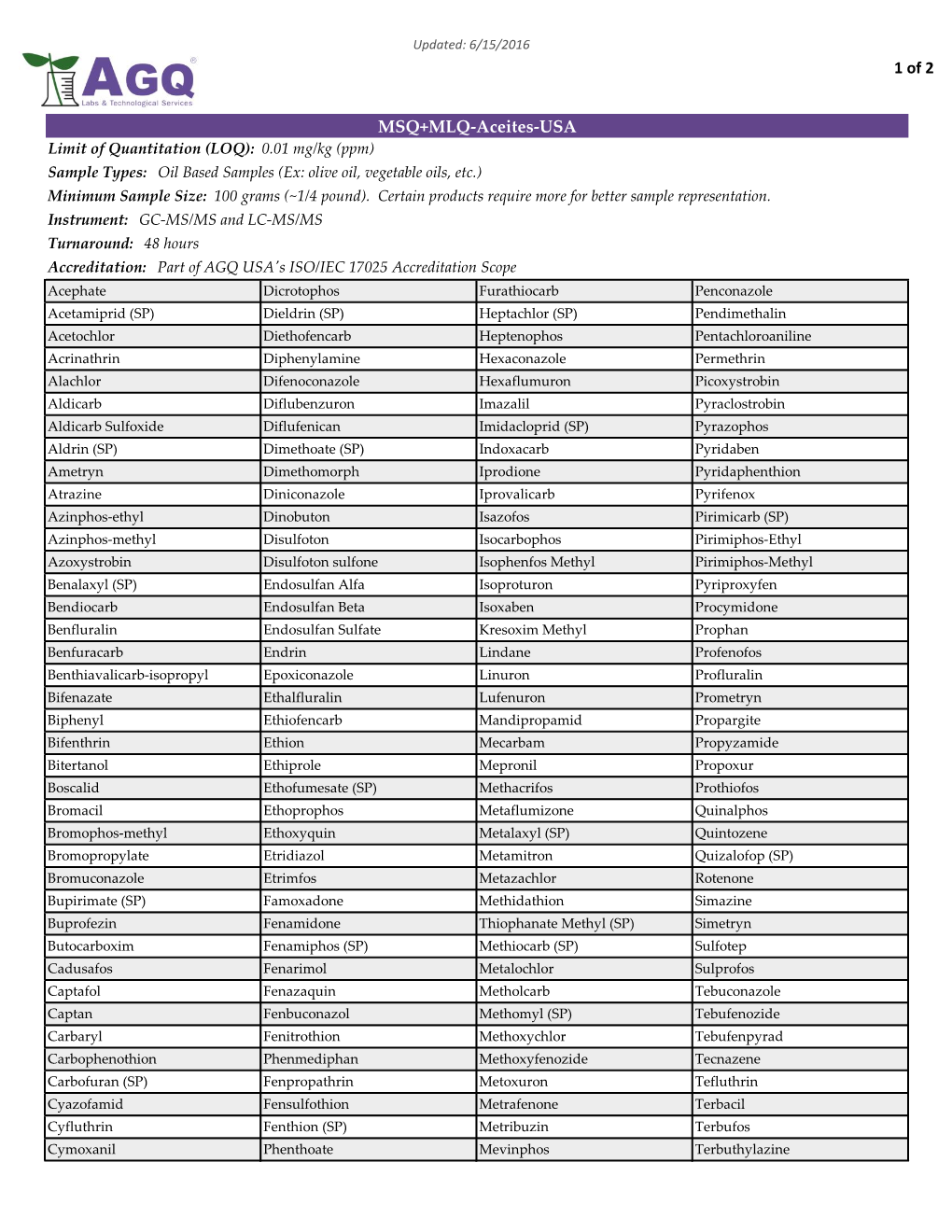
1 of 2 MSQ+MLQ-Aceites-USA
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Pesticide Residues in Food 2007 – Report, 2007 (E)
FAO Pesticide residues PLANT PRODUCTION in food 2007 AND PROTECTION PAPER Joint FAO/WHO Meeting on Pesticide Residues 191 Report of the Joint Meeting of the FAO Panel of Experts on Pesticide Residues in Food and the Environment and the WHO Core Assessment Group on Pesticide Residues Geneva, Switzerland, 18–27 September 2007 WORLD HEALTH ORGANIZATION FOOD AND AGRICULTURE ORGANIZATION OF THE UNITED NATIONS Rome, 2007 The designations employed and the presentation of material in this information product do not imply the expression of any opinion whatsoever on the part of the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO) concerning the legal or development status of any country, territory, city or area or of its authorities, or concerning the delimitation of its frontiers or boundaries. The mention of specific companies or products of manufacturers, whether or not these have been patented, does not imply that these have been endorsed or recommended by FAO in preference to others of a similar nature that are not mentioned. ISBN 978-92-5-105918-0 All rights reserved. Reproduction and dissemination of material in this information product for educational or other non-commercial purposes are authorized without any prior written permission from the copyright holders provided the source is fully acknowledged. Reproduction of material in this information product for resale or other commercial purposes is prohibited without written permission of the copyright holders. Applications for such permission should be addressed to: Chief Electronic -

