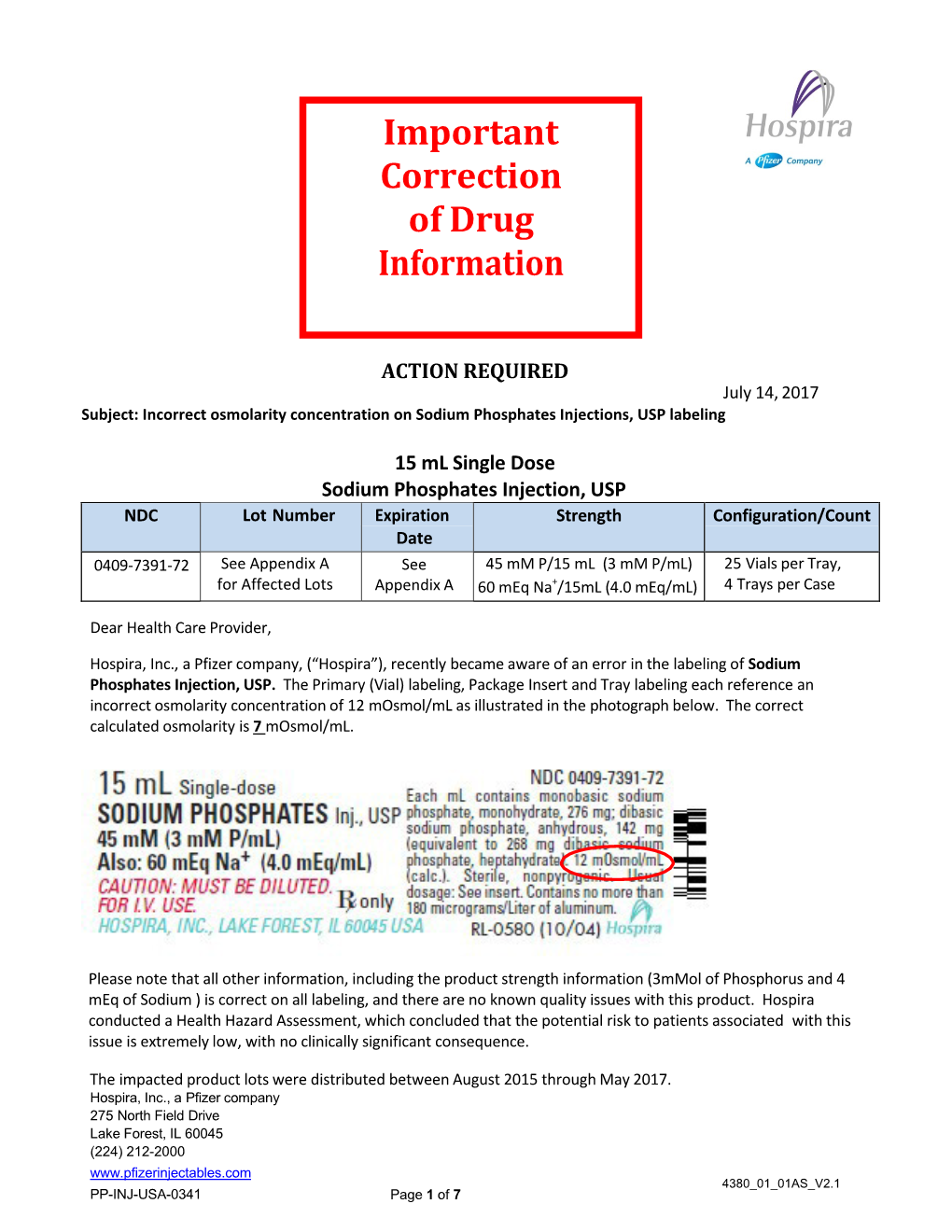
Drug Shortages: Sodium Phosphate Notification Letter
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

