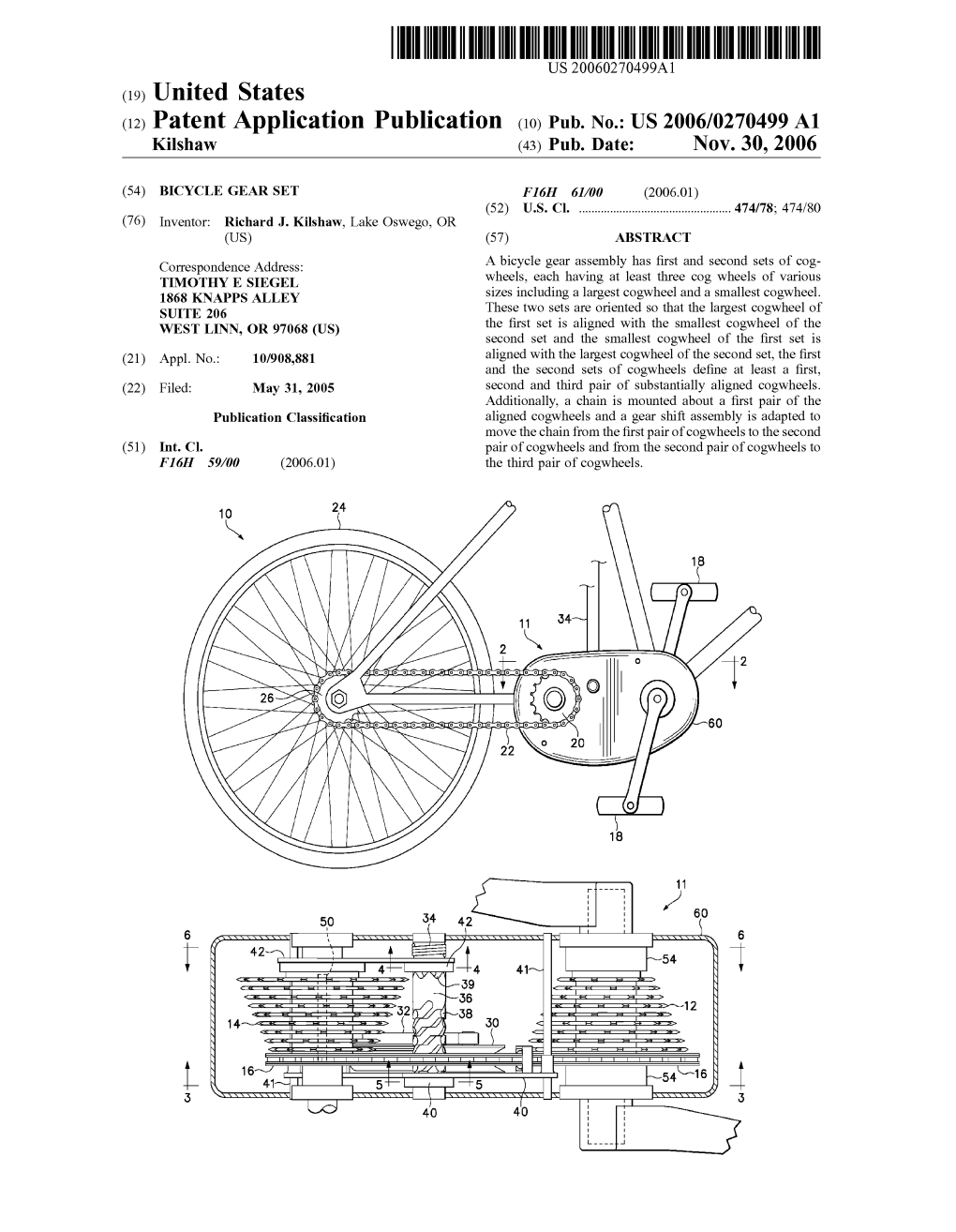
(19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Title of PAPER
Journal of Special Topics P2_7 Power Curves and Gear Ratios in Bicycles J. Anand, A. Buccheri, M. Gorley, I. Weaver Department of Physics and Astronomy, University of Leicester, Leicester, LE1 7RH. November 19, 2009 Abstract This article investigates how the power exerted by a cyclist varies with cyclist speed, and gear ratio. From Hill’s relation, both relations are determined and plotted. Suggestions are made on how these results might be useful to recreational and competitive cyclists. P2_2 Sports Science pedalling rates than contraction velocity (as in Hill’s relation), so we substitute v=ωr where r Introduction is the pedal crank arm length. Originally, Hill Gears in bicycles are often misused. Many used parameters for the mechanics of muscle people have experienced that pedalling in a fibres to determine the unknowns in this high gear from stationary is very difficult, and equation. However, since the cyclic pedalling produces very little acceleration. Equally, a motion is not as well studied as basic linear low gear at high speeds is inefficient. This contraction, values for a, b and c must be article explores the relationship between found from the special cases. That it, at ω=0 bicycle gearing, and the cyclist power output. where F=F0, and at F=0 where ω=ω0. Power Functions (1) (2) The force exerted by any engine is always applied in 2 different areas. The first is These 2 equations alone are not enough to accelerating engine components, and the determine values for the 3 unknowns. other is in the system on which you want to However, by considering the maximum power do work. -

