Table 1: Institutions, Programmes and Degrees in German Higher Education
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Postgraduate Education in Europe Harmonising with a Dissonance?
Sakari Ahola & Osmo Kivinen Postgraduate Education in Europe Harmonising with a dissonance? This presentation deals with the emerging European postgraduate policies and their larger EU-dimensions which have motivated the establishing of a co-operative network (PG-NET) of eight European countries. The focus is on the harmonisation of the European higher education scene, especially from the Finnish point of view. The ongoing Bologna process can be seen as an expression of the will to create a common higher education market in Europe in order to promote the free mobility of students and the labour force. In this respect the speculation taken furthest is that already in the near future the effort to maintain the distinction between universities and polytechnics will be given up. In this way Europe will probably follow in the footsteps of the US, and gradually move towards a three-phase model of higher education with abroad access and initial three-year programmes leading to the bachelor’s degree that provides advanced training but that are not closely linked with the world of academic research. In the next phase a smaller part will advance through selective procedures to the master’s level on which studies are also more closely connected with scientific work. Only at the post-master’s level leading to a doctorate will the humboldtian ideal of the integrated nexus of teaching, research and learning be attained. It is argued in the paper that this kind of a two (or three) tier structure would be suitable especially from the perspective of the European Graduate School model and beneficial also to the functioning of the Finnish higher education system with its special problem points. -

Translating Degrees and Academic Titles Abbreviations: Challenges and Perspectives
Slađana Milinković TRANSLATING DEGREES AND ACADEMIC TITLES ABBREVIATIONS: CHALLENGES AND PERSPECTIVES SLAĐANA MILINKOVIĆ Th e Court Interpreters and Translators Association of Serbia E-mail: [email protected] Egyetemi fokozatok és tudományos címek rövidítéseinek fordítása: kihívások és perspektí- vák. Az ember társas lény, ezért természetes szükséglete a kommunikáció. Az emberi kommuni- káció fontosságát már évezredekkel ezelőtt felismerték, és gyökerei sokkal messzebbre nyúlnak vissza, mint amiről az írott történelem beszámol. Az emberi kommunikáció alapja az együttmű- ködés és a közös szándék, ahogy azt az antroposzemiotika is tanítja. Idáig azonban hosszú utat kellett bejárni. „Ἐν ἀρχῇ ἦν ὁ λόγος”,1 tanítja a Biblia, de az igét meg kell hallgatni, és terjeszteni kell. Minél messzebbre kellett eljutnia, annál fontosabb volt, hogy valamilyen módon lejegyezzék. És az em- ber másik természetes szükséglete, hogy nyomot hagyjon a világban – valamilyen képpel, szám- mal vagy betűvel. Nézzük meg röviden ennek a történetét. Kulcsszavak: latin nyelvű oklevelek, egyetemi fokozatok fordítása, tudományos címek rövidítése, bírósági tolmácsolás, a terminológia alakulása Since man is a social being, one of his innate needs is the desire to communicate. Th e importance of human communication has been recognised for thousands of years, far longer than demonstrated through recorded history. Human communication is rooted in cooperative and shared intentions, as anthroposemiotics teaches us. But it was a long road to get us here. “Ἐν ἀρχῇ ἦν ὁ λόγος”, the Bible has taught us, but it has to be heard and spread. Th e further it needed to go, the greater was the need to record it in some way. And the second man’s innate need was to make a mark in the world – with a picture of some kind, a certain sign, numeral or letter. -

