Lab group #______Chicken Wing Anatomy Lab
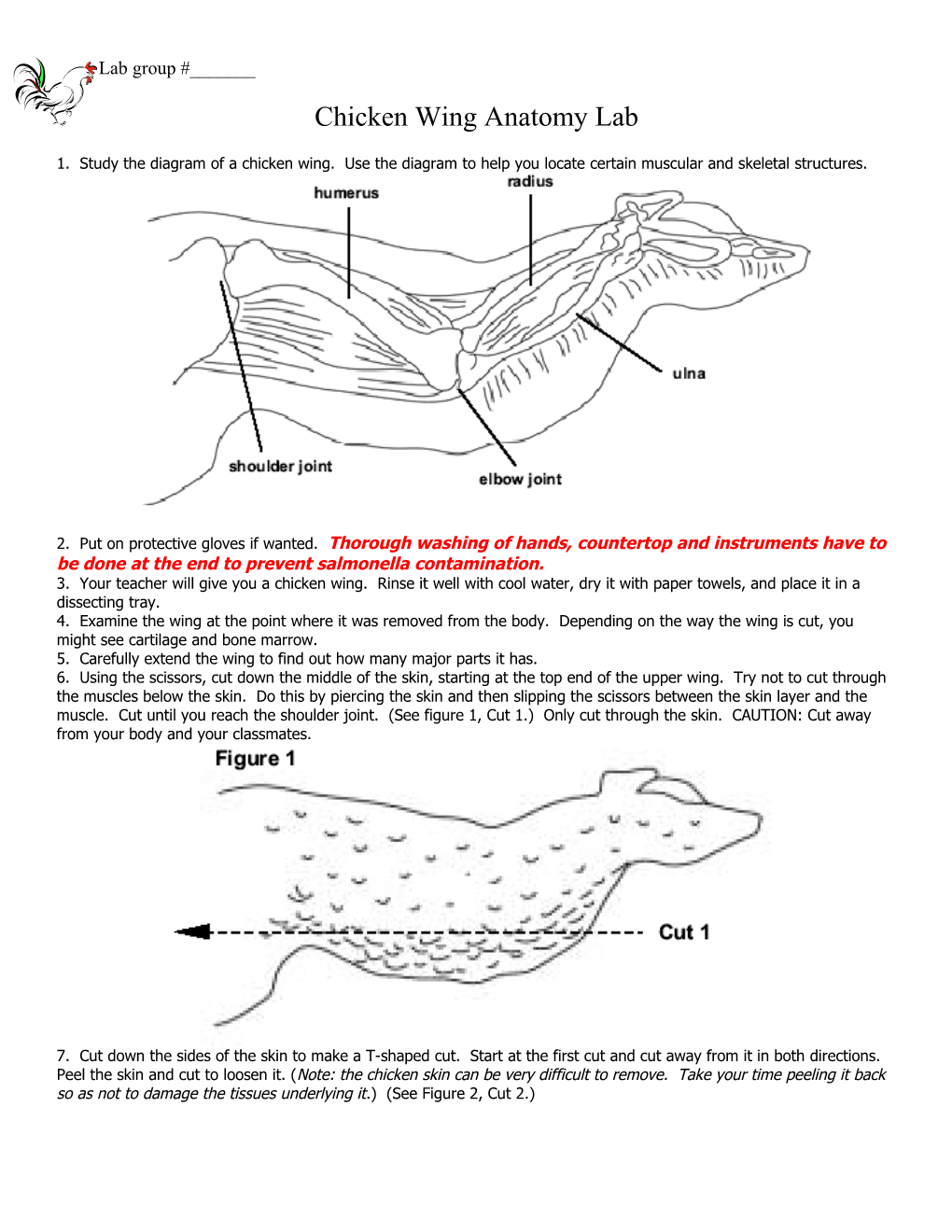
1. Study the diagram of a chicken wing. Use the diagram to help you locate certain muscular and skeletal structures.
2. Put on protective gloves if wanted. Thorough washing of hands, countertop and instruments have to be done at the end to prevent salmonella contamination. 3. Your teacher will give you a chicken wing. Rinse it well with cool water, dry it with paper towels, and place it in a dissecting tray. 4. Examine the wing at the point where it was removed from the body. Depending on the way the wing is cut, you might see cartilage and bone marrow. 5. Carefully extend the wing to find out how many major parts it has. 6. Using the scissors, cut down the middle of the skin, starting at the top end of the upper wing. Try not to cut through the muscles below the skin. Do this by piercing the skin and then slipping the scissors between the skin layer and the muscle. Cut until you reach the shoulder joint. (See figure 1, Cut 1.) Only cut through the skin. CAUTION: Cut away from your body and your classmates.
7. Cut down the sides of the skin to make a T-shaped cut. Start at the first cut and cut away from it in both directions. Peel the skin and cut to loosen it. (Note: the chicken skin can be very difficult to remove. Take your time peeling it back so as not to damage the tissues underlying it.) (See Figure 2, Cut 2.) 8. Look for yellowish tissue clumped together beneath the skin. This is fat tissue, made of fat cells.
9. Examine the muscles, the bundles of pink tissue around the bones. Find the two groups of muscles in the upper arm. Hold the arm down at the shoulder, and alternately pull on each muscle group. Observe what happens on each muscle group.
Show teacher that you did this. Teacher initials: ______
10. Find the two groups of muscles in the lower arm. Hold down the arm at the elbow, and alternately pull on each muscle group. Find the tendons--shiny white tissue at the ends of the muscles. Notice what parts the tendons connect. Pull on the tendon to see how it helps the chicken move its wing.
Show teacher that you did this. Teacher initials: ______
11. Remove the muscles and tendons. Two bones come together at a joint. Bend and straighten the elbow joint and observe how the bones fit together. Find the ligaments, the whitish ribbon like structures between bones. Ligaments connect bones to other bones at joints. They look like a shiny white covering of the joint surfaces. Closely examine the elbow joint between the upper wing and the lower wing and identify the ligaments.
Show teacher that you found this. Teacher initials: ______
12. Between the bones is another shiny white material that is slippery. This is cartilage, which helps the bones move without grinding against one another, or without causing trauma.
Show teacher that you found this. Teacher initials: ______
CLEAN UP Dispose the chicken parts according to your teacher's instructions. Wash your hands with soap and water. Wash all equipment. Thoroughly wash the lab countertop with soap and water. Thoroughly wash the scissors with hot soapy water and brush. Set instruments and dish aside to dry.
Show teacher that you did this.
Teacher initials: ______
Name: ______QUESTIONS
1. Identify the bones
A. ______
B. ______
C. ______
D. ______
2. Draw the biceps muscle where it is correctly attached (to bones) with the tendon. Draw tendons in red, muscles in grey. Label the biceps muscle.
3. Label the ball and socket joint, hinge joint, and the gliding joint in the diagram.
4. Answer: What part of the chicken wing is commonly referred to as the meat? ______
5. Based on your observations, explain the roles of muscles, tendons, bones, and joints in the back-and-forth movement of the lower chicken wing. How does the arm use the muscular and skeletal system to produce movment?
6. Name the system each part belongs to. a.i.1.a.i.1.a. Skin: ______
a.i.1.a.i.1.b. Bones: ______
a.i.1.a.i.1.c. Muscles: ______
7. How does the skin help cells get rid of waste?
8. How do the bones help cells receive oxygen and nutrients? 9. How do the muscles help cells receive oxygen and nutrients?