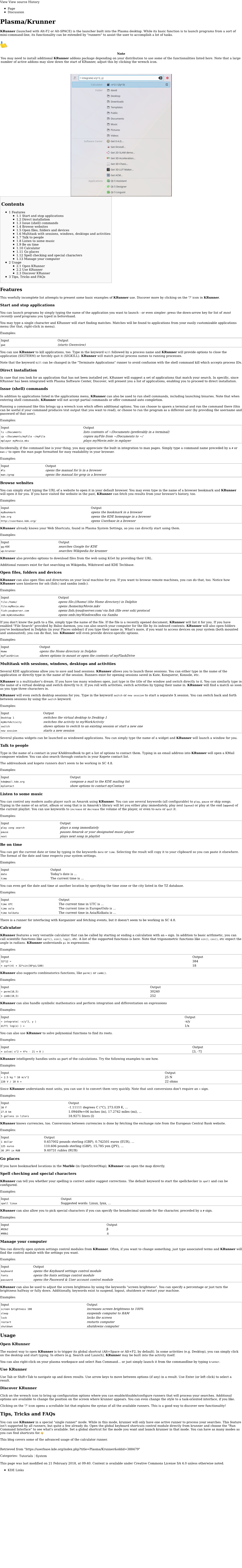
Plasma/Krunner
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Excerpts of Chapters From
Excerpts of Chapters from A Practical Guide to Ubuntu Linux® FOURTH EDITION Mark G. Sobell ISBN-13: 978-0-13-392731-3 CopyrightExcerpt © 2015 Mark G. Sobell Upper Saddle River, NJ • Boston • Indianapolis • San Francisco New York • Toronto • Montreal • London • Munich • Paris • Madrid Capetown • Sydney • Tokyo • Singapore • Mexico City Blank Excerpt 3 Step-by-Step Installation 3Chapter3 In This Chapter Objectives Booting Ubuntu and Running a After reading this chapter you should be able to: Live Session. 56 Run a live session and use gnome-disks to view and Automatic Boot Sequence . 56 change disk partitioning Running a Live Session. 59 Install Ubuntu from a live session Installing from a Live Session . 60 Install Ubuntu using the Server Image Installing from the Desktop Modify system behavior using boot parameters Boot Menu . 61Excerpt Modify partitions during installation The ubiquity Graphical Installer. 61 The ubiquity Advanced Partitioning List the requirement and considerations for a dual- Screen. 67 boot configuration Advanced Installation. 71 Modifying Boot Parameters (Options) . 75 debian-installer: The Ubuntu Textual Installer . 78 gnome-disks: The GNOME Disk Utility . 88 Setting Up a Dual-Boot System . 91 5555 56 Chapter 3 Step-by-Step Installation Chapter 2 covered planning the installation of Ubuntu: determining the requirements; planning the layout of the hard disk; obtaining the files you need for the installation, including how to download and burn or write Desktop and Server Images to installa- tion media; and collecting information about the system. This chapter focuses on installing Ubuntu. Frequently the installation is quite simple, especially if you have done a good job of planning. -

Netop Remote Control User's Guide
USER'S GUIDE 27 September 2017 Netop Remote Control User's Guide Copyright© 1981-2017 Netop Business Solutions A/S. All Rights Reserved. Portions used under license from third parties. Please send any comments to: Netop Business Solutions A/S Bregnerodvej 127 DK-3460 Birkerod Denmark E-mail: [email protected] Internet: www.netop.com Netop™ is a trademark of Netop Business Solutions A/S. All other products mentioned in this document are trademarks of their respective manufacturers. Netop Business Solutions A/S denies any and all responsibility for damages caused directly or indirectly as a result of using this document. The content of this document is subject to change without notice. Netop Business Solutions A/S retains the copyright to this document. The document is optimized for double-sided printing. 27 September 2017 Netop Remote Control User's Guide Contents 1 Overview ....................................................................................................................................................4 1.1 Remote Control modules ...............................................................................................................................................4 1.2 Security ...........................................................................................................................................4 1.3 Communication profiles ...............................................................................................................................................5 2 Managing Hosts ........................................................................................................................................6 -

