Andorra: Freedom in the World 2019 Country Report
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
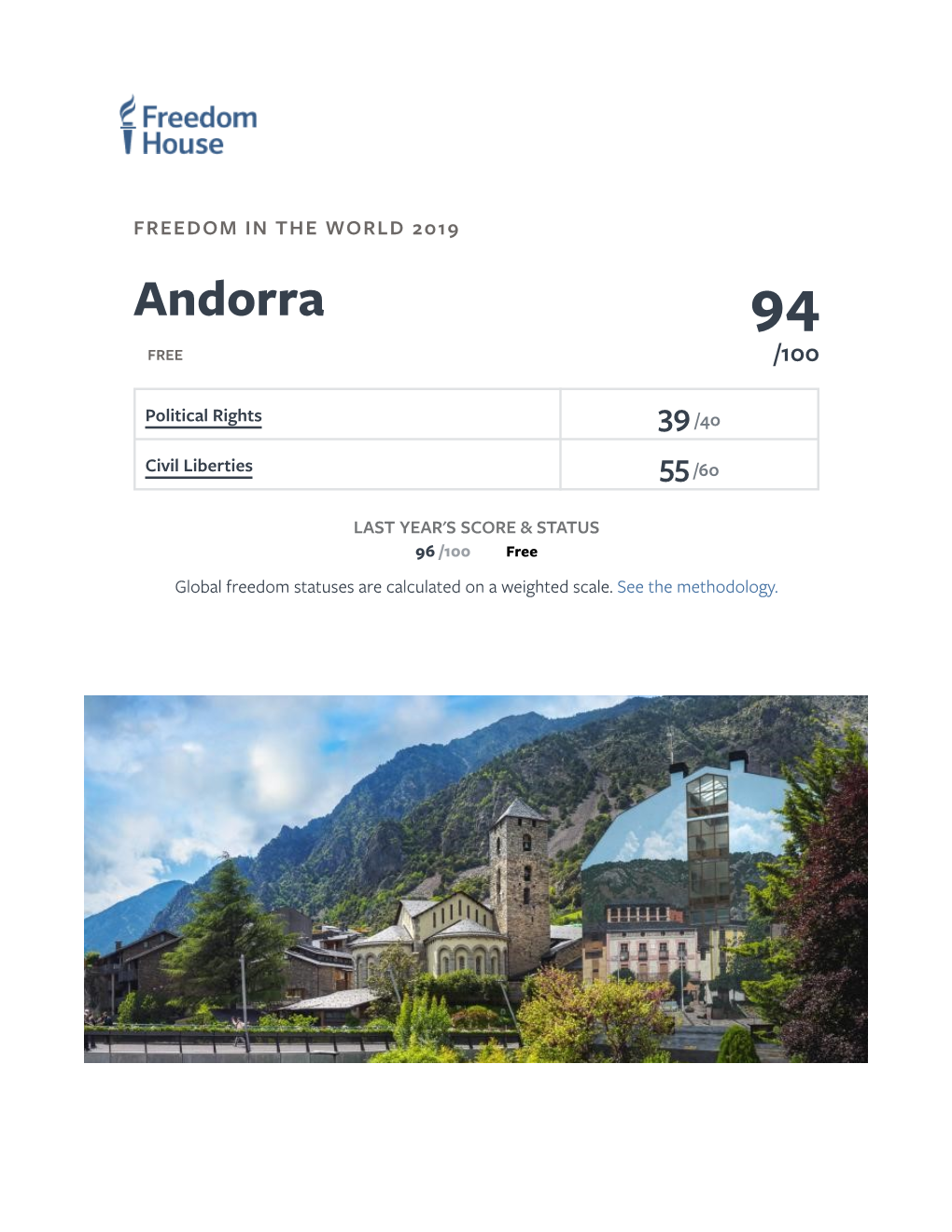
Load more
Recommended publications
-

