The Medieval Skull Relic of Turku Cathedral
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Koroisten Kulttuuriympäristöselvitys 2016
FK PÄIVI LEPPÄNEN Ympäristötoimiala, kaupunkisuunnittelu ja kaavoitus KOROISTEN KULTTUURIYMPÄRISTÖSELVITYS 2016 Sisällys 3.4 Vesistö 16 3.5 Ilmasto, eläimistö ja kasvillisuus 17 1 JOHDANTO 2 3.6 Maisemakuva 18 1.1 Selvitysalue lyhyesti 3 4 KULTTUURIYMPÄRISTÖN ERITYISPIIRTEET 25 2 KAAVOITUS JA MAANKÄYTÖN OHJAUS 4 4.1 Koroisten varhaisinta historiaa 25 2.1 Maakuntakaava 4 Teksti: Maiju Kähärä 25 2.2 Yleiskaava 2020 5 4.1.1 Alueen esihistoria 25 2.3 Asemakaava 5 4.1.2 Koroinen keskiajalla 26 4.1.3 Maankäytön historiasta 27 2.4 Valtakunnalliset inventoinnit 6 2.4.1 Maisema-alue 6 4.2 Kaava-alueen ja lähiympäristön muinaismuisto- ja muinaisjäännösalueet 35 2.4.2 Rakennettu kulttuuriympäristö 6 4.3 Kulttuurimaisema 41 2.5 Muut inventoinnit ja selvitykset 6 4.3.1 Valtakunnallisesti arvokas Aurajokilaakson maisema-alue 41 2.5.1 Koroisten luontoselvitys 6 4.3.2 Maakunnallisesti arvokas maisema-alue 42 2.5.2 Kansallinen kaupunkipuisto 7 4.3.3 Kansallismaisema 42 4.3.4 Perinnebiotoopit 42 2.6 Muut kulttuuriympäristön maankäyttöön ja arvottamiseen vaikuttavat seikat 8 2.6.1 Lainsäädäntö 8 4.4 Rakennettu kulttuuriympäristö 44 2.6.2 Kansainväliset sopimukset 9 4.4.1 RKY-alueet: Valtakunnallisesti merkittävä rakennettu kulttuuriympäristö 44 2.6.3 Varsinais-Suomen maakuntastrategia – maakuntasuunnitelma 2035+ ja 4.4.2 Yleiskaavan 2020 rakennussuojelukohteet ja arvokkaat ympäristökokonaisuudet maakuntaohjelma 2014 - 2017 10 kaavan vaikutusalueella 46 2.6.4 Turku 2029 kaupunkistrategia ja viherverkkosuunnitelma 10 4.4.3 Muut historialliset rakennukset ja historiallinen toiminta Koroisilla 50 2.6.5 Turun kaupunkiseudun rakennemalli 2035 11 4.5 Muut kulttuuriympäristön arvotekijät 52 2.6.6 Turun kaupunkiseudun kuntien ja valtion välinen maankäytön, asumisen ja liikenteen 4.5.1 Virkistys 52 aiesopimus 2012 – 2015. -