FLEET® Enemas Are Designed for Quick, Convenient Administration by Nurse, Patient Or Caregiver According to Instructions
Reference Safety Information – Fleet Enema FLEET® ENEMA, A SALINE LAXATIVE FLEET® ENEMA EXTRA®, A SALINE LAXATIVE FLEET® PEDIA-LAX® ENEMA, A SALINE LAXATIVE, FLEET® ENEMA FOR CHILDREN, A SALINE LAXATIVE FLEET® enemas are designed for quick, convenient administration by nurse, patient or caregiver according to instructions. Each is disposable after a single use. COMPOSITION: FLEET® ENEMA: Each FLEET® Enema unit, with a 2-inch, pre-lubricated Comfortip®, contains 4.5 fl. oz. (133 mL) of enema solution in a ready-to-use squeeze bottle which is not made with natural rubber latex. Each enema unit delivers a dose of 118 mL, which contains 19 g monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate and 7 g dibasic sodium phosphate heptahydrate. Each Fleet® Enema 118 mL delivered dose contains 4.4 grams sodium. FLEET® ENEMA EXTRA®: Each FLEET® Enema EXTRA® unit, with a 2-inch, pre-lubricated Comfortip®, contains 7.8 fl. oz. (230 mL) of enema solution in a ready-to-use squeeze bottle which is not made with natural rubber latex. Each enema unit delivers a dose of 197 mL, which contains 19 g monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate and 7 g dibasic sodium phosphate heptahydrate. Each Fleet® Enema EXTRA® 197 mL delivered dose contains 4.4 grams sodium. FLEET® PEDIA-LAX® ENEMA and FLEET® ENEMA FOR CHILDREN: Each Fleet® Pedia- Lax® Enema and FLEET® Enema for Children unit, with a 2-inch, pre-lubricated Comfortip®, contains 2.25 fl. oz. (66 mL) of enema solution in a ready-to use squeeze bottle which is not made with natural rubber latex. Each enema unit delivers a dose of 59 mL, which contains 9.5 g monobasic sodium phosphate monohydrate and 3.5 g dibasic sodium phosphate heptahydrate. -

Product Information Sheet
September 17, 2015 productISOVACTIN information AA PLUS Nutrients 8.5 fl oz (250mL) per 100mL SKU 37002 Calories 186 74 Calories From Fat 57 23 NET WEIGHT 2 GAL (7.5 L) Protein Equivalent, g 20 8 Free Amino Acids, g 22 9 SERVING SIZE 8.5 fl oz (250mL) Carbohydrates, g 13 5 Sugar, g 5 2 SERVINGS PER PACKAGE 30 Sugar Alcohols, g 0 0 Dietary Fiber, g 2.8 1 Fat, g 6 2.4 24359-0702-03 REIMBURSEMENT CODE Saturated Fat, g 0.5 0.2 (for USA only) Trans Fat, g 0.0 0.0 DHA, mg 150.0 60.0 Cholesterol, mg 0.4 0 MEDICAL FOOD PRODUCT Vitamin A, IU 1100.0 440.0 For the dietary management of Isovaleric Acidemia. Dispensed by prescription. Vitamin C, mg 40.0 16.0 Isovactin AA Plus is a ready-to-drink metabolic formula product for Isovaleric Acidemia Vitamin D, IU 620.0 248.0 patients, over 1 year of age. Isovactin contains an advanced fortification blend. Product Vitamin E, IU 10.0 4.0 Vitamin K1, mcg 20.0 8.0 comes in a 250 mL carton. Vitamin K2 (MK-7), mcg 20.0 8.0 Thiamin (B1), mg 0.5 0.2 Riboflavin (B2), mg 0.5 0.2 Niacin (B3), mg 6.6 2.6 PRECAUTIONS For the dietary management of Isovaleric Acidemia (IVA) and Vitamin B6, mg 0.5 0.2 other disorders of leucine metabolism. Use as directed by physician. Must be Folic acid, mcg 186.0 74.4 administered under medical supervision only. -