List of Participants Liste Des Participants
LIST OF PARTICIPANTS LISTE DES PARTICIPANTS 142nd IPU Assembly and Related Meetings (virtual) 24 to 27 May 2021 - 2 - Mr./M. Duarte Pacheco President of the Inter-Parliamentary Union Président de l'Union interparlementaire Mr./M. Martin Chungong Secretary General of the Inter-Parliamentary Union Secrétaire général de l'Union interparlementaire - 3 - I. MEMBERS - MEMBRES AFGHANISTAN RAHMANI, Mir Rahman (Mr.) Speaker of the House of the People Leader of the delegation EZEDYAR, Mohammad Alam (Mr.) Deputy Speaker of the House of Elders KAROKHAIL, Shinkai (Ms.) Member of the House of the People ATTIQ, Ramin (Mr.) Member of the House of the People REZAIE, Shahgul (Ms.) Member of the House of the People ISHCHY, Baktash (Mr.) Member of the House of the People BALOOCH, Mohammad Nadir (Mr.) Member of the House of Elders HASHIMI, S. Safiullah (Mr.) Member of the House of Elders ARYUBI, Abdul Qader (Mr.) Secretary General, House of the People Member of the ASGP NASARY, Abdul Muqtader (Mr.) Secretary General, House of Elders Member of the ASGP HASSAS, Pamir (Mr.) Acting Director of Relations to IPU Secretary to the delegation ALGERIA - ALGERIE GOUDJIL, Salah (M.) Président du Conseil de la Nation Président du Groupe, Chef de la délégation BOUZEKRI, Hamid (M.) Vice-Président du Conseil de la Nation (RND) BENBADIS, Fawzia (Mme) Membre du Conseil de la Nation Comité sur les questions relatives au Moyen-Orient KHARCHI, Ahmed (M.) Membre du Conseil de la Nation (FLN) DADA, Mohamed Drissi (M.) Secrétaire Général, Conseil de la Nation Secrétaire général -

Comparative European Party Systems
COMPARATIVE EUROPEAN PARTY SYSTEMS Comparative European Party Systems, Second Edition, provides a comprehensive analysis across 48 party systems of party competition, electoral systems and their effects, and the classification of party systems and governments from 1945 through late-2018. The book consists of three parts. Part I provides a comparative and quantitative overview of party systems according to party families, patterns of party competition, electoral systems and their effects, and classification of party systems and governments. Part II consists of 38 detailed country profiles of longstanding democracies and of the European Union (plus nine profiles on regions such as in Spain and the UK), providing essential detail on the electoral systems, parties, party patterns and systems, dimensions of political competition, and governments. Part III provides an analysis of 10 additional country profiles of oscillating regimes such as Russia, Ukraine, and Balkan and Transcaucasus states. Comparative European Party Systems provides an excellent overview of topical issues in comparative election and party system research and presents a wealth of information and quantitative data. It is a crucial reference for scholars and students of European and comparative politics, elections, electoral systems, and parties and party systems. Alan Siaroff is Professor of Political Science at the University of Lethbridge, Canada. COMPARATIVE EUROPEAN PARTY SYSTEMS An Analysis of Parliamentary Elections Since 1945 Second Edition Alan Siaroff Second edition published 2019 by Routledge 2 Park Square, Milton Park, Abingdon, Oxon OX14 4RN and by Routledge 52 Vanderbilt Avenue, New York, NY 10017 Routledge is an imprint of the Taylor & Francis Group, an informa business © 2019 Alan Siaroff The right of Alan Siaroff to be identified as author of this work has been asserted by him in accordance with sections 77 and 78 of the Copyright, Designs and Patents Act 1988. -

