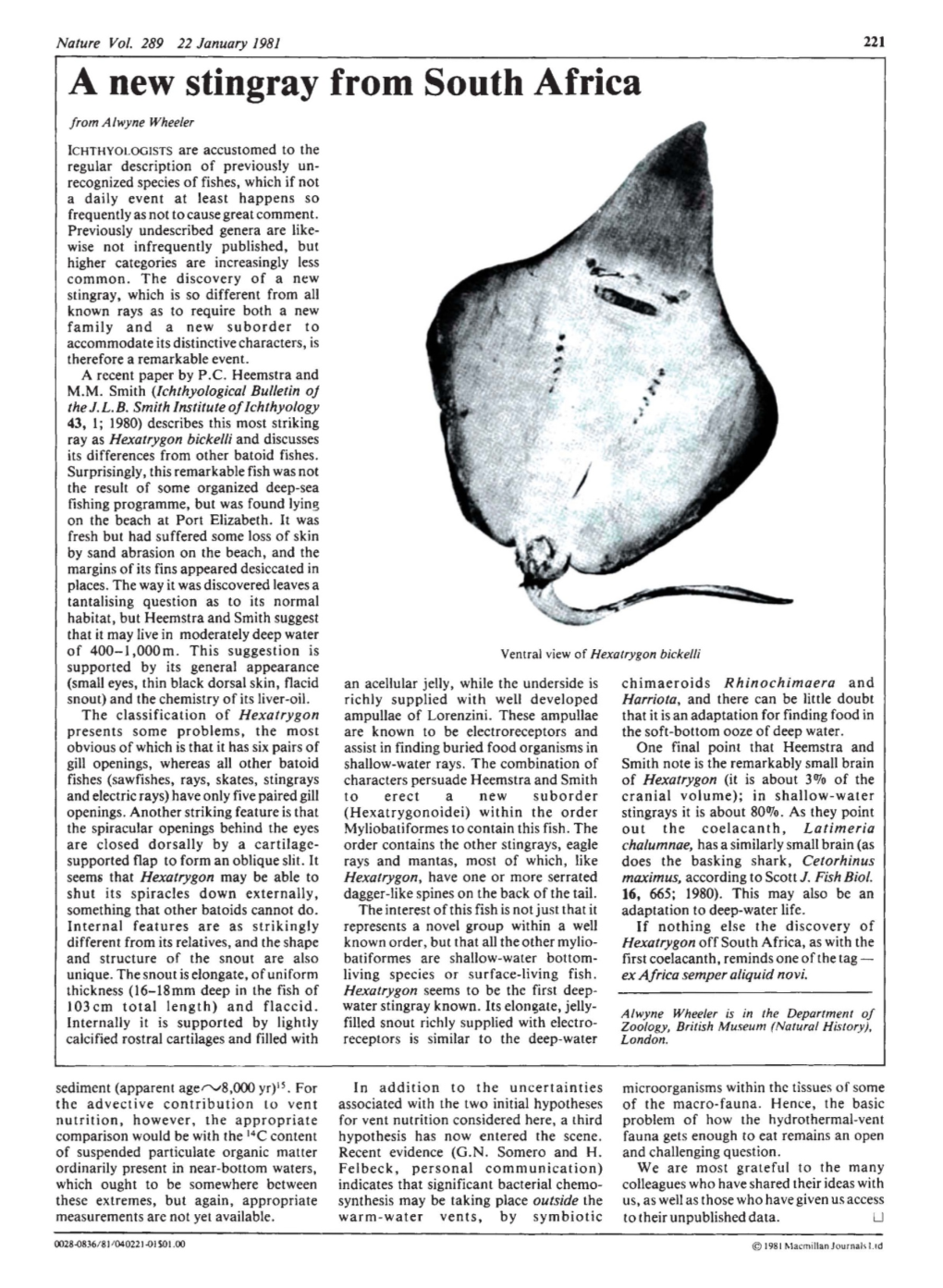
A New Stingray from South Africa
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Coral Reef Monitoring in Kofiau and Boo Islands Marine Protected Area, Raja Ampat, West Papua. 2009—2011
August 2012 Indo-Pacific Division Indonesia Report No 6/12 Coral Reef Monitoring in Kofiau and Boo Islands Marine Protected Area, Raja Ampat, West Papua. 2009—2011 Report Compiled By: Purwanto, Muhajir, Joanne Wilson, Rizya Ardiwijaya, and Sangeeta Mangubhai August 2012 Indo-Pacific Division Indonesia Report No 6/12 Coral Reef Monitoring in Kofiau and Boo Islands Marine Protected Area, Raja Ampat, West Papua. 2009—2011 Report Compiled By: Purwanto, Muhajir, Joanne Wilson, Rizya Ardiwijaya, and Sangeeta Mangubhai Published by: TheNatureConservancy,Indo-PacificDivision Purwanto:TheNatureConservancy,IndonesiaMarineProgram,Jl.Pengembak2,Sanur,Bali, Indonesia.Email: [email protected] Muhajir: TheNatureConservancy,IndonesiaMarineProgram,Jl.Pengembak2,Sanur,Bali, Indonesia.Email: [email protected] JoanneWilson: TheNatureConservancy,IndonesiaMarineProgram,Jl.Pengembak2,Sanur,Bali, Indonesia. RizyaArdiwijaya:TheNatureConservancy,IndonesiaMarineProgram,Jl.Pengembak2,Sanur, Bali,Indonesia.Email: [email protected] SangeetaMangubhai: TheNatureConservancy,IndonesiaMarineProgram,Jl.Pengembak2, Sanur,Bali,Indonesia.Email: [email protected] Suggested Citation: Purwanto,Muhajir,Wilson,J.,Ardiwijaya,R.,Mangubhai,S.2012.CoralReefMonitoringinKofiau andBooIslandsMarineProtectedArea,RajaAmpat,WestPapua.2009-2011.TheNature Conservancy,Indo-PacificDivision,Indonesia.ReportN,6/12.50pp. © 2012012012201 222 The Nature Conservancy AllRightsReserved.Reproductionforanypurposeisprohibitedwithoutpriorpermission. AllmapsdesignedandcreatedbyMuhajir. CoverPhoto: -