Powerview Command Reference
PowerView Command Reference TRACE32 Online Help TRACE32 Directory TRACE32 Index TRACE32 Documents ...................................................................................................................... PowerView User Interface ............................................................................................................ PowerView Command Reference .............................................................................................1 History ...................................................................................................................................... 12 ABORT ...................................................................................................................................... 13 ABORT Abort driver program 13 AREA ........................................................................................................................................ 14 AREA Message windows 14 AREA.CLEAR Clear area 15 AREA.CLOSE Close output file 15 AREA.Create Create or modify message area 16 AREA.Delete Delete message area 17 AREA.List Display a detailed list off all message areas 18 AREA.OPEN Open output file 20 AREA.PIPE Redirect area to stdout 21 AREA.RESet Reset areas 21 AREA.SAVE Save AREA window contents to file 21 AREA.Select Select area 22 AREA.STDERR Redirect area to stderr 23 AREA.STDOUT Redirect area to stdout 23 AREA.view Display message area in AREA window 24 AutoSTOre .............................................................................................................................. -

PATACS Posts Newsletterofthe Potomacareatechnology and Computersociety
PATACS Posts Newsletterofthe PotomacAreaTechnology and ComputerSociety May 2014 www.patacs.org Page 1 Useful Bits & Pieces Entertaining Web Sites On occasion it can be fun to explore off-beat Web CboyluLmonrrisitn, PRo.toGmaarcsAornea Technology and Computer Society sites. Here are a few sites for your entertainment pleasure: Free Antivirus Software for Apple Computers • See http://www.dumblaws.com/. Did you know that in Virginia “No animal may be Whether to use antivirus software on Apple hunted on Sunday with the exception of computers has been a controversial issue for raccoons, which may be hunted until 2:00 years. Major providers such as Symantec, AM?” Well, now you know. Kaspersky, Panda and Trend-Micro offer products for a fee. In the table below is a list of • See http://www.funnytypos.com/. An amusing some free offerings for Macs. See collection of typos like “world famuos”, “no http://goo.gl/VA1iHz for a comprehensive list of smorking” and “free chicken stips with antivirus software for PCs, Macs, Linux, Unix, purchas”. smartphones, etc. Also search the term • See http://whitewhine.com/. Want to learn “antivirus” in Apple’s App Store for numerous what people are complaining about? For antimalware apps (free and for fee). example, “I hate it when I have money to spend and can’t find anything I want.” Poor baby! • See http://www.craigslist.org/about/best/all for offers voted best by Craiglist readers. For example: “I have 2 dozen goats I need to get rid of. I had no idea raising goats would be this hard. These little ***** keep eating all my wife's flowers and climbing on our **** cars. -

Kubuntu Desktop Guide
Kubuntu Desktop Guide Ubuntu Documentation Project <[email protected]> Kubuntu Desktop Guide by Ubuntu Documentation Project <[email protected]> Copyright © 2004, 2005, 2006 Canonical Ltd. and members of the Ubuntu Documentation Project Abstract The Kubuntu Desktop Guide aims to explain to the reader how to configure and use the Kubuntu desktop. Credits and License The following Ubuntu Documentation Team authors maintain this document: • Venkat Raghavan The following people have also have contributed to this document: • Brian Burger • Naaman Campbell • Milo Casagrande • Matthew East • Korky Kathman • Francois LeBlanc • Ken Minardo • Robert Stoffers The Kubuntu Desktop Guide is based on the original work of: • Chua Wen Kiat • Tomas Zijdemans • Abdullah Ramazanoglu • Christoph Haas • Alexander Poslavsky • Enrico Zini • Johnathon Hornbeck • Nick Loeve • Kevin Muligan • Niel Tallim • Matt Galvin • Sean Wheller This document is made available under a dual license strategy that includes the GNU Free Documentation License (GFDL) and the Creative Commons ShareAlike 2.0 License (CC-BY-SA). You are free to modify, extend, and improve the Ubuntu documentation source code under the terms of these licenses. All derivative works must be released under either or both of these licenses. This documentation is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AS DESCRIBED IN THE DISCLAIMER. Copies of these licenses are available in the appendices section of this book. Online versions can be found at the following URLs: • GNU Free Documentation License [http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.html] • Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 [http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/2.0/] Disclaimer Every effort has been made to ensure that the information compiled in this publication is accurate and correct. -

