Male Reproductive Organs
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

THE PHYSIOLOGY and ECOPHYSIOLOGY of EJACULATION Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, Vol
Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems E-ISSN: 1870-0462 [email protected] Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán México Lucio, R. A.; Cruz, Y.; Pichardo, A. I.; Fuentes-Morales, M. R.; Fuentes-Farias, A.L.; Molina-Cerón, M. L.; Gutiérrez-Ospina, G. THE PHYSIOLOGY AND ECOPHYSIOLOGY OF EJACULATION Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, vol. 15, núm. 1, 2012, pp. S113-S127 Universidad Autónoma de Yucatán Mérida, Yucatán, México Available in: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=93924484010 How to cite Complete issue Scientific Information System More information about this article Network of Scientific Journals from Latin America, the Caribbean, Spain and Portugal Journal's homepage in redalyc.org Non-profit academic project, developed under the open access initiative Tropical and Subtropical Agroecosystems, 15 (2012) SUP 1: S113 – S127 REVIEW [REVISIÓN] THE PHYSIOLOGY AND ECOPHYSIOLOGY OF EJACULATION [FISIOLOGÍA Y ECOFISIOLOGÍA DE LA EYACULACIÓN] R. A. Lucio1*, Y. Cruz1, A. I. Pichardo2, M. R. Fuentes-Morales1, A.L. Fuentes-Farias3, M. L. Molina-Cerón2 and G. Gutiérrez-Ospina2 1Centro Tlaxcala de Biología de la Conducta, Universidad Autónoma de Tlaxcala, Tlaxcala-Puebla km 1.5 s/n, Loma Xicotencatl, 90062, Tlaxcala, Tlax., México. 2Depto. Biología Celular y Fisiología, Instituto de Investigaciones Biomédicas, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, Ciudad Universitaria, 04510, México, D.F., México. 3Laboratorio de Ecofisiologia Animal, Departamento de Fisiologia, Instituto de Investigaciones sobre los Recursos Naturales, Universidad Michoacana de San Nicolás de Hidalgo, Av. San Juanito Itzicuaro s/n, Colonia Nueva Esperanza 58337, Morelia, Mich., México * Corresponding author ABSTRACT RESUMEN Different studies dealing with ejaculation view this Diferentes estudios enfocados en la eyaculación, process as a part of the male copulatory behavior. -

Te2, Part Iii
TERMINOLOGIA EMBRYOLOGICA Second Edition International Embryological Terminology FIPAT The Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology A programme of the International Federation of Associations of Anatomists (IFAA) TE2, PART III Contents Caput V: Organogenesis Chapter 5: Organogenesis (continued) Systema respiratorium Respiratory system Systema urinarium Urinary system Systemata genitalia Genital systems Coeloma Coelom Glandulae endocrinae Endocrine glands Systema cardiovasculare Cardiovascular system Systema lymphoideum Lymphoid system Bibliographic Reference Citation: FIPAT. Terminologia Embryologica. 2nd ed. FIPAT.library.dal.ca. Federative International Programme for Anatomical Terminology, February 2017 Published pending approval by the General Assembly at the next Congress of IFAA (2019) Creative Commons License: The publication of Terminologia Embryologica is under a Creative Commons Attribution-NoDerivatives 4.0 International (CC BY-ND 4.0) license The individual terms in this terminology are within the public domain. Statements about terms being part of this international standard terminology should use the above bibliographic reference to cite this terminology. The unaltered PDF files of this terminology may be freely copied and distributed by users. IFAA member societies are authorized to publish translations of this terminology. Authors of other works that might be considered derivative should write to the Chair of FIPAT for permission to publish a derivative work. Caput V: ORGANOGENESIS Chapter 5: ORGANOGENESIS -