Chondrichthyes: Dasyatidae)
1 Ichthyological Exploration of Freshwaters/IEF-1089/pp. 1-6 Published 16 February 2019 LSID: http://zoobank.org/urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:DFACCD8F-33A9-414C-A2EC-A6DA8FDE6BEF DOI: http://doi.org/10.23788/IEF-1089 Contemporary distribution records of the giant freshwater stingray Urogymnus polylepis in Borneo (Chondrichthyes: Dasyatidae) Yuanita Windusari*, Muhammad Iqbal**, Laila Hanum*, Hilda Zulkifli* and Indra Yustian* Stingrays (Dasyatidae) are found in marine (con- species entering, or occurring in freshwater. For tinental, insular shelves and uppermost slopes, example, Fluvitrygon oxyrhynchus and F. signifer one oceanic species), brackish and freshwater, and were only known from five or fewer major riverine are distributed across tropical to warm temperate systems (Compagno, 2016a-b; Last et al., 2016a), waters of the Atlantic, Indian and Pacific oceans though recent surveys yielded a single record of (Nelson et al., 2016). Only a small proportion of F. oxyrhynchus and ten records of F. signifier in the dasyatid rays occur in freshwater, and include Musi drainage, South Sumatra, indicating that obligate freshwater species (those found only in both species are more widely distributed than freshwater) and euryhaline species (those that previously expected (Iqbal et al., 2017, 2018). move between freshwater and saltwater) (Last et Particularly, the dasyatid fauna of Borneo al., 2016a). Recently, a total of 89 species of Dasy- includes the giant freshwater stingray Urogymnus atidae has been confirmed worldwide (Last et al., polylepis. The occurrence of U. polylepis in Borneo 2016a), including 14 species which are known to has been reported from Sabah and Sarawak in enter or live permanently in freshwater habitats of Malaysia and the Mahakam basin in Kaliman- Southeast Asia [Brevitrygon imbricata, Fluvitrygon tan of Indonesia (Monkolprasit & Roberts, 1990; kittipongi, F. -