COMBINED LIST of Particularly Hazardous Substances
COMBINED LIST of Particularly Hazardous Substances revised 2/4/2021 IARC list 1 are Carcinogenic to humans list compiled by Hector Acuna, UCSB IARC list Group 2A Probably carcinogenic to humans IARC list Group 2B Possibly carcinogenic to humans If any of the chemicals listed below are used in your research then complete a Standard Operating Procedure (SOP) for the product as described in the Chemical Hygiene Plan. Prop 65 known to cause cancer or reproductive toxicity Material(s) not on the list does not preclude one from completing an SOP. Other extremely toxic chemicals KNOWN Carcinogens from National Toxicology Program (NTP) or other high hazards will require the development of an SOP. Red= added in 2020 or status change Reasonably Anticipated NTP EPA Haz list COMBINED LIST of Particularly Hazardous Substances CAS Source from where the material is listed. 6,9-Methano-2,4,3-benzodioxathiepin, 6,7,8,9,10,10- hexachloro-1,5,5a,6,9,9a-hexahydro-, 3-oxide Acutely Toxic Methanimidamide, N,N-dimethyl-N'-[2-methyl-4-[[(methylamino)carbonyl]oxy]phenyl]- Acutely Toxic 1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-1-nitrosourea (Methyl-CCNU) Prop 65 KNOWN Carcinogens NTP 1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl-1-nitrosourea (CCNU) IARC list Group 2A Reasonably Anticipated NTP 1-(2-Chloroethyl)-3-cyclohexyl-1-nitrosourea (CCNU) (Lomustine) Prop 65 1-(o-Chlorophenyl)thiourea Acutely Toxic 1,1,1,2-Tetrachloroethane IARC list Group 2B 1,1,2,2-Tetrachloroethane Prop 65 IARC list Group 2B 1,1-Dichloro-2,2-bis(p -chloropheny)ethylene (DDE) Prop 65 1,1-Dichloroethane -

Historical Perspectives on Apple Production: Fruit Tree Pest Management, Regulation and New Insecticidal Chemistries
Historical Perspectives on Apple Production: Fruit Tree Pest Management, Regulation and New Insecticidal Chemistries. Peter Jentsch Extension Associate Department of Entomology Cornell University's Hudson Valley Lab 3357 Rt. 9W; PO box 727 Highland, NY 12528 email: [email protected] Phone 845-691-7151 Mobile: 845-417-7465 http://www.nysaes.cornell.edu/ent/faculty/jentsch/ 2 Historical Perspectives on Fruit Production: Fruit Tree Pest Management, Regulation and New Chemistries. by Peter Jentsch I. Historical Use of Pesticides in Apple Production Overview of Apple Production and Pest Management Prior to 1940 Synthetic Pesticide Development and Use II. Influences Changing the Pest Management Profile in Apple Production Chemical Residues in Early Insect Management Historical Chemical Regulation Recent Regulation Developments Changing Pest Management Food Quality Protection Act of 1996 The Science Behind The Methodology Pesticide Revisions – Requirements For New Registrations III. Resistance of Insect Pests to Insecticides Resistance Pest Management Strategies IV. Reduced Risk Chemistries: New Modes of Action and the Insecticide Treadmill Fermentation Microbial Products Bt’s, Abamectins, Spinosads Juvenile Hormone Analogs Formamidines, Juvenile Hormone Analogs And Mimics Insect Growth Regulators Azadirachtin, Thiadiazine Neonicotinyls Major Reduced Risk Materials: Carboxamides, Carboxylic Acid Esters, Granulosis Viruses, Diphenyloxazolines, Insecticidal Soaps, Benzoyl Urea Growth Regulators, Tetronic Acids, Oxadiazenes , Particle Films, Phenoxypyrazoles, Pyridazinones, Spinosads, Tetrazines , Organotins, Quinolines. 3 I Historical Use of Pesticides in Apple Production Overview of Apple Production and Pest Management Prior to 1940 The apple has a rather ominous origin. Its inception is framed in the biblical text regarding the genesis of mankind. The backdrop appears to be the turbulent setting of what many scholars believe to be present day Iraq. -