Andorra-Andorre-En.Pdf
Andorra Official Title: Principality of Andorra General Information: Capital Andorra la Vella Population (million) n/a Total Area 468 km² Currency 1 CAN$=0.651 EURO (EUR) (2020 - Annual average) National Holiday September 8, Our Lady of Meritxell Day Language(s) Catalan, French, Castilian, Portuguese Political Information: Type of State Principality Type of Government Parliamentary democracy. Retains as its Heads of State a coprincipality; the two princes are the President of France and the Bishop of Seo de Urgel, Spain. Unicameral parliament with an 28-seat General Council of the Valleys (Consell General). Executive Council President elected by the General Council and formally appointed by the co-princes. Administrative Bilateral Product trade divisions: 7 parishes. Governing party: Democrats for Andorra. Canada - Andorra 1.2 1 Balance 0.8 Head of State Head of Government 0.6 Can. 0.4 President, Bishop of Urgel Prime Minister Exports 0.2 Coprince Emmanuel Macron, Coprince Joan Antoni Martí Can. 0 Imports E.V. Sicilia Millions -0.2 Total -0.4 Trade Ministers: Foreign : Maria Ubach Font -0.6 Finances : Jordi Cinca Mateos -0.8 2016 2017 2018 2019 2020 Statistics Canada Main Political Parties Democrats for Andorra (15); Liberal Party of Andorra (8); Social Democratic Party (3); Social Canadian Imports Democracy and Progress (2). from: Andorra M ach. M ech. Elec. Prod. Paper Prod. Chemical Prod. Specialized Inst. Base M etal Prod. Elections: Membersn/a of the General Council of the Valleys (4 year terms): next in 2019. Textiles Prod. 2020 Plastics, Rubber Economic Information: (2020) IMF (estimates) Statistics Canada Andorra Canada GDP: (billion) n/a $2,162.38 Canadian Exports GDP per capita: n/a $56,945.03 to: Andorra GDP Growth rate: (%) n/a -5.40 V ehicles and Equip. -

Summary Records of the Proceedings of the 130 IPU Assembly Geneva
Summary Records of the Proceedings of the 130th IPU Assembly Geneva 16-20 March 2014 Table of contents Page(s) Introduction ........................................................................................................................ 4 Opening of the 130th Assembly · Speech by Mr. M. Abdelwahad Radi, President of the Inter-Parliamentary Union ........... 5 · Speech by Mr. Michael Møller, Acting Director-General of the United Nations Office at Geneva ..................................................................................................................... 6 · Tribute to Mr. Anders B. Johnsson, outgoing General Secretary of the Inter- Parliamentary Union ……………………………… ............................................................ 7 Organization of the work of the Assembly · Opening of the General Debate .................................................................................... 9 · Consideration of requests for the inclusion of an emergency item in the Assembly agenda ......................................................................................................... 18 · Final agenda ................................................................................................................. 20 General Debate on the overall theme: The IPU at 125: Renewing our commitment to peace and democracy ...................................................................................................... 9 · Speech by Mr. Mustafa Ben Jaafar, Speaker of the National Constituent Assembly of Tunisia ......................................................................................................................... -

ANDORRA This File Contains Election Results for the Andorran General
ANDORRA This file contains election results for the Andorran General Council for 1997, 2001, 2005, 2009, 2011, and 2015. For 2005, the proportion rather than the number of votes is reported for the parish returns. Year, Geography, and Turnout YEAR Election Year PARISH Parish (Region and Constituency) ELEC Number of Eligible Voters BALLOTS Total Ballots Cast VALID_P Valid Votes in Parish Constituencies BLANK_P Black Votes in Parish Constituencies INVALID_P Invalid Votes in Parish Constituencies VALID_N Valid Votes in National Constituency BLANK_N Blank Votes in National Constituency INVALID_N Invalid Votes in National Constituency Candidates in Parish Constituencies (Parroquial) by Party ULIB_C Unió Liberal (UL, Liberal Union) PLA_C Partit Liberal d'Andorra (PLA, Liberal Party of Andorra), renamed Liberal Union PLA-IE_C Joint Partit Liberal d'Andorra (PLA, Liberal Party of Andorra) and Independent Candidates in Encamp PLA-IND_C Joint Partit Liberal d'Andorra (PLA, Liberal Party of Andorra) and Independent Candidates CR_C Coalició Reformista (CR, Reformist Coalition) DA_C Demòcrates per Andorra (DA, Democrats for Andorra) UP_C Unió del Progres (Union of Progress) DA-UP_C Joint Demòcrates per Andorra (DA, Democrats for Andorra) and Unió del Progres (Union of Progress) Candidates in Encamp AC-DA_C Joint Acció Comunal d'Ordino (Community Action of Ordino) and Demòcrates per Andorra (DA, Democrats for Andorra) DA-MM_C Joint Demòcrates per Andorra (DA, Democrats for Andorra) and Movimenet Massanenc (Movement Massana) DA-CI_C Joint Demòcrates -