Electrosensory Pore Distribution and Feeding in the Basking Shark Cetorhinus Maximus (Lamniformes: Cetorhinidae)
Vol. 12: 33–36, 2011 AQUATIC BIOLOGY Published online March 3 doi: 10.3354/ab00328 Aquat Biol NOTE Electrosensory pore distribution and feeding in the basking shark Cetorhinus maximus (Lamniformes: Cetorhinidae) Ryan M. Kempster*, Shaun P. Collin The UWA Oceans Institute and the School of Animal Biology, The University of Western Australia, 35 Stirling Highway, Crawley, Western Australia 6009, Australia ABSTRACT: The basking shark Cetorhinus maximus is the second largest fish in the world, attaining lengths of up to 10 m. Very little is known of its sensory biology, particularly in relation to its feeding behaviour. We describe the abundance and distribution of ampullary pores over the head and pro- pose that both the spacing and orientation of electrosensory pores enables C. maximus to use passive electroreception to track the diel vertical migrations of zooplankton that enable the shark to meet the energetic costs of ram filter feeding. KEY WORDS: Ampullae of Lorenzini · Electroreception · Filter feeding · Basking shark Resale or republication not permitted without written consent of the publisher INTRODUCTION shark Rhincodon typus and the megamouth shark Megachasma pelagios, which can attain lengths of up Electroreception is an ancient sensory modality that to 14 and 6 m, respectively (Compagno 1984). These 3 has evolved independently across the animal kingdom filter-feeding sharks are among the largest living in multiple groups (Scheich et al. 1986, Collin & White- marine vertebrates (Compagno 1984) and yet they are head 2004). Repeated independent evolution of elec- all able to meet their energetic costs through the con- troreception emphasises the importance of this sense sumption of tiny zooplankton. -

Stingray Injuries
Stingray Injuries FINDLAY E. RUSSELL, M.D. inflicted by stingrays are com¬ the integumentary sheath surrounding the INJURIESmon in several areas of the coastal waters spine is ruptured and the venom escapes into of North America (1-4). Approximately 750 the victim's tissues. In withdrawing the spine, people a year along our coasts are stung by the integumentary sheath may be torn free and these elasmobranchs. The largest number of remain in the wound. stings are reported from southern California, Unlike the injuries inflicted by many venom¬ the Gulf of California, the Gulf of Mexico, and ous animals, wounds produced by the stingray the south Atlantic coast (5). may be large and severely lacerated, requiring Of 1,097 stingray injuries reported over a 5- extensive debridement and surgical closure. A year period in the United States (5, tf), 232 sting no wider than 5 mm. may produce a were seen by a physician at some time during wound 3.5 cm. long (#), and larger stings may the course of the recovery of the victim. Sixty- produce wounds 7 inches long (7). Occasion¬ two patients were hospitalized; the majority of ally, the sting itself may be broken off in the these required surgical closure of their wounds wound. or treatment for secondary infection, or both. The sting, or caudal spine, is a bilaterally ser¬ At least 10 of the 62 victims were hospitalized rated dentinal structure located on the dorsal for treatment for overexuberant first aid care. surface of the animal's tail. The sharp serra¬ Only eight patients were hospitalized for the tions are curved cephalically and as such are treatment of the systemic effects produced by responsible for the lacerating effects as the sting the venom. -

Biology, Husbandry, and Reproduction of Freshwater Stingrays
Biology, husbandry, and reproduction of freshwater stingrays. Ronald G. Oldfield University of Michigan, Department of Ecology and Evolutionary Biology Museum of Zoology, 1109 Geddes Ave., Ann Arbor, MI 48109 U.S.A. E-mail: [email protected] A version of this article was published previously in two parts: Oldfield, R.G. 2005. Biology, husbandry, and reproduction of freshwater stingrays I. Tropical Fish Hobbyist. 53(12): 114-116. Oldfield, R.G. 2005. Biology, husbandry, and reproduction of freshwater stingrays II. Tropical Fish Hobbyist. 54(1): 110-112. Introduction In the freshwater aquarium, stingrays are among the most desired of unusual pets. Although a couple species have been commercially available for some time, they remain relatively uncommon in home aquariums. They are often avoided by aquarists due to their reputation for being fragile and difficult to maintain. As with many fishes that share this reputation, it is partly undeserved. A healthy ray is a robust animal, and problems are often due to lack of a proper understanding of care requirements. In the last few years many more species have been exported from South America on a regular basis. As a result, many are just recently being captive bred for the first time. These advances will be making additional species of freshwater stingray increasingly available in the near future. This article answers this newly expanded supply of wild-caught rays and an anticipated increased The underside is one of the most entertaining aspects of a availability of captive-bred specimens by discussing their stingray. In an aquarium it is possible to see the gill slits and general biology, husbandry, and reproduction in order watch it eat, as can be seen in this Potamotrygon motoro. -

