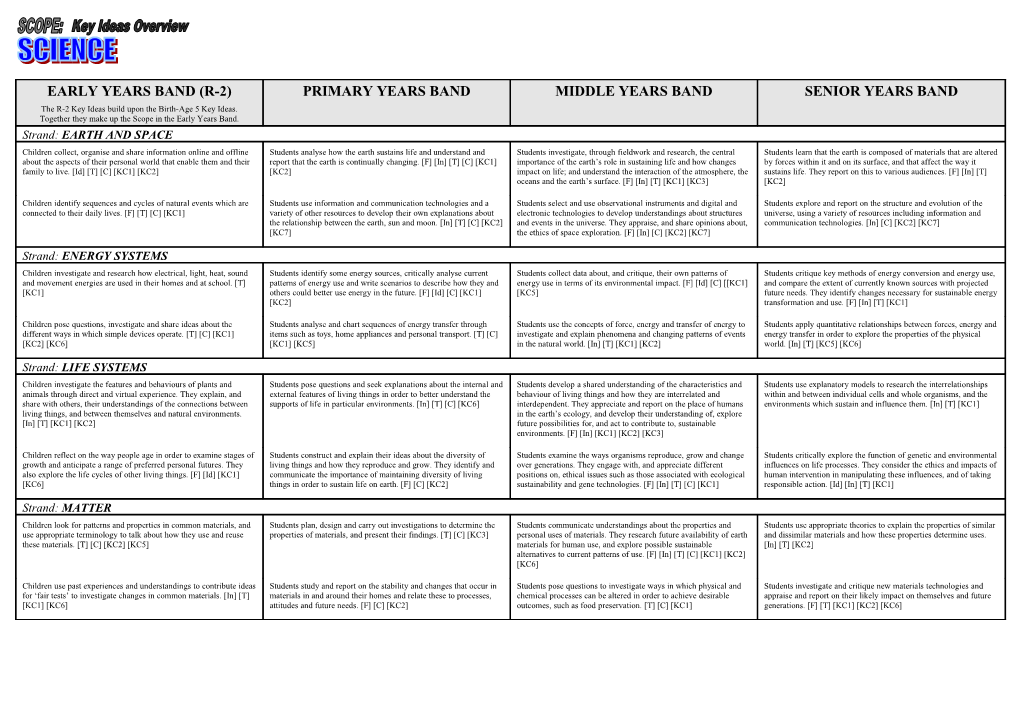
EARLY YEARS BAND (R-2) PRIMARY YEARS BAND MIDDLE YEARS BAND SENIOR YEARS BAND The R-2 Key Ideas build upon the Birth-Age 5 Key Ideas. Together they make up the Scope in the Early Years Band. Strand: EARTH AND SPACE Children collect, organise and share information online and offline Students analyse how the earth sustains life and understand and Students investigate, through fieldwork and research, the central Students learn that the earth is composed of materials that are altered about the aspects of their personal world that enable them and their report that the earth is continually changing. [F] [In] [T] [C] [KC1] importance of the earth’s role in sustaining life and how changes by forces within it and on its surface, and that affect the way it family to live. [Id] [T] [C] [KC1] [KC2] [KC2] impact on life; and understand the interaction of the atmosphere, the sustains life. They report on this to various audiences. [F] [In] [T] oceans and the earth’s surface. [F] [In] [T] [KC1] [KC3] [KC2]
Children identify sequences and cycles of natural events which are Students use information and communication technologies and a Students select and use observational instruments and digital and Students explore and report on the structure and evolution of the connected to their daily lives. [F] [T] [C] [KC1] variety of other resources to develop their own explanations about electronic technologies to develop understandings about structures universe, using a variety of resources including information and the relationship between the earth, sun and moon. [In] [T] [C] [KC2] and events in the universe. They appraise, and share opinions about, communication technologies. [In] [C] [KC2] [KC7] [KC7] the ethics of space exploration. [F] [In] [C] [KC2] [KC7]
Strand: ENERGY SYSTEMS Children investigate and research how electrical, light, heat, sound Students identify some energy sources, critically analyse current Students collect data about, and critique, their own patterns of Students critique key methods of energy conversion and energy use, and movement energies are used in their homes and at school. [T] patterns of energy use and write scenarios to describe how they and energy use in terms of its environmental impact. [F] [Id] [C] [[KC1] and compare the extent of currently known sources with projected [KC1] others could better use energy in the future. [F] [Id] [C] [KC1] [KC5] future needs. They identify changes necessary for sustainable energy [KC2] transformation and use. [F] [In] [T] [KC1]
Children pose questions, investigate and share ideas about the Students analyse and chart sequences of energy transfer through Students use the concepts of force, energy and transfer of energy to Students apply quantitative relationships between forces, energy and different ways in which simple devices operate. [T] [C] [KC1] items such as toys, home appliances and personal transport. [T] [C] investigate and explain phenomena and changing patterns of events energy transfer in order to explore the properties of the physical [KC2] [KC6] [KC1] [KC5] in the natural world. [In] [T] [KC1] [KC2] world. [In] [T] [KC5] [KC6]
Strand: LIFE SYSTEMS Children investigate the features and behaviours of plants and Students pose questions and seek explanations about the internal and Students develop a shared understanding of the characteristics and Students use explanatory models to research the interrelationships animals through direct and virtual experience. They explain, and external features of living things in order to better understand the behaviour of living things and how they are interrelated and within and between individual cells and whole organisms, and the share with others, their understandings of the connections between supports of life in particular environments. [In] [T] [C] [KC6] interdependent. They appreciate and report on the place of humans environments which sustain and influence them. [In] [T] [KC1] living things, and between themselves and natural environments. in the earth’s ecology, and develop their understanding of, explore [In] [T] [KC1] [KC2] future possibilities for, and act to contribute to, sustainable environments. [F] [In] [KC1] [KC2] [KC3]