Transmission (Mechanics) - Wikipedia 8/28/20, 1�19 PM
Transmission (mechanics) - Wikipedia 8/28/20, 119 PM Transmission (mechanics) A transmission is a machine in a power transmission system, which provides controlled application of the power. Often the term 5 speed transmission refers simply to the gearbox that uses gears and gear trains to provide speed and torque conversions from a rotating power source to another device.[1][2] In British English, the term transmission refers to the whole drivetrain, including clutch, gearbox, prop shaft (for rear-wheel drive), differential, and final drive shafts. In American English, however, the term refers more specifically to the gearbox alone, and detailed Single stage gear reducer usage differs.[note 1] The most common use is in motor vehicles, where the transmission adapts the output of the internal combustion engine to the drive wheels. Such engines need to operate at a relatively high rotational speed, which is inappropriate for starting, stopping, and slower travel. The transmission reduces the higher engine speed to the slower wheel speed, increasing torque in the process. Transmissions are also used on pedal bicycles, fixed machines, and where different rotational speeds and torques are adapted. Often, a transmission has multiple gear ratios (or simply "gears") with the ability to switch between them as speed varies. This switching may be done manually (by the operator) or automatically. Directional (forward and reverse) control may also be provided. Single-ratio transmissions also exist, which simply change the speed and torque (and sometimes direction) of motor output. In motor vehicles, the transmission generally is connected to the engine crankshaft via a flywheel or clutch or fluid coupling, partly because internal combustion engines cannot run below a particular speed. -

A Constant Force Bicycle Transmission
Rochester Institute of Technology RIT Scholar Works Theses 8-1-1983 A constant force bicycle transmission Thomas Chase Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.rit.edu/theses Recommended Citation Chase, Thomas, "A constant force bicycle transmission" (1983). Thesis. Rochester Institute of Technology. Accessed from This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by RIT Scholar Works. It has been accepted for inclusion in Theses by an authorized administrator of RIT Scholar Works. For more information, please contact [email protected]. A CONSTANT FORCE BICYCLE TRANSMISSION by Thomas R. Chase A Thesis Project Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of MASTER OF SCIENCE in Mechanical Engineering Approved by: Prof. Richard Budynas Thesis Adviser Prof. Dr. Bhalchandra V. Karlekar Department Head Prof. '"egible Signature Prof. Ray C. Johnson DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ROCHESTER INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY ROCHESTER, NHJ YORK August 1983 A CONSTANT FORCE BICYCLE TRANSMISSION ABSTRACT A prototype design for a human powered automatic transmission intended for use on an ordinary touring bicycle is presented. The transmission is intended to automatically adjust the gearing of the bicycle to maintain an optimum pedal force, regardless of the current riding conditions. Therefore, the transmission eliminates the need for the cyclist to manually adjust the bicycle gearing. The entire transmission is a self-contained unit designed to bolt onto the rear wheel of an otherwise unmodified 27-inch bicycle. The transmission combines a unique adaptation of a commercially popular continuously variable traction drive with a totally mechanical integral feedback controller. The features of the traction drive unique to its application to a bicycle are outlined in detail, along with an analysis of the important traction drive design parameters. -