Simultaneous Analysis of Residual Pesticides in Foods Via the Quechers 71 Method Utilizing GC�MS/MS
LAAN-J-MS-E071 GC-MS Gas Chromatograph Mass Spectrometer Simultaneous Analysis of Residual Pesticides in Foods via the QuEChERS 71 Method Utilizing GC-MS/MS Analytical standards (0.001 mg/L to 0.1 mg/L), as well as samples (0.01 mg/L) created by pretreating paprika with the QuEChERS method and then adding pesticides to the resulting solution, were measured using the analysis conditions shown in Table 1. Experimental The European Union Reference Laboratory (EURL) has reported their results on evaluating the validity of residual pesticide analysis utilizing GC-MS/MS and LC-MS/MS 1) . In their report, the measurement of 66 pesiticides using GC-MS/MS was recommended. This data sheet presents selected results of analysis of these pesticides using the triple quadrupole GCMS-TQ8030. Table 1 Analytical Conditions GC-MS :GCMS-TQ8030 Column :Rxi-5Sil MS (30 m length, 0.25 mm I.D., df=0.25 µm) Glass Liner :Sky Liner, Splitless Single Taper Gooseneck w/Wool (Restek Corporation, catalog # 567366) [GC] [MS] Injection Temp. :250 °C Interface Temp. :250 °C Column Oven Temp.:70 °C (2 min) → (25 °C /min) → 150 °C → (3 °C/min) →200 °C → Ion Source Temp. :230 °C (8 °C/min) → 280 °C (10 min) Data Acquisition Mode :MRM (See the below.) Injection Mode :Splitless Flow Control Mode :Linear velocity (58.1 cm/sec.) Injection volume :1 µL MRM Monitoring m/z Quantitative Transition Qualitative Transition Quantitative Transition Qualitative Transition Compound Name Precursor>Product CE (V) Precursor>Product CE (V) Compound Name Precursor>Product CE (V) Precursor>Product -

Bayesian Nonparametric Model for Clustering Individual Co-Exposure to Pesticides Found in the French Diet
Bayesian nonparametric model for clustering individual co-exposure to pesticides found in the French diet. Amélie Crépet, Jessica Tressou To cite this version: Amélie Crépet, Jessica Tressou. Bayesian nonparametric model for clustering individual co-exposure to pesticides found in the French diet.. 2009. hal-00438796v2 HAL Id: hal-00438796 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00438796v2 Preprint submitted on 12 Jan 2011 (v2), last revised 4 Feb 2011 (v3) HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Bayesian nonparametric model for clustering individual co-exposure to pesticides found in the French diet. Am´elieCr´epet a & Jessica Tressoub January 12, 2011 aANSES, French Agency for Food, Environmental and Occupational Health Safety, 27-31 Av. G´en´eralLeclerc, 94701 Maisons-Alfort, France bINRA-Met@risk, Food Risk Analysis Methodologies, National Institute for Agronomic Re- search, 16 rue Claude Bernard, 75231 Paris, France Keywords Dirichlet process; Bayesian nonparametric modeling; multivariate Normal mixtures; clustering; multivariate exposure; food risk analysis. Abstract This work introduces a specific application of Bayesian nonparametric statistics to the food risk analysis framework. The goal was to determine the cocktails of pesticide residues to which the French population is simultaneously exposed through its current diet in order to study their possible combined effects on health through toxicological experiments. -

