(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2015/0254416 A1 Shih (43) Pub
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
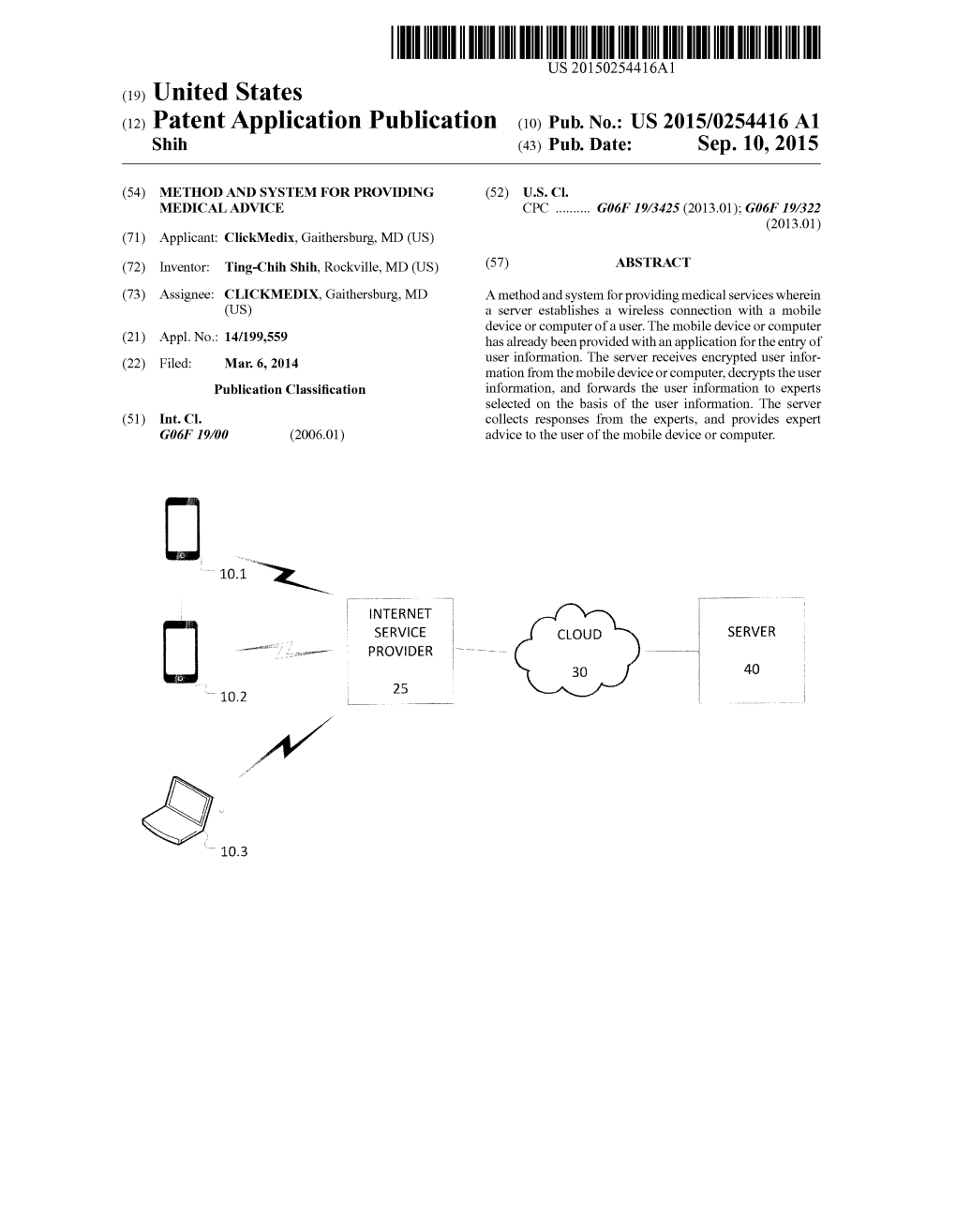
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Multiprocessing in Mobile Platforms: the Marketing and the Reality
Multiprocessing in Mobile Platforms: the Marketing and the Reality Marco Cornero, Andreas Anyuru ST-Ericsson Introduction During the last few years the mobile platforms industry has aggressively introduced multiprocessing in response to the ever increasing performance demanded by the market. Given the highly competitive nature of the mobile industry, multiprocessing has been adopted as a marketing tool. This highly visible, differentiating feature is used to pass the oversimplified message that more processors mean better platforms and performance. The reality is much more complex, because several interdependent factors are at play in determining the efficiency of multiprocessing platforms (such as the effective impact on software performance, chip frequency, area and power consumption) with the number of processors impacting only partially the overall balance, and with contrasting effects linked to the underlying silicon technologies. In this article we illustrate and compare the main technological options available in multiprocessing for mobile platforms, highlighting the synergies between multiprocessing and the disruptive FD-SOI silicon technology used in the upcoming ST-Ericsson products. We will show that compared to personal computers (PCs), the performance of single-processors in mobile platforms is still growing and how, from a software performance perspective, it is more profitable today to focus on faster dual-core rather than slower quad-core processors. We will also demonstrate how FD-SOI benefits dual-core processors even more by providing higher frequency for the same power consumption, together with a wider range of energy efficient operating modes. All of this results in a simpler, cheaper and more effective solution than competing homogeneous and heterogeneous quad-processors. -