Dec. 28, 1948. S. ARGYRIS - 2,457,430 ELECTRIC BICYCLE Filed Feb
Dec. 28, 1948. S. ARGYRIS - 2,457,430 ELECTRIC BICYCLE Filed Feb. 20, 1946 Patented Dec. 28, 1948 2,457,430 UNITED STATES PATENT OFFICE 2,457,430 ELECTRIC Bf YCLE Stefanos Argyris, New York, N. Y. Application February 20, 1946, Serial No. 648,971 2 Clains. (C. 80-34) 2 The object of the invention is to provide means conductive material extending between the rear for easily and quickly attaching electrical pro ends of the rear forks 6 and and the hudguard pulsion means to existing conventional bicycles. 28. Many ways finay be resörted to for supporting Attempts have been made in past years to propel the batteries and the inventioh is not limited in bicycles by electric motiors and batteries. How this respect. They may be hung from the top ever, the great weight of the batteries, the rapid frame bar 2 or supported from the rear forks T. ity with which they becaine exhausted and the I preferably use two narrow batteries rather than long time required to re-charge then has hereto. ore large one and motiat them in like positions fore discouraged efforts to provide this form of upon opposite sides of the rear wheel to secure propulsion for light weight bicycles. 10 The time has now come when it is possible goodjoalalee of the vehicle. The two batteries are by means of my improvements to successfully indicated at B in Figure 3. The motor is Cons provide electric propulsion for bicycles. The trolled from the handlebar 22 through a rheostat quick charge apparatus now found at almost 23, the control handle of which is indicated at 24. -

Date:- 13/05/2020 Class:- Diploma 6Th Sem (Auto) Sub. Teacher:- Mr
M.O.V Date:- 13/05/2020 Class:- Diploma 6th sem (Auto) Sub. Teacher:- Mr. Abhishek Chandra Bhatt Unit:- Power Transmission Topic:- Gear Transmission Automatic Epicyclic gearing or planetary gearing as used in an automatic transmission. Most modern North American, and some European and Japanese cars have an automatic transmission that selects an appropriate gear ratio without any operator intervention. They primarily use hydraulics to select gears, depending on pressure exerted by fluid within the transmission assembly. Rather than using a clutch to engage the transmission, a fluid flywheel, or torque converter is placed in between the engine and transmission. It is possible for the driver to control the number of gears in use or select reverse, though precise control of which gear is in use may or may not be possible. Automatic transmissions are easy to use. However, in the past, some automatic transmissions of this type have had a number of problems; they were complex and expensive, sometimes had reliability problems (which sometimes caused more expenses in repair), have often been less fuel-efficient than their manual counterparts (due to "slippage" in the torque converter), and their shift time was slower than a manual making them uncompetitive for racing. With the advancement of modern automatic transmissions, this has changed. Attempts to improve fuel efficiency of automatic transmissions include the use of torque converters that lock up beyond a certain speed or in higher gear ratios, eliminating power loss, and overdrive gears that automatically actuate above certain speeds. In older transmissions, both technologies could be intrusive, when conditions are such that they repeatedly cut in and out as speed and such load factors as grade or wind vary slightly. -

Technical -Data-Schlumpf-High-Speed-Drive
Haberstock Mobility - Schlumpf High Speed Drive Technical data Principle Planetary gearing system with two switch positions: direct drive 1:1, overdrive 1:2.5 Shifting Direct shifting via push buttons or "easy-shift" - levers on both ends of the spindle. No cables, no rods. New ergonomic design of the gear shift push buttons. Easy-shift levers As an option, there are "easy-shift" - levers available, which make shifting very simple, even with click-in pedals or small shoes. Gear housing Corrosion resistant, completely encased and protected against dust and spray water. Gear housing with integrated 27 tooth chainring and trouser guard. Axle Rides on (replaceable) cartridge bearings. You can expect a lifetime of more than 20'000 miles for the bearings and much more for the high-speed-drive. Axle length Rides on (replaceable) cartridge bearings. You can expect a lifetime of more than 20'000 miles for the bearings and much more for the high-speed-drive. Bottom brackets The high-speed-drive unit is designed for an inner diameter of the bottom bracket of 33.6 - 34.5mm. Chainline Distance between centerline of frame and midth of chain: 45mm. Compatibility Generally, you can combine any bicycle gearing system with high-speed- drive. Please note, that high-speed-drive in combination with internal hubs sometimes can act like a violin body. This means, that in certain gears (often the first gear) you may feel some roughness, although high-speed-drive runs perfectly smooth and silent. 1 Cranks Crankarms sit conventionally on square spindle sections. Standard length is 170mm Standard material: aluminum Available lengths: 155 (straight shape), 160, 165, 170, 172.5, 175mm (all offset shape). -