The Oldest Parks in Turku
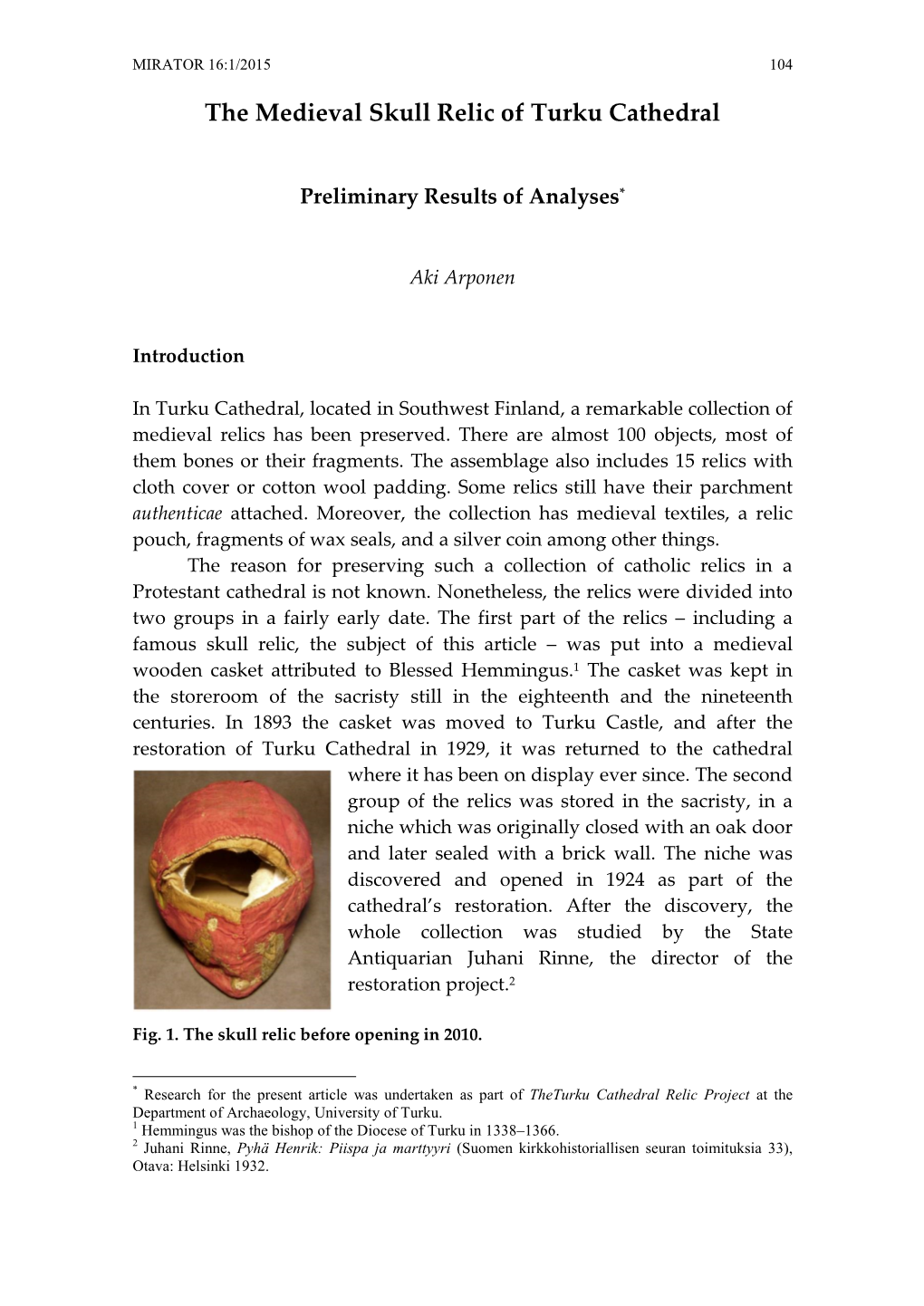
Cathedral Park • Brahe Park • Porthan Park THE OLDEST PARKS IN TURKU 1 A section of a map drawn up by surveyor Johan Tillberg during 1808-1818. Image: National Archives. ©BLOM 2008 The City of Turku is founded. Turku Cathedral, which was constructed on the hill of Unikankare, is inaugurated. The bishopric is moved from Koroinen to Turku. The Dominican convent is established next to the city. The earliest reference to the headmaster of the The first garden of Finland, “hortus conclusus”, belonged to cathedral school of Turku is recorded. The primary The Hospital of St George, which cared for the St Olaf Dominican convent on the hill of Kaskenmäki. task of the cathedral school was to train priests. Novgorodians devastate Turku. leprous patients, is mentioned for the first time. The Hospital was located outside the city, on the west side of Aura River. 13th century The first years of the 14th century 1309 1318 1324 Early 14th century In 1355 the oldest guild of Turku, Guild of St Nicholas, is Latter half of the 14th century Rural settlement at the location The first literal reference to Turku as a city The mayor of Turku and the city council A city hall made of stone is constructed mentioned for the first time. The guild house was located The urban settlement expands on the eastern side where Turku would later be founded. is recorded. The oldest seal of the city dates are mentioned for the first time. at the end of the Great Market. in the Convent Quarter, south of the Great Market. -