Liquid and Gas Chromatographic Multi-Residue Pesticide Determination in Animal Tissues
Pestic. Sci. 1997, 49,56È64 Liquid and Gas Chromatographic Multi-residue Pesticide Determination in Animal Tissues Aurora Navas Dj az,* Angeles Garcj a Pareja & Francisco Garcj aSanchez Departamento de Qu•mica Anal•tica, Facultad de Ciencias, Universidad de Malaga, 29071-Malaga, Spain (Received 13 June 1995; revised version received 17 April 1996; accepted 16 August 1996) Abstract: A liquid chromatography multi-residue method with photometric detection has been developed. The method is applicable to the quantitative deter- mination of organochlorine (tetradifon, dicofol, chlorfenson, chlorobenzilate), organophosphorus (fenitrothion, azinphos-ethyl) and carbamate (pirimicarb) pesticides in animal tissues. The extracted residues are cleaned up by gel- permeation chromatography. A further fractionation on silica Sep-Pack car- tridges is included in the procedure. A gas chromatographic method with electron-capture detection for the analysis of the same pesticides was carried out and the results in the two cases compared. Lower detection and quantitation limits and similar recoveries of pesticides from spiked pig liver and brain samples were obtained by the LC method. Key words: liquid chromatography, gas chromatography, multi-residue pesti- cides, animal tissues 1 INTRODUCTION by various element-sensitive detectors, leading to reli- ance on mass spectrometry because of its ability to help Pest control in modern agriculture includes treatment to deÐne the structure. This has especially been true in of crops pre- and post-harvest with a variety of chemi- the case of the combination of gas chromatography cals, such as herbicides and insecticides in the pre- with mass spectrometry (GC/MS). One of the obvious harvest stage and with fungicides and rodenticides in Ðelds of application for this technique was the analysis the storage stage of the total harvest process. -

Multi-Residue Analysis of 210 Pesticides in Food Samples by Triple Quadrupole UHPLC-MS/MS
Multi-Residue Analysis of 210 Pesticides in Food Samples by Triple Quadrupole UHPLC-MS/MS David R. Baker1, Chris Titman1, Alan J. Barnes1, Neil J. Loftus1, Alexander Mastoroudes2, Simon Hird3 1Shimadzu Corporation, Manchester, UK 2Kings College London, London, UK 3Food and Environment Research Agency, York, UK Abstract Pesticides and their metabolites are of great concern to society as they are harmful to human health, pollute natural resources and disturb the equilibrium of the ecosystem. Consequently, stricter food safety regulations are being enforced around the world, placing pesticide analysis laboratories under increasing pressure to expand the list of targeted pesticides, detect analytes at lower levels and with greater precision, reduce analysis turnaround times, and all the while maintaining or reducing costs. In this study a method was successfully developed for the quantitation of 210 commonly analysed pesticides in food samples using the Nexera UHPLC and LCMS-8040. Initial validation was performed to demonstrate instrument capabilities. Limits of detection (LOD) for 90 % of compounds were less than 0.001 mg kg-1 (1 ppb) and all compounds were less than 0.01 mg kg-1 (10 ppb) for both the quantifying and qualifying transitions using only a 2 µL injection. Repeatability at the 0.01 mg kg-1 reporting level was typically less than 5 %RSD for compounds and correlation coefficients were typically greater than 0.997 in a variety of studied food extracts. Consequently, the LCMS-8040 is ideally suited for routine monitoring of pesticides below the 0.01 mg kg-1 default level set by EU and Japanese legislation. Keywords: Pesticides; Multi-residue analysis; LCMS-8040; Food safety; Fruit; Vegetables 1. -