GETTING IT RIGHT 43,000 Fact-Checkers Can’T Be Wrong
Cyclesense GETTING IT RIGHT 43,000 fact-checkers can’t be wrong. But I can. by John Schubert Did you know there are no new $300 road bikes sold in the U.S.? I used to think that, but now I know better. My recent article decrying the lack of entry-priced touring bikes included the sweeping statement that there are no dropped-handlebar bikes in that price range sold in the U.S. And then I heard, uh, cor - rective missives from two folks. One was Tom Shaddox, an esteemed Adventure Cyclist contributor, and the other was an old client of mine, Arnold Kamler, the president of Kent Bicycles. quite spiffy, and they make quite the As Tom and Arnold pointed out, ecological statement. Kent offers the 14-speed Kent GMC By the way, Hubbub also sells Yukon XL road bike for $325 (the price custom-fitted bikes with sensible spoke I found — your price may vary). For patterns. This is good news for riders that tidy sum, you get a welded alu - who want a really nice custom bike but minum frame, STI shifting, three frame are put off by the goofball spoking that sizes, reasonable components, light - has become nearly universal in the weight aluminum rims, and 25C tires. medium and high-price range. Goofball Mass merchants are Kent’s primary spoking usually can’t be shade-tree- E L P retail outlets. mechanic-serviced, the parts aren’t I S G E Arnold, that looks like a sharp bike standard, and if anything breaks, you’re R G for the price! . -

BY MATT WIEBE Running from 21 to 100 Inches
SETH NEILSON NEILSON SETH Editor’s Note: In last year’s Cyclists’ Travel Guide (April 2015), we looked at “The Drivetrain Dilemma,” a dearth of components to provide adequate gearing for the self-supported touring cyclist. The void — caused in part by Shimano’s decision to end the cross compatibility of road and moun- A tain bike drivetrain components in 2010 and the steady migration of drivetrains to 10- and 11-speed models — left product managers for many bike brands scrambling for combinations of holdovers (Shimano’s still-manufactured, cross-compatible 9-speed XT derailer), third-party components (Microshift bar end shifters), or high-end alternatives (Rohloff internal geared hubs). Or they just BIG built bikes with rack mounts and touring geometry but saddled them with standard road bike gearing to take advantage of the OEM options most readily available to hit customer-demanded price points. What a difference a year makes. As Bicycle Retailer & Industry News’ Matt Wiebe discovers, a touring cyclist suddenly has the world on SHIFT a string, or perhaps a derailer cable. gear range of touring, but new products from bou- NEW FOCUS FROM COMPONENT MAKERS BIG AND 22 to 93 inches. tique manufacturers like Gevenalle and SMALL CHANGING THE GAME FOR TOURING DRIVETRAINS Match a 40/28T Lindarets/Wolf Tooth work around mini-compact Shimano’s issues for adventure riders. crank with an 11-36T cassette for gears After years of complaining about the BY MATT WIEBE running from 21 to 100 inches. Or spec a lack of low touring gears with matching more traditional 50/39/30T triple with dropbar levers, why the sudden embar- an 11-34T cassette for a range of 24 to 125 rassment of riches? ix months ago, who would have inches. -

Experimental Study of Home Automation by Bicycle Pedal Power Using of Different Sprocket Ram Singh ME (MD) Sem Student Jabalpur Engg
International Journal of Engineering Trends and Technology (IJETT) – Volume 8 Number 2- Feb 2014 Experimental Study of Home Automation by Bicycle Pedal Power Using of Different Sprocket Ram Singh ME (MD) sem student Jabalpur Engg. College Jabalpur (M P) Prof. Mrs. D.C. Sharma Assistant professor ,Jabalpur Engg. College Jabalpur (M P) Abstract- This study attempts to measure 1 -Introduction- A preliminary user survey the optimal pedaling rates for given power revealed that the average utilization of output levels as well as design the optimal multi-speed gear system is less than 40%. number of gears and the corresponding gear Thus, hard to use because of the many ratios. With respect to human performance number of unnecessary shifts. This study not and power efficiency, the gear system in only measures the optimal pedaling rates for typical multi-speed bicycles is often biased given power output levels, but also designs and redundant. The efficiency are increased the optimal number of gears and by using of five different sprocket with corresponding gear ratios. The having various teeth. A bicycle gear system measurement are obtain at five different is frequently designed without ergonomic power output levels (40, 80,120,140 and 160 expertise in terms of performance and W) and four different pedaling rate levels efficiency. The optimal performance during (60,100,125 ,150 and 175 rpm). Various bicycle riding, thereby facilitating the riding conditions including slope gradient efficiency and effectiveness of human and cruising velocity are also converted to exercise using a bicycle. the equivalent power output level. Pedal power is the transfer of energy from a Key Word- Gear ratio; Bicycle riding; human source through the use of a foot Ergonomic design; pedal and crank system. -