Children reflect on the way people age in order to examine stages of Students construct and explain their ideas about the diversity of Students examine the ways organisms reproduce, grow and change Students critically explore the function of genetic and environmental growth and anticipate a range of preferred personal futures. They living things and how they reproduce and grow. They identify and over generations. They engage with, and appreciate different influences on life processes. They consider the ethics and impacts of also explore the life cycles of other living things. [F] [Id] [KC1] communicate the importance of maintaining diversity of living positions on, ethical issues such as those associated with ecological human intervention in manipulating these influences, and of taking [KC6] things in order to sustain life on earth. [F] [C] [KC2] sustainability and gene technologies. [F] [In] [T] [C] [KC1] responsible action. [Id] [In] [T] [KC1]
Strand: MATTER Children look for patterns and properties in common materials, and Students plan, design and carry out investigations to determine the Students communicate understandings about the properties and Students use appropriate theories to explain the properties of similar use appropriate terminology to talk about how they use and reuse properties of materials, and present their findings. [T] [C] [KC3] personal uses of materials. They research future availability of earth and dissimilar materials and how these properties determine uses. these materials. [T] [C] [KC2] [KC5] materials for human use, and explore possible sustainable [In] [T] [KC2] alternatives to current patterns of use. [F] [In] [T] [C] [KC1] [KC2] [KC6]
Children use past experiences and understandings to contribute ideas Students study and report on the stability and changes that occur in Students pose questions to investigate ways in which physical and Students investigate and critique new materials technologies and for ‘fair tests’ to investigate changes in common materials. [In] [T] materials in and around their homes and relate these to processes, chemical processes can be altered in order to achieve desirable appraise and report on their likely impact on themselves and future [KC1] [KC6] attitudes and future needs. [F] [C] [KC2] outcomes, such as food preservation. [T] [C] [KC1] generations. [F] [T] [KC1] [KC2] [KC6] SCIENCE
DEVELOPMENTAL LEARNING AT STANDARD 1, TOWARDS THE END AT STANDARD 2, TOWARDS THE END AT STANDARD 3, TOWARDS THE END AT STANDARD 4, TOWARDS THE END AT STANDARD 5, TOWARDS THE END OUTCOMES YEAR 12 STANDARDS OF YEAR 2, THE CHILD: OF YEAR 4, THE STUDENT: OF YEAR 6, THE STUDENT: OF YEAR 8, THE STUDENT: OF YEAR 10, THE STUDENT: BIRTH-AGE 3 & AGE 3-AGE 5 STRAND: Earth and Space 1.1 2.1 3.1 4.1 5.1 The Developmental Learning Outcomes Identifies and shares information Expresses ideas about changes that Describes the characteristics that Identifies and investigates Researches and analyses The Year 12 Standards for science are deliberately broad long-term about features of their natural and occur in their local environment, sustain life on the earth and changes, both natural and human- contemporary theories about comprise the capabilities of the Essential accomplishments. They reflect the built local environment that affect and considers implications for changes to these characteristics induced, on the earth and suggests geological features, such as plate Learnings demonstrated along with integration of learning and development living things, including themselves. sustainable environments. [F] [In] and their impact over time. [F] [In] ideas which encourage the tectonics, and investigates their standards from external curriculum. through the Essential Learnings and all [Id] [T] [KC1] [KC2] [KC1] [KC2] [T] [KC2] preservation of the natural effects on sustaining life on earth. Learning Areas and allow for different External curriculum is quality assured at developmental pathways. environment for all living things. [F] [In] [T] [KC1] [KC6] Year 12 level by the accrediting authority [F] [In] [T] [KC1] [KC6] under the Australian Qualifications Children develop trust and 1.2 2.2 3.2 4.2 5.2 Framework or equivalent. confidence. [F] [Id] Children develop a positive sense of Compares the apparent position of Explores the apparent motion of Describes various components of Investigates and analyses Critically examines theories of The Essential Learnings are: self and a confident personal and the sun to patterns of behaviour in the sun in relation to the earth and the solar system and the effects of astronomical features and changes astronomy and how they have group identity. [Id] [In] everyday life. [F] [T] [KC1] develops models of their these on our everyday lives. [F] as seen from the earth and debates contributed to our understandings Futures Children develop a sense of being understanding. [In] [T] [C] [KC6] [In] [C] [KC2] the ways scientists examine and about the universe, and articulates Identity connected with others and their explain these. [F] [In] [C] [KC2] personal theoretical preferences. Interdependence worlds. [F] [Id] [In] [In] [C] [KC1] Thinking Children are intellectually inquisitive. Communication. [F] [T] [C] Children develop a range of thinking External curriculum is defined by: skills. [F] [T] [C] Children are effective communicators. Relevant SACE Curriculum [T] [C] Statements Children develop a sense of physical . Biology wellbeing. [Id] [In] . Chemistry Children develop a range of physical . Geology competencies. [Id] . Laboratory Operations (VET) . Physics . Science