THESIS by MAGISTER PROGRAM of ENGLISH EDUCATION TEACHER
perpustakaan.uns.ac.id digilib.uns.ac.id THESIS THE EFFECTIVENESS OF DISCUSSION METHOD IN TEACHING SPEAKING SKILL VIEWED FROM THE STUDENTS’ INTELLIGENCE QUOTIENT (An Experimental Research on the Tenth Grade of SMA Negeri 7 Purworejo in the Academic Year of 2012/2013) By BAMBANG HIRUSETYADI (S 891108024) Submitted as a Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Graduate Degree of English Education MAGISTER PROGRAM OF ENGLISH EDUCATION TEACHER TRAINING AND EDUCATION FACULTY SEBELAS MARET UNIVERSITY SURAKARTA commit2014 to user perpustakaan.uns.ac.id digilib.uns.ac.id APPROVAL THESIS THE EFFECTIVENESS OF DISCUSSION METHOD IN TEACHING SPEAKING SKILL VIEWED FROM THE STUDENTS’ INTELLIGENCE QUOTIENT (An Experimental Research on the Tenth Grade of SMA Negeri 7 Purworejo in the Academic Year of 2012/2013) By Bambang Hirusetyadi (S 891108024) This thesis has been approved by the Consultants and Head of Magister Program of English Education of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of Sebelas Maret University Surakarta In December 2013 Consultant I Consultant II Dr. Ngadiso, M. Pd Dra. Dewi Rochsantiningsih, M.Ed., Ph.D. NIP 196212311988031009 NIP 19600918 198702 2001 Approved by Head of English Education Department of Teacher Training and Education Faculty of Sebelas Maret University Dr. Abdul Asib, M.Pd NIP 19520307commit to 19user8003 1 005 ii perpustakaan.uns.ac.id digilib.uns.ac.id commit to user perpustakaan.uns.ac.id digilib.uns.ac.id PRONOUNCEMENT This is to certify that I myself write this thesis entitled “The Effectiveness of Discussion Method in Teaching Speaking Skill Viewed from The Students’ Intelligence Quotient” (An Experimental Research on the Tenth Grade of SMA Negeri 7 Purworejo in the Academic Year of 2012/2013). -

Diploma Supplement
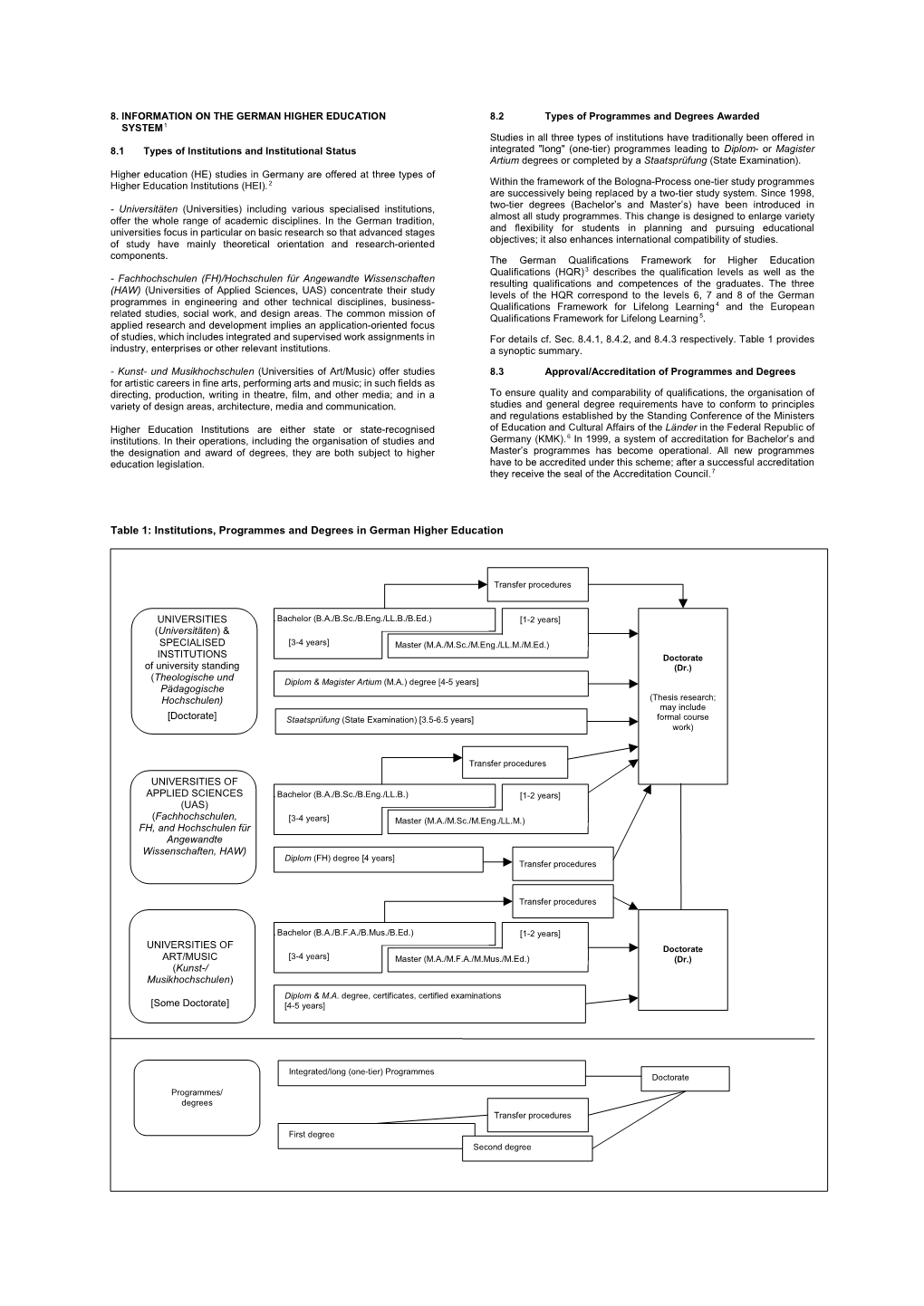
Diploma Supplement 8. INFORMATION ON THE GERMAN HIGHER EDUCATION 8.2 Types of Programmes and Degrees Awarded SYSTEM 1 Studies in all three types of institutions have traditionally been offered in 8.1 Types of Institutions and Institutional Status integrated "long" (one-tier) programmes leading to Diplom- or Magister Artium degrees or completed by a Staatsprüfung (State Examination). Higher education (HE) studies in Germany are offered at three types of Higher Education Institutions (HEI). 2 Within the framework of the Bologna-Process one-tier study programmes are successively being replaced by a two-tier study system. Since 1998, - Universitäten (Universities) including various specialised institutions, two-tier degrees (Bachelor’s and Master’s) have been introduced in offer the whole range of academic disciplines. In the German tradition, almost all study programmes. This change is designed to enlarge variety universities focus in particular on basic research so that advanced stages and flexibility for students in planning and pursuing educational of study have mainly theoretical orientation and research-oriented objectives; it also enhances international compatibility of studies. components. The German Qualifications Framework for Higher Education Qualifications (HQR) 3 describes the qualification levels as well as the - Fachhochschulen (FH)/Hochschulen für Angewandte Wissenschaften resulting qualifications and competences of the graduates. The three (HAW) (Universities of Applied Sciences, UAS) concentrate their study levels of the HQR correspond to the levels 6, 7 and 8 of the German programmes in engineering and other technical disciplines, business- Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning 4 and the European related studies, social work, and design areas. The common mission of Qualifications Framework for Lifelong Learning 5. -

