EXAFS and XANES Study on the Zirconium Local Structures in Tektites and Natural Glasses
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
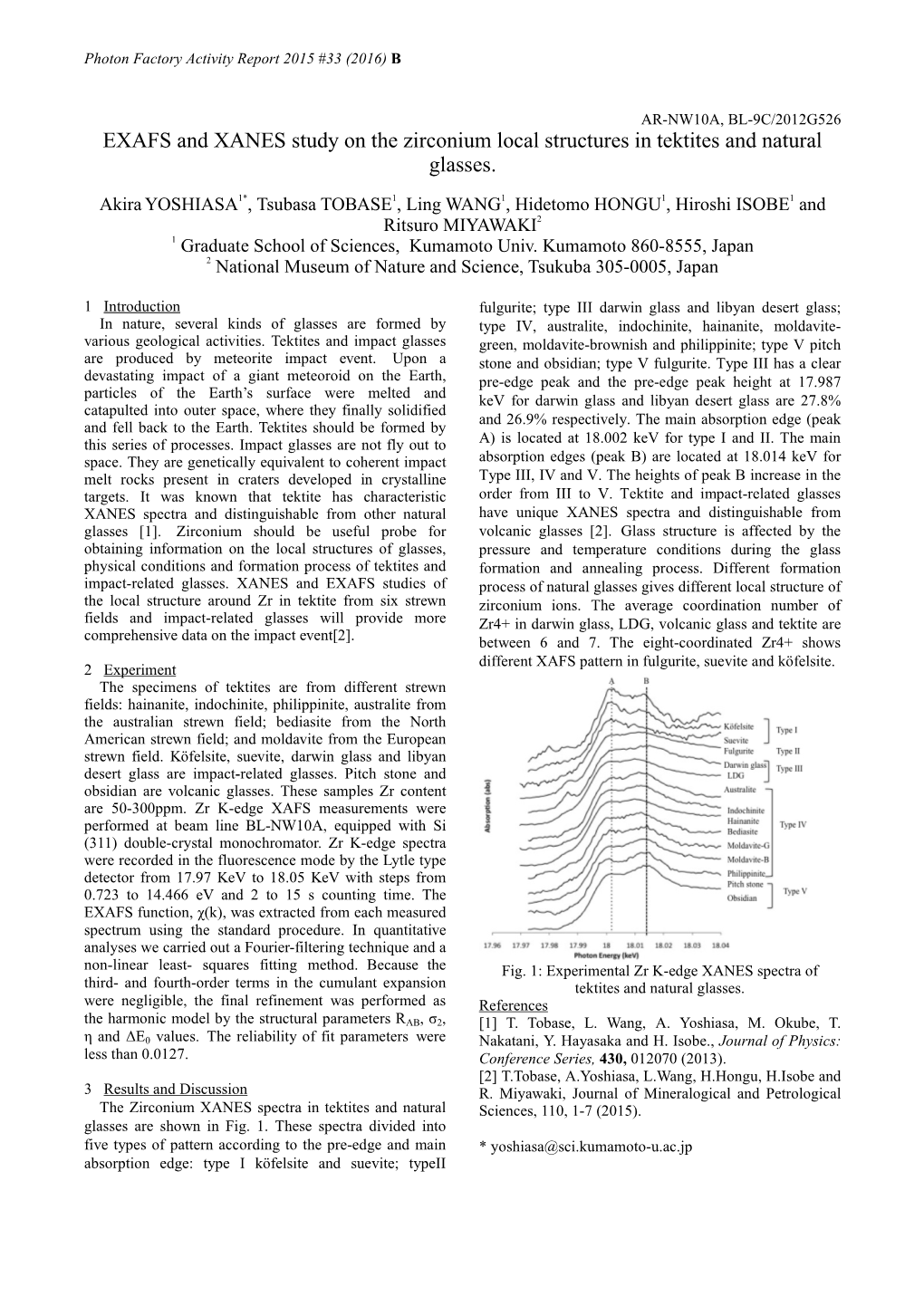
Load more
Recommended publications
-

