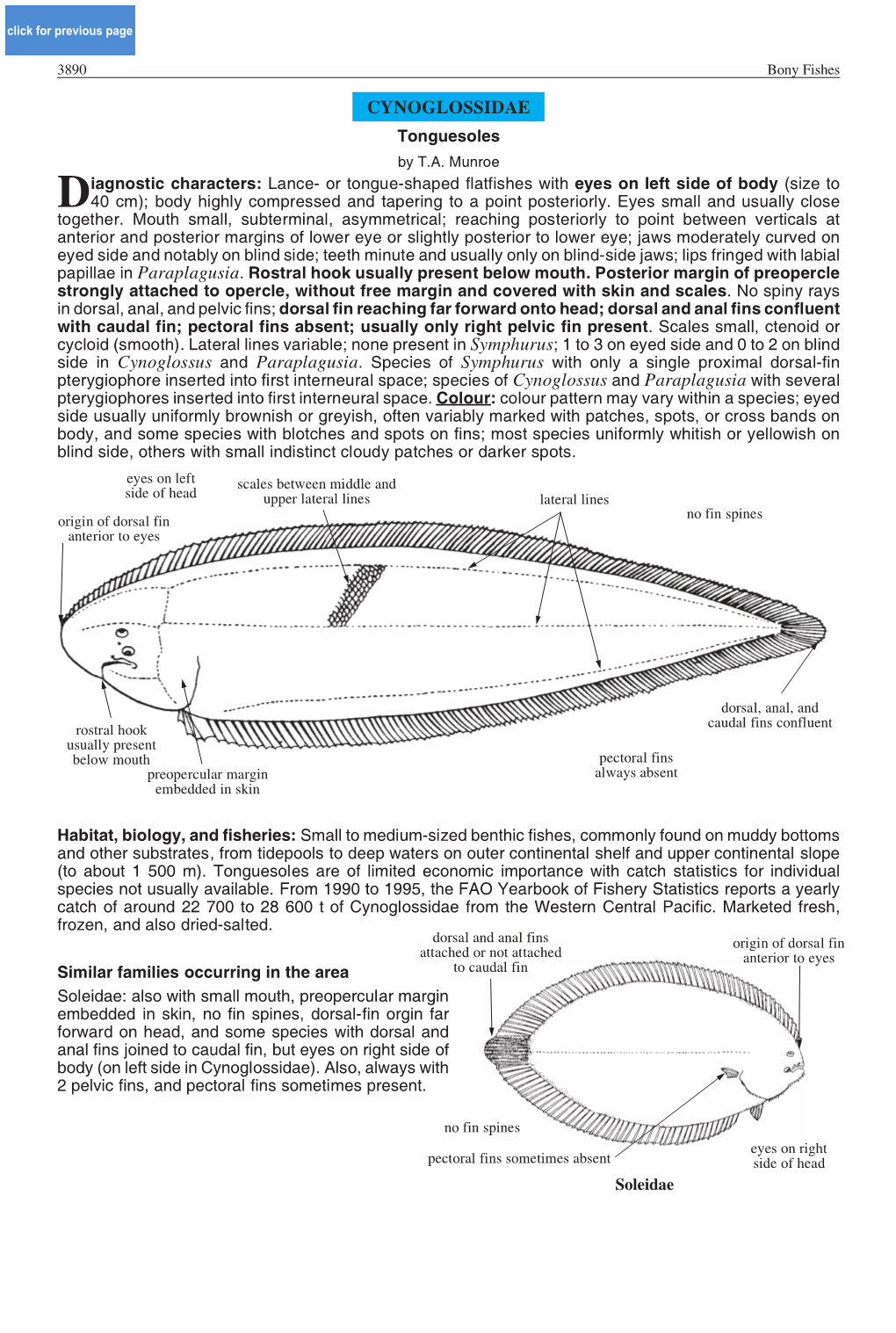
CYNOGLOSSIDAE Tonguesoles by T.A
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Redalyc.A Review of the Flatfish Fisheries of the South Atlantic Ocean
Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía ISSN: 0717-3326 [email protected] Universidad de Valparaíso Chile Díaz de Astarloa, Juan M. A review of the flatfish fisheries of the south Atlantic Ocean Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía, vol. 37, núm. 2, diciembre, 2002, pp. 113-125 Universidad de Valparaíso Viña del Mar, Chile Available in: http://www.redalyc.org/articulo.oa?id=47937201 How to cite Complete issue Scientific Information System More information about this article Network of Scientific Journals from Latin America, the Caribbean, Spain and Portugal Journal's homepage in redalyc.org Non-profit academic project, developed under the open access initiative Revista de Biología Marina y Oceanografía 37 (2): 113 - 125, diciembre de 2002 A review of the flatfish fisheries of the south Atlantic Ocean Una revisión de las pesquerías de lenguados del Océano Atlántico sur Juan M. Díaz de Astarloa1 2 1CONICET, Departamento de Ciencias Marinas, Facultad de Ciencias Exactas y Naturales, Universidad Nacional de Mar del Plata, Funes 3350, 7600 Mar del Plata, Argentina. [email protected] 2 Current address: Laboratory of Marine Stock-enhancement Biology, Division of Applied Biosciences, Graduate School of Agriculture, Kyoto University, kitashirakawa-oiwakecho, sakyo-ku, Kyoto, 606-8502 Japan. [email protected] Resumen.- Se describen las pesquerías de lenguados del Abstract.- The flatfish fisheries of the South Atlantic Atlántico sur sobre la base de series de valores temporales de Ocean are described from time series of landings between desembarcos pesqueros entre los años 1950 y 1998, e 1950 and 1998 and available information on species life información disponible sobre características biológicas, flotas, history, fleets and gear characteristics, and economical artes de pesca e importancia económica de las especies importance of commercial species. -