Macroeconomic Background 1
PRINCIPALITY OF ANDORRA MACROECONOMIC BACKGROUND 1. The Principality of Andorra, the IMF’s newest member since October 2020, participated in its first Article IV consultation. The authorities are committed to further enhance transparency as they integrate into the international financial community. A coalition government took office in April 2019 with Prime Minister Xavier Espot Zamora from the Democrats for Andorra at the helm. The country enjoys political stability and has a good track-record of fiscal discipline, a gender-balanced work force, and ski resorts not dependent on air travel. The authorities successfully tested the appetite of foreign investors through successful private debt placements in 2020 and issued its first public international bond in late April 2021. 2. Banking services and tourism Figure 1. Employment Shares, 2019 dominate economic activity and (Percent of total employment) employment. With consolidated bank assets 70 70 Trade-tourism-arts over 500 percent of GDP, jobs in finance and 60 Finance-Real estate 60 real estate comprise 20 percent of employment, 50 50 40 40 a disproportionate size compared to the region 30 30 (Figure 1). Trade and tourism activity, accounting 20 20 for a fifth of the economy’s gross value added 10 10 (GVA) and 40 percent of employment, is 0 0 Andorra Spain Euro Area France comparable to Spain’s. However, with various Sources: Govern d'Andorra, Eurostat, and IMF staff estimates. Note: The figure for Finance and Real Estate for Andorra may be overstated due to other sectors connected to tourism, the share of the inclusion of ‘business services’ that are not included in that category for other the latter could be more than half of the countries. -