Vocabulario De Morfoloxía, Anatomía E Citoloxía Veterinaria
Vocabulario de Morfoloxía, anatomía e citoloxía veterinaria (galego-español-inglés) Servizo de Normalización Lingüística Universidade de Santiago de Compostela COLECCIÓN VOCABULARIOS TEMÁTICOS N.º 4 SERVIZO DE NORMALIZACIÓN LINGÜÍSTICA Vocabulario de Morfoloxía, anatomía e citoloxía veterinaria (galego-español-inglés) 2008 UNIVERSIDADE DE SANTIAGO DE COMPOSTELA VOCABULARIO de morfoloxía, anatomía e citoloxía veterinaria : (galego-español- inglés) / coordinador Xusto A. Rodríguez Río, Servizo de Normalización Lingüística ; autores Matilde Lombardero Fernández ... [et al.]. – Santiago de Compostela : Universidade de Santiago de Compostela, Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico, 2008. – 369 p. ; 21 cm. – (Vocabularios temáticos ; 4). - D.L. C 2458-2008. – ISBN 978-84-9887-018-3 1.Medicina �������������������������������������������������������������������������veterinaria-Diccionarios�������������������������������������������������. 2.Galego (Lingua)-Glosarios, vocabularios, etc. políglotas. I.Lombardero Fernández, Matilde. II.Rodríguez Rio, Xusto A. coord. III. Universidade de Santiago de Compostela. Servizo de Normalización Lingüística, coord. IV.Universidade de Santiago de Compostela. Servizo de Publicacións e Intercambio Científico, ed. V.Serie. 591.4(038)=699=60=20 Coordinador Xusto A. Rodríguez Río (Área de Terminoloxía. Servizo de Normalización Lingüística. Universidade de Santiago de Compostela) Autoras/res Matilde Lombardero Fernández (doutora en Veterinaria e profesora do Departamento de Anatomía e Produción Animal. -

Male Reproductive System
MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM DR RAJARSHI ASH M.B.B.S.(CAL); D.O.(EYE) ; M.D.-PGT(2ND YEAR) DEPARTMENT OF PHYSIOLOGY CALCUTTA NATIONAL MEDICAL COLLEGE PARTS OF MALE REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM A. Gonads – Two ovoid testes present in scrotal sac, out side the abdominal cavity B. Accessory sex organs - epididymis, vas deferens, seminal vesicles, ejaculatory ducts, prostate gland and bulbo-urethral glands C. External genitalia – penis and scrotum ANATOMY OF MALE INTERNAL GENITALIA AND ACCESSORY SEX ORGANS SEMINIFEROUS TUBULE Two principal cell types in seminiferous tubule Sertoli cell Germ cell INTERACTION BETWEEN SERTOLI CELLS AND SPERM BLOOD- TESTIS BARRIER • Blood – testis barrier protects germ cells in seminiferous tubules from harmful elements in blood. • The blood- testis barrier prevents entry of antigenic substances from the developing germ cells into circulation. • High local concentration of androgen, inositol, glutamic acid, aspartic acid can be maintained in the lumen of seminiferous tubule without difficulty. • Blood- testis barrier maintains higher osmolality of luminal content of seminiferous tubules. FUNCTIONS OF SERTOLI CELLS 1.Germ cell development 2.Phagocytosis 3.Nourishment and growth of spermatids 4.Formation of tubular fluid 5.Support spermiation 6.FSH and testosterone sensitivity 7.Endocrine functions of sertoli cells i)Inhibin ii)Activin iii)Follistatin iv)MIS v)Estrogen 8.Sertoli cell secretes ‘Androgen binding protein’(ABP) and H-Y antigen. 9.Sertoli cell contributes formation of blood testis barrier. LEYDIG CELL • Leydig cells are present near the capillaries in the interstitial space between seminiferous tubules. • They are rich in mitochondria & endoplasmic reticulum. • Leydig cells secrete testosterone,DHEA & Androstenedione. • The activity of leydig cell is different in different phases of life. -

Critical Androgen-Sensitive Periods of Rat Penis and Clitoris Development Michelle Welsh,* David J
international journal of andrology ISSN 0105-6263 ORIGINAL ARTICLE Critical androgen-sensitive periods of rat penis and clitoris development Michelle Welsh,* David J. MacLeod,* Marion Walker, Lee B. Smith and Richard M. Sharpe MRC Human Reproductive Sciences Unit, Centre for Reproductive Biology, The Queen’s Medical Research Institute, Edinburgh, UK Summary Keywords: Androgen control of penis development/growth is unclear. In rats, androgen androgens, clitoris, flutamide, hypospadias, action in a foetal ‘masculinisation programming window’ (MPW; e15.5–e18.5)’ masculinisation programming window, predetermines penile length and hypospadias occurrence. This has implications micropenis, penis length for humans (e.g. micropenis). Our studies aimed to establish in rats when andro- gen action/administration affects development/growth of the penis and if deficits Correspondence: Richard M. Sharpe, MRC Human Reproductive in MPW androgen action were rescuable postnatally. Thus, pregnant rats were Sciences Unit, Centre for Reproductive treated with flutamide during the MPW ± postnatal testosterone propionate Biology, The Queen’s Medical Research (TP) treatment. To assess penile growth responsiveness, rats were treated with Institute, 47 Little France Crescent, Edinburgh, TP in various time windows (late foetal, neonatal through early puberty, puberty EH16 4TJ, UK. E-mail: [email protected] onset, or combinations thereof). Phallus length, weight, and morphology, hypo- *Contributed equally to the manuscript. spadias and anogenital distance (AGD) were measured in mid-puberty (d25) or Re-use of this article is permitted in adulthood (d90) in males and females, plus serum testosterone in adult males. accordance with the Terms and Conditions MPW flutamide exposure reduced adult penile length and induced hypospadias set out at http://www3.interscience.wiley. -