NEW HIGH-PRECISION POTASSIUM ISOTOPES of TEKTITES. Y. Jiang1,2, H
49th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference 2018 (LPI Contrib. No. 2083) 1311.pdf NEW HIGH-PRECISION POTASSIUM ISOTOPES OF TEKTITES. Y. Jiang1,2, H. Chen2, B. Fegley, Jr.2, K. Lodders2, W. Hsu3, S. B. Jacobsen4, K. Wang (王昆)2. 1CAS Key Laboratory of Planetary Sciences, Purple Moun- tain Observatory, Chinese Academy of Sciences ([email protected]), 2Dept. Earth & Planetary Sciences and McDonnell Center for the Space Sciences, Washington University in St. Louis ([email protected]), 3Space Sci- ence Institute, Macau University of Science and Technology, 4Dept. Earth & Planetary Sciences, Harvard University. Introduction: Tektites are natural glassy objects crater of Hawaii (BHVO-1), are also analyzed. Hainan formed from the melting and rapid cooling of terrestri- Tektite is a typical splash-form tektite from Hainan al rocks during the high-energy impacts of meteorites, Island, China and of a dumbbell shape. We analyzed K comets, or asteroids upon the surface of the Earth [1]. isotopes of 15 chips along the longitudinal axis of its Chemical and isotopic compositions indicate that pre- profile, on a Neptune Plus MC-ICP-MS at Washington cursor components of tektites are the upper terrestrial University in St. Louis [14]. Except for Hainan tektite, continental crust, rather than extraterrestrial rocks. all other samples were only analyzed in bulk, with a Tektites are characterized by the depletion of volatile GV Instruments IsoProbe P MC-ICP-MS at Harvard elements and water, and heavy Cd, Sn, Zn and Cu iso- University following the description in [13]. K isotope topic compositions [2-5]. Since volatilities of elements compositions are reported using the per mil (‰) nota- 41 41 39 41 39 are defined by their 50% condensation temperature (Tc) tion, where δ K = ([( K/ K)sample/( K/ K)standard – of the solar nebula gas at 10-4 bars [6], there is no rea- 1]×1000). -

A Review of Evidence for a Gulf of Tonkin Location for the Australasian Tektite Source Crater Aubrey Whymark* Consultant Wellsite Geologist, Manila, Philippines
Thai Geoscience Journal 2(2), 2021, p. 1-29 1 Copyright © 2021 by the Department of Mineral Resources of Thailand ISSN-2730-2695; DOI-10.14456/tgj.2021.2 A review of evidence for a Gulf of Tonkin location for the Australasian tektite source crater Aubrey Whymark* Consultant Wellsite Geologist, Manila, Philippines. *Corresponding author: [email protected] Received 5 March 2021; Accepted 17 June 2021. Abstract Australasian tektites (AAT) occur across Southeast Asia, Australia, the Indian Ocean, and southwest Pacific Ocean. AAT form the youngest and most extensive major tektite strewn field. Unlike other tektite strewn fields, AAT have no known source crater. Review of the literature establishes that a single ~ 43 km post-impact diameter crater exists, possibly significantly enlarged by slumping. The obliquity of the impact that formed the AAT would result in a crater that is less pervasive in depth but with greater downrange shock effects and melt ejection. Multiple lines of evidence, historically viewed in isolation, were examined, concatenated, contextualized, and discussed. Tektite morpho- logy and distribution; microtektite regressions; geochemical considerations, comparisons, and iso- -concentration regressions; lithological characteristics; age of source rock; and regional geological considerations are reviewed. The source material is predicted to be an abnormally thick sequence of rapidly deposited, poorly compacted, deltaic to shallow marine, shales to clay-rich siltstones of early Pleistocene to Pliocene age. The impact likely occurred in a shallow marine environment. Forty- two maps of positive and negative parameters are presented and overlain. These indicate the AAT source crater probably lies in the central to northwestern Yinggehai - Song Hong Basin / Gulf of Tonkin. -