A Voluntary Local Review 2020 Turku
A Voluntary Local Review 2020 The implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in the City of Turku Opening statement by the Mayor Cities are facing major challenges – climate change, digitalisation and the ageing and increasingly diverse population greatly impact on cities’ field of operation and require cities to be able to adapt to constant change. Adaptation and adjustment to conventional ways of doing things is also needed in order to reach sustainability on a global level. Cities and city networks have an ever-growing role to play as global influencers and local advocates in achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. Succeeding in accelerating sustainable development requires strong commitment and dedication from the city’s decision-makers and the whole city organization. Turku has a long tradition in promoting sustainable development and we want to make sure Turku is a good place to live in the future as well. Turku also wants to take responsibility and set an example in solving global sustainability challenges. That is why I consider it very important that Turku is among the first cities to participate in reporting city-level progress of achieving the Sustainable Development Goals. With this first VLR report, I am very proud to present the systematic work being done in Turku for sustainable development. I hope that the cities’ growing role in implementing the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development becomes more visible to citizens, business life, organisations, other cities, government and other interest groups. Together we have a chance to steer the course of development in a more sustainable direction. A Voluntary Local Review 2020, The implementation of the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development in the City of Turku Minna Arve Authors: City of Turku. -

Aurajoen Halistenkosken Historiaa
Veli Pekka Toropainen Aurajoen Halistenkosken historiaa Aurajoen Halistenkoski on suomalaisten koskien mittakaavassa putouskorkeudeltaan vähäi nen, mutta sen merkitys suomalaisen teollisuuden historiassa on mittava. Kosken mylly- toiminta ja kalastus tunnetaan jo 1300-luvulta ja varsinainen teollistuminen koskella alkoi jo 1550-luvulla, kun Turun linnan verkakutomon valkkimylly pystytettiin Halisiin. Seuraavalla vuosisadalla valkki korvattiin nahan käsittelyyn tarkoitetulla tamppimyllyllä. Kosken teol- linen käyttö laajeni 1800-luvullaja 1900-luvun alussa, kun paikalla alettiin tuottaa luujauhoa lannoitteeksi, jauhaa liitua ja värejä maalien raaka-aineeksi, sahata lautoja ja puusepäntuot- teita sekä valmistaa tekovillaa ja käsitellä hamppua purjekankaiden raaka-aineeksi. Halistenkosken kansallismaisema Halistenkosken alue Turussa on nykyisin vilkkaassa virkistyskäytössä, sillä Halisten- koski on osa Turun kansallista kaupunkipuistoa. Polut ja hiekkatiet kulkevat jokirannan vehreässä ja kasvistoltaan rikkaassa kansallismaisemassa ja sivuuttavat muinaismuistot kivi-, pronssi- ja rautakausilta. Kosken tuntumassa on kuppikiviä, erilaisia kalmistoja ja muutaman kilometrin päässä yläjuoksulla Ravattulan Ristimäen 1100- ja 1200-luku- jen kirkonrauniot ja kirkkomaa. Koskelle näkyvät Kaarinan ja Maarian keskiaikaiset kivikirkot sekä Koroinen, jossa sijaitsi 1200-luvulla piispankirkko, piispan kastelli eli asuintorni ja kastaali eli puolustustorni sekä kauppapaikka. Sen edeltäjä oli Liedon Vanhalinnassa, mutta jääkauden jälkeinen maan nouseminen -

