Normal labor Labor: is the process by which the fetus, placenta and membranes are expelled through the birth canal :Labor is said to be normal when It occurs at term Fetus presents by vertex Onset is spontaneous Completed within 18 hours .No complications occurs :Stage and duration of labor :Labor is divided into four stages first stage : begins with true uterine contractions and ends with .1 (complete dilatation of the cervix(10 cms second stage: begins with full dilatation of the cervix and ends with the.2 .expulsion of the fetus third stage : begins from the birth of the baby and ends with the .3 .complete expulsion of the placenta and membranes
Fourth stage: is one hour following the expulsion of placenta and .membranes
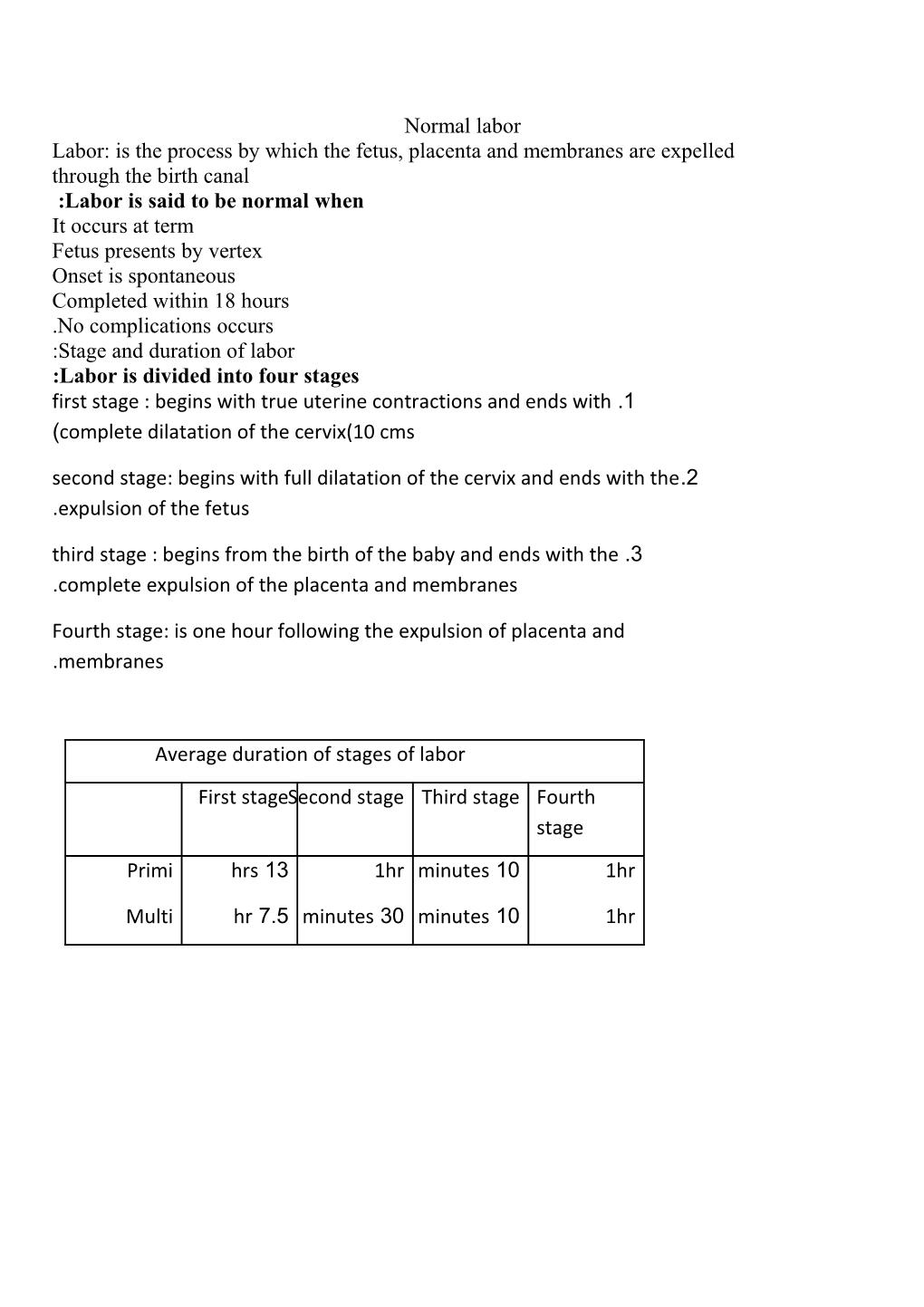
Average duration of stages of labor First stageSecond stage Third stage Fourth stage Primi hrs 13 1hr minutes 10 1hr
Multi hr 7.5 minutes 30 minutes 10 1hr
:factors leading to onset of labor
Hormonal factors: Hormones such as oxytocin, progerone , .1 .oestrogen and prostaglandins influence labor
.Pressure on the cervix .2
. Over distension .3
:Assessment of woman in normal labor
. Assess the women for the signs and symptoms of impending labor.1
. a. Lightening
.b. Cervical changes
C. Show
.d. Frequency
:Assessment of woman during labor
The first stage of labor:1. Contraction and retraction of the upper uterine segment.2. cervical effacement and dilatation.3. show .4. rupture of .(membrane (ROM
The second stage of labor : The transition from first to second stage is not always .clinically apparent Physiological changes: contractions become stronger and longer but may be less frequent , giving the mother and fetus a recovery period during the resting phase, the nature the contractions changes they become more expulsive as pressure is exerted on the rectum and the pelvic floor . The mother feels a compelling urge to .push
:Assessment of presumptive signs and symptoms of second stage of labor .1 show - Expulsive uterine contractions - .Rupture of membranes - Dilatation and gaping of the anus - Congestion of the vulva - .Appearance of the presenting part -
:Assessment of uterine contractions , maternal and fetal well being .2
.Contraction : frequency , duration and intensity - Maternal physical status : coping abilities, physical exhaustion dilatation , vital signs - . progress of labor Fetal well : fetal heart rate , movements descent of fetal head and appearance of - .presenting part
: Second stage .fatigue related to inability to rest during labor pushing efforts the second stage .1 .Anxiety related to unknown outcome of labor process .2 Pain related to descent of the fetus and stretching of vaginal perinea tissues .3 .High risk for infection .4
:Nursing planning and intervention . continue same comfort measures as 1 stage of labor .1 Encourage her to rest and let all muscles relax in between contractions , sips of water may .be used to provide moisture a relieve dryness of mouth
Assist the woman in pushing efforts : Encourage her to relax between contraction and to .2 . push during contractions , maternal and fetal monitor every 15 minutes Preparation of the delivery room : The delivery room should always be ready for the .3 conduct of labor , safety of the laboring mother should always be ensured .If woman is to be transferred from one bed to mother adequately , provide enough privacy . maintain strict . asepsis in the conduct of labor , make sure that the room is warm enough for the baby
Conduction of labor : after being positioned for delivery , the perineum is cleaned and .4 .delivery under strict aseptic precautions
Episiotomy : it is a surgical incision made on the perineum to enlarge the vulval outlet .5 during delivery when is indicated. The perinea area is infiltrated with local anesthetic prior .to making the incision
:Care of a woman during third and fourth stage of labor
