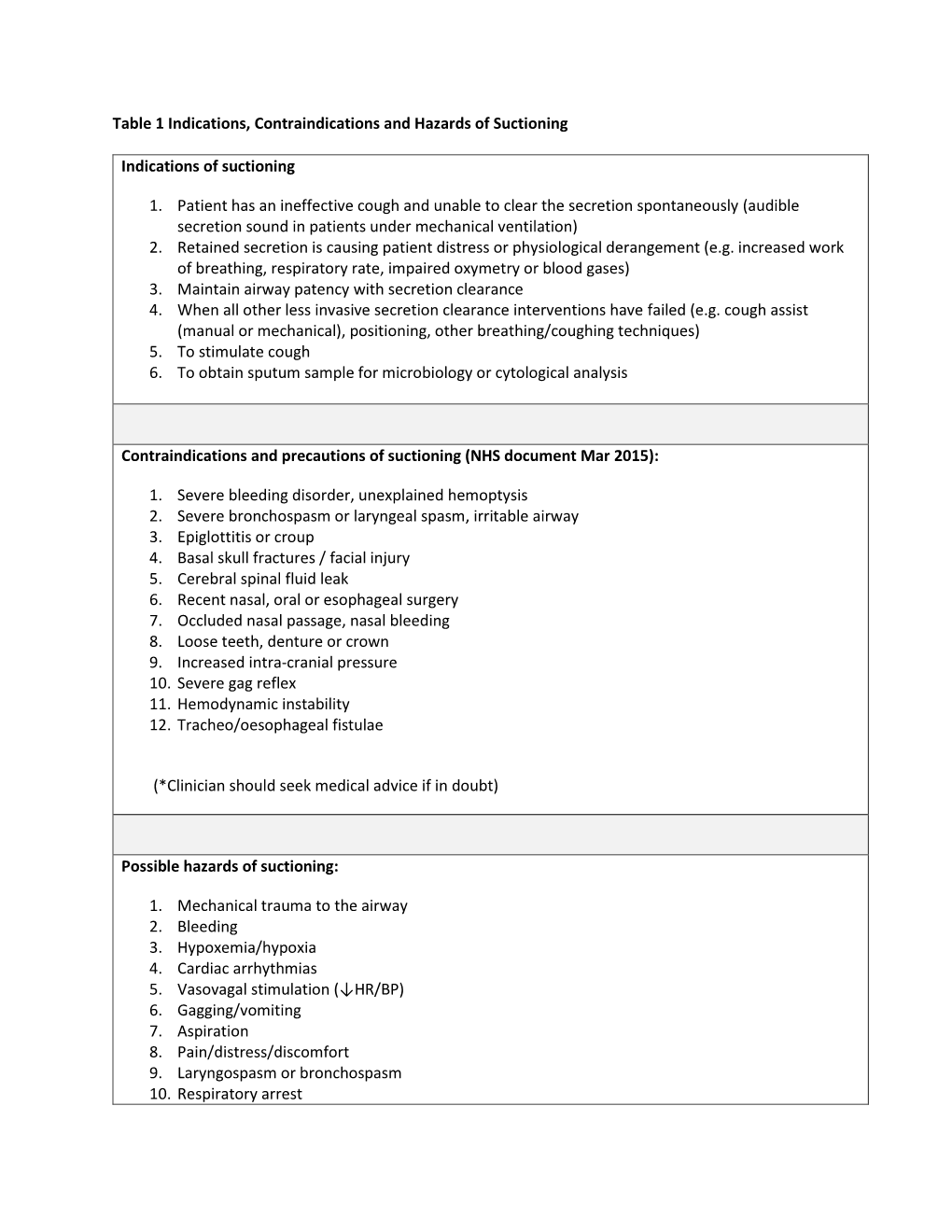
Table 1 Indications, Contraindications and Hazards of Suctioning
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Laryngospasm Caused by Removal of Nasogastric Tube After Tracheal Extubation: Case Report
Yanaka A, et al. J Anesth Clin Care 2021, 8: 061 DOI: 10.24966/ACC-8879/100061 HSOA Journal of Anesthesia & Clinical Care Case Report pCO2: Partial pressure of carbon dioxide pO : Partial pressure of oxygen Laryngospasm Caused by 2 mmHg: Millimeter of mercury Removal of Nasogastric Tube mg/dl: Milligram per deciliter mmol/L: Millimole per litter after Tracheal Extubation: Case Introduction Report Background Laryngospasm (spasmodic closure of the larynx) is an airway Ayumi Yanaka1 and Takuo Hoshi2* complication that may occur when a patient emerges from general 1Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Ibaraki Prefectur- anesthesia. It is a protective reflex, but may sometimes result in al Central Hospital, Japan pulmonary aspiration, pulmonary edema, arrhythmia and cardiac 2Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care Medicine, Clinical and Edu- arrest [1]. It does not often cause severe hypoxemia in the patient, and cational Training Center, Tsukuba University Hospital, Japan our review of the literature revealed no previous reports of such cases that cause of the laryngospasm was the removal of nasogastric tube. Here, we describe this significant adverse event in a case and suggest Abstract ways to lessen the possibility of its occurrence. We obtained written informed consent for publication of this case report from the patient. Background: We report a case of laryngospasm during nasogastric tube removal. Laryngospasm is a severe airway complication after Case report surgery and there have been no reports associated with the removal of nasogastric tubes. A 54-year-old woman height, 157 cm; weight, 61 kg underwent abdominal surgery (partial hepatectomy with right partial Case Report: After abdominal surgery, the patient was extubated the tracheal tube, and was removed the nasogastric tube. -