VET National Training Packages
Other Year 12 level curriculum approved for certification by the appropriate authority under the Australian Qualifications Framework or equivalent. STRAND: Energy Systems 1.3 2.3 3.3 4.3 5.3 The Developmental Learning Outcomes Identifies sources of energy and Identifies, plans and acts on ways Investigates and reports on Investigates ways of obtaining, Analyses aspects of energy The Year 12 Standards for science are deliberately broad long-term describes the ways in which energy in which they can better use energy patterns of energy use in the home, transferring and using energy sustainability, including energy comprise the capabilities of the Essential accomplishments. They reflect the is used in daily life. [T] [C] [KC1] in their lives. [F] [In] [C] [KC1] school and other places. [F] [Id] (including from sustainable energy resources, energy production and Learnings demonstrated along with integration of learning and development [KC2] [KC2] [C] [KC1] [KC2] [KC5] sources and from fossil fuels) for distribution, and challenges for standards from external curriculum. through the Essential Learnings and all particular purposes. [F] [C] [KC6] future ‘worldwide’ uses of energy. Learning Areas and allow for different External curriculum is quality assured at developmental pathways. [F] [In] [KC1] Year 12 level by the accrediting authority 1.4 2.4 3.4 4.4 5.4 under the Australian Qualifications Children develop trust and Framework or equivalent. confidence. [F] [Id] Poses questions and explores the Identifies, observes and describes Uses the idea of force to describe Plans and evaluates investigations Explains energy input/output Children develop a positive sense of ways in which different objects energy transfer, such as light, and explain different ways of that focus on the transfer and devices using concepts of work, The Essential Learnings are: self and a confident personal and move. [T] [KC2] sound, heat or movement, through transferring energy. [In] [T] [KC2] transformation of energy. [In] [T] force and power, and explores, group identity. [Id] [In] common objects. [T] [C] [KC1] [KC3] through investigations, various Futures Children develop a sense of being [KC2] systems for the transfer and Identity connected with others and their transformation of energy. [In] [T] Interdependence worlds. [F] [Id] [In] Thinking Children are intellectually inquisitive. [KC2] Communication. [F] [T] [C] Children develop a range of thinking External curriculum is defined by: skills. [F] [T] [C] Children are effective communicators. Relevant SACE Curriculum [T] [C] Statements Children develop a sense of physical . Biology wellbeing. [Id] [In] . Chemistry Children develop a range of physical . Geology competencies. [Id] . Laboratory Operations (VET) . Physics . Science
VET National Training Packages
Other Year 12 level curriculum approved for certification by the appropriate authority under the Australian Qualifications Framework or equivalent. STRAND: Life Systems 1.5 2.5 3.5 4.5 5.5 The Developmental Learning Outcomes Investigates the features and needs Explores relationships between Explains the interrelationships Investigates and explains the Interprets and uses information The Year 12 Standards for science are deliberately broad long-term of living things, and demonstrates living things by posing investigable between systems within living functioning of living systems from about the structure and function of comprise the capabilities of the Essential accomplishments. They reflect the an understanding of their questions about features and things, and between living things the microscopic to the living systems and their Learnings demonstrated along with integration of learning and development interdependence with each other functions. [In] [T] [KC6] in ecological systems. They relate macroscopic. [F] [In] [KC1] [KC2] relationship to survival of standards from external curriculum. through the Essential Learnings and all and the physical world. [In] [T] [C] these ideas to the health of ecosystems. [In] [T] [KC1] Learning Areas and allow for different External curriculum is quality assured at developmental pathways. [KC1] individuals