Fedora 14 User Guide
Fedora 14 User Guide Using Fedora 14 for common desktop computing tasks Fedora Documentation Project User Guide Fedora 14 User Guide Using Fedora 14 for common desktop computing tasks Edition 1.0 Author Fedora Documentation Project [email protected] Copyright © 2010 Red Hat, Inc. and others. The text of and illustrations in this document are licensed by Red Hat under a Creative Commons Attribution–Share Alike 3.0 Unported license ("CC-BY-SA"). An explanation of CC-BY-SA is available at http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0/. The original authors of this document, and Red Hat, designate the Fedora Project as the "Attribution Party" for purposes of CC-BY-SA. In accordance with CC-BY-SA, if you distribute this document or an adaptation of it, you must provide the URL for the original version. Red Hat, as the licensor of this document, waives the right to enforce, and agrees not to assert, Section 4d of CC-BY-SA to the fullest extent permitted by applicable law. Red Hat, Red Hat Enterprise Linux, the Shadowman logo, JBoss, MetaMatrix, Fedora, the Infinity Logo, and RHCE are trademarks of Red Hat, Inc., registered in the United States and other countries. For guidelines on the permitted uses of the Fedora trademarks, refer to https://fedoraproject.org/wiki/ Legal:Trademark_guidelines. Linux® is the registered trademark of Linus Torvalds in the United States and other countries. Java® is a registered trademark of Oracle and/or its affiliates. XFS® is a trademark of Silicon Graphics International Corp. or its subsidiaries in the United States and/or other countries. -

MX-19.2 Users Manual
MX-19.2 Users Manual v. 20200801 manual AT mxlinux DOT org Ctrl-F = Search this Manual Ctrl+Home = Return to top Table of Contents 1 Introduction...................................................................................................................................4 1.1 About MX Linux................................................................................................................4 1.2 About this Manual..............................................................................................................4 1.3 System requirements..........................................................................................................5 1.4 Support and EOL................................................................................................................6 1.5 Bugs, issues and requests...................................................................................................6 1.6 Migration............................................................................................................................7 1.7 Our positions......................................................................................................................8 1.8 Notes for Translators.............................................................................................................8 2 Installation...................................................................................................................................10 2.1 Introduction......................................................................................................................10 -

Download File from Terminal Linux 5 Ways to Open a Terminal in Ubuntu
download file from terminal linux 5 Ways to Open a Terminal in Ubuntu. Why would one want to use a command-line in Linux? Get to know the reasons and also the ways you can launch the Terminal on your Ubuntu PC. You can use keyboard shortcuts as well as a few GUI ways, as described in this guide. E ven though Ubuntu supports many applications with amazing Graphical User Interfaces (GUI), there are always reasons why users prefer using the Terminal to perform different tasks. Here are several reasons why you might need to use the Ubuntu command-line. Reasons to use command-line on Linux. Linux Terminal gives you access to some of the powerful Linux commands to perform actions you can’t do with GUI applications, for instance, you can even kill frozen GUI using command-line. The ‘apt-get’ package manager lets users install applications quicker by running a set of commands. Terminal is also an essential utility for developers working with different programming languages. It is easier to compile and run programs via the Ubuntu command-line. There are some powerful Linux applications meant to run on the Terminal. Some even require you to configure them in the Terminal. One more reason why the Terminal is useful is that even most solutions you find online concerning the challenges you might face working with Ubuntu, require you to use the Terminal. Ways to open a Terminal on Ubuntu. We will show five ways that you can use to launch the Terminal and carry out your tasks easily. -

LESSON 2 ESSENTIAL COMMANDS Lesson 2: Essential Commands
LESSON 2 ESSENTIAL COMMANDS Lesson 2: Essential Commands WARNING The Hacker Highschool Project is a learning tool and as with any learning tool there are dangers. Some lessons, if abused, may result in physical injury. Some additional dangers may also exist where there is not enough research on possible effects of emanations from particular technologies. Students using these lessons should be supervised yet encouraged to learn, try, and do. However ISECOM cannot accept responsibility for how any information herein is abused. The following lessons and workbooks are open and publicly available under the following terms and conditions of ISECOM: All works in the Hacker Highschool Project are provided for non-commercial use with elementary school students, junior high school students, and high school students whether in a public institution, private institution, or a part of home-schooling. These materials may not be reproduced for sale in any form. The provision of any class, course, training, or camp with these materials for which a fee is charged is expressly forbidden without a license, including college classes, university classes, trade-school classes, summer or computer camps, and similar. To purchase a license, visit the LICENSE section of the HHS web page at http://www.hackerhighschool.org/licensing.html. The Hacker Highschool Project Project is an open community effort and if you find value in this project, we ask that you support us through the purchase of a license, a donation, or sponsorship. 2 Lesson 2: Essential Commands Table -