Pleuronectidae, Poecilopsettidae, Achiridae, Cynoglossidae
1536 Glyptocephalus cynoglossus (Linnaeus, 1758) Pleuronectidae Witch flounder Range: Both sides of North Atlantic Ocean; in the western North Atlantic from Strait of Belle Isle to Cape Hatteras Habitat: Moderately deep water (mostly 45–330 m), deepest in southern part of range; found on mud, muddy sand or clay substrates Spawning: May–Oct in Gulf of Maine; Apr–Oct on Georges Bank; Feb–Jul Meristic Characters in Middle Atlantic Bight Myomeres: 58–60 Vertebrae: 11–12+45–47=56–59 Eggs: – Pelagic, spherical Early eggs similar in size Dorsal fin rays: 97–117 – Diameter: 1.2–1.6 mm to those of Gadus morhua Anal fin rays: 86–102 – Chorion: smooth and Melanogrammus aeglefinus Pectoral fin rays: 9–13 – Yolk: homogeneous Pelvic fin rays: 6/6 – Oil globules: none Caudal fin rays: 20–24 (total) – Perivitelline space: narrow Larvae: – Hatching occurs at 4–6 mm; eyes unpigmented – Body long, thin and transparent; preanus length (<33% TL) shorter than in Hippoglossoides or Hippoglossus – Head length increases from 13% SL at 6 mm to 22% SL at 42 mm – Body depth increases from 9% SL at 6 mm to 30% SL at 42 mm – Preopercle spines: 3–4 occur on posterior edge, 5–6 on lateral ridge at about 16 mm, increase to 17–19 spines – Flexion occurs at 14–20 mm; transformation occurs at 22–35 mm (sometimes delayed to larger sizes) – Sequence of fin ray formation: C, D, A – P2 – P1 – Pigment intensifies with development: 6 bands on body and fins, 3 major, 3 minor (see table below) Glyptocephalus cynoglossus Hippoglossoides platessoides Total myomeres 58–60 44–47 Preanus length <33%TL >35%TL Postanal pigment bars 3 major, 3 minor 3 with light scattering between Finfold pigment Bars extend onto finfold None Flexion size 14–20 mm 9–19 mm Ventral pigment Scattering anterior to anus Line from anus to isthmus Early Juvenile: Occurs in nursery habitats on continental slope E. -