Stochastic Modeling and Performance Analysis of Multimedia Socs
Stochastic Modeling and Performance Analysis of Multimedia SoCs Balaji Raman, Ayoub Nouri, Deepak Gangadharan, Marius Bozga, Ananda Basu, Mayur Maheshwari, Jérôme Milan, Axel Legay, Saddek Bensalem, Samarjit Chakraborty To cite this version: Balaji Raman, Ayoub Nouri, Deepak Gangadharan, Marius Bozga, Ananda Basu, et al.. Stochastic Modeling and Performance Analysis of Multimedia SoCs. SAMOS XIII - Embedded Computer Sys- tems: Architectures, Modeling, and Simulation, Jul 2013, Agios konstantinos, Samos Island, Greece. pp.145-154, 10.1109/SAMOS.2013.6621117. hal-00878094 HAL Id: hal-00878094 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00878094 Submitted on 29 Oct 2013 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Stochastic Modeling and Performance Analysis of Multimedia SoCs Balaji Raman1, Ayoub Nouri1, Deepak Gangadharan2, Marius Bozga1, Ananda Basu1, Mayur Maheshwari1, Jerome Milan3, Axel Legay4, Saddek Bensalem1, and Samarjit Chakraborty5 1 VERIMAG, France, 2 Technical Univeristy of Denmark, 3 Ecole Polytechnique, France, 4 INRIA Rennes, France, 5 Technical University of Munich, Germany. E-mail: [email protected] Abstract—Quality of video and audio output is a design-time to estimate buffer size for an acceptable output quality. The constraint for portable multimedia devices. -

FAN53525 3.0A, 2.4Mhz, Digitally Programmable Tinybuck® Regulator
FAN53525 — 3.0 A, 2.4 MHz, June 2014 FAN53525 3.0A, 2.4MHz, Digitally Programmable TinyBuck® Regulator Digitally Programmable TinyBuck Digitally Features Description . Fixed-Frequency Operation: 2.4 MHz The FAN53525 is a step-down switching voltage regulator that delivers a digitally programmable output from an input . Best-in-Class Load Transient voltage supply of 2.5 V to 5.5 V. The output voltage is 2 . Continuous Output Current Capability: 3.0 A programmed through an I C interface capable of operating up to 3.4 MHz. 2.5 V to 5.5 V Input Voltage Range Using a proprietary architecture with synchronous . Digitally Programmable Output Voltage: rectification, the FAN53525 is capable of delivering 3.0 A - 0.600 V to 1.39375 V in 6.25 mV Steps continuous at over 80% efficiency, maintaining that efficiency at load currents as low as 10 mA. The regulator operates at Programmable Slew Rate for Voltage Transitions . a nominal fixed frequency of 2.4 MHz, which reduces the . I2C-Compatible Interface Up to 3.4 Mbps value of the external components to 330 nH for the output inductor and as low as 20 µF for the output capacitor. PFM Mode for High Efficiency in Light Load . Additional output capacitance can be added to improve . Quiescent Current in PFM Mode: 50 µA (Typical) regulation during load transients without affecting stability, allowing inductance up to 1.2 µH to be used. Input Under-Voltage Lockout (UVLO) ® At moderate and light loads, Pulse Frequency Modulation Regulator Thermal Shutdown and Overload Protection . (PFM) is used to operate in Power-Save Mode with a typical . -