Nuitka User Manual Contents
Nuitka User Manual Contents Overview 1 Usage 1 Requirements 1 Command Line 3 Installation 3 License 3 Tutorial Setup and build on Windows 3 Setup 4 Install Python 4 Install Nuitka 4 Write some code and test 4 Create a folder for the Python code 4 Test your program 4 Build it using 4 Run it 5 Distribute 5 Use Cases 5 Use Case 1 - Program compilation with all modules embedded 5 Use Case 2 - Extension Module compilation 6 Use Case 3 - Package compilation 7 Use Case 4 - Program Distribution 7 Tweaks 8 Icons 8 Splash screen 9 Typical Problems 9 Memory issues and compiler bugs 9 Avoid 32 bit C compiler/assembler memory limits 9 Use LTO compilation or not 10 Switch the C compiler to clang 10 Add a larger swap file to your embedded Linux 10 Limit the amount of compilation jobs 10 Dynamic sys.path 10 Missing data files in standalone 10 Missing DLLs in standalone 10 Dependency creep in standalone 10 Onefile: Finding files 11 Windows Programs without console give no errors 11 Tips 11 Nuitka Options in the code 11 Python command line flags 12 Caching compilation results 12 Control where Caches live 12 Runners 12 Fastest C Compilers 12 Unexpected Slowdowns 13 Standalone executables and dependencies 13 Windows errors with resources 13 Windows standalone program redistribuation 13 Detecting Nuitka at run time 14 Performance 14 pystone results 14 Where to go next 14 Follow me on Twitter 14 Report issues or bugs 14 Word of Warning 15 Join Nuitka 15 Donations 15 Unsupported functionality 15 The co_code attribute of code objects 15 PDB 16 Optimization 16 -

Q4OS User Manual
Q4OS User Guide Version 0.3 Table of Contents Q4OS setup and using................................................................................................................................5 Introduction...........................................................................................................................................5 Testing...................................................................................................................................................5 Live CD............................................................................................................................................5 In Virtualbox.....................................................................................................................................5 Installation.............................................................................................................................................5 Live media........................................................................................................................................5 Installation CD..................................................................................................................................5 Postinstall steps.................................................................................................................................6 Wireless network setup..........................................................................................................................6 Print and Scan........................................................................................................................................6 -

The Krusader Handbook the Krusader Handbook
The Krusader Handbook The Krusader Handbook 2 Contents 1 Introduction 14 1.1 Package description . 14 1.2 Welcome to Krusader! . 14 2 Features 17 3 User Interface 21 3.1 OFM User Interface . 21 3.2 Krusader Main Window . 21 3.3 Toolbars . 21 3.3.1 Main Toolbar . 21 3.3.2 Job Toolbar . 23 3.3.3 Actions Toolbar . 23 3.3.4 Location Toolbar . 23 3.3.5 Panel Toolbar . 23 3.4 Panels . 24 3.4.1 List Panel . 24 3.4.2 Sidebar . 25 3.4.3 Folder History . 26 3.5 Command Line / Terminal Emulator . 26 3.5.1 Command Line . 26 3.5.2 Terminal Emulator . 27 3.6 Function (FN) Keys Bar . 27 3.7 Folder Tabs . 28 3.8 Buttons . 28 4 Basic Functions 29 4.1 Controls . 29 4.1.1 General . 29 4.1.2 Moving Around . 29 4.1.3 Selecting . 30 4.1.4 Executing Commands . 30 4.1.5 Quick search . 31 4.1.6 Quick filter . 31 The Krusader Handbook 4.1.7 Quick select . 31 4.1.8 Context Menu . 31 4.2 Basic File Management . 32 4.2.1 Executing Files . 32 4.2.2 Copying and Moving . 32 4.2.3 Queue manager . 32 4.2.4 Deleting - move to Plasma Trash . 33 4.2.5 Shred Files . 33 4.2.6 Renaming Files, Creating Directories and Link Handling . 33 4.2.7 Viewing and Editing files . 33 4.3 Archive Handling . 34 4.3.1 Browsing Archives . 34 4.3.2 Unpack Files .