Aspects of the Life History of Hornyhead Turbot, Pleuronichthys Verticalis, Off Southern California
Aspects of the Life History of Hornyhead Turbot, Pleuronichthys verticalis, off Southern California he hornyhead turbot T(Pleuronichthys verticalis) is a common resident flatfish on the mainland shelf from Magdalena Bay, Baja Califor- nia, Mexico to Point Reyes, California (Miller and Lea 1972). They are randomly distributed over the bottom at a density of about one fish per 130 m2 and lie partially buried in the sediment (Luckinbill 1969). Hornyhead turbot feed primarily on sedentary, tube-dwelling polychaetes (Luckinbill 1969, Allen 1982, Cross et al. 1985). They pull the tubes from the sediment, Histological section of a fish ovary. extract the polychaete, and then eject the tube (Luckinbill 1969). Hornyhead turbot are Orange County, p,p’-DDE Despite the importance of batch spawners and may averaged 362 μg/kg wet the hornyhead turbot in local spawn year round (Goldberg weight in hornyhead turbot monitoring programs, its life 1982). Their planktonic eggs liver and 5 μg/kg dry weight in history has received little are 1.00-1.16 mm diameter the sediments (CSDOC 1992). attention. The long-term goal (Sumida et al. 1979). Their In the same year in Santa of our work is to determine larvae occur in the nearshore Monica Bay, p,p’-DDE aver- how a relatively low trophic plankton throughout the year aged 7.8 mg/kg wet weight in level fish like the hornyhead (Gruber et al. 1982, Barnett et liver and 81 μg/kg dry weight turbot accumulates tissue al. 1984, Moser et al. 1993). in the sediments (City of Los levels of chlorinated hydrocar- Several agencies in South- Angeles 1992). -

Cynoglossus Westraliensis, a New Species of Tonguesole from Western Australia (Teleostei: Cynoglossidae)
FishTaxa (2019) 4(2): 31-40 Journal homepage: www.fishtaxa.com © 2019 FISHTAXA. All rights reserved Cynoglossus westraliensis, a new species of tonguesole from Western Australia (Teleostei: Cynoglossidae) Ronald FRICKE* Im Ramstal 76, 97922 Lauda-Königshofen, Germany. Corresponding author: *E-mail: [email protected] Abstract The Western Australian deep-water tonguesole Cynoglossus westraliensis n. sp. is described from off North West Cape, Western Australia, based on two specimens collected at a depth of 250 metres. The new species is characterised within the Cynoglossus carpenteri species group by the snout relatively long, bluntly rounded; head length 21-25% of SL, snout length 9.3-11.6% of SL (43.4-46.5% of HL); eyes not contiguous; corner of mouth nearer to posterior edge of opercle than to tip of snout; ocular side with 3 lateral lines, midlateral-line scales 111-115, scale rows between midlateral and dorsolateral lines 20, blind side without lateral lines; ctenoid scales on ocular side, cycloid scales on blind side; dorsal-fin-rays 120-126; anal-fin rays 105-106; caudal-fin rays 8; gill chamber and peritoneum black. A key to the species of the Cynoglossus carpenteri species-group is presented. Keywords: Tonguesole, Cynoglossidae, Western Australia, New species, Identification key, Distribution. Zoobank: urn:lsid:zoobank.org:pub:C72DC2E5-9875-4DA0-9313-7967FB81C5C9 urn:lsid:zoobank.org:act:97081CA2-8CBA-4D70-8732-8BEA54017555 Introduction Tonguesoles of the family Cynoglossidae are small to medium sized benthic fishes, which are common in marine waters from tidal pools to the continental shelf and upper slope to a maximum depth of 1,500 m (Munroe 2001). -

Taxonomical Identification and Diversity of Flat Fishes from Mudasalodai Fish Landing Centre (Trawl by Catch), South East Coast of India
ISSN: 2642-9020 Review Article Journal of Marine Science Research and Oceanography Taxonomical Identification and Diversity of Flat Fishes from Mudasalodai Fish Landing Centre (Trawl by Catch), South East Coast of India Gunalan B* and E Lavanya *Corresponding author B Gunalan, PG & Research Department of Zoology, Thiru Kollanjiyapar PG & Research Department of Zoology, Thiru Kollanjiyapar Government Arts College, Viruthachalam. Cuddalore-Dt, Tamilnadu, India Government Arts College, Viruthachalam Submitted: 31 Jan 2020 Accepted: 05 Feb 2020; Published: 07 Mar 2020 Abstract Bycatch and discards are common and pernicious problems faced by all fisheries globally. It is recognized as unavoidable in any kind of fishing but the quantity varies according to the gear operated. In tropical countries like India, bycatch issue is more complex due to the multi-species and multi-gear nature of the fisheries. Among the different fishing gears, trawling accounts for a higher rate of bycatch, due to comparatively low selectivity of the gear. A study was conducted during June 2018 - Dec 2019 in the Mudasalodai fish landing centre, southeast coast of India. During the study period six sp. of flat fishes collected and identified taxonomically. Keywords: Flat fish, tongue fish, sole fish, bycatch, fish landing, waters of Parangipettai. The study was conducted for a period of diversity, taxonomy one and half year (June 2018 - Dec 2019), no sampling was done in the month of May, due to the fishing holiday in the coast of Introduction Tamil Nadu. The collected flat fishes were kept in ice boxes and Fish forms an important source of food and is man’s important transferred to the laboratory and washed in tap water. -