Hanging, Strangulation and Other Forms of Asphyxiation
Hanging, Strangulation and Other Forms of Asphyxiation Steven Campman, M.D. Chief Deputy Medical Examiner San Diego County 16 October 2018 Overview • Terms • Other forms of asphyxiation • Neck Compression –Hanging –Strangulation Asphyxia • The physical and chemical state caused by the interference with normal respiration. • A condition that interferes with cells ability to receive or use oxygen. General Effects • Decrease and cessation of breathing • Leads to bradycardia and eventually asystole • Slowing, then flattening of the EEG Many Terms • Gag: to obstruct the mouth • Choke: to compress or otherwise obstruct the airway • Strangle: asphyxia by external compression of the throat •Throttle: same as strangle; especially manual strangulation • Garrote: strangle; especially ligature strangulation •Burking: chest compression and smothering. Many Terms • Suffocate: (broad term) a layperson’s synonym for asphyxiation, sometimes used to mean smother. • Choke –a layperson’s term for strangulation –A medical term for internal blocking of the airway Classification of Asphyxia Neck Airway Mechanical Exclusion Compression Obstruction Asphyxia of Oxygen Airway Obstruction •Smothering •Gagging •Choking (laryngeal blockage, aspiration, food bolus) Suicide Kit Choking Internal obstruction of airway • Mouth: gag • Larynx or trachea: obstruction by foreign body, “café coronary,” anaphylaxis, laryngospasm, epiglottitis • Tracheobronchial tree: aspiration, drowning FOOD BOLUS Anaphylaxis from Wasp Stings Mechanical Asphyxia Ability to breath is compromised -

The “Best” Way to Breath
Journal of Lung, Pulmonary & Respiratory Research Case Report Open Access The “Best” way to breath Abstract Volume 2 Issue 2 - 2015 A “best” way to breath is described resulting from discovering a pre-Heimlich method Samuel A Nigro of preventing choking. Because of four episodes in three months of terrifying complete laryngospasm, the physician-patient-writer, consistent with many medical discoveries Retired, Assistant Clinical Professor Psychiatry, Case Western Reserve University School of Medicine, USA in history, discovered a method of aborting the episodes. Breathing has always been taken for granted as spontaneously and naturally most efficient. To the contrary, Correspondence: Samuel A Nigro, Retired, Assistant Clinical nasal breathing is best with first closing the mouth which enhances oxygenation and Professor Psychiatry, Case Western Reserve University School trans-laryngeal respiration. Physiologic aspects are reviewed including nasal and oral of Medicine, 2517 Guilford Road, Cleveland Heights, Ohio respiratory distinctions, laryngeal musculature and structures, diaphragm control and 44118, USA, Tel (216) 932-0575, Email [email protected] neuro-functional speculations. Proposed is the SAM: Shut your mouth, Air in nose, and then Mouth cough (or exhale). Benefits include prevention of choking making the Received: January 07, 2015 | Published: January 26, 2015 Heimlich unnecessary; more efficient clearing of the throat and coughs; improving oxygenation at molecular level of likely benefit for pre-cardiac or pre-stroke anoxic crises; improving exertion endurance; and offering a psycho physiologic method for emotional crises as panics, rages, and obsessive-compulsive impulses. This is a simple universal public health technique needing universal promulgation for the integration of care for all work forces and everyone else. -