Technical-Data-Schlumpf-Mountain
Haberstock Mobility - Schlumpf Mountain Drive Technical data Principle Planetary gearing system with two switch positions: direct drive 1:1, low gear 2.5:1 Shifting Direct shifting via push bttons or "easy-shift" - levers on both ends of the spindle. No cables, no rods. Easy-shift levers As an option, there are "easy-shift" - levers available, which make shifting very simple, even with click-in pedals or small shoes. Gear housing Corrosion resistant, completely encased and protected against dust and spray water. Axle Rides on (replaceable) cartridge bearings. Please expect a lifetime of more than 20'000 miles for the bearings and much more for the mountain-drive). Axle length Standard is 138mm for bottom bracket widths of 68 - 73mm. A 10mm longer axle is available for bottom bracket withs up to 84mm. Bottom brackets The mountain-drive unit is designed for an inner diameter of the bottom bracket of 33.6 - 34mm. The mountain-drive part, which is slid into the b.b., has no thread. Shims to equalize an eventual play are included in the shipment. Adapters for larger diameters are available (please specify diameter when ordering). Chainline Distance between centerline of frame and midth of chain: 43, 45 or 50mm for a 68mm wide bottom bracket shell. For 43mm, please ask for 2mm spacers, which can be set between spider and chainring. For the 50mm-chainline please use the steel spider, which is available as an option (recommended for higher loads such as on tandems, rikshaws, transportation bikes). Also recommended for two chainrings (one fitted to the left, one to the right side of the spider). -

A Study on Power Assists for Bicycle Rickshaws in India, Including Fabrication of Test Apparatus
A Study on Power Assists for Bicycle Rickshaws in India, including Fabrication of Test Apparatus by Madeline R. Hickman SUBMITTED TO THE DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE IN MECHANICAL ENGINEERING ARCHIVES AT THE MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY MASSCHUETTSINSITUTE I OF TEC1" NCLC>2'Y JUNE 2011 OCT 2 2011 @ 2011 Massachusetts Institute of Technology. All rights reserved. The author hereby grants to MIT permission to reproduce and to distribute publicly paper and electronic copies of this thesis document in whole or in part in any medium now known or hereafter created. Signature of Author: Department of Mechanical Engineering May 20, 2011 Certified by:. ~' 3 '- / Daniel D. Frey, PhD Associate Professor of Mecha e Sstems Accepted by: Dim~~~!t;a ff PhD Samuel C. C oe of Mechanical Engineering Undergraduate Officer 2 A Study on Power Assists for Bicycle Rickshaws in India, including Fabrication of Test Apparatus by Madeline R. Hickman Submitted to the Department of Mechanical Engineering on May 20, 2011 in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Bachelor of Science in Mechanical Engineering ABSTRACT Bicycle rickshaws impose significant physical burdens on their drivers. Used throughout India for transportation, these rickshaws are not designed for driver comfort and safety. Instead, traditional rickshaws are only single-speed, with an extremely high gear ratio that makes it difficult for drivers to pedal with large loads. Particularly in India, many rickshaw drivers are under-nourished, and the physical exertion required to pedal passengers over rough roads and uneven terrain leads to serious health consequences. -
Business Plan Development for a Start-Up Company
BUSINESS PLAN DEVELOPMENT FOR A START-UP COMPANY Bachelor’s thesis Valkeakoski, Industrial Management Spring 2017 Andriy Sytnyk ABSTRACT Industrial Management Valkeakoski Author Andriy Sytnyk Year 2017 Subject Business plan development for a start-up company Supervisor(s) Hannu Rossi ABSTRACT This study was commissioned by Häme University of Applied Sciences. The aim of the study was to come up with a business plan for developing the new product and starting a new company in Finland in the electric bicycle market. The main objectives of the study were: to collect and analyse suitable theoretical background, including business planning and product development theory as well as information on financial instruments available particularly in Finland. The second objective was to develop and conduct research based on the examined theory that will cover the most important issues on product development and funding. The third objective was to develop the idea in a way it will be clear to be presented to investors and mentors. The last objective was to accumulate from the outcomes of the first three objectives and to compose a holistic business plan. The theoretical concepts, which this research covers, include: business model generation including a business model canvas and a business model environment, the blue ocean strategy, the lean start-up approach, and the funding options for businesses. The research methods used were: literature research, consultations with potential and existing customers, attending presentations of start-up advisors and representatives of public funding. The main outcome of this work is a created business plan, financial calculations for the first product development stage and a financial roadmap.