. ➢Some membrane proteins are located and function on one side or another of the membrane (peripheral proteins). -

The Endomembrane System and Proteins
Chapter 4 | Cell Structure 121 Endosymbiosis We have mentioned that both mitochondria and chloroplasts contain DNA and ribosomes. Have you wondered why? Strong evidence points to endosymbiosis as the explanation. Symbiosis is a relationship in which organisms from two separate species depend on each other for their survival. Endosymbiosis (endo- = “within”) is a mutually beneficial relationship in which one organism lives inside the other. Endosymbiotic relationships abound in nature. We have already mentioned that microbes that produce vitamin K live inside the human gut. This relationship is beneficial for us because we are unable to synthesize vitamin K. It is also beneficial for the microbes because they are protected from other organisms and from drying out, and they receive abundant food from the environment of the large intestine. Scientists have long noticed that bacteria, mitochondria, and chloroplasts are similar in size. We also know that bacteria have DNA and ribosomes, just like mitochondria and chloroplasts. Scientists believe that host cells and bacteria formed an endosymbiotic relationship when the host cells ingested both aerobic and autotrophic bacteria (cyanobacteria) but did not destroy them. Through many millions of years of evolution, these ingested bacteria became more specialized in their functions, with the aerobic bacteria becoming mitochondria and the autotrophic bacteria becoming chloroplasts. The Central Vacuole Previously, we mentioned vacuoles as essential components of plant cells. If you look at Figure 4.8b, you will see that plant cells each have a large central vacuole that occupies most of the cell's area. The central vacuole plays a key role in regulating the cell’s concentration of water in changing environmental conditions. -

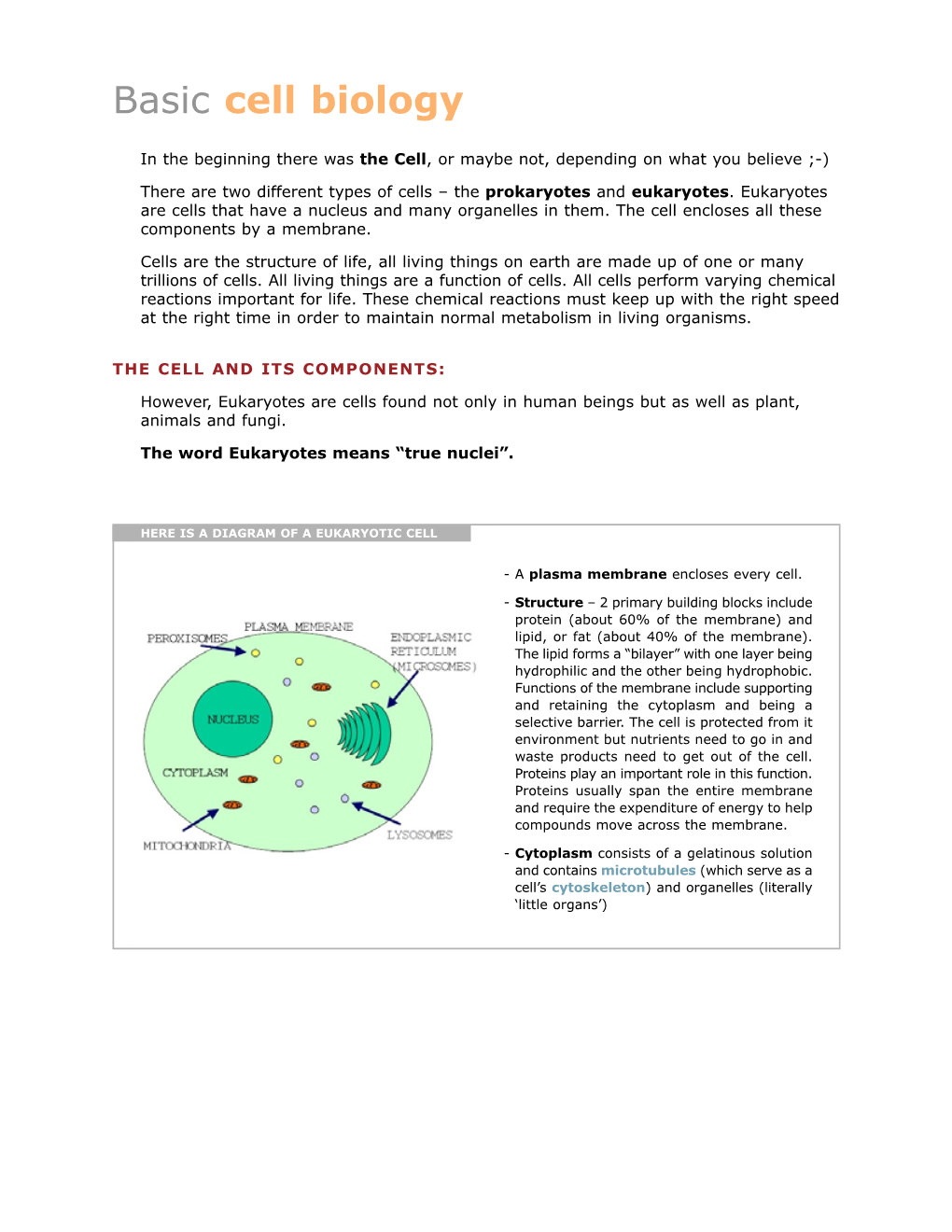
Standard 2: CELL BIOLOGY – REVIEW of BASICS
Standard 2: CELL BIOLOGY – REVIEW OF BASICS CELL PART OR TYPE OF CELL WHERE FOUND WHAT DOES IT FUNCTION: MISCELLANEOUS ORGANELLE Prokaryotic cell Plant cell LOOK LIKE: Job it does in INFORMATION: things Eukaryotic cell Animal cell Describe or Draw the cell such as color, what it is Both Both made of, size, etc. plasma/cell See diagram Holds cell together Phospholipid bilayer with membrane both both Regulates what goes proteins in/out of cell Semipermeable cytoplasm both Clear thick jelly- Supports/protects both like material in cell cell organelles See diagram Control center nucleus eukaryotic both Contains DNA See diagram Where proteins are ribosome both both made See diagram Process proteins Golgi complex eukaryotic both that go to other /apparatus parts of cell Membrane-bound Digests materials lysosome eukaryotic animal sac of digestive within the cell enzymes Membrane-bound Stores water, food, One large one in plants vacuole eukaryotic both storage area waste and dissolved Many smaller ones in minerals animals endoplasmic Network of Transport materials Can be rough (with reticulum eukaryotic both membrane tubes throughout the cell ribosomes attached) or smooth (without ribosomes) See diagram Where cell respiration Called Powerhouse of cell mitochondria eukaryotic both occurs (releases Makes ATP from energy for cell to use) breaking down glucose See diagram Where photosynthesis Contains chlorophyll chloroplast eukaryotic plant takes place Converts light energy into chemical energy in glucose Some pro- and plant (also fungi Rigid structure -