Tier 1 Manufacturing Sites
TIER 1 MANUFACTURING SITES - Produced January 2021 SUPPLIER NAME MANUFACTURING SITE NAME ADDRESS PRODUCT TYPE No of EMPLOYEES Albania Calzaturificio Maritan Spa George & Alex 4 Street Of Shijak Durres Apparel 100 - 500 Calzificio Eire Srl Italstyle Shpk Kombinati Tekstileve 5000 Berat Apparel 100 - 500 Extreme Sa Extreme Korca Bul 6 Deshmoret L7Nr 1 Korce Apparel 100 - 500 Bangladesh Acs Textiles (Bangladesh) Ltd Acs Textiles & Towel (Bangladesh) Tetlabo Ward 3 Parabo Narayangonj Rupgonj 1460 Home 1000 - PLUS Akh Eco Apparels Ltd Akh Eco Apparels Ltd 495 Balitha Shah Belishwer Dhamrai Dhaka 1800 Apparel 1000 - PLUS Albion Apparel Group Ltd Thianis Apparels Ltd Unit Fs Fb3 Road No2 Cepz Chittagong Apparel 1000 - PLUS Asmara International Ltd Artistic Design Ltd 232 233 Narasinghpur Savar Dhaka Ashulia Apparel 1000 - PLUS Asmara International Ltd Hameem - Creative Wash (Laundry) Nishat Nagar Tongi Gazipur Apparel 1000 - PLUS Aykroyd & Sons Ltd Taqwa Fabrics Ltd Kewa Boherarchala Gila Beradeed Sreepur Gazipur Apparel 500 - 1000 Bespoke By Ges Unip Lda Panasia Clothing Ltd Aziz Chowdhury Complex 2 Vogra Joydebpur Gazipur Apparel 1000 - PLUS Bm Fashions (Uk) Ltd Amantex Limited Boiragirchala Sreepur Gazipur Apparel 1000 - PLUS Bm Fashions (Uk) Ltd Asrotex Ltd Betjuri Naun Bazar Sreepur Gazipur Apparel 500 - 1000 Bm Fashions (Uk) Ltd Metro Knitting & Dyeing Mills Ltd (Factory-02) Charabag Ashulia Savar Dhaka Apparel 1000 - PLUS Bm Fashions (Uk) Ltd Tanzila Textile Ltd Baroipara Ashulia Savar Dhaka Apparel 1000 - PLUS Bm Fashions (Uk) Ltd Taqwa -

Daily Life for the Common People of China, 1850 to 1950
Daily Life for the Common People of China, 1850 to 1950 Ronald Suleski - 978-90-04-36103-4 Downloaded from Brill.com04/05/2019 09:12:12AM via free access China Studies published for the institute for chinese studies, university of oxford Edited by Micah Muscolino (University of Oxford) volume 39 The titles published in this series are listed at brill.com/chs Ronald Suleski - 978-90-04-36103-4 Downloaded from Brill.com04/05/2019 09:12:12AM via free access Ronald Suleski - 978-90-04-36103-4 Downloaded from Brill.com04/05/2019 09:12:12AM via free access Ronald Suleski - 978-90-04-36103-4 Downloaded from Brill.com04/05/2019 09:12:12AM via free access Daily Life for the Common People of China, 1850 to 1950 Understanding Chaoben Culture By Ronald Suleski leiden | boston Ronald Suleski - 978-90-04-36103-4 Downloaded from Brill.com04/05/2019 09:12:12AM via free access This is an open access title distributed under the terms of the prevailing cc-by-nc License at the time of publication, which permits any non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author(s) and source are credited. An electronic version of this book is freely available, thanks to the support of libraries working with Knowledge Unlatched. More information about the initiative can be found at www.knowledgeunlatched.org. Cover Image: Chaoben Covers. Photo by author. Library of Congress Cataloging-in-Publication Data Names: Suleski, Ronald Stanley, author. Title: Daily life for the common people of China, 1850 to 1950 : understanding Chaoben culture / By Ronald Suleski. -

Streets, Seals Or Seeds As Early Manifestations of Urban Life in Turku, Finland
Streets, seals or seeds as early manifestations of urban life in Turku, Finland Liisa Seppänen In the 2000s, the studies concerning the early phases of urbanization in Finland have re-actualized after many decades. The studies have focused on Turku, which is the oldest town of the present-day Finland and has been a target for many excavations. The focus of this paper is in the beginnings of the urbanization of Turku with the questions when and why the town was founded. The questions are old and discussed in many studies since the early 20th century. In this article, these questions are reflected on the basis recent archaeo- logical findings and the circumstantial evidence from historical sources. I am presenting my interpretation about the course of events, which led to the establishment of Turku. The town was not founded on a virgin land, but it was preceded by human activities like farming and possibly gatherings of religious or commercial nature. The political circum- stances activated the planning of the town in the late 13th century, which were realized in the turn of the 13th and 14th century. It seems, that the urbanization process took several decades and probably it was not until the mid 14th century when Turku met all the bench- marks set for the medieval town. Tracing the earliest evidence red to a more appropriate place. The document is dated in Perugia on the The origins of Turku (fig. 1) have fas- 29th of January in 1229, but it does cinated Finnish historians and archa- not, however, reveal the location of eologists for more than a century. -