Seasonal Changes in Benthic Fish Population Influenced by Salinity and Sediment Morphology in a Tropical Bay
Examines in Marine CRIMSON PUBLISHERS C Wings to the Research Biology and Oceanography: Open Access ISSN 2578-031X Research Article Seasonal Changes in Benthic Fish Population Influenced by Salinity and Sediment Morphology in a Tropical Bay Srinivasa MR, Vijaya Bhanu C and Annapurna C* Department of Zoology, Andhra University, India *Corresponding author: Annapurna C, Department of Zoology, Andhra University, Visakhapatnam-530 003, India Submission: November 13, 2017; Published: February 23, 2018 Abstract Coastal Bays are productive habitats used by a variety of fishes and other benthic organisms but little information is available on the ecology and population dynamics of benthic fishes of coastal bays in the tropical zones. This paper deals with the biodiversity, faunal assemblages, seasonal variations successivein the benthic post fish monsoons population and of pre a shallow monsoons tropical during Bay 2006 named to 2008.Nizampatnam Water and Bay, sediment located insamples southern were province collected of Bayfrom of 20 Bengal, stations East covering coast of 10, India. 20 Theand standing stock of benthic fishes and associated environmental factors of the study area were also reported in this paper. Sampling was done in two 6 orders and 1 class were recorded in this study dominated by Cociella crocodilus and Pisodonophis boro. The mean of Shannon Wiener diversity index 30 m zones. Altogether, 128 biological samples were collected with a Naturalist’s dredge. Thirty benthic fish species belonging to 21 genera, 12 families, H’ was recorded 1.3±0.4 during post-monsoon and 1.2±0.2 at pre-monsoonCociella crocodilus, suggesting Cynoglossus that the benthic lida, Cynoglossus fish diversity punticeps of this andBay wasAstroscopus poor. -

참서대과 (Pisces: Cynoglossidae) 자어 2종의 미토콘드리아 DNA에 의한 형태동정의 타당성
Kor J Fish Aquat Sci 43(5), 482-488 한수지, 43(5), 482-488, 2010 참서대과 (Pisces: Cynoglossidae) 자어 2종의 미토콘드리아 DNA에 의한 형태동정의 타당성 권혁준・김진구✽ 부경대학교 자원생물학과 Validation of Morphology-based Identification of Two Cynoglossidae Larvae using Mitochondrial DNA Hyuck Joon Kwun and Jin Koo Kim* Department of Marine Biology, Pukyong National University, Busan 608-737, Korea Three specimens of Cynoglossidae larvae were collected from the southern Korean Sea in May and August of 2009, and were identified using morphological and molecular analysis. Specimens were divided into two groups based on the number of elongated dorsal fin rays on the top of the head: Cynoglossidae sp. A was defined as having two elongated dorsal fin rays, while Cynoglossidae sp. B possessed a single elongated dorsal fin ray. One specimen of Cynoglossidae sp. A, a post-larva with a notochord length (NL) of 5.8 mm was thought to be a Cynoglossus joyneri larva based on the presence of 115 dorsal pterogiophores, 85 anal pterogiophores, and 50 myomeres. Two specimens of Cynoglossidae sp. B, a 4.1 mm NL larva and a 11.3 mm NL juvenile, were thought to be Cynoglossus abbreviatus based on the presence of yolk in the former and 133 dorsal fin rays, 105 anal fin rays, and 63 myomeres in the latter. To test this morphology-based identification, molecular analysis was conducted using 419-422 bp of mitochondrial DNA 16S rRNA. Cynoglossidae sp. A was clearly matched to a Cynoglossus joyneri adult (d=0.000) and Cynoglossidae sp. B clustered closely with Cynoglossus abbreviatus adults (d=0.002). -