Introduction to the Cell Cell History Cell Structures and Functions
Introduction to the cell cell history cell structures and functions CK-12 Foundation December 16, 2009 CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the “FlexBook,” CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning. Copyright ©2009 CK-12 Foundation This work is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 United States License. To view a copy of this license, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/us/ or send a letter to Creative Commons, 171 Second Street, Suite 300, San Francisco, California, 94105, USA. Contents 1 Cell structure and function dec 16 5 1.1 Lesson 3.1: Introduction to Cells .................................. 5 3 www.ck12.org www.ck12.org 4 Chapter 1 Cell structure and function dec 16 1.1 Lesson 3.1: Introduction to Cells Lesson Objectives • Identify the scientists that first observed cells. • Outline the importance of microscopes in the discovery of cells. • Summarize what the cell theory proposes. • Identify the limitations on cell size. • Identify the four parts common to all cells. • Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Introduction Knowing the make up of cells and how cells work is necessary to all of the biological sciences. Learning about the similarities and differences between cell types is particularly important to the fields of cell biology and molecular biology. -

Cell Wall Ribosomes Nucleus Chloroplast Cytoplasm
Cell Wall Ribosomes Nucleus Nickname: Protector Nickname: Protein Maker Nickname: Brain The cell wall is the outer covering of a Plant cell. It is Ribosomes read the recipe from the The nucleus is the largest organelle in a cell. The a strong and stiff and made of DNA and use this recipe to make nucleus directs all activity in the cell. It also controls cellulose. It supports and protects the plant cell by proteins. The nucleus tells the the growth and reproduction of the cell. holding it upright. It ribosomes which proteins to make. In humans, the nucleus contains 46 chromosomes allows water, oxygen and carbon dioxide to pass in out They are found in both plant and which are the instructions for all the activities in your of plant cell. animal cells. In a cell they can be found cell and body. floating around in the cytoplasm or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. Chloroplast Cytoplasm Endoplasmic Reticulum Nickname: Oven Nickname: Gel Nickname: Highway Chloroplasts are oval structures that that contain a green Cytoplasm is the gel like fluid inside a The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is the transportation pigment called chlorophyll. This allows plants to make cell. The organelles are floating around in center for the cell. The ER is like the conveyor belt, you their own food through the process of photosynthesis. this fluid. would see at a supermarket, except instead of moving your groceries it moves proteins from one part of the cell Chloroplasts are necessary for photosynthesis, the food to another. The Endoplasmic Reticulum looks like a making process, to occur. -