Doctoral Examination Regulations of the Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences, Friedrich Schiller University Jena, As at 17 July 2018
President Doctoral examination regulations of the Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences, Friedrich Schiller University Jena, as at 17 July 2018 In accordance with section 3 subsection 1 in conjunction with section 38 subsection 3 of the Thuringian Higher Education Act (Thüringer Hochschulgesetz, ThürHG) from 10 May 2019 (published in the journal of legal notices of the Federal State of Thuringia, GVBl., p. 149), the Friedrich Schiller University Jena issues the present Doctoral Examination Regulations of the Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences. The regulations were approved by the faculty council on 27 June 2018 and agreed by the Senate of the University on 17 July 2018. The president gave his consent on the regulations on 17 July 2018. Contents I. Right to confer doctoral degree II. Admission requirements III. Admission as a doctoral candidate and supervision IV. Opening of the doctoral examination procedure V. Doctoral committee VI. Doctoral thesis VII. Oral examination VIII. Final mark of the doctorate IX. Award of the doctorate and doctoral degree certificate X. Joint doctoral examination procedures XI. Deception and revocation of the doctorate XII. Right of inspection XIII. Right of appeal in the doctoral examination procedure XIV. Honorary doctorate and jubilee doctorate XV. Mediation with ombudspersons XVI. Transitional provisions Page 1 I. Right to confer doctoral degree § 1 (1) 1The University, represented by the Faculty of Social and Behavioural Sciences, confers the doctoral degree “doctor philosophiae” (Dr. phil.). 2Upon formal request from the doctoral candidate, the University may confer the doctoral degree “Doctor of Philosophy” (PhD). (2) 1Represented by the Faculty, the University can also confer an honorary doctorate (“doctor honoris causa”, Dr. -

Documentation Requirements – by Country
Documentation Requirements – by Country Afghanistan • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Bachelor/Licence • Master Degree with transcripts (if applicable) • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Albania • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Diplome with titull • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Algeria • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Licentiate • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Andorra • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Diplomatura en….. (Bachelor Degree) • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Angola • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Bacharelato • Licenciado (if applicable) • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Anguilla • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Bachelor Degree • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Antigua & Barbuda • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Bachelor Degree • A syllabus or course description for all accounting, business and communication courses at the post-secondary level. Argentina • Final high school transcript • Transcripts • Bachiller Superior/Bachelor -