(GSI), Hepatosomatic Index (HIS) and Condition Factor
Australian Journal of Basic and Applied Sciences, 5(9): 1640-1646, 2011 ISSN 1991-8178 Annual Changes in Gonadosomatic Index (GSI), Hepatosomatic Index (HIS) and Condition Factor (K) of Largescale Tonguesole Cynoglossus arel (Bloch & Schneider, 1801) In The Coastal Waters of Bandar Abbas, Persian Gulf. 1Hamze Ghaffari, 1Aria Ashja Ardalan, 2Homayon Hosseinzadeh Sahafi, 1Mohsen Mekhanik Babaei and 1Rashed Abdollahi 1Faculty of Marine Science and Technology, North Tehran Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran. 2Iranian Fisheries Research Organization, Tehran, Iran. Abstract: Bony fish includes the largest groups of fishes that have high economic value. Among these fish the Pleuronectiformes order have about 678 extant species that are recognized in approximately 134 genera and 14 families. Among the tonguefishes (Cynoglossidae) family, the species of Cynoglossus arel has remarkable distribution in Persian Gulf region. The purpose of this study was to determine the timing and duration of the spawning season from the monthly data on the incidence of changes in the gonadosomatic index (GSI), hepatosomatic index (HSI) and condition factor (K). In this study a total of 905 C. arel specimens were collected from the coastal waters of Bandar Abbas, south coast of Iran (27˚17’N, 56˚26’E) from October 2009 to September 2010. Then, in laboratory total length, body weight and sex were recorded, also gonads and liver were removed and weighted. The average of total length and total weight in males were 210.6 ± 1.91 mm and 43.0 ± 1.19 g, also the average of total length and total weight in females were 226.1 ± 1.81 mm and 54.2 ± 1.41 g. -

Identification of Larvae of Three Arctic Species of Limanda (Family Pleuronectidae)
Identification of larvae of three arctic species of Limanda (Family Pleuronectidae) Morgan S. Busby, Deborah M. Blood & Ann C. Matarese Polar Biology ISSN 0722-4060 Polar Biol DOI 10.1007/s00300-017-2153-9 1 23 Your article is protected by copyright and all rights are held exclusively by 2017. This e- offprint is for personal use only and shall not be self-archived in electronic repositories. If you wish to self-archive your article, please use the accepted manuscript version for posting on your own website. You may further deposit the accepted manuscript version in any repository, provided it is only made publicly available 12 months after official publication or later and provided acknowledgement is given to the original source of publication and a link is inserted to the published article on Springer's website. The link must be accompanied by the following text: "The final publication is available at link.springer.com”. 1 23 Author's personal copy Polar Biol DOI 10.1007/s00300-017-2153-9 ORIGINAL PAPER Identification of larvae of three arctic species of Limanda (Family Pleuronectidae) 1 1 1 Morgan S. Busby • Deborah M. Blood • Ann C. Matarese Received: 28 September 2016 / Revised: 26 June 2017 / Accepted: 27 June 2017 Ó Springer-Verlag GmbH Germany 2017 Abstract Identification of fish larvae in Arctic marine for L. proboscidea in comparison to the other two species waters is problematic as descriptions of early-life-history provide additional evidence suggesting the genus Limanda stages exist for few species. Our goal in this study is to may be paraphyletic, as has been proposed in other studies. -

A Review of Soles of the Genus Aseraggodes from the South Pacific, with Descriptions of Seven New Species and a Diagnosis of Synclidopus
Memoirs of Museum Victoria 62(2): 191–212 (2005) ISSN 1447-2546 (Print) 1447-2554 (On-line) http://www.museum.vic.gov.au/memoirs/index.asp A review of soles of the genus Aseraggodes from the South Pacific, with descriptions of seven new species and a diagnosis of Synclidopus. JOHN E. RANDALL Bishop Museum, 1525 Bernice St. Honolulu, Hawai’i 96817–2704, USA ([email protected]) Abstract Randall, J.E. 2005. A review of soles of the genus Aseraggodes from the South Pacific, with descriptions of seven new species and a diagnosis of Synclidopus. Memoirs of Museum Victoria 62(2): 191–212 The soleid genus Parachirus Matsubara and Ochiai is referred to the synonymy of Aseraggodes Kaup. Aseraggodes persimilis (Günther) and A. ocellatus Weed are reclassified in the genus Pardachirus Günther. Synclidopus macleayanus (Ramsay) from Queensland and NSW is redescribed. A diagnosis is given for Aseraggodes, and a key and species accounts provided for the following 12 species of the genus from islands of Oceania in the South Pacific and the east coast of Australia: A. auroculus, sp. nov. from the Society Islands; A. bahamondei from Easter Island and Lord Howe Island; A. cyclurus, sp. nov. from the Society Islands; A. lateralis, sp. nov. from the Marquesas Islands; A. lenisquamis, sp. nov. from NSW; A. magnoculus sp. nov. from New Caledonia; A. melanostictus (Peters) from 73 m off Bougainville and a first record for the Great Barrier Reef from 115 m; A. nigrocirratus, sp. nov. from NSW; A. normani Chabanaud from southern Queensland and NSW; A. pelvicus, sp. nov. -