Dive Medicine Aide-Memoire Lt(N) K Brett Reviewed by Lcol a Grodecki Diving Physics Physics
Dive Medicine Aide-Memoire Lt(N) K Brett Reviewed by LCol A Grodecki Diving Physics Physics • Air ~78% N2, ~21% O2, ~0.03% CO2 Atmospheric pressure Atmospheric Pressure Absolute Pressure Hydrostatic/ gauge Pressure Hydrostatic/ Gauge Pressure Conversions • Hydrostatic/ gauge pressure (P) = • 1 bar = 101 KPa = 0.987 atm = ~1 atm for every 10 msw/33fsw ~14.5 psi • Modification needed if diving at • 10 msw = 1 bar = 0.987 atm altitude • 33.07 fsw = 1 atm = 1.013 bar • Atmospheric P (1 atm at 0msw) • Absolute P (ata)= gauge P +1 atm • Absolute P = gauge P + • °F = (9/5 x °C) +32 atmospheric P • °C= 5/9 (°F – 32) • Water virtually incompressible – density remains ~same regardless • °R (rankine) = °F + 460 **absolute depth/pressure • K (Kelvin) = °C + 273 **absolute • Density salt water 1027 kg/m3 • Density fresh water 1000kg/m3 • Calculate depth from gauge pressure you divide press by 0.1027 (salt water) or 0.10000 (fresh water) Laws & Principles • All calculations require absolute units • Henry’s Law: (K, °R, ATA) • The amount of gas that will dissolve in a liquid is almost directly proportional to • Charles’ Law V1/T1 = V2/T2 the partial press of that gas, & inversely proportional to absolute temp • Guy-Lussac’s Law P1/T1 = P2/T2 • Partial Pressure (pp) – pressure • Boyle’s Law P1V1= P2V2 contributed by a single gas in a mix • General Gas Law (P1V1)/ T1 = (P2V2)/ T2 • To determine the partial pressure of a gas at any depth, we multiply the press (ata) • Archimedes' Principle x %of that gas Henry’s Law • Any object immersed in liquid is buoyed -

Near Drowning
Near Drowning McHenry Western Lake County EMS Definition • Near drowning means the person almost died from not being able to breathe under water. Near Drownings • Defined as: Survival of Victim for more than 24* following submission in a fluid medium. • Leading cause of death in children 1-4 years of age. • Second leading cause of death in children 1-14 years of age. • 85 % are caused from falls into pools or natural bodies of water. • Male/Female ratio is 4-1 Near Drowning • Submersion injury occurs when a person is submerged in water, attempts to breathe, and either aspirates water (wet) or has laryngospasm (dry). Response • If a person has been rescued from a near drowning situation, quick first aid and medical attention are extremely important. Statistics • 6,000 to 8,000 people drown each year. Most of them are within a short distance of shore. • A person who is drowning can not shout for help. • Watch for uneven swimming motions that indicate swimmer is getting tired Statistics • Children can drown in only a few inches of water. • Suspect an accident if you see someone fully clothed • If the person is a cold water drowning, you may be able to revive them. Near Drowning Risk Factor by Age 600 500 400 300 Male Female 200 100 0 0-4 yr 5-9 yr 10-14 yr 15-19 Ref: Paul A. Checchia, MD - Loma Linda University Children’s Hospital Near Drowning • “Tragically 90% of all fatal submersion incidents occur within ten yards of safety.” Robinson, Ped Emer Care; 1987 Causes • Leaving small children unattended around bath tubs and pools • Drinking -

Cough and Laryngospasm Prevention During Orotracheal Extubation In
Brazilian Journal of Anesthesiology 71 (2021) 90---95 LETTER TO THE EDITOR −1 −1 0.25 mg.kg and ketamine 0.25 mg.kg also have showed Cough and laryngospasm 4 being effective for such purpose. prevention during orotracheal The timing of extubation according to the child’s breath- extubation in children with ing cycle is another point of interest. The author of an SARS-CoV-2 infection educational review about extubation in children mentions that he extubates the child at the end of spontaneous inspi- Dear Editor, ration without suction or positive pressure, arguing that at this point the child’s lungs are full of O2-enriched air and that Little is mentioned about the importance of avoiding cough the first trans laryngeal movement of air that follows directs and laryngospasm during extubation in the Operating Room all secretions away from the laryngeal structures decreasing 5 (OR) in pediatric patients with suspected or confirmed SARS- the risk of laryngospasm. CoV-2 infection. Coughing is an important source of viral According to the former, from the perspective of respira- contagion among humans and must be considered a high-risk tory complications associated with extubation, it is safer for complication for the health workers. Laryngospasm, more the health personnel to perform the extubation to a deep frequent in children than in adults, compels to intervene anesthetized patient, during spontaneous ventilation at the with positive pressure on the patient’s airway increasing the end of inspiration and in lateral decubitus. Special attention described risk. Different from intubation in the OR, where must be given to the use of the medications described for the anesthesiologist has certain control on the procedure, coughing and laryngospasm prevention after the withdrawal extubation and emergence from anesthesia have a greater of the orotracheal tube. -

