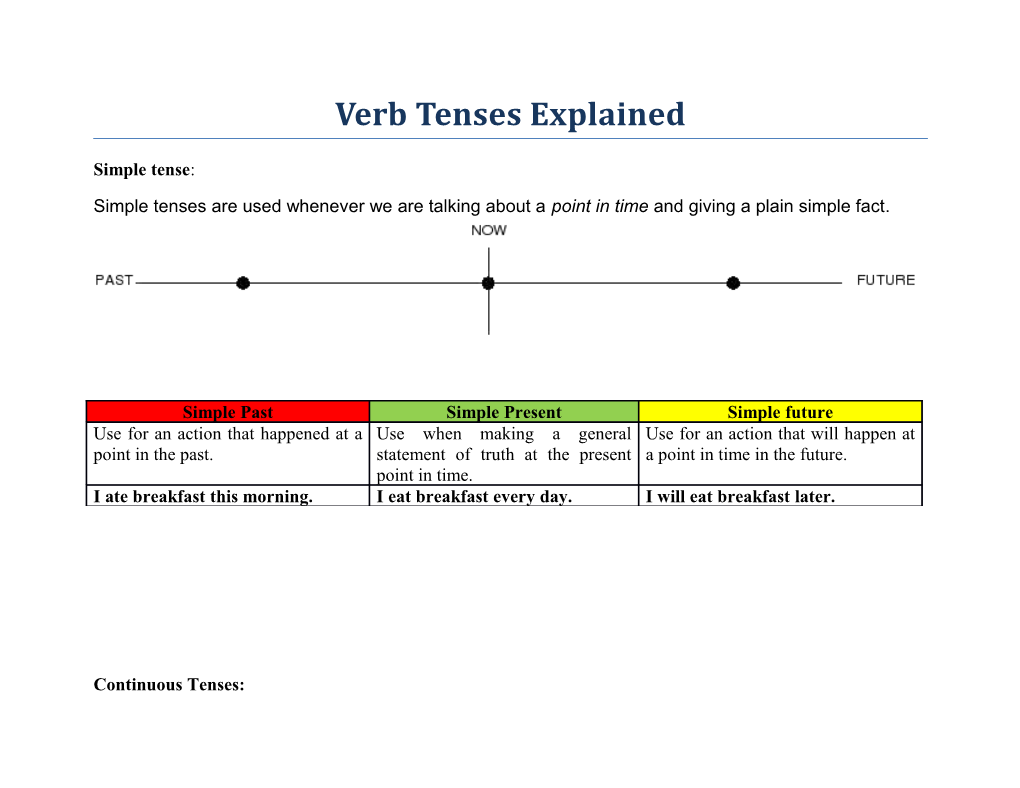
Verb Tenses Explained
Simple tense:
Simple tenses are used whenever we are talking about a point in time and giving a plain simple fact.
Simple Past Simple Present Simple future Use for an action that happened at a Use when making a general Use for an action that will happen at point in the past. statement of truth at the present a point in time in the future. point in time. I ate breakfast this morning. I eat breakfast every day. I will eat breakfast later.
Continuous Tenses: Continuous tenses are used whenever we are talking about length of time. 2 actions happening AT THE SAME TIME Auxiliary “to be” + -ing form of the verb
Past Continuous Present Continuous Future Continuous Use for an action that was happening Use for an action that is happening Use for an action that will be for a length of time in the past when now. happening for a length of time in the another action happened in the future when another action will middle of it. happen in the middle of it. I was eating breakfast when my Right now, I am eating I will be eating breakfast when my brother arrived. breakfast. brother arrives this morning. Perfect Tenses: Perfect tenses are used whenever we are talking about a point in time before another point in time. 2 actions happening ONE AFTER THE OTHER Auxiliary “to have” + past participle form of the verb
Past Perfect Present Perfect Future Perfect Use for an action that happened in Use for an action that happened in Use for an action that will happen in the past before another action. the past before the present the future before another action. moment. I had already eaten breakfast I have already eaten breakfast. I will have already eaten breakfast when my brother arrived. by the time my brother arrives.
Perfect Continuous Tenses: Perfect Continuous tenses are used whenever we are talking about a length of time up to a point in time. 2 actions happening ONE AFTER THE OTHER WITH A DURATION OF TIME Auxiliary “to have” +”to be”+ past participle form of the verb + -ing form of the verb
Past Perfect Continuous Present Perfect Continuous Future Perfect Continuous Use for an action that was happening Use for an action that was Use for an action that will be for a length of time in the past up to happening for a length of time up happening in the future for a length the moment when another action to the present moment. of time up to the moment when happened. another action will happen. I had been eating breakfast for 30 I have been eating my breakfast I will have been eating my minutes when my brother arrived. for 30 minutes. breakfast for 30 minutes by the time you arrive.
Referring to the past Referring to the present Referring to the future