Class Wars: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes Dominance in Chesapeake Bay, 2002-2012
Class Wars: Chondrichthyes and Osteichthyes dominance in Chesapeake Bay, 2002-2012. 01 July 2013 Introduction The objective of this analysis was to demonstrate a possible changing relationship between two Classes of fishes, Osteichthyes (the bony fishes) and Chondrichthyes (the cartilaginous fishes) in Chesapeake Bay based on 11 years of monitoring. If any changes between the two Classes appeared to be significant, either statistically or anecdotally, the data were explored further in an attempt to explain the variation. The Class Osteichthyes is characterized by having a skeleton made of bone and is comprised of the majority of fish species worldwide, while the Chondrichthyes skeleton is made of cartilage and is represented by the sharks, skates, and rays (the elasmobranch fishes) and chimaeras1. Many shark species are generally categorized as apex predators, while skates and rays and some smaller sharks can be placed into the mesopredator functional group (Myers et al., 2007). By definition, mesopredators prey upon a significant array of lower trophic groups, but also serve as the prey base for apex predators. Global demand for shark and consequential shark fishing mortality, estimated at 97 million sharks in 2010 (Worm et al., 2013), is hypothesized to have contributed to the decline of these apex predators in recent years (Baum et al., 2003 and Fowler et al., 2005), which in turn is suggested to have had a cascading effect on lower trophic levels—an increase in mesopredators and subsequent decrease in the prey base (Myers et al., 2007). According to 10 years of trawl survey monitoring of Chesapeake Bay, fish species composition of catches has shown a marked change over the years (Buchheister et al., 2013). -

Ray by Design Stingray
Sponsored by Blue Lagoon Island & Vendors from Nassau Dolphin Encounters - Project BEACH Contest Deadline: March 4th, 2016 Beautifully graceful underwater, Southern The unique hunting abilities of a stingray – stingrays choose the turquoise waters of digging, sucking, and crushing – also benefit The Bahamas as their home. Like many other reef animals looking for lunch. These other reef animals, stingrays play an gentle winged fish are key predators in a important role in our marine ecosystem. healthy, marine habitat, so it’s time to “Rays the Roof” and start protecting our stingrays! When a stingray hunts along the bottom, it mixes the sand and stirs up hidden Learn more about this unique animal and the creatures in search of food. Sea birds challenges it faces from the MEPC 2016 Info will often follow the path of a stingray Sheet and express your feelings through art hoping to make a meal from the animals in the Marine Education Poster Contest 2016. disturbed by the ray. Call for a FREE Marine Assembly Program at your school to introduce you to the marine topic “Rays the Roof!” Ray By Design Southern stingrays can be gills As masters of disguise Stingray 101 found in tropical and (camouflage), stingrays can subtropical waters of the completely bury themselves in Animal Type: Boneless Fish southern Atlantic Ocean, the sand or soft seafloor. Caribbean and Gulf of When swimming, if viewed Diet: Carnivore Mexico. These rays have been ventral side mouth from below, the bright belly Ave. Lifespan: 15-25 years found in depths of up to 180 of the ray matches the bright feet and are usually found Unlike sharks, rays crush their sky above, helping to escape Maximum Width: 4 feet roaming the ocean alone or in food -- prey such as conch, large predatory fish such as Maximum Weight: 200+ lbs. -

