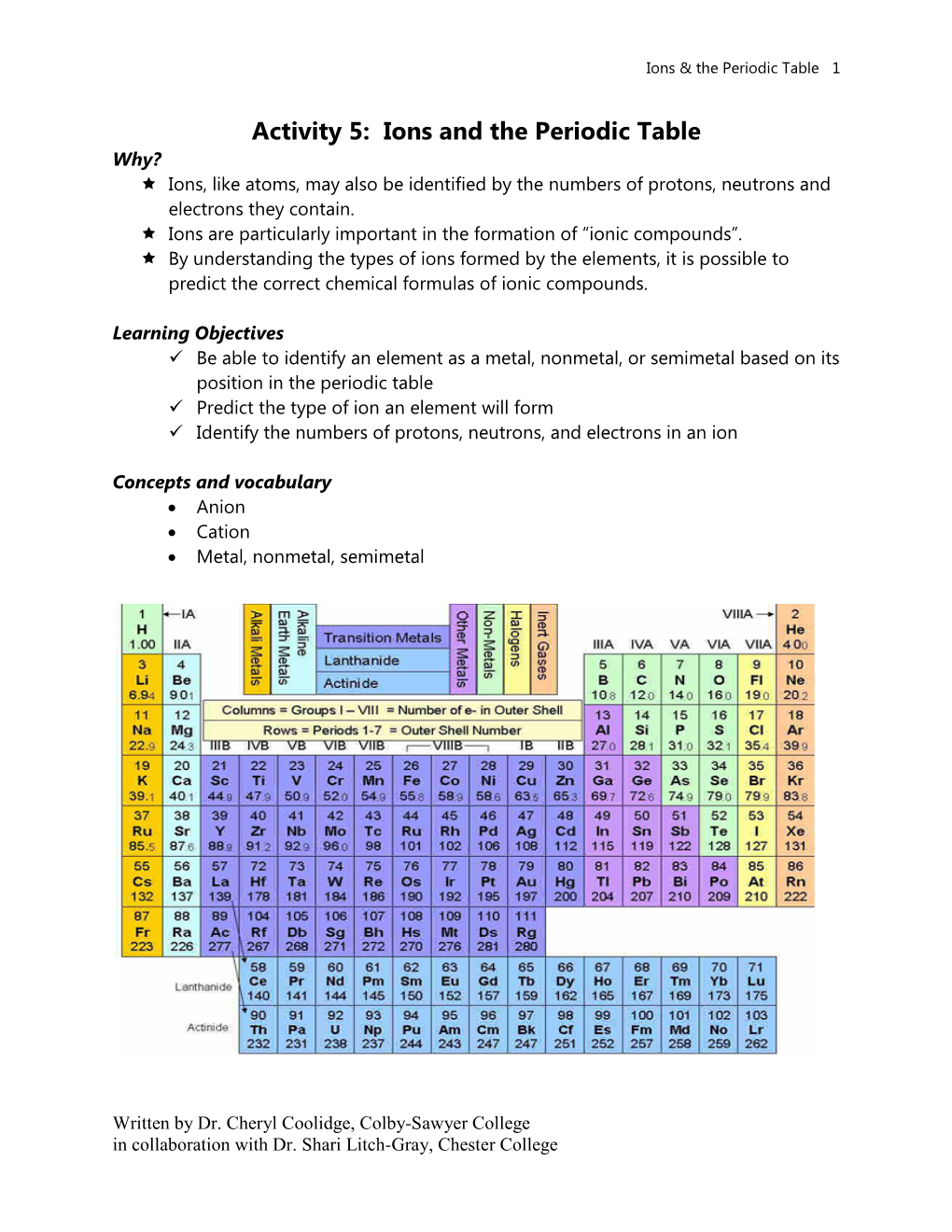
Ions and the Periodic Table Why? Ions, Like Atoms, May Also Be Identified by the Numbers of Protons, Neutrons and Electrons They Contain
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Chemistry Grade Level 10 Units 1-15
COPPELL ISD SUBJECT YEAR AT A GLANCE GRADE HEMISTRY UNITS C LEVEL 1-15 10 Program Transfer Goals ● Ask questions, recognize and define problems, and propose solutions. ● Safely and ethically collect, analyze, and evaluate appropriate data. ● Utilize, create, and analyze models to understand the world. ● Make valid claims and informed decisions based on scientific evidence. ● Effectively communicate scientific reasoning to a target audience. PACING 1st 9 Weeks 2nd 9 Weeks 3rd 9 Weeks 4th 9 Weeks Unit 1 Unit 2 Unit 3 Unit 4 Unit 5 Unit 6 Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit Unit 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 1.5 wks 2 wks 1.5 wks 2 wks 3 wks 5.5 wks 1.5 2 2.5 2 wks 2 2 2 wks 1.5 1.5 wks wks wks wks wks wks wks Assurances for a Guaranteed and Viable Curriculum Adherence to this scope and sequence affords every member of the learning community clarity on the knowledge and skills on which each learner should demonstrate proficiency. In order to deliver a guaranteed and viable curriculum, our team commits to and ensures the following understandings: Shared Accountability: Responding -