Brain Pulsatility and Pulsatile Tinnitus: Clinical Types
EDITORIAL International Tinnitus Journal. 2012;17(1):2-3. Brain pulsatility and pulsatile tinnitus: clinical types The purpose of this commentary is to share our supported in the literature by animal and human studies evolving clinical experience with the tympanic membrane ongoing since 1980. The raw data analysis of the IPPA displacement (TMD) analyzer which has focused on wave in patients with nonpulsatile, predominantly central- brain pulsatility in nonpulsatile, predominantly central- type severe disabling SIT resistant to attempts for tinnitus type severe disabling subjective idiopathic tinnitus relief with instrumentation or medication are published (SIT) patients resistant to attempts for tinnitus relief with in this issue of the International Tinnitus Journal (see the instrumentation or medication. article “The Tympanic Membrane Displacement Test and One outcome of this evolving TMD experience Tinnitus”). has been the establishment of a classification system for In our experience, the extensive otologic, pulsatile tinnitus and its clinical translation for diagnosis neurotologic, and neuroradiolgical workup for pulsatile and treatment. tinnitus is frequently negative, and the etiology of the A new discipline, brain pulsatility, has been pulsation is a vascular hypothesis based predominantly emerging in the last 50-60 years, the principles of which on the clinical history and or physical examination. The are based on physical principles of matter, volume, and establishment of an accurate diagnosis and treatment pressure relationships in a confined area (i.e., brain) of pulsatile tinnitus has a satisfactory outcome to the and find clinical translation to the ear and the discipline patient and physician when a pathological process is of tinnitology - in particular, pulsatile tinnitus. -

Acute Laryngeal Dystonia
Collins N, Sager J. J Neurol Neuromedicine (2018) 3(1): 4-7 Neuromedicine www.jneurology.com www.jneurology.com Journal of Neurology & Neuromedicine Mini Review Open Access Acute laryngeal dystonia: drug-induced respiratory failure related to antipsychotic medications Nathan Collins*, Jeffrey Sager Santa Barbara Cottage Hospital Department of Internal Medicine Santa Barbara, CA, USA Article Info ABSTRACT Article Notes Acute laryngeal dystonia (ALD) is a drug-induced dystonic reaction that can Received: December 10, 2017 lead to acute respiratory failure and is potentially life-threatening if unrecognized. Accepted: January 16, 2018 It was first reported in 1978 when two individuals were noticed to develop *Correspondence: difficulty breathing after administration of haloperidol. Multiple cases have since Dr. Nathan Collins MD been reported with the use of first generation antipsychotics (FGAs) and more Santa Barbara Cottage Hospital recently second-generation antipsychotics (SGAs). Acute dystonic reactions (ADRs) Department of Internal Medicine, Santa Barbara, CA, USA, have an occurrence rate of 3%-10%, but may occur more frequently with high Email: [email protected] potency antipsychotics. Younger age and male sex appear to be the most common risk factors, although a variety of metabolic abnormalities and illnesses have also © 2018 Collins N. This article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License been associated with ALD as well. The diagnosis of ALD can go unrecognized as other causes of acute respiratory failure are often explored prior to ALD. The exact mechanism for ALD remains unclear, yet evidence has shown a strong correlation with extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) and dopamine receptor blockade. -

NORTH – NANSON CLINICAL MANUAL “The Red Book”
NORTH – NANSON CLINICAL MANUAL “The Red Book” 2017 8th Edition, updated (8.1) Medical Programme Directorate University of Auckland North – Nanson Clinical Manual 8th Edition (8.1), updated 2017 This edition first published 2014 Copyright © 2017 Medical Programme Directorate, University of Auckland ISBN 978-0-473-39194-2 PDF ISBN 978-0-473-39196-6 E Book ISBN 978-0-473-39195-9 PREFACE to the 8th Edition The North-Nanson clinical manual is an institution in the Auckland medical programme. The first edition was produced in 1968 by the then Professors of Medicine and Surgery, JDK North and EM Nanson. Since then students have diligently carried the pocket-sized ‘red book’ to help guide them through the uncertainty of the transition from classroom to clinical environment. Previous editions had input from many clinical academic staff; hence it came to signify the ‘Auckland’ way, with students well-advised to follow the approach described in clinical examinations. Some senior medical staff still hold onto their ‘red book’; worn down and dog-eared, but as a reminder that all clinicians need to master the basics of clinical medicine. The last substantive revision was in 2001 under the editorship of Professor David Richmond. The current medical curriculum is increasingly integrated, with basic clinical skills learned early, then applied in medical and surgical attachments throughout Years 3 and 4. Based on student and staff feedback, we appreciated the need for a pocket sized clinical manual that did not replace other clinical skills text books available. Attention focussed on making the information accessible to medical students during their first few years of clinical experience. -