Conference Proceedings
European PhD Programmes in Biomedicine and Health Sciences Editors: Zdravko Lacković and Jadranka Božikov Proceedings of the Second European Conference on Harmonisation of PhD Programmes in Biomedicine and Health Sciences - Final version - Zagreb, Croatia, April 22–24, 2005 http://bio.mef.hr/conference Organised by UNIVERSITY OF ZAGREB - MEDICAL SCHOOL With the support of: Association of Medical Schools in Europe (AMSE) Association of Schools of Public Health in the European Region (ASPHER) European Medical Association (EMA) Association for Medical Education in Europe (AMEE) Sponsored by: National Foundation for Science, Higher Ministry of Science, Education and Education and Technological Development Sports of the Republic of Croatia of the Republic of Croatia Zagreb, June 21, 2005 PREFACE This monograph represents proceedings of the Second European Conference on Harmonisation of PhD Programmes in Medicine and Health Sciences held in Zagreb, April 22-24, 2005. The monograph was published prior to the Conference and the underlying final version includes “Guidelines for Organisation of PhD Programmes in Biomedicine and Health Sciences” convened during the Conference as well as the letter, both sent to the Ministerial Conference in Bergen immediately after the Conference. We would like to thank all the contributors including those who sent us their contributions although they were not able to attend the Conference in Zagreb. Editors: Professor Zdravko Lacković, MD, PhD Assoc. Professor Jadranka Božikov, PhD Zagreb, June 17, 2005 C O N T -

DIPLOMA SUPPLEMENT This Diploma Supplement Model Was Developed by the European Commission, Council of Europe and UNESCO/CEPES
DIPLOMA SUPPLEMENT This Diploma Supplement model was developed by the European Commission, Council of Europe and UNESCO/CEPES. The purpose of the supplement is to provide sufficient independent data to improve the international ‘transparency’ and fair academic and professional recognition of qualifications (diplomas, degrees, certificates etc.). It is designed to provide a description of the nature, level, context, content and status of the studies that were pursued and successfully completed by the individual named on the original qualification to which this supplement is appended. It should be free from any value judgements, equivalence statements or suggestions about recognition. Information in all eight sections should be provided. Where information is not provided, an explanation should give the reason why. 1. HOLDER OF THE QUALIFICATION 1.1 Family Name / 1.2 First Name Family name, first name 1.3 Citizenship/Nationality Nationality (in English notation) 1.4 Student ID Number or Code n. a. 2. QUALIFICATION 2.1 Name of Qualification (full, abbreviated; in original language) Master of Science (M.Sc.) Title Conferred (full, abbreviated; in original language) n.a. - n.a. 2.2 Main Field(s) of Study Computational Logic 2.3 Institutions Awarding the Qualification (in original language) Technische Universität Dresden Universidade Nova de Lisboa Technische Universität Wien Libera Università di Bolzano-Freie Universität Bozen Status (Type / Control) University / State Institution 2.4 Institution Administering Studies (in original language) [same] Status (Type / Control) [same / same] 2.5 Language(s) of Instruction/Examination English Certification Date: Date in English notation Head of Examination Committee Diploma Supplement first name, family name Page 2 of 5 3. -

Doctorate 1 Doctorate
Doctorate 1 Doctorate A doctorate is an academic degree or professional degree that, in most countries, qualifies the holder to teach at the university level in the specific field of his or her degree, or to work in a specific profession. The research doctorate, or the Doctor of Philosophy (Ph.D.) and its equivalent titles, represents the highest academic qualification. While the structure of U.S. doctoral programs is more formal and complex than in some other systems, the research doctorate is not awarded for the preliminary advanced study that leads to doctoral candidacy, but rather for successfully completing and defending the independent research presented in the form of the doctoral dissertation (thesis). Several first-professional degrees use the term “doctor” in their title, such as the Juris Doctor and the US version of the Doctor of Medicine, but these degrees do not universally contain an independent research component or always require a dissertation (thesis) and should not be confused with PhD degrees or other research doctorates.[1] In fact many universities offer Ph.D followed by a professional doctorate degree or joint Ph.D. with the professional degree (most often Ph.D. work comes sequential to the professional degree): eg. Ph.D. in law after J.D. or equivalent [2][3][4][5] in physical therapy after DPT,[6][7] in pharmacy after DPharm.[8][9] Often such professional degrees are refereed as entry level doctorate program [10][11][12] and Ph.D as postprofessional doctorate. In some countries, the highest degree in a given field is called a terminal degree, although this is by no means universal (the term is not in general use in the UK, for example), practice varies from country to country. -