Population Polygons of Tektite Specific Gravity for Various Localities in Australasia
Reprinted from GEOCHIMICA ET COSMOCHIMICA ACTA Vol. 28, NO. 6,pp. 821-839 t II d 0 i (CA'TECORYI I {NASA CR OR TMX OR AD NUMBER1 ! POPULATION POLYGONS OF TEKTITE SPECIFIC GRAVITY FOR VARIOUS LOCALITIES IN AUSTRALASIA DEANR. CHAPMAN,HOWARD K. LARSONand LEROYC. SCHEIBER N.A.S.A., Ames Research Center, Moffett Field, California PERGAMON PRESS NEWYORK * OXFORD - LONDON - PARIS 1964 Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta 1984, Val. 28, pp. 821 to 839. Pergamon Press Ltd. Printed in Northern Ireland Population polygons of tektite specific gravity for various localities in Australasia* DEANR. CHAPMAN,HOWARD K. LARSON and LEROYC. SCHEIBER N.A.S.A., Ames Research Ccnter, Moffett Field, California 31- Abstract-~Ieasurements of specific gravity by the method of liquid flotation have been made on about 6000 tektites from 18 different localities in Australasia, from 1 locality in Texas and 2 in Czechoslovakia. Comparison of specific-gravity population polygons for various localities has led to the unanticipated conclusion that the amtralite population in southwest Australia is essentially the same as the philippinite population, rather than the population elsewhere in Australia. The javanite population appears closely related to certain populations in Australia. In several localities the presence of two superimposed populations is demonstrated. The specific- gravity evidence indicates that the Australasian tektites represent a single event comprising many distinguishable clusters, some of which have partially overlapped. INTRODUCTION #e AT the turn of this century, the Austrian geologist SUESS(1900) gave the collective name of “tektites” to three widely separated groups of natural glass objects then known to be scattered over parts of Australia, Czechoslovakia and the island of Billiton. -

Isotopic Fractionation of Zn in Tektites
Isotopic fractionation of Zn in tektites Frederic Moynier1, 2,*, Pierre Beck3, Fred Jourdan4, Qing-zhu Yin2, Christian Koeberl5, and Uwe Reimold6 1Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences, Washington University in St Louis, One Brookings Drive, St Louis, MO 63130 2Department of Geology, University of California Davis. One Shields Avenue, Davis, CA 95616 3Laboratoire de Planetologie, Universite Joseph Fourier, CNRS/INSU, Bat. Physique D, BP 53, 38041 Grenoble cedex 9, France 4 Western Australian Argon Isotope Facility, Department of Applied Geology & JdL-CMS, Curtin university of Technology, GPO Box U1987, Perth, WA 6845; Australia. 5Department of Lithospheric Research, University of Vienna, Althanstrasse 14, A-1090 Vienna, Austria 6Museum f. Natural History (Mineralogy), Humbold University Berlin, Invalidenstrasse 43, 10115 Berlin, Germany *Corresponding author: [email protected], Tel: +1 314-935-8634, Fax: +1 314-935-7361 Abstract: Tektites are terrestrial natural glasses, produced during a hypervelocity impact of an asteroid (or comet nucleus) into the Earth surface. The similarity between the chemical and isotopic compositions of tektites and terrestrial upper continental crust implies they formed from the target rocks. The mechanism of the loss of water as well as the behavior of volatile species during tektites formation is still debated, and volatilization at high temperature is a possible way. Volatilization can fractionate isotopes, and, therefore, comparing the isotope composition of volatile elements in tektites with their source rocks may help to understand the conditions of evaporation. In this study, we have measured the Zn isotopic composition of 20 tektites from the four different strewn fields. Almost all the samples are enriched in heavy isotopes of Zn compared to the upper continental crust. -

256-Microtektites-GCA2004.Pdf
Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, Vol. 68, No. 19, pp. 3971-4006, 2004 Copyright © 2004 Elsevier Ltd Pergamon Printed in the USA. All rights reserved 0016-7037/04 $30.00 ϩ .00 doi:10.1016/j.gca.2004.02.026 Geochemistry of Cenozoic microtektites and clinopyroxene-bearing spherules 1, 2 2 BILLY P. GLASS, *HEINZ HUBER, and CHRISTIAN KOEBERL 1Geology Department, University of Delaware, Newark, Delaware 19716, USA 2Department of Geological Sciences, University of Vienna, Althanstrasse 14, A-1090 Vienna, Austria (Received July 1, 2003; accepted in revised form February 18, 2004) Abstract—We have determined the major and trace element compositions of 176 individual microtektites/ spherules from the Australasian, Ivory Coast, and North American microtektite and clinopyroxene-bearing (cpx) spherule layers. Trace element contents for up to 30 trace elements were determined by instrumental neutron activation analysis (INAA), and major element compositions were determined using energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) analysis in combination with a scanning electron microscope (SEM). In addition, petrographic data were obtained for the cpx spherules using the SEM and EDX. This is the first trace element study of individual Australasian microtektites, and the data revealed the presence of a previously unrecognized group of Australasian microtektites with high contents of Ni (up to 471 ppm). In previous studies the high-Mg (HMg) Australasian microtektites were thought to be related to the HMg Australasian tektites, but our trace element data suggest that the high-Ni (HNi) Australasian microtektites, rather than the high-Mg microtektites, are related to the high-Mg Australasian tektites. We find that Cenozoic microtektites/spherules from a given layer can be distinguished from microtektites/spherules from other layers as a group, but it is not always possible to determine which layer an individual microtektite/spherule came from based only on trace element compositions. -