Spatial Variation in Non-Target Effects of the Insecticides Chlorpyrifos
Pesticide Science Pestic Sci 55:875±886 (1999) Spatial variation in non-target effects of the insecticides chlorpyrifos, cypermethrin and pirimicarb on Collembola in winter wheat Geoffrey K Frampton* Biodiversity and Ecology Division, School of Biological Sciences, University of Southampton, Bassett Crescent East, Southampton, SO16 7PX, UK Abstract: Contiguous winter wheat ®elds of similar cropping history and soil type were used in a study of the responses of Collembola to summer sprays of cypermethrin and pirimicarb in southern England. Chlorpyrifos was included in the study as a toxic standard. Epigeic arthropods were captured by suction sampling and crop-inhabiting species obtained by dissecting wheat ears. Eight genera of Collembola responded signi®cantly to the insecticide treatments. Collembolan abundance decreased after chlorpyrifos was applied but increased after use of cypermethrin. Negative effects of cypermethrin and pirimicarb on Collembola were not detected in this study. Effects of chlorpyrifos varied spatially as a result of faunal heterogeneity among the ®elds, despite apparent homogeneity of the site. Some species known to be susceptible to chlorpyrifos were absent from one or more of the ®elds. The implications of these ®ndings for the interpretation of non-target pesticide effects and the potential use of Collembola as bioindicators in ®eld studies with pesticides are discussed. # 1999 Society of Chemical Industry Keywords: insecticides; chlorpyrifos; cypermethrin; pirimicarb; Collembola; side-effects; bioindicators -

(12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,528,079 B2 Podszun Et Al
US006528079B2 (12) United States Patent (10) Patent No.: US 6,528,079 B2 PodsZun et al. (45) Date of Patent: *Mar. 4, 2003 (54) SHAPED BODIES WHICH RELEASE 4,845,106 A 7/1989 Shiokawa et al. .......... 514/342 AGROCHEMICALACTIVE SUBSTANCES 4,849,432 A 7/1989 Shiokawa et al. .......... 514/341 4.882,344 A 11/1989 Shiokawa et al. .......... 514/342 (75) Inventors: Wolfgang Podszun, Köln (DE); Uwe 4.914,113 A 4/1990 Shiokawa et al. .......... 514/333 Priesnitz, Solingen (DE); Jirgen 4,918,086 A 4/1990 Gsell .......................... 514/351 4,918,088 A 4/1990 Gsell .......................... 514/357 Hölters, Leverkusen (DE); Bodo 4.948.798.2- Y - A 8/1990 Gsell .......................... 514/275 Rehbold, Köln (DE); Rafel Israels, 4,963,572 A 10/1990 Gsell .......................... 514/357 Monheim (DE) 4,963,574. A 10/1990 Bachmann et al. ......... 514/357 4,988,712 A 1/1991 Shiokawa et al. .......... 514/340 (73) Assignee: Bayer Aktiengesellschaft, Leverkusen 5,001,138 A 3/1991 Shiokawa et al. .......... 514/342 (DE) 5,034.404 A 7/1991. Uneme et al. .............. 514/365 5,034,524 A 7/1991 Shiokawa et al. .......... 544/124 (*) Notice: This patent issued on a continued pros- 5,039,686 A 8/1991 Davies et al. ............... 514/341 ecution application filed under 37 CFR 5,049,571. A 9/1991 Gsell .......................... 514/345 1.53(d), and is subject to the twenty year SE A :1: S. - - - - - - - -tal.5 E.s pass" provisions of 35 U.S.C. 5,166,1642Y- - - 2 A 11/1992 NanjoOKaWa et al. -

Determination of Butocarboxim Residue in Agricultural Products by HPLC with Post-Column Derivatization System
Journal of Food and Drug Analysis 1999. 7(4) : 269-277 Determination of Butocarboxim Residue in Agricultural Products by HPLC with Post-Column Derivatization System SU-HSIANG TSENG*, PI-CHIOU CHANG AND SHIN-SHOU CHOU A method using high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the determination of butocarboxim in agricultural products was developed. Butocarboxim was extracted from samples with acetone and the extract solution was concentrated. The residue was dissolved in sodium chloride solution and partitioned with n-hexane. The aqueous phase was collected fol- lowed by extracted with dichloromethane, which was then evaporated to a volume of 2 mL prior to passing through an aminopropyl cartridge for sample clean-up. Determination of butocarboxim residue in crops was carried out by HPLC equipped with a post-column deriva- tization system and a fluorescence detector. HPLC separation was performed on a Lichrospher 60 RP-Select B column eluted with a mobile phase of acetonitrile-water (25:75, v/v). Butocarboxim was hydrolyzed at 90°C under alkaline conditions and subsequently react- ed with o-phthaldialdehyde (OPA) / 2-mercaptoethanol reagent via a post-column reactor to generate a fluorophore, which was then detected with a fluorescence detector at Ex 340 nm and Em 455 nm. Average recoveries from radishes and bamboo sprouts, which were spiked with 0.1~0.3 and 0.2 ppm butocarboxim, respectively, were in the range of 81.9~82.6%. The detection limit was 0.05 ppm. No butocarboxim residue was detected in 10 commercial prod- ucts including radishes, carrots, and bamboo sprouts. Key words: agricultural products, butocarboxim, aminopropyl cartridge, high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC), post-column derivatization system, fluorescence detection. -