Prebiological Evolution and the Metabolic Origins of Life
Prebiological Evolution and the Andrew J. Pratt* Metabolic Origins of Life University of Canterbury Keywords Abiogenesis, origin of life, metabolism, hydrothermal, iron Abstract The chemoton model of cells posits three subsystems: metabolism, compartmentalization, and information. A specific model for the prebiological evolution of a reproducing system with rudimentary versions of these three interdependent subsystems is presented. This is based on the initial emergence and reproduction of autocatalytic networks in hydrothermal microcompartments containing iron sulfide. The driving force for life was catalysis of the dissipation of the intrinsic redox gradient of the planet. The codependence of life on iron and phosphate provides chemical constraints on the ordering of prebiological evolution. The initial protometabolism was based on positive feedback loops associated with in situ carbon fixation in which the initial protometabolites modified the catalytic capacity and mobility of metal-based catalysts, especially iron-sulfur centers. A number of selection mechanisms, including catalytic efficiency and specificity, hydrolytic stability, and selective solubilization, are proposed as key determinants for autocatalytic reproduction exploited in protometabolic evolution. This evolutionary process led from autocatalytic networks within preexisting compartments to discrete, reproducing, mobile vesicular protocells with the capacity to use soluble sugar phosphates and hence the opportunity to develop nucleic acids. Fidelity of information transfer in the reproduction of these increasingly complex autocatalytic networks is a key selection pressure in prebiological evolution that eventually leads to the selection of nucleic acids as a digital information subsystem and hence the emergence of fully functional chemotons capable of Darwinian evolution. 1 Introduction: Chemoton Subsystems and Evolutionary Pathways Living cells are autocatalytic entities that harness redox energy via the selective catalysis of biochemical transformations. -

4.2 Ionic Bonds Vocabulary: Ion – Polyatomic Ion – Ionic Bond – Ionic Compound – Chemical Formula – Subscript –
4.2 Ionic Bonds Vocabulary: Ion – Polyatomic ion – Ionic bond – Ionic compound – Chemical formula – Subscript – Crystal - An ion is an atom or group of atoms that has an electric charge. When a neutral atom loses a valence electron, it loses a negative charge. It becomes a positive ion. When a neutral atom gains an electron, it gains a negative charge and becomes a negative ion. Common Ions: Name Charge Symbol/Formula Lithium 1+ Li+ Sodium 1+ Na+ Potassium 1+ K+ Ammonium 1+ NH₄+ Calcium 2+ Ca²+ Magnesium 2+ Mg²+ Aluminum 3+ Al³+ Fluoride 1- F- Chloride 1- Cl- Iodide 1- I- Bicarbonate 1- HCO₃- Nitrate 1- NO₃- Oxide 2- O²- Sulfide 2- S²- Carbonate 2- CO₃²- Sulfate 2- SO₄²- Notice that some ions are made of several atoms. Ammonium is made of 1 nitrogen atom and 4 hydrogen atoms. Ions that are made of more than 1 atom are called polyatomic ions. Ionic bonds: When atoms that easily lose electrons react with atoms that easily gain electrons, valence electrons are transferred from one type to another. The transfer gives each type of atom a more stable arrangement of electrons. 1. Sodium has 1 valence electron. Chlorine has 7 valence electrons. 2. The valence electron of sodium is transferred to the chlorine atom. Both atoms become ions. Sodium atom becomes a positive ion (Na+) and chlorine becomes a negative ion (Cl-). 3. Oppositely charged particles attract, so the ions attract. An ionic bond is the attraction between 2 oppositely charged ions. The resulting compound is called an ionic compound. In an ionic compound, the total overall charge is zero because the total positive charges are equal to the total negative charges. -