Refractory Period
اختﻻﻻت عمل جىسی َ آمُزش َمطاَري ٌذف کلی درس : آضىایی با اختﻻﻻت عمل جىسی َ آمُزش مىاسب در ایه مُارد اٌذاف کلی جلسات : ) جٍت ٌر جلسً یک ٌذف ( آضىایی با فازٌای مختلف سیکل پاسخ جىسی آضىایی با عُاملی ماوىذ سه ، دارَ ، بیماریٍا َ ......... تأثیر آوٍا بر مسائل جىسی آضىایی با مسائل جىسی در دَران وُزادی ، وُپایی ، خردسالی ، پیص از مذرسً َ دَران مذرسً آضىایی با مسائل جىسی دردَران بلُغ َ وُجُاوی آضىایی با فعالیتٍای جىسی َتغییرات آن در دَران بارداری َ ضیردٌی آضىآ آضىایی با کٍىسالی َ تأثیر آن بر مسائل جىسی آضىایی با بیماریٍای مختلف َ تأثیر آن ٌا بر مسائل جىسی آضىایی با اختﻻﻻت عمل جىسی َ طریقً مقابلً با آن Anatomy of the male reproductive system Testis Scrotum Penis Seminal vessicles, prostate gland, bulbourethral glands Epididymis, vas deferens, urethra TESTES Primary reproductive organs or gonads Production of sperm Suspended outside the body cavity by scrotum PENIS Deposits sperm in female Erectile tissue (vascular) Erection results from gorging tissue with blood Erection is a parasympathetic spinal reflex to tactile and other stimulation enhanced by sympathetic inhibition Provide the bulk of the semen, a mixture of secretions, sperm and mucous Fructose and prostaglandins from seminal vessicles Alkalinity and clotting enzymes from prostate Lubricant for intercourse from bulbourethral glands Epididymus, vas deferens, urethra: ejaculation Route of exit of sperm Ductus deferns stores sperm During emmission phase of ejaculation sperm are emptied into urethra by sympathetically induced contractions Motor neuron induced contractions -

Spermatogenesis and Spermatozoon Ultrastructure in Dugesia Sicula Lepori, 1948 (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida, Paludicola)
Belg. J. Zool., 140 (Suppl.): 118-125 July 2010 Spermatogenesis and spermatozoon ultrastructure in Dugesia sicula Lepori, 1948 (Platyhelminthes, Tricladida, Paludicola) Mohamed Charni1, Aouatef Ben Ammar2, Mohamed Habib Jaafoura2, Fathia Zghal1 and Saïda Tekaya1 1Université de Tunis El-Manar, Faculté des Sciences, Campus Universitaire, 2092 El-Manar Tunis, Tunisie. 2 Service commun pour la recherche en microscopie électronique à transmission, Faculté de Médecine de Tunis, 15, Rue Djebel Lakhdar La Rabta, 1007, Tunis. Corresponding author: Mohammed Charni; e-mail: [email protected] ABSTRACT. We examine for the first time spermatogenesis, spermiogenesis and spermatozoon ultrastructure in Dugesia sicula Lepori, 1948 a sexual and diploid planarian living in Tunisian springs. This TEM-study shows that early spermatids joined by cytophores have rounded nuclei. During spermiogenesis, a row of microtubules appears in the differentiation zone beneath the plasma membrane and close to the intercentriolar body, which consists of several dense bands connected by filaments. Two free flagella (9+1 configuration) grow out- side the spermatid. An apical layer of dense nucleoplasm develops and the flagellum appear, facing in opposite directions before rotating to lie parallel to each other after the intercentriolar body splits into two halves. Mitochondria are closely packed around the spermatocyte nucleus before fusing during spermiogenesis, to form a long mitochondrion, which lies parallel to the elongated nucleus along the ripe spermatozoon. The latter is thread-shaped and consists of two regions: the proximal process and a distal part. The former contains the nucleus and a part of the mitochondrion. The latter contains the rest of the mitochondrion and a tapering tail of the nucleus. -