Brochure-Product-Range.Pdf
PRODUCT RANGE 2015 edition ANSI Standard 60 NSF® CERTIFIED HALAL M ISLAMIC FOOD AND NUTRITION ® COUNCIL OF AMERICA Rue Joseph Wauters, 144 ISO 9001:2008 (Quality) / OHSAS 18001:2007 (Health/ B-4480 Engis Safety) / ISO 14001:2004 (Environment) / ISO 22000:2005 www.globulebleu.com (Food Safety) / FSSC 22000:2013 (Food Safety). Tel. +32 (0) 4 273 93 58 Our food grade phosphates are allergen free, GMO free, Fax. +32 (0) 4 275 68 36 BSE/TSE free. www.prayon.com mail. [email protected] Design by www.prayon.com PRODUCT RANGE | 11 TABLE OF CONTENTS HORTICULTURE APPLICATIONS HORTIPRAY® RANGE FOR HORTICULTURE* FOOD AND INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS PRODUCT NAME Bulk density P O pH N-NH Made 2 5 4 MONOAMMONIUM PHOSPHATE - NH4H2PO4 in 3 3 % 1% % Sodium orthophosphates ................................................................................... 03 g/cm lbs/ft indicative indicative indicative Water-soluble fertilisers. Sodium pyrophosphates .................................................................................... 04 HORTIPRAY® MAP Horticultural Grade 0.9 56 61 4.5 12 Sodium tripolyphosphates ................................................................................. 05 HORTIPRAY® MAP 12.60 Horticultural Grade 0.9 56 60 5 12.1 Water-soluble fertilisers; Sodium polyphosphates ..................................................................................... 06 HORTIPRAY® MAP anticalc Horticultural Grade 0.9 56 61 4.5 12 preventive action against clogging. Potassium orthophosphates ............................................................................. -

(12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143022 A1 Wicker Et Al
US 20170143022A1 (19) United States (12) Patent Application Publication (10) Pub. No.: US 2017/0143022 A1 Wicker et al. (43) Pub. Date: May 25, 2017 (54) COMPOSITIONS INCORPORATING AN (52) U.S. Cl. UMLAM FLAVORAGENT CPC ............... A2.3L 27/20 (2016.08); A23L 27/88 (2016.08); A23L 2/56 (2013.01); A23L 2780 (71) Applicant: Senomyx, Inc., San Diego, CA (US) (2016.08); A23L 27/30 (2016.08); A23K 20/10 (2016.05); A23K 50/40 (2016.05); A61K 47/22 (72) Inventors: Sharon Wicker, Carlsbad, CA (US); (2013.01) Tanya Ditschun, San Diego, CA (US) (21) Appl. No.: 14/948,101 (57) ABSTRACT The present invention relates to compositions containing (22) Filed: Nov. 20, 2015 flavor or taste modifiers, such as a flavoring or flavoring agents and flavor or taste enhancers, more particularly, Publication Classification savory (“umami”) taste modifiers, savory flavoring agents (51) Int. Cl. and savory flavor enhancers, for foods, beverages, and other AOIN 25/00 (2006.01) comestible compositions. Compositions comprising an A23K2O/It (2006.01) umami flavor agent or umami taste-enhancing agent in A6 IK 47/22 (2006.01) combination with one or more other food additives, prefer A2.3L 2/56 (2006.01) ably including a flavorant, herb, Spice, fat, or oil, are A23K 50/40 (2006.01) disclosed. US 2017/O 143022 A1 May 25, 2017 COMPOSITIONS INCORPORATING AN tions WO 02/06254, WO 00/63166 art, WO 02/064631, and UMAM FLAVORAGENT WO 03/001876, and U.S. Patent publication US 2003 0232407 A1. The entire disclosures of the articles, patent BACKGROUND OF THE INVENTION applications, -

General Properties of the Alkaline Phosphates: - Major Food and Technical Applications
Phosphorus Research Bulletin Vol. 15 (2004) p. 85-94 General Properties of the Alkaline Phosphates: - Major Food and Technical Applications P.HOURANT Deputy Business Line Manager, Prayon S.A., Business Unit Phosphates, Rue Joseph Wauters, 144 4480 Engis, Belgium; E-mail: [email protected] INTRODUCTION The alkaline phosphates are used for many food and technical applications. Phosphates have two characteristics that explain their four main properties: buffer agent, sequestering power, dispersing power and water holding capability. Those properties allow phosphates to be used in many food and technical applications. The main food applications are meat and seafood processing, baking and processed cheese, but others such as cereals, French fries, fruits and vegetables, beverages, noodles and so on also may need the use of phosphates. On the technical side, the main applications are the detergent products, the water treatment and the metal treatment. As for the food, many other applications require phosphates such as ceramics, bone china, paper and paints,... In meat products, phosphates salts interact in a unique way to bind water with proteins and improve the tenderness in meats. Treated products will maintain their juicy appearance as well as their natural nutritional properties texture and colour. In fish and seafood products, phosphates salts allow the retention of the natural juices of frozen fish fillets, prawns, shrimps, scallops and other seafood. Phosphates also help prevent the build-up of struvite crystals in tinned tuna and crabmeat. In processed cheese, phosphates are crucially important in the production of processed cheese. These products ensure a homogeneous and uniform melt of raw cheese and product stability. -