An Emerging Architecture in Smart Phones
International Journal of Electronic Engineering and Computer Science Vol. 3, No. 2, 2018, pp. 29-38 http://www.aiscience.org/journal/ijeecs ARM Processor Architecture: An Emerging Architecture in Smart Phones Naseer Ahmad, Muhammad Waqas Boota * Department of Computer Science, Virtual University of Pakistan, Lahore, Pakistan Abstract ARM is a 32-bit RISC processor architecture. It is develop and licenses by British company ARM holdings. ARM holding does not manufacture and sell the CPU devices. ARM holding only licenses the processor architecture to interested parties. There are two main types of licences implementation licenses and architecture licenses. ARM processors have a unique combination of feature such as ARM core is very simple as compare to general purpose processors. ARM chip has several peripheral controller, a digital signal processor and ARM core. ARM processor consumes less power but provide the high performance. Now a day, ARM Cortex series is very popular in Smartphone devices. We will also see the important characteristics of cortex series. We discuss the ARM processor and system on a chip (SOC) which includes the Qualcomm, Snapdragon, nVidia Tegra, and Apple system on chips. In this paper, we discuss the features of ARM processor and Intel atom processor and see which processor is best. Finally, we will discuss the future of ARM processor in Smartphone devices. Keywords RISC, ISA, ARM Core, System on a Chip (SoC) Received: May 6, 2018 / Accepted: June 15, 2018 / Published online: July 26, 2018 @ 2018 The Authors. Published by American Institute of Science. This Open Access article is under the CC BY license. -

Sitara™ Am57x Processor with Dual ARM® Cortex®-A15 Cores
Sitara™ AM57x processor with dual ARM® Cortex®-A15 cores In today’s industrial automation market, (PLCs) and industrial computers consumers are seeing an evolution to human machine interface (HMI), that requires new technology featuring industrial peripherals and factory amplified performance and capabilities. communication, automation systems The factory automation floor is rapidly require cuttingedge technologies to advancing to become more user meet stringent customer requirements friendly with the incorporation of ele for high reliability in missioncritical ments like user interfaces that are environments. increasingly similar to those we use in our everyday lives and video compe Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) has tencies that grant the ability to view a strategic commitment to the factory machines running on the opposite side automation industry, ranging from an of factories. This shift necessitates extensive, reliable solution portfolio to solutions very complex, expensive new processors that afford industrial a long product life supply as well as a and resistant to evolution even though system developers the capacity to suc strong localbased support. Industrial industry standards are changing. cessfully address these everevolving automation applications have been challenges. With applications ranging implemented using a variety of external Meeting the need for high from programmable logic controllers components making yesterday’s performance AM57x block diagram In industrial HMI and PLC systems, there is an increasing trend towards achieving x86level performance in fanless enclosures and smaller form factors. At the same time, communica tions requirements are ever increasing for these systems, as is the need for intuitive user interface and highperfor mance graphics in HMI systems. -

OMAP 3 Family of Multimedia Applications
OMAP™ 3 family of multimedia applications processors Revolutionizing entertainment and productivity Key features in wireless handheld commumications • Combines mobile entertainment and high-performance productivity applications. Product Bulletin • Integrates the advanced Superscalar ARM Cortex-A8 RISC core, enabling up to The OMAP™ 3 family of multimedia applications processors from Texas Instruments (TI) 3x gain in performance versus ARM11. introduces a new level of performance that enables laptop-like productivity and advanced • Designed in 45-nm (OMAP36x platform) entertainment in multimedia-enabled handsets. OMAP 3 devices support all levels of and 65-nm (OMAP34x platform) CMOS handsets, from the entry-level multimedia-enabled handsets to high-end Mobile Internet process technologies for less power Devices (MIDs). consumption and increased device performance. Entry-level Mid-level High-end • Includes integrated IVA hardware multimedia-enabled multimedia-enabled multimedia-enabled accelerators to enable multi-standard encode handsets handsets handsets decode up to HD resolution. OMAP3410 OMAP3420 OMAP3430/3440 • Available integrated image signal OMAP3610 OMAP3620 OMAP3630/3640 processor (ISP) enables faster, higher quality image capture, lower system cost TI’s OMAP 3 family of applications processors These devices can operate at a higher and lower power consumption. • Provides seamless connectivity to hard integrate the ARM Cortex-A8 superscalar frequency than previous-generation OMAP diskdrive (HDD) devices for mass storage. microprocessor -