Full Text in Pdf Format
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 164: 263-271,1998 Published April 9 Mar Ecol Prog Ser Intraspecific and interspecific relationships between host size and the abundance of parasitic larval gnathiid isopods on coral reef fishes Alexandra S. Grutter 'l*, Robert poulin2 'Department of Parasitology, The University of Queensland. Brisbane, Queensland 4072, Australia 'Department of Zoology, University of Otago. PO Box 56. Dunedin. New Zealand ABSTRACT: Parasitic gnathud isopod larvae on coral reef teleosts and elasmobranchs were quantified at Lizard and Heron Islands (Great Barrier Reef), and Moreton Bay, Australia. The relationship between gnathlid abundance and host size was examined across and within species. Of the 56 species examined. 70 % had gnathiids, with counts ranging from 1 to 200 per fish and the elasmobranchs hav- ing the highest numbers. Pomacentrids rarely had gnathiids. In contrast, most labrids had gnathiids. Gnathiid abundance was positively correlated with host size in the species Chlorurus sordidus, Ctenochaetus stnatus, Hernigyrnnus melapterus, Siganus dollatus, and Thalassorna lunare, but not for Scolopsis b~lineatus.Mean gnathlid abundance per host species also correlated with host size across species, even after controlling for the potential confounding effects of uneven sampling effort and host phylogeny Thus host size explains much of the intraspecific and interspecific variation In gnathiid abundance on fish. KEY WORDS: Gnathiidae . Ectoparasites . Coral reef fish . Host-parasite interactions . Fish size . Great Barrier Reef INTRODUCTION gnathiids on fish (Grutter 1996a). When present in 'large' numbers (Paperna & Por 1977) and when fish Until recently, there was little evidence that para- have 'around a hundred' (Mugridge & Stallybrass sites were important in fish cleaning behavior (Losey 1983),gnathiids can cause fish mortality in captive fish 1987), however, current studies on the Great Barrier (Paperna & Por 1977). -

Estimating Taxonomic Diversity Using Centrum Growth Profiles and Stinger Morphology of 36 Million Year Old Stingrays from North Dakota
Columbus State University CSU ePress Theses and Dissertations Student Publications 5-2020 Estimating Taxonomic Diversity Using Centrum Growth Profiles and Stinger Morphology of 36 Million Year Old Stingrays From North Dakota Persia S. Tillman Follow this and additional works at: https://csuepress.columbusstate.edu/theses_dissertations Part of the Biology Commons Recommended Citation Tillman, Persia S., "Estimating Taxonomic Diversity Using Centrum Growth Profiles and Stinger Morphology of 36 Million Year Old Stingrays From North Dakota" (2020). Theses and Dissertations. 382. https://csuepress.columbusstate.edu/theses_dissertations/382 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Student Publications at CSU ePress. It has been accepted for inclusion in Theses and Dissertations by an authorized administrator of CSU ePress. COLUMBUS STATE UNIVERSITY ESTIMATING TAXONOMIC DIVERSITY USING CENTRUM GROWTH PROFILES AND STINGER MORPHOLOGY OF 36 MILLION YEAR OLD STINGRAYS FROM NORTH DAKOTA A THESIS SUBMITTED TO THE HONORS COLLEGE IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR HONORS IN THE DEGREE OF BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY COLLEGE OF LETTERS AND SCIENCES BY Persia S. Tillman Copyright © 2020 Persia S. Tillman All Rights Reserved. ESTIMATING TAXONOMIC DIVERSITY USING CENTRUM GROWTH PROFILES AND STINGER MORPHOLOGY OF 36 MILLION YEAR OLD STINGRAYS FROM NORTH DAKOTA By Persia S. Tillman Coauthors: Michael Newbrey, Clint Boyd, and Todd Cook A Thesis Submitted to the HONORS COLLEGE In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for Honors in the Degree of BACHELOR OF SCIENCE DEPARTMENT OF BIOLOGY COLLEGE OF LETTERS & SCIENCES Approved by Dr. Michael Newbrey, Committee Chair Dr. Daniel Holt, Committee Member Dr. Cindy Ticknor, Committee Member & Dean Columbus State University May 2020 ABSTRACT Stingrays are a diverse and popular group of vertebrates; however, nothing is known about the relationships between growth biology and climate change. -

Sensory Biology of Aquatic Animals
Jelle Atema Richard R. Fay Arthur N. Popper William N. Tavolga Editors Sensory Biology of Aquatic Animals Springer-Verlag New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo JELLE ATEMA, Boston University Marine Program, Marine Biological Laboratory, Woods Hole, Massachusetts 02543, USA Richard R. Fay, Parmly Hearing Institute, Loyola University, Chicago, Illinois 60626, USA ARTHUR N. POPPER, Department of Zoology, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA WILLIAM N. TAVOLGA, Mote Marine Laboratory, Sarasota, Florida 33577, USA The cover Illustration is a reproduction of Figure 13.3, p. 343 of this volume Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Sensory biology of aquatic animals. Papers based on presentations given at an International Conference on the Sensory Biology of Aquatic Animals held, June 24-28, 1985, at the Mote Marine Laboratory in Sarasota, Fla. Bibliography: p. Includes indexes. 1. Aquatic animals—Physiology—Congresses. 2. Senses and Sensation—Congresses. I. Atema, Jelle. II. International Conference on the Sensory Biology - . of Aquatic Animals (1985 : Sarasota, Fla.) QL120.S46 1987 591.92 87-9632 © 1988 by Springer-Verlag New York Inc. x —• All rights reserved. This work may not be translated or copied in whole or in part without the written permission of the publisher (Springer-Verlag, 175 Fifth Avenue, New York 10010, U.S.A.), except for brief excerpts in connection with reviews or scholarly analysis. Use in connection with any form of Information storage and retrieval, electronic adaptation, Computer Software, or by similar or dissimilar methodology now known or hereafter developed is forbidden. The use of general descriptive names, trade names, trademarks, etc. -