Phosphates' Function in Poultry Products
[Salt/Sodium Reduction] Vol. 17 No. 8 August 2007 ww Phosphates’ Function in Poultry Products By Andrew G. Ebert, Ph.D., Contributing Editor Food-grade phosphates perform a number of functions in processed poultry products. These properties include raising pH, increasing ionic strength and reacting with protein, which improves the water-holding capacity of the functional myofibrillar protein in poultry, thereby decreasing cook-cool loss, and creating improved and uniform yields. Phosphates protect against oxidation of lipids by binding metal ions that accelerate oxidation. They protect and preserve the natural flavor and color of poultry, and they solubilize protein, which is required in producing formed and restructured products, such as delicatessen rolls and chicken nuggets. Additive effects Studies with poultry products began over 40 years ago. Early applications involved static holding in solutions containing sodium tripolyphosphate (STPP), an alkaline phosphate, and sodium hexametaphosphate (SHMP). The most-notable food-technological effects were a 6.2% increase in moisture content and a rise in pH from 6.1 to 6.6, due to the addition of phosphate. With levels of phosphates used today, a more-modest rise (0.1 to 0.3 pH units, depending upon the phosphate or blend) would be anticipated. More recent studies have shown that the use of phosphates increases the temperature required for denaturation of protein and, thus, reduces cook-cool loss, leading to an end product with greater succulence. The addition of STPP and sodium chloride (NaCl) in poultry-processing formulations has been shown to have a number of advantages. First, STPP and NaCl increase ionic strength and synergistically extract myofibrillar protein. -

Use of Thin Layer Chromatography in Detecting the Addition and Degradation of Sodium Phosphates in Seafood Products
USE OF THIN LAYER CHROMATOGRAPHY IN DETECTING THE ADDITION AND DEGRADATION OF SODIUM PHOSPHATES IN SEAFOOD PRODUCTS By PHILLIP BLAINE HOLMBERG A THESIS PRESENTED TO THE GRADUATE SCHOOL OF THE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA IN PARTIAL FULFILLMENT OF THE REQUIREMENTS FOR THE DEGREE OF MASTER OF SCIENCE UNIVERSITY OF FLORIDA 2010 1 © 2010 Phillip Blaine Holmberg 2 To my parents, Eric and Helen Holmberg, and to all who nurtured my intellectual curiosity, academic interests, and sense of scholarship throughout my lifetime, making this milestone possible 3 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS I would like to thank my major advisor, Dr. Otwell, for all of his advice, support and opportunities to gain knowledge and experience. I would also like to thank my other graduate committee members, Dr. Marty Marshall and Dr. Frank Chapman. I extend a special thanks to Sven-Eric Ebeling and everyone at Chemische Fabrik Budenheim KG for their teachings and generous hospitality during my research in Germany. I thank Laura Garrido for helping me with everything along the way. I also thank Victor Garrido and all of my lab mates, past and present, Steven D’uva, Alex Fortunado, Marcus Ladd, Zach Lowenstein, Kelley Zhou, and Ivan Lozano. I thank Zina Williams for all of her help and support. Finally, I would like to thank my friends and family for all the good times and always being there for me. 4 TABLE OF CONTENTS page ACKNOWLEDGMENTS .................................................................................................. 4 LIST OF TABLES ........................................................................................................... -