Cell Structure and Function in the Bacteria and Archaea
4 Chapter Preview and Key Concepts 4.1 1.1 DiversityThe Beginnings among theof Microbiology Bacteria and Archaea 1.1. •The BacteriaThe are discovery classified of microorganismsinto several Cell Structure wasmajor dependent phyla. on observations made with 2. theThe microscope Archaea are currently classified into two 2. •major phyla.The emergence of experimental 4.2 Cellscience Shapes provided and Arrangements a means to test long held and Function beliefs and resolve controversies 3. Many bacterial cells have a rod, spherical, or 3. MicroInquiryspiral shape and1: Experimentation are organized into and a specific Scientificellular c arrangement. Inquiry in the Bacteria 4.31.2 AnMicroorganisms Overview to Bacterialand Disease and Transmission Archaeal 4.Cell • StructureEarly epidemiology studies suggested how diseases could be spread and 4. Bacterial and archaeal cells are organized at be controlled the cellular and molecular levels. 5. • Resistance to a disease can come and Archaea 4.4 External Cell Structures from exposure to and recovery from a mild 5.form Pili allowof (or cells a very to attach similar) to surfacesdisease or other cells. 1.3 The Classical Golden Age of Microbiology 6. Flagella provide motility. Our planet has always been in the “Age of Bacteria,” ever since the first 6. (1854-1914) 7. A glycocalyx protects against desiccation, fossils—bacteria of course—were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion 7. • The germ theory was based on the attaches cells to surfaces, and helps observations that different microorganisms years ago. On any possible, reasonable criterion, bacteria are—and always pathogens evade the immune system. have been—the dominant forms of life on Earth. -

Endomembrane System
Cell Structure & Function Cell Theory Cells are fundamental to biology Cells are the basic living units within organisms (all chemical rxns. of life take place within cells) All organisms are made of cells Single-celled organisms (bacteria/protists) Multicellular organisms (plants/animals/fungi) Cell Structure & Function Basic Aspects of Cell Structure & Function Plasma membrane Lipid bilayer Proteins DNA-containing region Cytoplasm Eukaryotic v. Prokaryotic cells Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Two major classes of cells Prokaryotic cells (pro-, “before”) Cell lacks a “true” nucleus DNA is coiled in a nucleoid region Cells lack nuclear membrane Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells [attachment structure] [DNA location] [organelles that synthesize proteins] [enclosing the cytoplasm] [rigid structure outside the p.m. ] [jelly-like outer coating] [locomotion organelle] Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Eukaryotic cells (eu-, “true”) Nucleus contains most of the cells nuclear material, DNA usually the largest organelle Bordered by a membranous envelope Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Plant v. Animal Cells Both contain Plasma membrane (functions as a selective barrier) Nucleus (gene-containing organelle) Cytoplasm (region between nucleus and p.m.) Consists of organelles in a fluid (cytosol) Prokaryotic v. Eukaryotic Cells Plant v. Animal Cells Organelles Bordered by internal membranes Compartmentalizes the functions of a cell Maintains organelle’s unique environment Most organelles are found in both plant and animal cells Plant v. Animal Cells -

Cell Life Cycle and Reproduction the Cell Cycle (Cell-Division Cycle), Is a Series of Events That Take Place in a Cell Leading to Its Division and Duplication
Cell Life Cycle and Reproduction The cell cycle (cell-division cycle), is a series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication. The main phases of the cell cycle are interphase, nuclear division, and cytokinesis. Cell division produces two daughter cells. In cells without a nucleus (prokaryotic), the cell cycle occurs via binary fission. Interphase Gap1(G1)- Cells increase in size. The G1checkpointcontrol mechanism ensures that everything is ready for DNA synthesis. Synthesis(S)- DNA replication occurs during this phase. DNA Replication The process in which DNA makes a duplicate copy of itself. Semiconservative Replication The process in which the DNA molecule uncoils and separates into two strands. Each original strand becomes a template on which a new strand is constructed, resulting in two DNA molecules identical to the original DNA molecule. Gap 2(G2)- The cell continues to grow. The G2checkpointcontrol mechanism ensures that everything is ready to enter the M (mitosis) phase and divide. Mitotic(M) refers to the division of the nucleus. Cell growth stops at this stage and cellular energy is focused on the orderly division into daughter cells. A checkpoint in the middle of mitosis (Metaphase Checkpoint) ensures that the cell is ready to complete cell division. The final event is cytokinesis, in which the cytoplasm divides and the single parent cell splits into two daughter cells. Reproduction Cellular reproduction is a process by which cells duplicate their contents and then divide to yield multiple cells with similar, if not duplicate, contents. Mitosis Mitosis- nuclear division resulting in the production of two somatic cells having the same genetic complement (genetically identical) as the original cell. -