Andorra 2019 Human Rights Report
ANDORRA 2019 HUMAN RIGHTS REPORT EXECUTIVE SUMMARY The Principality of Andorra is a constitutional, parliamentary democracy. Two co- princes--the president of France and the Spanish bishop of Urgell--serve with joint authority as heads of state. On April 7, the country held free and fair multiparty elections for the 28 seats in parliament (the General Council of the Valleys), which selects the head of government. Having won a majority in parliament, the Democrats for Andorra (DA) formed a coalition with Liberals of Andorra (L’A) and Committed Citizens (CCs), and elected Xavier Espot Zamora from DA head of government. The country’s only security forces are the police, prison officers, traffic police, and forestry officials. The national police maintained internal and external security. The Ministry of Justice and Interior maintained effective civilian control over the security forces. There were no reports of significant human rights abuses. The government took steps to identify, investigate, and prosecute officials who committed human rights abuses. Section 1. Respect for the Integrity of the Person, Including Freedom from: a. Arbitrary Deprivation of Life and Other Unlawful or Politically Motivated Killings There were no reports that the government or its agents committed arbitrary or unlawful killings. b. Disappearance There were no reports of disappearances by or on behalf of government authorities. c. Torture and Other Cruel, Inhuman, or Degrading Treatment or Punishment The constitution and law prohibit such practices, and there were no reports that government officials employed them. ANDORRA 2 Prison and Detention Center Conditions There were no significant reports regarding prison or detention center conditions that raised human rights concerns. -
Andorra#.Vff3r-8R6yc.Cleanprint
https://freedomhouse.org/report/freedom-world/2015/andorra#.VfF3R-8r6yc.cleanprint Andorra freedomhouse.org The Andorran government continued to make efforts to address the country’s reputation as a tax haven and to bring its financial laws into compliance with the standards of the Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD). In April 2014, the organization released a peer review of Andorra’s implementation of OECD standards on transparency and the exchange of information for taxation purposes, concluding that the country was partially compliant. The report commended the introduction of a system of sanctions in 2014 to ensure companies’ compliance with transparency laws but also noted weaknesses in the maintenance of accounting records. In June, Andorra signed the OECD Declaration on Automatic Exchange of Information in Tax Matters, which obliges signatories to implement a global standard for the automatic exchange of information. Andorra also signed financial exchange agreements with Switzerland and Slovakia in March and September, respectively. In May 2014, the government passed a new personal income tax law, set to go into effect in 2015. Political Rights and Civil Liberties: Political Rights: 39 / 40 [Key] A. Electoral Process: 12 / 12 Andorra is governed under a parliamentary system. Two “co-princes,” the French president and the bishop of La Seu d’Urgell, Spain, serve jointly as ceremonial heads of state. Popular elections are held every four years for the 28-member Consell General, which selects the executive council president—the head of government. Half of the members are chosen in two-seat constituencies known as parishes, and the other half are chosen through a national system of proportional representation. -

Democrats Would Win the Election Today With
www.elperiodic.ad DIMARTS, 10 DE JULIOL DEL 2018 el Periòdic d’Andorra 12 CONEIXEMENT SOBRE d'Andorra L’ÚS DE LES TECNOLOGIES elelENGLISHTema PeriòdicPeriòdic del EDITION dia NewsST A U T E 1xx 9 1 CRES survey Increased confidence in authorities and institutions 3 PHOTO ANA/E.C. GRAPHIC PAKO TEMPRADO PS 23,9 % DA 56,2 % TERCERAVIA 7,6 % LdA 8 % SDP 2,2 % CC 1,5 % WHICH PARTY WOULD YOU VOTE IF GENERAL UPA 0,4 % ELECTIONS WERE HELD NOW? (VOTE DECIDED) TERCERAVIA PS 30,6 % 12,5 % LdA 10,4 % DA SDP 5,9 % 35,1 % RESULTS CC 0,8% 2019 UPA 0,5% The Director of CRES, Joan Micó. Democrats would win the election today with 56.2% of the vote The Social Democratic Party would be the second More than half of the population is satisfied with the most voted force with 23.9%, according to the CRES functioning of democracy in the country EL PERIÒDIC den vote exceeds 40% of the results. so denotes the assessment made by the citizens have made of the gene- CONSOLIDATION OF DEMOCRACY With SANT JULIÀ DE LÒRIA And it is that, according to the com- the population of the health crisis ral political situation of Andorra at the health crisis, the functioning/ of @PeriodicAND parison of the results of the pre-elec- by the political authorities, which the present, which has come to be democracy would also have acquired emocrats for Andorra (DA toral survey carried out by the rese- have achieved a better mark than in considered, by 55.2% of the sample, more solidity and stability, according + Independents) would arch center with those of the gene- recent years. -