QUALITY CHOICE SINGLE SALINE ENEMA LAXATIVE Drug Facts
QUALITY CHOICE SINGLE SALINE LAXATIVE- sodium phosphate, dibasic and sodium phosphate, monobasic, unspecified form enema CDMA Disclaimer: Most OTC drugs are not reviewed and approved by FDA, however they may be marketed if they comply with applicable regulations and policies. FDA has not evaluated whether this product complies. ---------- QUALITY CHOICE SINGLE SALINE ENEMA LAXATIVE Drug Facts Active ingredients (in each 118mL Purpose delivered dose) Dibasic Sodium Phosphate 7 g Saline laxative Monobasic Sodium Phosphate 19 g Saline laxative Use Relieves occasional constipation Warnings For rectal use only. Dosage warning Using more than one enema in 24 hours can be harmful. Ask a doctor before use if you already used a laxative for more than 1 week have kidney disease have heart problems are dehydrated are 55 years old or older are on a sodium-restricted diet Ask a doctor before using any laxative if you have abdominal pain, nausea, or vomiting a sudden change in bowel habits lasting more than 2 weeks already used a laxative for more than 1 week When using this product do not use more than directed. Serious side effects may occur from excess dosage do not use for more than 3 days Stop use and ask a doctor if you have bleeding the condtion worsens or does not improve within 7 days you have no bowel movement within 30 minutes of enema use you have symptoms of dehydration (thirstiness, dizziness, vomiting, urinating less often than normal) These symptoms may indicate a serious condition. If pregnant or breast-feeding, ask a health professional before use. Keep out of reach of children. -

Federal Register/Vol. 63, No. 98/Thursday, May 21, 1998/Rules and Regulations
27836 Federal Register / Vol. 63, No. 98 / Thursday, May 21, 1998 / Rules and Regulations concludes that the proposed use of the (address above) between 9 a.m. and 4 document. Any objections received in additive is safe, that the additive will p.m., Monday through Friday. response to the regulation may be seen achieve its intended technical effect, Any person who will be adversely in the Dockets Management Branch and therefore, that the regulations in affected by this regulation may at any between 9 a.m. and 4 p.m., Monday § 178.2010 should be amended as set time on or before June 22, 1998, file through Friday. forth below. with the Dockets Management Branch List of Subjects in 21 CFR Part 178 In accordance with § 171.1(h) (21 CFR (address above) written objections thereto. Each objection shall be Food additives, Food packaging. 171.1(h)), the petition and the Therefore, under the Federal Food, documents that FDA considered and separately numbered, and each numbered objection shall specify with Drug, and Cosmetic Act and under relied upon in reaching its decision to authority delegated to the Commissioner approve the petition are available for particularity the provisions of the regulation to which objection is made of Food and Drugs and redelegated to inspection at the Center for Food Safety the Director, Center for Food Safety and and Applied Nutrition by appointment and the grounds for the objection. Each numbered objection on which a hearing Applied Nutrition, 21 CFR part 178 is with the information contact person amended as follows: listed above. -

Long-Term Calcium-Phosphorus Studies in Confined Dairy Cows
Long-Term Calcium-Phosphorus Studies in Confined Dairy Cows George Ward, Ph.D. E. P. Call, Ph.D. Dept. of Animal Sciences and Insdustry Kansas State University Manhattan, Kansas 66506 Modern dairy cows are under considerable stress ~tudy (Figures 1 and 2). Comparison of Figures 3 and consuming and metabolizing large quantities of feed 4 shows the influence of supplemental vitamin D on and synthesizing large quantities of milk. The calcium utilization. Cows producing more than 15 kg nutrient requirement for peak production in a cow's milk without vitamin D supplement had negative lactation usually exceeds her capacity for feed. The calcium balances with intakes to 250 g/day. We es combination of deficit consumption and obligatory timated the calcium requirement from the balances nutrient balance required for milk synthesis com with cows supplemented with vitamin Da and produc pounds that stress. Attempts to satisfy energy re ing in excess of 15 kg milk in Figure 4. We drew the quirements result in inordinate skewing of the ration requirement line where it included negative balances toward a large proportion of concentrate. above the line equal in number to positive balances Combination of extreme variation among rations below the line (10). This estimate was nearly twice and the vast requirement for nutrients to support the NRC requirement (11). Some of our contem heavy lactation emphasizes the need for adequate in poraries ascribe the deviation to short-time balances formation concerning nutrient requirements, but few longer ones are being reported. Graphic treatment of data from Forbes, et al. (3), availabilities, and interactions. -