Color and Learn: Sharks of Massachusetts!
COLOR AND LEARN: SHARKS OF MASSACHUSETTS! This book belongs to: WHAT IS A SHARK? Sharks are fish that have vertebrae (skeletons) made ofcartilage instead of bones. Sharks come in all different shapes, sizes, and colors. Sharks have different kinds of teeth, feeding patterns, swimming styles, and behaviors that help them to survive in all different kinds of aquatic habitats! Can you label the different parts of a shark? second dorsal fin caudal (tail) fin pelvic fin gills anal fin pectoral fin nostril mouth eye Dorsal fin There are around 500 species of sharks in the world. Massachusetts coastal waters provide ideal habitat for several kinds of Atlantic Ocean sharks that visit our waters each season! Massachusetts HOW LONG HAVE SHARKS BEEN ON EARTH? Sharks have been on Earth since before the dinosaurs! Scientists learn about early sharks by studying fossils. Shark fossils can tell us a lot about what food the shark ate, what their habitat looked like, and how they are related to other sharks. The ancient sharks on this page are extinct. Acanthodes (ah-can-tho-deez), or “spiny shark,” was the first fish to have a cartilage skeleton! Cladoselache (clay-do-sel-ah-kee) had a body and tail shaped for swimming fast. It did not have the same kind of skin that we see in modern sharks today. Stethacanthus (stef-ah-can-thus), or “anvil shark”, had a dorsal fin shaped like an ironing board! 450 370 360 200 145 60 6.5 MILLIONS OF YEARS AGO DINOSAURS EVOLVE WHAT ARE “MODERN” SHARKS? “Modern” sharks are species that have body parts (both inside and out!) that can be found on sharks living today. -

Intrinsic Vulnerability in the Global Fish Catch
The following appendix accompanies the article Intrinsic vulnerability in the global fish catch William W. L. Cheung1,*, Reg Watson1, Telmo Morato1,2, Tony J. Pitcher1, Daniel Pauly1 1Fisheries Centre, The University of British Columbia, Aquatic Ecosystems Research Laboratory (AERL), 2202 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia V6T 1Z4, Canada 2Departamento de Oceanografia e Pescas, Universidade dos Açores, 9901-862 Horta, Portugal *Email: [email protected] Marine Ecology Progress Series 333:1–12 (2007) Appendix 1. Intrinsic vulnerability index of fish taxa represented in the global catch, based on the Sea Around Us database (www.seaaroundus.org) Taxonomic Intrinsic level Taxon Common name vulnerability Family Pristidae Sawfishes 88 Squatinidae Angel sharks 80 Anarhichadidae Wolffishes 78 Carcharhinidae Requiem sharks 77 Sphyrnidae Hammerhead, bonnethead, scoophead shark 77 Macrouridae Grenadiers or rattails 75 Rajidae Skates 72 Alepocephalidae Slickheads 71 Lophiidae Goosefishes 70 Torpedinidae Electric rays 68 Belonidae Needlefishes 67 Emmelichthyidae Rovers 66 Nototheniidae Cod icefishes 65 Ophidiidae Cusk-eels 65 Trachichthyidae Slimeheads 64 Channichthyidae Crocodile icefishes 63 Myliobatidae Eagle and manta rays 63 Squalidae Dogfish sharks 62 Congridae Conger and garden eels 60 Serranidae Sea basses: groupers and fairy basslets 60 Exocoetidae Flyingfishes 59 Malacanthidae Tilefishes 58 Scorpaenidae Scorpionfishes or rockfishes 58 Polynemidae Threadfins 56 Triakidae Houndsharks 56 Istiophoridae Billfishes 55 Petromyzontidae