Andorra - the World Factbook
Andorra - The World Factbook https://www.cia.gov/the-world-factbook/countries/andorra/ Explore All Countries — Andorra Europe INTRODUCTION Background The landlocked Principality of Andorra is one of the smallest states in Europe, nestled high in the Pyrenees between the French and Spanish borders. For 715 years, from 1278 to 1993, Andorrans lived under a unique coprincipality, ruled by French and Spanish leaders (from 1607 onward, the French chief of state and the Bishop of Urgell). In 1993, this feudal system was modified with the introduction of a modern constitution; the co-princes remained as titular heads of state, but the government transformed into a parliamentary democracy. Andorra has become a popular tourist destination visited by approximately 8 million people each year drawn by the winter sports, summer climate, and duty-free shopping. Andorra has also become a wealthy international commercial center because of its mature banking sector and low taxes. As part of its effort to modernize its economy, Andorra has opened to foreign investment, and engaged in other reforms, such as advancing tax initiatives aimed at supporting a broader infrastructure. Although not a member of the EU, Andorra enjoys a special relationship with the bloc that is governed by various customs and cooperation agreements and uses the euro as its national currency. GEOGRAPHY Location Southwestern Europe, Pyrenees mountains, on the border between France and Spain Geographic coordinates 42 30 N, 1 30 E 1 of 14 4/26/2021, 12:12 PM Andorra - The World Factbook -

Global Election Review 2019
GLOBAL ELECTION REVIEW 2019 Global Election Review 2019 Contact: +44 (0)1202 795 801 SOLACEGLOBAL.COM Email: [email protected] Global Election Forecast • APRIL 2019 GLOBAL ELECTION REVIEW 2019 Finland Andorra 14 April 7 April Macedonia 21 April Spain 28 April India Israel April-May 9 April Benin Maldives 28 April 6 April Solomon Islands 3 April Indonesia 17 April Contact: +44 (0)1202 795 801 SOLACEGLOBAL.COM Email: [email protected] Solomon Islands GLOBAL ELECTION REVIEW 2019 LOW Risk Date: 3 April Key Issues: Economic reform Specific Risks: Political Political System: Constitutional Monarchy (Commonwealth) Public corruption Travel Election Type: Presidential and Legislative Foreign policy Main Political Factions: United Party (Peter Kenilorea Jr) Terrorism West Honiara (John Kwaita) Civil Unrest The Solomon Islands general election will take place on 3 April for 50 seats in the National Parliament. These will be the first ones since the conclusion of the Regional Assistance Mission to Solomon Islands (RAMSI) in the summer of 2017, making it crucial in determining the path ahead. The lack of a well-defined and historically grounded political party system means that a coalition is unlikely to be immediately established after the election date. One key element that will be determined by the outcome of these elections is the diplomatic ties that the Solomon Islands historically have kept with Taiwan, in exchange for significant economic contributions. In fact, due to increasing exports to China, overshadowing the economic potential of maintaining a relationship with Taipei that grants little long-term growth prospects, the candidates running up to the election are considering the possibility of severing the diplomatic ties. -

The World Factbook
The World Factbook Europe :: Andorra Introduction :: Andorra Background: The landlocked Principality of Andorra is one of the smallest states in Europe, nestled high in the Pyrenees between the French and Spanish borders. For 715 years, from 1278 to 1993, Andorrans lived under a unique co-principality, ruled by French and Spanish leaders (from 1607 onward, the French chief of state and the Bishop of Urgell). In 1993, this feudal system was modified with the introduction of a modern, constitution; the co-princes remained as titular heads of state, but the government transformed into a parliamentary democracy. Andorra has become a popular tourist destination visited by approximately ten million people each year drawn by the winter sports, summer climate, and duty-free shopping. Andorra has also become a wealthy international commercial center because of its mature banking sector and low taxes. As part of its effort to modernize its economy, Andorra has opened to foreign investment, and engaged in other reforms, such as advancing tax initiatives aimed at supporting a broader infrastructure. Although not a member of the European Union (EU), Andorra enjoys a special relationship with the EU and uses the euro as its national currency. Geography :: Andorra Location: Southwestern Europe, Pyrenees mountains, on the border between France and Spain Geographic coordinates: 42 30 N, 1 30 E Map references: Europe Area: total: 468 sq km country comparison to the world: 196 land: 468 sq km water: 0 sq km Area - comparative: 2.5 times the size of Washington,