Federal Register/Vol. 63, No. 98/Thursday, May 21, 1998/Proposed Rules
27886 Federal Register / Vol. 63, No. 98 / Thursday, May 21, 1998 / Proposed Rules (301) 504±0800 or delivered to the allow garments sized for a child nine PART 1616ÐSTANDARD FOR THE Office of the Secretary, Room 501, 4330 months and under and tight-fitting FLAMMABILITY OF CHILDREN'S East-West Highway, Bethesda, Maryland garments in sizes above nine months to SLEEPWEAR: SIZES 7 THROUGH 14 20814. Copies should be submitted in be sold and used as sleepwear. five copies and captioned ``Sleepwear Therefore, the Commission proposes to 1. The authority citation for part 1616 Policy Statement.'' Comments may also modify the policy statements at continues to read as follows: be filed by telefacsimile to (301) 504± 1615.64(d) and 1616.65(d) to provide Authority: Sec. 4, 67 Stat. 112, as 0127 or by e-mail to cpsc [email protected]. that infant garments (defined in the amended, 81 Stat. 569±70; 15 U.S.C. 1193. FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT: amended sleepwear standard at 16 CFR 2. Section 1616.65 is amended by Patricia Fairall, Program Manager, 1615.1(c)(1) as sized for a child nine revising paragraph (d) introductory text Office of Compliance, Consumer months and under) and ``tight-fitting'' to read as follows: Product Safety Commission, garments (defined in the amended Washington, D.C. 20207; telephone sleepwear standard at 16 CFR 1615.1(o) § 1616.65 Policy scope of the standard. (301) 504±0400, extension 1369. and 1616.2(m)) can be marketed and * * * * * SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: promoted with other sleepwear. (d) Retailers, distributors, and For the reasons stated above and wholesalers, as well as manufacturers, A. -

Monosodium Phosphate 1 of 9 Anhydrous
SAFETY DATA SHEET Monosodium Phosphate 1 of 9 Anhydrous Complying with 1907/2006/EEC Regulation of 18 December 2006 Section 1. IDENTIFICATION OF THE SUBSTANCE/PREPARATION AND OF THE COMPANY/UNDERTAKING REACH Product name: Monosodium Phosphate Anhydrous Trade names: Monosodium Phosphate Anhydrous; MSP-Gr; MSP-Pw; Hi-C-510; Hi-C-511; Hi-C-512; Hi-C-516. Synonyms: Sodium Phosphate, Monobasic; Monosodium Dihydrogen Phosphate; Phosphoric acid, monosodium salt; MSP Chemical formula: NaH2PO4 Fertilizer formula: Not applicable Product type: Solid (powder or granular) Cas number: 7558-80-7 Use of the substance/preparation: Food processing-buffer, emulsifier. Pharmacopoeia - nutrient, buffer. Industries – water treatment, metal treatment, corrosion control, drilling mud, ceramics, acid-base cleaners. Company/undertaking identification Supplier/Manufacturer: Haifa Chemicals Ltd. P.O.B 10809, Haifa Bay 26120, Israel Tel: +972-4-8469961 Fax: +972-4-8469955 E-mail address of person responsible for this SDS: [email protected] Emergency telephone number: +972-4-8469603/4 (with hours of operation) Section 2. HAZARDS IDENTIFICATION Classification: The substance is not classified as dangerous according to Directive 67/548/EEC and its amendments. Most important hazards: CAUTION! Dust in high concentration may cause eye, skin and respiratory tract irritation. See section 11 for more detailed information on health effects and symptoms. SAFETY DATA SHEET Monosodium Phosphate 2 of 9 Anhydrous Section 3. COMPOSITION/INFORMATION ON INGREDIENTS Substance/preparation: Ingredient name CAS % EC number Classification number Monosodium Phosphate 7558-80-7 100% 231-449-2 - Anhydrous See section 16 for the full text of the R-phrases declared above There are no additional ingredients present which, within the current knowledge of the supplier and in the concentrations applicable, are classified as hazardous to health or the environment and hence require reporting in this section.