Genic Induction of an Inherited Cytoplasmic Difference
PROCEEDINGS OF THE NATIONAL ACADEMY OF SCIENCES Volume 29 December 15, 1943 Number ll Copyight 1943 yg the National Academy of Slene GENIC INDUCTION OF AN INHERITED CYTOPLASMIC DIFFERENCE By M. M. RHOADES DEPARTMENT OF BOTANY, COLUMBIA UNIVERSITY Communicated November 16,1943 Although many biologists consider the genes to be the sole determiners of heredity, there are those wbo feel that the cytoplasm contains a system of independent entities which in some cases controls the expression of certain characteristics. The terms genome and plasmone have been used to denote the system of genes and of t-ytoplasmic entities, respec- tively. Although the development of chlorophyll has been shown in hundreds of cases to be under genic control, there are a number of in- stances where chlorophyll variegation is inherited independently of the genome. These chlorophyll variegations, transmitted through the female line only, constitute the most compelling evidence for cytoplasmic inheritance. In these cases the physical entities in the cytoplasm are known to be the plastids; in other cases of plasmatic inheritance the nature of the entities in the cytoplasm can only be conjectured. In maize there are more than one hundred cases where the development of chlorophyll is under genic control. Two examples of cytoplasmically inherited chlorophyll variegation have been reported,1' 2 as has one case of the cytoplasmic inheritance of male sterility.3 Among the chloro- phyll characters in maize which are genically controlled is that of iojap. Maize plants homozygous for the recessive gene iojap (ij) exhibit a chloro- phyll striping or variegation.4 Considerable variation is found in the extent and pattern of the green and white areas of the leaves and culm. -

Chloroplasts Are the Food Producers of the Cell. the Organelles Are Only Found in Plant Cells and Some Protists Such As Algae
Name: ___________________________ Cell #2 H.W. due September 22nd, 2016 Period: _________ Chloroplasts are the food producers of the cell. The organelles are only found in plant cells and some protists such as algae. Animal cells do not have chloroplasts. Chloroplasts work to convert light energy of the Sun into sugars that can be used by cells. It is like a solar panel that changes sunlight energy into electric energy. The entire process is called photosynthesis and it all depends on the little green chlorophyll molecules in each chloroplast. In the process of photosynthesis, plants create sugars and release oxygen (O2). The oxygen released by the chloroplasts is the same oxygen you breathe every day. Chloroplasts are found in plant cells, but not in animal cells. The purpose of the chloroplast is to make sugars that feed the cell’s machinery. Photosynthesis is the process of a plant taking energy from the Sun and creating sugars. When the energy from the Sun hits a chloroplast and the chlorophyll molecules, light energy is converted into the chemical energy. Plants use water, carbon dioxide, and sunlight to make sugar and oxygen. During photosynthesis radiant energy or solar energy or light energy is transferred into chemical energy in the form of sugar (glucose). You already know that during photosynthesis plants make their own food. The food that the plant makes is in the form of sugar that is used to provide energy for the plant. The extra sugar that the plant does not use is stored as starch for later use. Mitochondria are known as the powerhouses of the cell. -

2019 Cell Biology Syllabus and Course Policies
Cell Biology 2019 Syllabus and Policies 1 of 6 COURSE POLICIES AND SYLLABUS CELL BIOLOGY AS.020.306 SPRING 2019 Learning Goals • Describe the structure and function of cellular components. • Explain how cellular components are localized and organized. • Explain the regulatory mechanisms that enable diversity and dynamics of cellular components. • Recognize, discuss examples, and apply common themes in cell biology. • Propose experiments to answer questions or test hypotheses about cellular structures and functions. • Predict experimental results, interpret experimental data, and use experimental evidence to generate and/or support a hypothesis. Specific learning objectives for each section of the course will be posted on Blackboard. Course material and assessments with be based on the learning goals and objectives. We encourage you to use the learning goals and objectives to guide your learning process during the course. Course Instructors Dr. Katie Tifft [email protected] Office: 183 UTL Dr. Yumi Kim [email protected] Office: 385 UTL Course Administration Dr. Tifft will be the course administrator who will handle course organization and logistics. If you have any questions about the course that are not directly related to the course content, please first check Blackboard and Piazza for relevant information and then contact Dr. Tifft by through Piazza (or by email). Textbook Bruce Alberts, et al. Molecular biology of the cell. Garland Science, 2015. 6th edition. ISBN: 9780815344322 Reading assignments for each class will be posted on Blackboard. The textbook is recommended but not required- all course material will be covered in class or through class materials provided online, but you may find the textbook is a good extra resource.