Geological Survey Research 1962
Geological Survey Research 1962 Synopsis of Geologic, Hydrologic, and Topographic Results GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 450-A Geological Survey Research 1962 THOMAS B. NOLAN, Director GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PROFESSIONAL PAPER 450 Asynopsis of results ofgeologic, hydro logic, and topo graphic investigations for fiscalyear 1962, accom panied by short papers in the fields of geology, hydrology, topography, and allied sciences. Pub lished separately as Chapters A, B, C, D, and E UNITED STATES GOVERNMENT PRINTING OFFICE, WASHINGTON : 1962 FOREWORD The reception accorded the 1960 and 1961 Annual Reviews of Geological Survey research has encouraged us to prepare this volume, "Geological Survey Research, 1962," in a con tinuing effort to publish more quickly the significant results of our current investigations. We continue to consider these reports as experimental and have again this year modified the content, format, and frequency of release of chapters in an attempt to serve better the interests of the users of the reports. The comments and suggestions of these users are here solicited and will be considered carefully as future volumes are planned. The current Annual Review consists of five chapters (Chapters A through E) of Pro fessional Paper 450. As in the preceding two Annual Reviews, Chapter A is a synopsis of recent findings in the many and varied lines of study pursued by Survey personnel. Chap ters, B, C, D, and E of this volume are collections of short articles in geology, hydrology, topography, and allied fields. These articles are numbered as follows: Prof. Paper 450-B Articles 1-59 Prof. Paper 450-C Articles 60-119 Prof. -

Planetary Surface Instrument Workshop Report (1995)
PLANETARY SURFACE INSTRUMENTS WORKSHOP Edited by Charles Meyer, Allan H. Treiman, and Theodor Kostiuk Held at Houston, Texas May 12–13, 1995 Sponsored by Lunar and Planetary Institute Lunar and Planetary Institute 3600 Bay Area Boulevard Houston TX 77058-1113 LPI Technical Report Number 95-05 LPI/TR--95-05 ii Planetary Surface Instruments Workshop Compiled in 1996 by LUNAR AND PLANETARY INSTITUTE The Institute is operated by the Universities Space Research Association under Contract No. NASW-4574 with the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. Material in this volume may be copied without restraint for library, abstract service, education, or personal research purposes; however, republication of any paper or portion thereof requires the written permission of the authors as well as the appropriate acknowledgment of this publication. This report may be cited as Meyer C., Treiman A. H., and Kostiuk T., eds. (1996) Planetary Surface Instruments Workshop. LPI Tech. Rpt. 95- 05, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston. 115 pp. This report is distributed by ORDER DEPARTMENT Lunar and Planetary Institute 3600 Bay Area Boulevard Houston TX 77058-1113 Mail order requestors will be invoiced for the cost of shipping and handling. Cover: MIMOS-II, a miniaturized Mössbauer instrument with two detector channels, developed for use in space missions with very limited power resources like the Small Stations of the Russian Mars ’96 Mission. LPI Technical Report 95-05 iii Introduction The next steps in the exploration of the solar system will include robotic missions to the surfaces of planets, moons, asteroids, and comets. For the greatest possible returns from these missions, their scientific rationales must be closely coordinated with development of appropriate instrumentation and with the constraints of mission and program planning. -