and to threats to the Year 12 level by the accrediting authority sustainability of ecological under the Australian Qualifications Children develop trust and systems. [F] [Id] [In] [KC1] [KC2] Framework or equivalent. confidence. [F] [Id] 1.6 2.6 3.6 4.6 5.6 Children develop a positive sense of The Essential Learnings are: self and a confident personal and Explores their own stages of Communicates understandings of Identifies, analyses and Explores how living things have Applies theories and conceptual group identity. [Id] [In] growth and those of other living life cycles and the importance of communicates confidently the changed over geological time and frameworks associated with Futures Children develop a sense of being things. They develop personal diversity for the future. [F] [T] [C] similarities and differences in the debates the value of species evolution, biodiversity, genetics, Identity connected with others and their future timelines. [F] [Id] [C] [KC6] [KC2] ways that living things reproduce, diversity and the ethics of human and the cycling of energy and Interdependence worlds. [F] [Id] [In] Thinking Children are intellectually inquisitive. and considers the ethics of related intervention. [F] [T] [C] [KC2] matter in biological and Communication. [F] [T] [C] issues. [F] [T] [C] [KC1] [KC2] [KC6] physiological systems. [In] [T] Children develop a range of thinking [KC1] External curriculum is defined by: skills. [F] [T] [C] Children are effective communicators. Relevant SACE Curriculum [T] [C] Statements Children develop a sense of physical . Biology wellbeing. [Id] [In] . Chemistry Children develop a range of physical . Geology competencies. [Id] . Laboratory Operations (VET) . Physics . Science
VET National Training Packages
Other Year 12 level curriculum approved for certification by the appropriate authority under the Australian Qualifications Framework or equivalent.
STRAND: Matter 1.7 2.7 3.7 4.7 5.7 The Developmental Learning Outcomes Identifies properties of materials Designs an investigation to explore Describes the structure of some Compares properties of materials Uses the particle model to explain The Year 12 Standards for science are deliberately broad long-term that are observable through the properties of common materials, common materials, explains how before and after physical or physical and chemical properties comprise the capabilities of the Essential accomplishments. They reflect the senses and recognises the uses of explaining why they have materials are used for different chemical change by planning, and change of matter. [In] [T] Learnings demonstrated along with integration of learning and development these materials. [T] [C] [KC1] particular uses. [T] [C] [KC2] purposes, and understands their conducting, evaluating and [KC2] standards from external curriculum. through the Essential Learnings and all [KC3] [KC6] impact on the environment. [F] communicating an investigation. Learning Areas and allow for different External curriculum is quality assured at developmental pathways. [In] [T] [C] [KC1] [KC2] [In] [T] [C] [KC1] [KC2] [KC3] Year 12 level by the accrediting authority 1.8 2.8 3.8 4.8 5.8 under the Australian Qualifications Children develop trust and Framework or equivalent. confidence. [F] [Id] Identifies and predicts materials Predicts, investigates and describes Uses the changes in properties and Recognises and describes Classifies chemical reactions and Children develop a positive sense of that change and do not change. [T] changes in common materials uses of materials in product life conditions that influence reactions identifies their importance in The Essential Learnings are: self and a confident personal and [KC1] when acted upon in various ways. cycles. [T] [C] [KC1] or change in materials. [T] [C] providing materials for present and group identity. [Id] [In] [F] [C] [KC6] [KC1] [KC2] future generations. [F] [T] [KC1] Futures Children develop a sense of being Identity connected with others and their Interdependence worlds. [F] [Id] [In] Thinking Children are intellectually inquisitive. Communication. [F] [T] [C] Children develop a range of thinking External curriculum is defined by: skills. [F] [T] [C] Children are effective communicators. Relevant SACE Curriculum [T] [C] Statements Children develop a sense of physical . Biology wellbeing. [Id] [In] . Chemistry Children develop a range of physical . Geology competencies. [Id] . Laboratory Operations (VET) . Physics . Science
VET National Training Packages
Other Year 12 level curriculum approved for certification by the appropriate authority under the Australian Qualifications Framework or equivalent.