Gazette 38/15 – 23
Gazette 38/15 – 23. September 2015 27 Please note: Only the German version of this regulations shall be valid exclusively Doctoral Regulations for the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences at Leuphana University Lüneburg The Faculty Council of the Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences passed the following Doctoral Regulations on 08 July 2015 in accordance with the first sentence of section 9 par. 3 NHG [Lower Saxony University Act]. The Presidential Committee approved the Regulations on 26 August 2015 in accordance with the third sentence of section 44 par. 1 NHG. Preamble The purpose of these Doctoral Regulations is to ensure high-quality doctorates at Leuphana University Lüneburg that will substantially shape national and international academic and scientific development. Responsibility for implementing doctoral programmes and examination procedures lies with the faculties. All doctoral candidates enrol on a doctoral programme based at the Graduate School at Leuphana University Lüneburg. § 1 Doctoral titles and purpose of the doctorate (1) The faculties of Leuphana University Lüneburg shall award the title of doctor in their respective fields following the successful completion of a doctoral assessment process. Pursuant to the first sentence of section 9 par. 1 NHG, a doctoral title may only be awarded if Leuphana University Lüneburg runs university- level Masters, Diplom or Magister degree programmes or equivalent degree programmes that lead to Staatsexamen examinations in the subjects in question. (2) The Faculty of Humanities and Social Sciences awards the following doctorate upon successful completion of a doctoral programme and thesis defence: Dr. phil. (3) By completing the doctoral programme, candidates demonstrate their ability to engage in in-depth, independent research. -

Europass Diploma Supplement
FACHHOCHSCHULE AACHEN EUROPASS DIPLOMA SUPPLEMENT This Diploma Supplement model was developed by the European Commission, Council of Europe and Unesco/CEPES. The purpose of the supplement is to provide sufficient independent data to improve the international ‘transparency’ and fair academic and professional recognition of qualifications (diplomas, degrees, certificates etc.). It is designed to provide a description of the nature, level, context, content and status of the studies that were pursued and successfully completed by the individual named on the original qualification to which this supplement is appended. It should be free from any value judgements, equivalence statements or suggestions about recognition. Information in all eight sections should be provided. Where information is not provided, an explanation should give the reason why. 1. HOLDER OF THE QUALIFICATION 1.1 Family name 1.2 First name Muster Martin 1.3 Date (DD/ MM /YYYY), place, country of birth 1.4 Student ID number or code 01/01/1985, Aachen, Germany 111111 2. QUALIFICATION 2.1 Name of qualification (full, abbreviated; in original language) Title conferred (full, abbreviated; in original language) Diplom-Kaufmann (FH), Dipl.-Kaufmann Diplom-Kaufmann (FH); Dipl.-Kaufmann n/a Explanatory note: Usually not applicable for Germany, except for some specialised professional designation which are awarded simultaneously with the academic degree. For these see 5.2. 2.2 Main field(s) of study Business Studies 2.3 Institution awarding the qualification (in original language) Status (Type / Control) Fachhochschule Aachen, Fachhochschule / federal Fachbereich Wirtschaftswissenschaften 2.4 Institution administering studies (in original language) Status (Type / Control) See 2.3 See 2.3 2.5 Language(s) of instruction/examination German 3. -

Republic of Poland
Credential Templates – Republic of Poland International Qualifications Assessment Service (IQAS), Government of Alberta Certificate of Completion of Basic Vocational School ................................................... 2 Certificate of Completion of General/ Specialized/ Supplementary General Secondary School and Matriculation Certificate ........................................................... 6 Certificate of Completion of Technical/ Supplementary Technical Secondary School and Matriculation Certificate ........................................................................................ 12 Certificate/ Diploma of Completion of Post-Lyceum School ...................................... 18 Title of Licentiate/ Title of Engineer ............................................................................. 21 Master’s Degrees (Old System)...................................................................................... 26 Master’s Degree (2nd Cycle) ........................................................................................... 30 Master’s Degree (Integrated 1st and 2nd Cycle) ............................................................ 34 University-level Credentials in Medicine/ Dentistry/ Veterinary Medicine (Integrated 1st and 2nd Cycle) ......................................................................................... 38 Master in Law (Integrated 1st and 2nd Cycle) ............................................................... 46 Doctoral Degree ..............................................................................................................