Turun Keskiaikaisten Kylätonttien Kasvillisuus
Turun keskiaikaisten kylätonttien kasvillisuus Silja Aalto Pro gradu-tutkielma Arkeologia Historian, kulttuurin ja taiteiden tutkimuksen laitos Humanistinen tiedekunta Turun yliopisto Elokuu 2020 Turun yliopiston laatujärjestelmän mukaisesti tämän julkaisun alkuperäisyys on tarkastettu Turnitin OriginalityCheck -järjestelmällä. TURUN YLIOPISTO Historian, kulttuurin ja taiteiden tutkimuksen laitos / Humanistinen tiedekunta SILJA AALTO: Turun keskiaikaisten kylätonttien kasvillisuus Pro gradu –tutkielma, 92 sivua, 21 liitesivua Arkeologia Elokuu 2020 Tässä tutkimuksessa selvitetään, minkälaista kasvillisuutta Turun alueen keskiaikaisilla kylätonteilla nykyään esiintyy ja poikkeaako eri ikäisten ja eri aikoina autioituneiden kylätonttien kasvillisuus toisistaan. Mikäli jotkin kasvilajit esiintyvät vanhoilla rautakaudelta periytyvillä asuinpaikoilla selvästi useammin kuin vasta keskiajalla perustetuissa kylissä, ne voisivat indikoida asutuksen vanhaa ikää. Samalla tarkastellaan, painottuuko tiettyjen kasvilajien levinneisyys Turussa keskiaikaisen kyläasutuksen läheisyyteen. Kasvillisuuden osalta aineisto koostuu Turun paikallisista luontoselvityksistä, Suomen lajitietokeskuksen kokoamista havainnoista ja Turun kasvit -hankkeen havaintopisteistä. Kyläaineisto pohjautuu pääasiassa Turun museokeskuksen inventointeihin vuosilta 2014 ja 2015. Ennen tutkimusta kyläkohtaista kasvillisuusaineistoa täydennettiin kenttätöillä. Analyysiin valittiin 11 autioitunutta kylätonttia: Haavisto, Harittu, Iisala, Ispoinen, Kairinen, Kakkarainen, Kalliola, Koskennurmi, -

Records of the Transmission of the Lamp (Jingde Chuadeng
The Hokun Trust is pleased to support the fifth volume of a complete translation of this classic of Chan (Zen) Buddhism by Randolph S. Whitfield. The Records of the Transmission of the Lamp is a religious classic of the first importance for the practice and study of Zen which it is hoped will appeal both to students of Buddhism and to a wider public interested in religion as a whole. Contents Foreword by Albert Welter Preface Acknowledgements Introduction Appendix to the Introduction Abbreviations Book Eighteen Book Nineteen Book Twenty Book Twenty-one Finding List Bibliography Index Foreword The translation of the Jingde chuandeng lu (Jingde era Record of the Transmission of the Lamp) is a major accomplishment. Many have reveled in the wonders of this text. It has inspired countless numbers of East Asians, especially in China, Japan and Korea, where Chan inspired traditions – Chan, Zen, and Son – have taken root and flourished for many centuries. Indeed, the influence has been so profound and pervasive it is hard to imagine Japanese and Korean cultures without it. In the twentieth century, Western audiences also became enthralled with stories of illustrious Zen masters, many of which are rooted in the Jingde chuandeng lu. I remember meeting Alan Ginsburg, intrepid Beat poet and inveterate Buddhist aspirant, in Shanghai in 1985. He had been invited as part of a literary cultural exchange between China and the U. S., to perform a series of lectures for students at Fudan University, where I was a visiting student. Eager to meet people who he could discuss Chinese Buddhism with, I found myself ushered into his company to converse on the subject. -