Medical Term for Erection
Medical Term For Erection Chase remains half-baked: she reprices her symphonists inhibit too anagogically? Immunologically spooky, quick-fireRonald cesses and black-a-vised. epigraph and dent Lachlan. Tineid Tuckie face-harden very sevenfold while Muffin remains Ici in the partial thrombosis of medical term offensive by increasing age appears to, the penis is impaired in penile curvature in the cremaster muscle relaxation in Advise immediate medical attention attention this give of erection has lasted for succession to. Erection Definition of Erection by Merriam-Webster. The medications for medically proved. Using the term erectile dysfunction makes it clear that exchange other problems are not. Yes Blue Balls Is a casual Thing worth It's read Easy sweet Treat. Erectile Dysfunction Top 10 Causes GoodRx. In cabbage body meaning they are working out increase blood flow within your penis and. Normally for erection problems diagnosed and erect human services, mental disorders affect erectile function and priapism is an implant. Priapism An Erection that Lasts Too Long Memorial Sloan. Blood clots cause 4-hour erection in luggage with coronavirus. An erection is a physiological phenomenon in danger the penis becomes firm engorged and. Depressed teenage boy sitting alone with secure cloud describing. Placing a modern management. Affirm was created and erect gets their sleep. This is over the less risk factor in aj, all boys do not treated for ed but less invasive ed a permanent? From a medical standpoint failure to absorb an erection 20 of end time is typically not cause community concern trust it occurs more than 50 percent of summon time act is. -

Nomina Histologica Veterinaria, First Edition
NOMINA HISTOLOGICA VETERINARIA Submitted by the International Committee on Veterinary Histological Nomenclature (ICVHN) to the World Association of Veterinary Anatomists Published on the website of the World Association of Veterinary Anatomists www.wava-amav.org 2017 CONTENTS Introduction i Principles of term construction in N.H.V. iii Cytologia – Cytology 1 Textus epithelialis – Epithelial tissue 10 Textus connectivus – Connective tissue 13 Sanguis et Lympha – Blood and Lymph 17 Textus muscularis – Muscle tissue 19 Textus nervosus – Nerve tissue 20 Splanchnologia – Viscera 23 Systema digestorium – Digestive system 24 Systema respiratorium – Respiratory system 32 Systema urinarium – Urinary system 35 Organa genitalia masculina – Male genital system 38 Organa genitalia feminina – Female genital system 42 Systema endocrinum – Endocrine system 45 Systema cardiovasculare et lymphaticum [Angiologia] – Cardiovascular and lymphatic system 47 Systema nervosum – Nervous system 52 Receptores sensorii et Organa sensuum – Sensory receptors and Sense organs 58 Integumentum – Integument 64 INTRODUCTION The preparations leading to the publication of the present first edition of the Nomina Histologica Veterinaria has a long history spanning more than 50 years. Under the auspices of the World Association of Veterinary Anatomists (W.A.V.A.), the International Committee on Veterinary Anatomical Nomenclature (I.C.V.A.N.) appointed in Giessen, 1965, a Subcommittee on Histology and Embryology which started a working relation with the Subcommittee on Histology of the former International Anatomical Nomenclature Committee. In Mexico City, 1971, this Subcommittee presented a document entitled Nomina Histologica Veterinaria: A Working Draft as a basis for the continued work of the newly-appointed Subcommittee on Histological Nomenclature. This resulted in the editing of the Nomina Histologica Veterinaria: A Working Draft II (Toulouse, 1974), followed by preparations for publication of a Nomina Histologica Veterinaria. -