Physiological changes: following birth of the baby , the size of the uterine cavity is reduced placenta from the uterine wall is pushed into the lower segment , from where it is expelled completing third stage of labor . Third stage usually lasts for 5 to 30 minutes and fourth .stage is the first one hour after the expulsion of placenta and membranes complete
: Nursing assessment uterine contractions and maternal vital signs are continuously assessed especially pulse - .and blood pressure : Assess for signs of placental separation -
.The uterus rises up in the abdomen and becomes round and hard * .A sudden gush of blood appears at the vulva * .Assessment of the placenta and membranes *
:Nursing diagnosis
.fatigue associated with inability to rest during labor and pushing efforts during labor .1 Alteration in comfort , pain related to episiotomy , perinea distension and muscle strain .2 .birth .Alteration in nutrition less than body requirement .3 . High risk for infection secondary to trauma during delivery / episiotomy .4
Nursing plan and implementation: 1. monitor vital signs 2. observe for signs of placental separation . 3. deliver the placenta by controlled cord traction . 4. make sure that the uterus is well contracted to prevent bleeding .5. careful inspection of vagina , perineum and labia .is important to detect any lacerations and assist in suturing Immediate care of the newborn
Remember the ABCW principle of delivery are to ensure that the baby is resuscitated . adequately
ABCW: A: AIRWAY , B: BREATHING, C: CIRCULATION, W: WARMTH
: Goals of initial care .Establish and maintain respiratory effort/function .1 . Provide warmth and prevent hypothermia .2 .Provide safely from injury or infection .3 .Identify actual or potential problems that might require immediate attention .4
:Assessment of the baby's condition This is done by the while she is clearing the airways and cutting the cord , this is recorded at 1 minute and 5 minutes after birth , this is done using the Apgar scoring system. This is involves consideration of 5 signs and the degree to which they are present or absent. Most babies will achieve a clear airway unaided . If necessary , the airway can be cleared with the help of gentle suctioning if necessary . With clear airways, breathing is established and the baby's colour quickly improves
Warmth : it is important that the baby is kept warm at birth because he will lose heat .rapidly through evaporation . He should be gently and wrapped in a warm dry towel
Umbilical cord : The cord is usually clamped and cut immediately after. A plastic clamp is placed 2-3 cms from the umbilicus and the excess cord is cut off. This clamp is disposable .and can be removed when the cord has dried up
Examinations: it is very important that the baby is examined properly to determine whether there are any abnormalities . When the baby is born the Apgar is being assessed . A full . examination should be made by the nurse when she is ready to weight the baby
. General appearance : 1. colour .2. Respiratory effort . 3. Muscle tone . 4. Temperature
: Assessment of head and neck
.observe and palpate head for any moulding .1 . Palpate fontanel's for fullness or depression .2 Ears – shape and position .3 .Eyes- size and shape , hemorrhage .4 .Neck – length , webbing , mobility .5 .Skin – spots , pustules , birth marks .6 .Nose – symmetry , septum , patency , flaring of nostrils .7 : Assessment of body measurements of weight and length .1 . General activity – posture , responsiveness .2 Skin – lanugo , vernix , colour , rash , pigmentation , meconium staining .3
Thorax : size , symmetry ,shap, breath sounds – respiratory rate, heart sounds- rhythm & . rate , breasts – engorgement
.Abdomen: shap , umbilicus – cord vessels
Genitals: appropriateness of sex , female – labia , discharge , male – urethral opening , .scrotum, testes , urine – amount, colour
Back : spine – vertebrae , symmetry .anus- patency , meconium
. Extremities : symmetry, abnormalities , movement
Neurological assessment : rooting and sucking reflex , grasp reflex – hand , feet , moro . reflex startle reflex