Gas-Phase Chemical Reduction (GPCR)
Gas-Phase Chemical Reduction (GPCR) Name of Process: Status: Gas-Phase Chemical Reduction (GPCR) A Commercial system operated in Australia for more than 5 years, treating Vendor: more than 2,500 tons of PCB’s, DDT and other POPs. In 1999 a full-scale test ELI Eco Logic International Inc. on HCB was conducted using the commercial plant. Web site: http://www.ecologic.ca Eco Logic’s partners in Japan have recently built a semi-mobile GPCR plant for Applicable Pesticides and related the treatment of PCB wastes, which will be operational in 2003. POPs wastes: Pesticides such as Hexachlorobenzene, In combination with Foster Wheeler and Kvaerner the company is DDT, Aldrin, Dieldrin, HCB’s, DDT, PCB’s, participating at present in the ACWA (Army Chemical Weapons Assessment) dioxins and furans and other POPs. Program for the destruction of chemical warfare agents. Eco Logic has partnered with Torftech Inc. for the treatment of soils and sediments at rates of up to 20 tons per hour. Eco Logic has also been selected by UNIDO for a pilot project for treatment of 1000 tons of PCB wastes in Slovakia. Additional approvals received: -for PCB and dioxin waste in Japan -for PCB’s TSCA permit in USA -for PCB’s and other toxic compounds in the Province of Ontario (Canada) Technology description: Eco Logic’s GPCR technology involves the gas-phase chemical reduction of organic compounds by hydrogen at a temperature of 850°C or higher. Chlorinated hydrocarbons, such as HCB, polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxins (dioxins) and other POPs, are chemically reduced to methane and hydrogen chloride (HCl). -

Pesticide Resistance in Bed Bugs Everywhere!!!!!
2/24/2018 Pesticide Resistance in Bed bugs were virtually eradicated from the U.S. in Bed Bugs the post WWII era due to DDT and other powerful Shujuan (Lucy) Li insecticides. University of Arizona Alvaro Romero New Mexico State University 2 By the 1960s, bed bugs had developed resistance Public housing Apartments to DDT, methoxychlor and analogues, BHC, Schools dieldrin and analogues , and pyrethrins ( Busvine 1958, Hospitals Nursing homes Cwilich & Mer 1957, Mallis and Miller 1964 ) . Homes Transportation Child care Medical facilities Hotels & motels Health care facilities Airports Movie theaters Department stores Products, vendors, or commercial services mentioned or pictured in this seminar are for Everywhere!!!!! illustrative purposes only and are not meant to be endorsements. 3 4 University of Arizona; Arizona Pest Management Center 1 2/24/2018 Possible reasons for treatment failure? Missed some Clutter Reintroduction Have you seen these after treatments? 5 6 Dose - response assays for field - collected strains Bed bugs survived direct insecticide sprays 99 deltamethrin 90 Ft. Dix F1 50 ) e l a c 10 s t CIN1 i b o 1.0 r p ( y t i l a t r 99 - cyhalothrin o m e 90 g a t n Resistance ratio (RR) at least 6,000 !!! e c Ft. Dix r 50 e P 10 CIN1 Suspend® ( Deltamethrin ) 1.0 10 -7 10 -6 10 -5 10 -4 10 -3 10 -2 10 -1 10 0 10 1 10 2 10 3 10 4 Treatment (mg active ingredient/cm 2 ) Products, vendors, or commercial services mentioned or pictured in this seminar are for illustrative purposes only and are not meant Romero et al.