Comparative Study of Various Systems on Chips Embedded in Mobile Devices
Innovative Systems Design and Engineering www.iiste.org ISSN 2222-1727 (Paper) ISSN 2222-2871 (Online) Vol.4, No.7, 2013 - National Conference on Emerging Trends in Electrical, Instrumentation & Communication Engineering Comparative Study of Various Systems on Chips Embedded in Mobile Devices Deepti Bansal(Assistant Professor) BVCOE, New Delhi Tel N: +919711341624 Email: [email protected] ABSTRACT Systems-on-chips (SoCs) are the latest incarnation of very large scale integration (VLSI) technology. A single integrated circuit can contain over 100 million transistors. Harnessing all this computing power requires designers to move beyond logic design into computer architecture, meet real-time deadlines, ensure low-power operation, and so on. These opportunities and challenges make SoC design an important field of research. So in the paper we will try to focus on the various aspects of SOC and the applications offered by it. Also the different parameters to be checked for functional verification like integration and complexity are described in brief. We will focus mainly on the applications of system on chip in mobile devices and then we will compare various mobile vendors in terms of different parameters like cost, memory, features, weight, and battery life, audio and video applications. A brief discussion on the upcoming technologies in SoC used in smart phones as announced by Intel, Microsoft, Texas etc. is also taken up. Keywords: System on Chip, Core Frame Architecture, Arm Processors, Smartphone. 1. Introduction: What Is SoC? We first need to define system-on-chip (SoC). A SoC is a complex integrated circuit that implements most or all of the functions of a complete electronic system. -

Overview of CPU Power Consumption and Management in Smartphones
Overview of CPU Power Consumption and Management in Smartphones Prof. Sasu Tarkoma University of Helsinki, Aalto University, Helsinki Institute for Information Technology Contents • Modern smartphone SoC and CPUs – The CPU: power states – Power management basics • Smartphone solutions – Linux CPU Frequency subsystem – Power models • Intra-device task offloading – Sensor hub – Heterogeneous multiprocessing • Computation offloading Smartphones • Smartphones have become hubs for applications and connecting with the Internet • Cloud has emerged as a backend for mobile applications • Mobile data and WiFi are the dominant protocols for connecting with Internet resources • The next generation solutions are addressing limitations of the current smartphones – Coordination of resource usage – Offloading in its many forms – Heterogeneous environment and the emergence of IoT / M2M / wearables Observations • Smartphone and mobile device hardware and software evolve rapidly • Multiple wireless protocols • Heterogeneous computing over multiple cores – Dedicated subsystems (sensor hubs) – Increasing number of sensing subsystems – Always-on sensing • Battery technology has not kept pace with the development • Software is not, in many cases, optimized • Difficult to balance between local versus distributed processing • Difficult to control traffic across interfaces Mobile Evolution 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 Processor Single Single Single Dual-core Quad-core and beyond, auxiliary processors, sensor hubs Cellular 2G 2.5-3G 3.5G Transition 4G generation toward 4G Standard GSM GPRS HSPA HSPA, LTE LTE, LTE-A Downlink (Mb/ 0.01 0.1 1 10 100 s) Display pixels 4 16 64 256 1024 (x1000) Communicatio - - WiFi, WiFi, WiFi, Bluetooth LE, ns modules Bluetooth Bluetooth RFID Battery 1 2 3 4 5 capacity (Wh) Software (MB) 0.1 1 10 100 1000 Example Smartphone SoC Modem Subsystem Multicore Subsystem Multimedia Subsystem LTE Adreno World KRAIT CPU KRAIT CPU GPU Modem Audio, GPS,Wi-Fi, Video HW, BT,FM Accelerator L1 Cache L1 Cache s DSP DSP DSP L2 Cache Multim. -

Nomadik Application Processor Andrea Gallo Giancarlo Asnaghi ST Is #1 World-Wide Leader in Digital TV and Consumer Audio
Nomadik Application Processor Andrea Gallo Giancarlo Asnaghi ST is #1 world-wide leader in Digital TV and Consumer Audio MP3 Portable Digital Satellite Radio Set Top Box Player Digital Car Radio DVD Player MMDSP+ inside more than 200 million produced chips January 14, 2009 ST leader in mobile phone chips January 14, 2009 Nomadik Nomadik is based on this heritage providing: – Unrivalled multimedia performances – Very low power consumption – Scalable performances January 14, 2009 BestBest ApplicationApplication ProcessorProcessor 20042004 9 Lowest power consumption 9 Scalable performance 9 Video/Audio quality 9 Cost-effective Nominees: Intel XScale PXA260, NeoMagic MiMagic 6, Nvidia MQ-9000, STMicroelectronics Nomadik STn8800, Texas Instruments OMAP 1611 January 14, 2009 Nomadik Nomadik is a family of Application Processors – Distributed processing architecture ARM9 + multiple Smart Accelerators – Support of a wide range of OS and applications – Seamless integration in the OS through standard API drivers and MM framework January 14, 2009 roadmap ... January 14, 2009 Some Nomadik products on the market... January 14, 2009 STn8815 block diagram January 14, 2009 Nomadik : a true real time multiprocessor platform ARM926 SDRAM SRAM General (L1 + L2) Purpose •Unlimited Space (Level 2 •Limited Bandwidth Cache System for Video) DMA Master OS Memory Controller Peripherals multi-layer AHB bus RTOS RTOS Multi-thread (Scheduler FSM) NAND Flash MMDSP+ Video •Unlimited Space MMDSP+ Audio 66 MHz, 16-bit •“No” Bandwidth 133 MHz, 24-bit •Mass storage -