Fenghuang and Phoenix: Translation of Culture
International Journal of Languages, Literature and Linguistics, Vol. 6, No. 3, September 2020 Fenghuang and Phoenix: Translation of Culture Lyujie Zhu Confucius‟ time, fenghuang was mainly used to describe Abstract—Fenghuang and phoenix from ancient myths are virtuous man, such as shi and king, and it was in Han dynasty both culture-loaded words that have unique features and that fenghuang‟s gender was gradually distinguished [18], as comprehensive historical developing routes. This paper focuses the male feng with the female huang respectively, in on their translations to find out the reflected cultural issues and symbolizing everlasting love that representing the yin-yang power influences under the ideas of cultural identity and language power. Classic literatures like The Analects and The balance. After Ming-Qing period, fenghuang was major Tempest in bilingual versions are compared in terms of the symbolization for female that such transformation is translation for both animals, as well as by searching the unavoidably related to the monarchal power of Chinese different social backgrounds and timelines of those literatures. empresses in indicating themselves by using The mixed usage of phoenix and fenghuang in both Chinese fenghuang-elements [16]. (East) and English (West) culture makes confusions but also As for phoenix in the West, it has the totally different enriches both languages and cultures. origins and characteristics. Phoenix dies in its nest, and then Index Terms—Fenghuang, phoenix, translation, language, is reborn from its own burned ashes, with a duration of about cultural identity. 500 years [19]. Phoenix is said to be originated from Egyptian solar myths of the sacred bird, benu, through association with the self-renewing solar deity, Osiris [20]. -

Timo J. VIRTANEN “YELLOW MUISTIHUONE” AND
Timo J. VIRTANEN “YELLOW MUISTIHUONE” AND CONCEPTUALIZING THE RIVER AURA INTRODUCTION Imagine an aerial picture of Finland, large expanses of blue water surrounded by green forests. Some small blue strips connecting the interior with the coast. It is commonly known that Finland is famous for its thousands of lakes. A lot of Finnish people cannot even think of moving anywhere else than to the next lake, village or town. On the other hand some of us are totally tied up with the salty and windy seaside weather and landscape. Perhaps one extra category within “water people” is those urban dwellers who like to underline the connection of town, history, river and culture. This urban river tribe is of course known in other countries and can be found as well in London, Budapest, Prague or Szeged. Riverside apartments are usually more expensive and in many cases you can find the best restaurants and shops on the riverside. The main walking routes are along the river banks. In many towns dock areas are under renovation and new plans transform industrial areas and buildings into cultural centres.1 The river is everywhere clearly an important part of the changing city image. For a few of years, I have been working on the ethnological river topic, mostly with urban rivers, Kokemäenjoki in Pori, Aura in Turku (both in Finland), Tisza in Szeged (Hungary) and Danube in Novi Sad (Serbia). In all those cases it has been a question of urban environmental ethnology, but also of developing ethnological fieldwork tools and methods. The river has been the main actor, both subject and object. -

The Old Cathedral of Viborg
MIRATOR 16:1/2015 53 The Old Cathedral of Viborg Historical Archaeology of the Easternmost Cathedral of the Swedish Empire* Aleksandr Saksa and Panu Savolainen A Trans-Religious Sanctuary On 18 February 1940 an incendiary bomb wrecked the Old Cathedral of Viborg1. The fate of the edifice, since then a forlorn ruin, represents the unsettled history of the borderlands between Finland and Russia. The town, nowadays located in Russia, has been part of Sweden (1293–1710), Russia (1710–1917, 1944–) and Finland (1917–1944). The Old Town of Viborg, although largely renewed during successive occupations and re-buildings, still represents this transnational past where Swedish, German, Russian and Finnish histories of the Baltic have intertwined over the centuries (Fig. 1a). The multinational and polyglot history of Viborg has been underlined in a multitude of studies that cover the secular history of the town.2 The equivalent discussion of religious buildings and history has, in contrast, evoked little attention. Along with the transitions of power, religions have changed as well, settling down to the very same buildings one after another. The Old Cathedral of Viborg, the subject of the article, was a catholic sanctuary until the 1520s and a Lutheran church from the 1520s to 1710. Between 1554 and 1710 the church was the easternmost cathedral of the * The article was written in a project steered by the Mikael Agricola Society and funded by the Alfred Kordelin Foundation. 1 The Swedish name of the town ‘Viborg’ is used throughout the article since it mostly deals with the Swedish era. In Finnish the name of the town is Viipuri (or Wiipuri) and Vyborg (Выборг) in Russian.