A Checklist of Key Cardio-Respiratory Interventions for Entry-Level Physical Therapy Students
A Checklist of Key Cardio-Respiratory Interventions for Entry-Level Physical Therapy Students Introduction Members of the National Association for Clinical Education in Physiotherapy (NACEP) identified the need to develop a strategy to increase clinical placement capacity in a number of geographical and practice areas. One approach which has received widespread endorsement is the development of a checklist to track key interventions for specific practice areas. Clinical research supports the assessment and treatment of the cardio-respiratory system by physiotherapists as a part of the holistic treatment of most patients. It also provides evidence for such assessments and treatments to be utilized in all practice areas, not simply those which are known to treat CR indicator conditions (e.g. heart failure, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, diabetes). Recognizing opportunities to assess and promote the ability to perform aerobic exercise and to identify its role in chronic disease prevention will provide the student with repeated occasions to observe and participate in CR clinical experiences. All instances where a student utilizes knowledge and skills related to cardio-respiratory conditions and interventions should therefore be considered as relevant and appropriate cardio-respiratory experiences. Objectives The objectives of the CR checklist are: (1) to ensure that physiotherapy students gain experience with essential clinical skills, attitudes and behaviours within CR in order to obtain the minimum entry-level cardio-respiratory competencies prior to graduation, (2) to provide clinical supervisors with guidance as to the practice settings and clinical situations in which competence may be assessed; and (3) to highlight for students, clinical instructors and facilities that any clinical setting has the potential to assist students in acquiring CR competencies. -

Impact of Environmental Tobacco Smoke Exposure on Anaesthetic and Surgical Outcomes in Children: a Systematic Review and Meta-An
ADC Online First, published on July 14, 2016 as 10.1136/archdischild-2016-310687 Original article Arch Dis Child: first published as 10.1136/archdischild-2016-310687 on 14 July 2016. Downloaded from Impact of environmental tobacco smoke exposure on anaesthetic and surgical outcomes in children: a systematic review and meta-analysis Christopher Chiswell,1 Yasmin Akram2 ▸ Additional material is ABSTRACT published online only. To view Background Tobacco smoke exposure in adults is What is already known on this topic? please visit the journal online (http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/ linked to adverse anaesthetic and surgical outcomes. Environmental tobacco smoke (ETS) exposure, including archdischild-2016-310687). ▸ Environmental tobacco smoke exposure has a passive smoking, causes a number of known harms in 1Department of Public Health, significant impact on paediatric health, children, but there is no established evidence review on Birmingham Children’s including frequency of respiratory illness, its impact on intraoperative and postoperative outcomes. Hospital, Birmingham, UK bacterial meningitis and ear infections. 2Institute of Applied Health Objectives To undertake a systematic review of the ▸ Smoking by adults increases their risk of Research, University of impact of ETS on the paediatric surgical pathway and to anaesthetic and surgical complications, Birmingham, Birmingham, UK establish if there is evidence of anaesthetic, including delayed wound healing, increased intraoperative and postoperative harm. Correspondence to respiratory complications and delayed Dr Christopher Chiswell, Eligibility criteria participants Children aged discharge. Department of Public Health, 0–18 years undergoing anaesthetic or surgical ’ ▸ Appropriate preoperative smoking cessation in Birmingham Children s procedures, any country, English language papers. Hospital, Steelhouse Lane, adults reduces the risk of these complications. -

Introduction to the Clinical Practice Guidelines
INTRODUCTION TO THE CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES First Nations and Inuit Health Branch (FNIHB) Clinical Practice Guidelines for Nurses in Primary Care. The content of this chapter was revised in December 2011. Table of Contents PURPOSE .................................................................................................................I–1 STRUCTURE ............................................................................................................I–1 Format of Body System Chapters .......................................................................I–1 Format of Medical Diagnosis/Condition Descriptions .........................................I–1 CULTURE ..................................................................................................................I–2 Commonly Cited Value ........................................................................................I–2 Culture and Health ..............................................................................................I–2 Culture and Health Care .....................................................................................I–3 TRAUMA INFORMED CARE ....................................................................................I–4 COMMUNICATION ....................................................................................................I–4 Therapeutic Relationships ..................................................................................I–4 History Taking ......................................................................................................I–4