Annadel Cabanban Emily Capuli Rainer Froese Daniel Pauly
Biodiversity of Southeast Asian Seas , Palomares and Pauly 15 AN ANNOTATED CHECKLIST OF PHILIPPINE FLATFISHES : ECOLOGICAL IMPLICATIONS 1 Annadel Cabanban IUCN Commission on Ecosystem Management, Southeast Asia Dumaguete, Philippines; Email: [email protected] Emily Capuli SeaLifeBase Project, Aquatic Biodiversity Informatics Office Khush Hall, IRRI, Los Baños, Laguna, Philippines; Email: [email protected] Rainer Froese IFM-GEOMAR, University of Kiel Duesternbrooker Weg 20, 24105 Kiel, Germany; Email: [email protected] Daniel Pauly The Sea Around Us Project , Fisheries Centre, University of British Columbia, 2202 Main Mall, Vancouver, British Columbia, Canada, V6T 1Z4; Email: [email protected] ABSTRACT An annotated list of the flatfishes of the Philippines was assembled, covering 108 species (vs. 74 in the entire North Atlantic), and thus highlighting this country's feature of being at the center of the world's marine biodiversity. More than 80 recent references relating to Philippine flatfish are assembled. Various biological inferences are drawn from the small sizes typical of Philippine (and tropical) flatfish, and pertinent to the "systems dynamics of flatfish". This was facilitated by FishBase, which documents all data presented here, and which was used to generate the graphs supporting these biological inferences. INTRODUCTION Taxonomy, in its widest sense, is at the root of every scientific discipline, which must first define the objects it studies. Then, the attributes of these objects can be used for various classificatory and/or interpretive schemes; for example, the table of elements in chemistry or evolutionary trees in biology. Fisheries science is no different; here the object of study is a fishery, the interaction between species and certain gears, deployed at certain times in certain places. -

Belgian Register of Marine Species
BELGIAN REGISTER OF MARINE SPECIES September 2010 Belgian Register of Marine Species – September 2010 BELGIAN REGISTER OF MARINE SPECIES, COMPILED AND VALIDATED BY THE VLIZ BELGIAN MARINE SPECIES CONSORTIUM VLIZ SPECIAL PUBLICATION 46 SUGGESTED CITATION Leen Vandepitte, Wim Decock & Jan Mees (eds) (2010). Belgian Register of Marine Species, compiled and validated by the VLIZ Belgian Marine Species Consortium. VLIZ Special Publication, 46. Vlaams Instituut voor de Zee (VLIZ): Oostende, Belgium. 78 pp. ISBN 978‐90‐812900‐8‐1. CONTACT INFORMATION Flanders Marine Institute – VLIZ InnovOcean site Wandelaarkaai 7 8400 Oostende Belgium Phone: ++32‐(0)59‐34 21 30 Fax: ++32‐(0)59‐34 21 31 E‐mail: [email protected] or [email protected] ‐ 2 ‐ Belgian Register of Marine Species – September 2010 Content Introduction ......................................................................................................................................... ‐ 5 ‐ Used terminology and definitions ....................................................................................................... ‐ 7 ‐ Belgian Register of Marine Species in numbers .................................................................................. ‐ 9 ‐ Belgian Register of Marine Species ................................................................................................... ‐ 12 ‐ BACTERIA ............................................................................................................................................. ‐ 12 ‐ PROTOZOA ...........................................................................................................................................