M-Line BROCHURE
The Novasom Industries M-line was created for those advanced multimedia applications where the computing power and the presence of specific HW accelerators are needed as much as the advanced connectivity to various kinds of displays while maintaining the classic low-level industrial connectivity. Novasom Industries M11 series, based on the new Intel Apollo Lake x5 6th generation Atom CPU with Microsoft Windows 10 and UHD (4k) video capabilities, is perfect for the typical Kiosks & Digital-Signage applications. The M7 is based on the Rockchip RK3328, a 4X A53 processor and can drive UHD (4k) displays, has USB3 & 2, HDMI and supports Android OS. Complete SBC with immediate bootstrap Native Android & Linux support O.S. (M7, M8 & M9) M8 board runs Qualcomm Snapdragon 410E with Android and Windows 10 IoT and can be connected to FHD displays. Native Window 10 and Linux (M11) Embedded UPS manager with battery and Redundant The M9, based on the Rockchip RK3399 offers an android like Power Input experience and high side multimedia application with UHD, multiple video and camera input. HD Audio output and Optical SPDIF mPCIe interface slot (M9, M7 & M11) All the M-Line boards support Linux OS. Fluidity and no scratch on Heavy UHD play RASPMOOD form factor for M7, M8 and M9: dimensions, guaranteed mechanical holes, expansion pin on strip, connector Fully certified board, visit kind and position are similar to the famous Pi Family. www.novasomindustries.com for details So if you've started with a toy-board and want to use in an industrial proposal, we are ready. -

QTEE STOR, Is Shown in Figure 4
Qualcomm Snapdragon, Qualcomm Trusted Execution Environment, Qualcomm Secure Storage Solutions, Qualcomm Secure Processing Unit, Qualcomm Secure File System, and Qualcomm Fast Trusted Storage are products of Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its subsidiaries. Qualcomm and Snapdragon are trademarks of Qualcomm Incorporated, registered in the United States and other countries. Other products and brand names may be trademarks or registered trademarks of their respective owners. The contents of this document are provided on an “as-is” basis without warranty of any kind. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. specifically disclaims the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular purpose. Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. 5775 Morehouse Drive San Diego, CA 92121 U.S.A. © 2019 Qualcomm Technologies, Inc. and/or its affiliated companies. All Rights Reserved. Overview .............................................................................................................................. 1 Acronyms ............................................................................................................................. 2 Limitation of pure software-based solutions ...................................................................... 3 Hardware building blocks .................................................................................................... 4 Qualcomm® Trusted Execution Environment ................................................................. 4 Hardware Crypto Engine ................................................................................................ -

Mediatek Inc
01 May 2015 Asia Pacific/Taiwan Equity Research Semiconductor Devices MediaTek Inc. (2454.TW / 2454 TT) Rating NEUTRAL* Price (30 Apr 15, NT$) 395.00 RESULTS Target price (NT$) 405.00¹ Upside/downside (%) 2.5 Mkt cap (NT$ mn) 708,117 (US$ 23,121) 2Q lacks growth, but a high bar is set for 2H Enterprise value (NT$ mn) 544,619 ■ 1Q15 results in line with CS, but below street. 1Q15 sales were already Number of shares (mn) 1,792.70 Free float (%) 89.1 reported at NT$47.5 bn, -14.3% QoQ. Smartphone shipments were 85 mn 52-week price range 535.0 - 390.0 (30mn LTE), down from 95-100mn in 4Q14 due to seasonality and emerging ADTO - 6M (US$ mn) 101.0 market weakness. GMs met our 47.3% vs 46-48% guidance and OpM was also *Stock ratings are relative to the coverage universe in each analyst's or each team's respective sector. in line at 16.1% on cost controls. Lower non-op income kept EPS only in line ¹Target price is for 12 months. with our NT$4.62 and below street's NT$4.97. Research Analysts ■ 2Q15 guidance below, inventory elevated. Sales were guided -5% to +3% Randy Abrams, CFA QoQ, below CS/street's +9%/+18% QoQ on 3G price pressure and 4G mix 886 2 2715 6366 [email protected] skewed to the entry level. Margins are in line, with GMs at 45.5-47.5% and Nickie Yue OpM at 12.5-16.5%. Inventory is elevated, at 102 days and guided to stay 886 2 2715 6364 98-110 days in 2Q15, requiring 2H15 acceleration.