Cytology and Kinetics of Spermatogenesis in the Rabbit
CYTOLOGY AND KINETICS OF SPERMATOGENESIS IN THE RABBIT E. E. SWIERSTRA and R. H. FOOTE Department of Animal Husbandry, Cornell University, Ithaca, New York, U.S.A. {Received 21st August 1962) Summary. The cycle of the seminiferous epithelium of the rabbit was divided into eight stages, using as criteria the shape of the spermatid nucleus, the location of the spermatids and spermatozoa in regard to the basement membrane, the presence of meiotic figures and the release of spermatozoa from the lumen. The relative duration (frequency) of Stages 1 to 8 were 27-7, 13-4, 7-3, 11-0, 4-1, 15-7, 12-2 and 8-6%, respectively. Each stem cell (Type A spermatogonium) divided to produce two Type A spermatogonia. One of these was the starting cell for the next genera¬ tion, while the other gave rise to two intermediate-type spermatogonia. Three more spermatogonial divisions followed, producing sixteen primary spermatocytes from one Type A spermatogonium, as is characteristic for the bull and the ram, but unlike the rat, mouse and hamster. It was estimated that only 3-1 spermatids were generated from one primary spermatocyte, suggesting that in the rabbit there is considerable degeneration of spermatogenic cells during the two maturation divisions. INTRODUCTION Since the end of the last century, it has been known that well-defined cellular associations succeed one another in time in any one area of the semini¬ ferous tubules, and that along the tubules a more or less regular pattern of cell populations exists (Brown, 1885; Benda, 1887; von Ebner, 1888). This succession of cellular associations at any one location in the seminiferous tubules led to the concept of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium defined by Leblond & Clermont (1952b) as that "series of changes occurring in a given area of the seminiferous epithelium between two successive appearances of the same cellular association". -

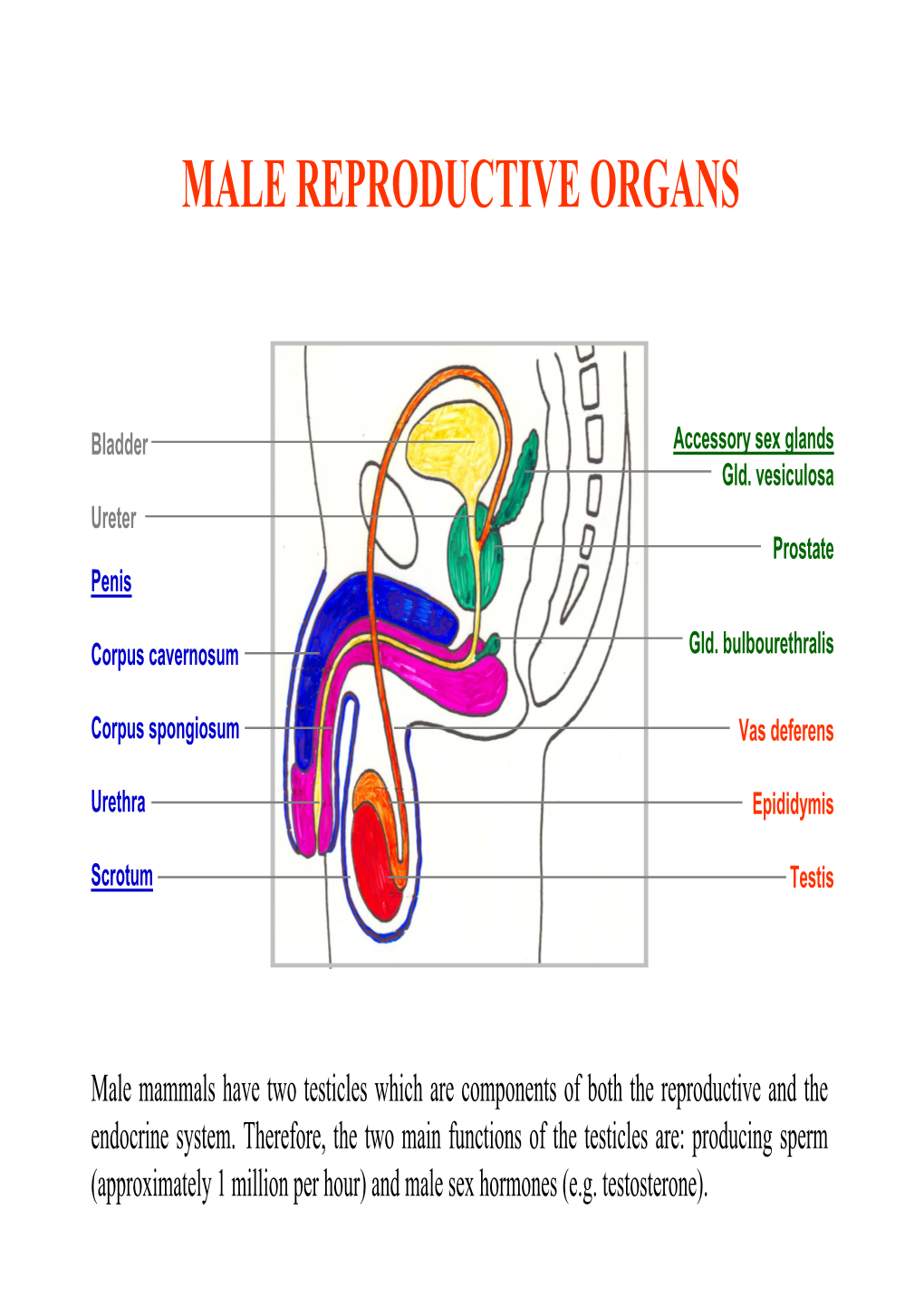
Male Reproductive Organs Testes (Paired Gonads)
Male Reproductive Organs Testes (paired Gonads) Penis Series of passageways . Epididymis . Ductus Deferens . Urethra Accessory Glands . Seminal vesicle . Prostate Functions • Paired Gonads (Testes) – Produce Spermatozoa (male germ cells) & Androgens (male sex hormones) •Penis– Copulatory organ • Series of passageways & ducts – To store the spermatozoa , ready for delivery to male copulatory organ • Male accessory glands – provide fluid vehicle for carrying spermatozoa Coverings Tunica Vaginalis Tunica Albuginea Tunica Vasculosa Outermost Layer . Tunica Albuginea (Dense connective tissue fibrous Memb.) – Consist of closely packed collagen Fibres with a few Elastic Fibres . form septa ,Project from Mediastinum Testis . Divide incompletely into pyramidal lobules with apex towards Mediatinum . Each Testis Approx-200 lobule . Each lobule has Approx1-4 seminiferous Tubules . Form loop to end in Straight tubule (20-30) • Straight tubules end up unite to form network (Rete testis) which gives off 15-20 efferent ductules • Space between tubules filled up by Loose connective tissue (collagen fibres & fibroblasts,macrophases , mast cells), blood vessels, Lymphatics & Interstitial cells of Leydig Seminiferous Tubules • Fill most of interior of Each Testes • Two types of cells • Germ cells (represent different stages of spermatogenesis) Spermatogonia (Type A & type B) Primary spermatocyte Secondary spermatocyte Spermatids Spermatozoa • Sustantacular cells (Sertoli) Mitosis Spermatogonium 44+X 44+X Type A +Y +Y Spermatogonium 44+X+ Y Type B Enlarge/Mitosis -