Moldavites: a Review
Bulletin of the Czech Geological Survey, Vol. 77, No. 4, 283–302, 2002 © Czech Geological Survey, ISSN 1210-3527 Moldavites: a review MILAN TRNKA1 – STANISLAV HOUZAR2 1Lithos Co., Ltd., Skoumalova 25, 600 00 Brno, Czech Republic; e-mail: [email protected] 2Dept. Mineralogy and Petrography, Moravian Museum, Zelný trh 6, 659 37 Brno, Czech Republic; e-mail: [email protected] Abstract. Moldavites from southern Bohemia, from western Moravia, from the Cheb Basin, from Lusatia (Germany), and from Waldviertel (Aus- tria) are the only known European tektites. In the present paper, we briefly sum up the existing knowledge about their strewn fields and geology, about their properties, and their origin. The present survey should enable a detailed comparison with other groups of tektites and separation of primary differ- ences from differences caused by earth history. The extent of moldavite occurrences is a result of intensive denudation and redeposition of the initial strewn field. All regions of moldavite occurrences are spatially associated with regional basins and depressions. The oldest moldavite-bearing sediments with very short-transported material are unsorted colluvio-fluvial gravelly sands and clays of Middle to Upper Miocene age. Fluvial transport of moldavites to more distant places determined their present distribution and led to a substantial lowering of their content in the sediments. Roughly 106 metric tons of mol- davite matter (macrotektites) formed initially. Only about 1% of this mass has been preserved till the present. Most moldavites are splash-form moldavites. No ablation features were found on their surface. Muong Nong type moldavites occur sporadically but their amount could be much higher at the time of their formation. -

Metallic Spherules in Impactite and Tektite
THE AMERICAN MINERAI-OGIST, VOL. 52, MAY-JUNE, 1967 METALLIC SPHERULESIN IMPACTITE AND TEKTITE GLASSES1 RonrNBnEtt, U. S. GeologicalSurvey, Washi.ngton, D. C. Asstrecr Electron microprobe analyses indicate that Ni-Fe spherules within impactite glass bombs from the Meteor Crater area, Arizona, contain from 20 to 65 weight percent Ni. Spherules from impactite glass at Wabar, Saudi Arabia, contain 8 to 41 percent Ni. The parent meteorites contain 7 to 8 percent Ni. The analyses indicate that glass in the vicinity of the spherules is enriched in Fe. Spherules in philippinite and indochinite tektites contain 1 to 3 and 4 to 6 percent Ni, respectively. The glass in the vicinity of tektite spherules is not enriched in Fe and contains from 3 to 6 percent Fe. It is proposed that spherules in impactite glasseswere partially oxidized prior to or dur- ing incorporation into impactite bombs. The almost Ni-free Fe oxide difiused into the glass, thus depleting the metal in Fe, and enriching the glass. Carbon dioxide and water may have contributed to the oxidation at Meteor Crater. Spherules in tektites were not oxidized because the tektites were formed in an atmo- sphere with extremely low partial pressure of oxygen. A less likely alternative is that the spherules were incorporated into the tektite glass instantaneously so that oxidation was prevented, fNrnoouctroN Impactite bombs consist predominantly of glassthat formed from rock and soil when a meteorite hit the earth. These impactite bombs, com- monly contain small Ni-Fe spherules. Previous analysesof metallic spherulesfrom meteorite impact craters indicate that the spherules are richer in Ni than the parent meteorite from which they were derived. -

57Fe Mossbauer Study of Tektites BJ Evans and LX Leung C-.) University
57Fe Mossbauer Study of Tektites r' B. J. Evans and L. X. Leung C-.) Department of Chemistry -rn University of Michigan C Ann Arbor, MI 48109 N176-31121 (NASA-CR-148774) Fe-57 MOESSBAUEB STUDY OF TEKTITES Final Report (Michigan Univ.) 55 p HC $4.50 CSCI 03B Unclas G3/91 50391 SE ABSTRACT 57 i Fe Mossbauer measurements have been made selected moldavite, australite, philippinite and georgia tektites. The spectra consist of two apparent lines but at least two quadru pole doublets can be fitted to these spectra.- The Mossbauer parameters for these doublets indicate that they arise from Fe2 + ions with local environments, which are relatively rich and relatively poor in calcium, respectively, similar to those in clinopyroxenes. No evidence for Fe3+/Fe 2 + ratios above 0.01 (estimated detection limit) have been found in any tektite. Tektites are considerably more reduced than previously believed and the extent of the reduction shows little or no variation among different types of tlktites. These results limit the source materials of tektites to minerals in which the iron is uniformly highly reduced and in which the iron is contained clinopyroxene-like phases. I. INTRODUCTION The origin and source materials of tektites continue to be a conundrum. On the one hand, there is agreement among some inves tigators on their connascence with terrestrial meteoritic impact events while, on the other hand, there is a concensus among a smaller, more active group of tektite investigators that tektites are lunar materials being either the ejecta from a lunar meteoritic impact or lunar volcanism.11 In his recent monograph on tektites O'Keefe has given a well balanced review of the different theories on the origins of tektites and their strengths and shortcomings in the light of the experimental evidence. -