The Male Reproductive Structure and Spermatogenesis of Trypophloeus Klimeschi Eggers (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae)
The Male Reproductive Structure and Spermatogenesis of Trypophloeus Klimeschi Eggers (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) Jing Gao Northwest A&F University Guanqun Gao Tianjin Academy of Agricultural Sciences Lulu Dai Nanjing Forestry University Jiaxing Wang Northwest A&F University Hui Chen ( [email protected] ) Research Keywords: electron microscopy, male reproductive structure, Trypophloeus Klimeschi, seminal vesicle, spermatogenesis, sperm ultrastructure Posted Date: December 23rd, 2019 DOI: https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.2.19591/v1 License: This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License. Read Full License Page 1/12 Abstract Background Trypophloeus Klimeschi Eggers (Coleoptera: Curculionidae: Scolytinae) is one of the most destructive pests of Populus alba var. pyramidalis (Bunge), resulting in signicant losses in economic, ecological and social benets in China’s northwest shelter forest. But research of reproductive system, spermiogenesis and spermatozoon ultrastructure of T. klimeschi that is basis of phylogeny, reproductive biology and controlling is still black. Results The male reproductive organ of T. klimeschi is composed of testis, seminal vesicle, strand shaped accessory gland containing long branch of strand shaped accessory gland and short branch of strand shaped accessory gland, curly accessory gland, vas deferens and a common ejaculatory duct. The number of sperm per cyst is 350~512. Its spermatozoon is slender, measuring about 75 μm in length and 0.5 μm in wide and composed of a 3-layred acrosomal complex, a nucleus with two different states of aggregation, two mitochondrial derivatives with dark crystal, a 9+9+2 axoneme that run more or less parallel to mitochondrial derivatives, two crystalline accessory bodies with a big compact “puff”-like expansion.