Schwarz Et Al
COEVAL AGES OF AUSTRALASIAN, WESTERN CANADIAN AND BELIZE TEKTITES. W.H. Schwarz 1, M. Trieloff 1, K. Bollinger 1, N. Gantert 1, V.A. Fernandes 2,1 , H.-P. Meyer 1, H. Povenmire 3, E.K. Jessberger 4, C. Koeberl 5 1Institute of Earth Sciences, Heidelberg University, Im Neuenheimer Feld 234-236, 69120 Heidelberg, Germany. 2Museum für Naturkunde, Leibniz-Institute, University Berlin, Invalidenstrasse 43, D-10115 Berlin, Ger- many 3Florida Institute of Technology, 215 Osage Drive, Indian Harbour Beach, FL32937 4Institut für Planetologie, Universität Münster, Wilhelm Klemm Straße 10, 48419 Münster,Germany 5Dept. Lithospheric Research, University of Vienna, Althanstrasse 14, 1090 Vienna, Austria, and Natural History Museum, Burgring 7, 1010 Vienna, Austria. Introduction: Tektites are natural glasses found in glasses from Indochina nor button-flanged tektites from four strewnfields: Australasian, North American, Ivory Australia for our study, because of possible Coast and Central European. They were formed by interference by excess argon [11]. Further two tektites, large-scale meteorite impacts on Earth and represent from Central America and from western Canada were primary (early) melt ejecta of sedimentary target chosen. The Western Canadian and Belize melt glasses materials [1]. While genetic links are established are round and dark-coloured comparable to Austral- between the Nördlinger Ries and the moldavites [2], asian tektites. Tektites were cut and only fresh glass the Bosumtwi impact crater and Ivory Coast tektites from the interior was used. Australasian tektites were [3], and North American tektites and the Chesapeake irradiated at the research reactor in Geesthacht Bay structure [4], the situation is different for the (Germany), the Belize and Western Canadian samples Australasian tektite strewn field: although it is the at the RPI reactor in Sacavém (ITN, Portugal). -

Department of the Interior United States Geological Survey Preceding Page Blank Not Filmed
ASTROGEOLOGIC STUDIES ANNUAL PROGRESS REPORT July 1, 1965 to July 1, 1966 PART C: COSMIC CHEMISTRY AND PETROLOGY October 1966 This preliminary report is distributed without editorial and technical review for conformity with official standards and nomenclature. It should not be quoted without permission. This report concerns work done on behalf of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration. DEPARTMENT OF THE INTERIOR UNITED STATES GEOLOGICAL SURVEY PRECEDING PAGE BLANK NOT FILMED. CONTENTS PART C.. COSMIC CHEMISTRY AND PETROLOGY Page Introduction ........................ v Metallic spherules in impactite and tektite glasses . by Robin Brett ...................... 1 f/ Introduction ..................... 1 Acknowledgment ................... 1 Description of spherules ............... 1 Iron and nickel content of spherules and glass .... 2 The system Fe-Ni-0 ..................10 Experimental work ................... 12 Conclusions ...................... 13 References cited ................... 17 Martha's Vineyard and selected Georgia tektites: New chemical data. by Frank Cuttita. R S Clarke Jr., . / M. K . Carron. and C . S . Anne11 .............. 21 Introduction ..................... 21 Major elements .................... 22 Minor elements .................... 23 Significance ..................... 24 References cited ................... 25 The occurrence and origin of lamellar troilite in iron meteorites. by Robin Brett and E . P . Henderson ......35 i/ Introduction ..................... 35 Previous work ..................... 35 Methods