Analysis of Multipolar Linear Paul Traps for Ion–Atom Ultracold Collision Experiments
atoms Article Analysis of Multipolar Linear Paul Traps for Ion–Atom Ultracold Collision Experiments M. Niranjan *, Anand Prakash and S. A. Rangwala * Raman Research Institute, C. V. Raman Avenue, Sadashivanagar, Bangalore 560080, India; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] (M.N.); [email protected] (S.A.R.) Abstract: We evaluate the performance of multipole, linear Paul traps for the purpose of studying cold ion–atom collisions. A combination of numerical simulations and analysis based on the virial theorem is used to draw conclusions on the differences that result, by considering the trapping details of several multipole trap types. Starting with an analysis of how a low energy collision takes place between a fully compensated, ultracold trapped ion and an stationary atom, we show that a higher order multipole trap is, in principle, advantageous in terms of collisional heating. The virial analysis of multipole traps then follows, along with the computation of trapped ion trajectories in the quadrupole, hexapole, octopole and do-decapole radio frequency traps. A detailed analysis of the motion of trapped ions as a function of the amplitude, phase and stability of the ion’s motion is used to evaluate the experimental prospects for such traps. The present analysis has the virtue of providing definitive answers for the merits of the various configurations, using first principles. Keywords: ion trapping; ion–atom collisions; linear multipole traps; virial theorem Citation: Niranjan, M.; Prakash, A.; Rangwala, S.A. Analysis of Multipolar Linear Paul Traps for 1. Introduction Ion–Atom Ultracold Collision Linear multipole Paul trap configurations are emerging as a natural choice for a wide Experiments. -

Introduction to Chemistry
Introduction to Chemistry Author: Tracy Poulsen Digital Proofer Supported by CK-12 Foundation CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook Introduction to Chem... materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based Authored by Tracy Poulsen collaborative model termed the “FlexBook,” CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and 8.5" x 11.0" (21.59 x 27.94 cm) distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide Black & White on White paper an adaptive environment for learning. 250 pages ISBN-13: 9781478298601 Copyright © 2010, CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org ISBN-10: 147829860X Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made Please carefully review your Digital Proof download for formatting, available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution/Non-Commercial/Share grammar, and design issues that may need to be corrected. Alike 3.0 Unported (CC-by-NC-SA) License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc- sa/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Commons from time to time (the “CC License”), We recommend that you review your book three times, with each time focusing on a different aspect. which is incorporated herein by this reference. Specific details can be found at http://about.ck12.org/terms. Check the format, including headers, footers, page 1 numbers, spacing, table of contents, and index. 2 Review any images or graphics and captions if applicable. -

The Power of Crowding for the Origins of Life
Orig Life Evol Biosph (2014) 44:307–311 DOI 10.1007/s11084-014-9382-5 ORIGIN OF LIFE The Power of Crowding for the Origins of Life Helen Greenwood Hansma Received: 2 October 2014 /Accepted: 2 October 2014 / Published online: 14 January 2015 # Springer Science+Business Media Dordrecht 2015 Abstract Molecular crowding increases the likelihood that life as we know it would emerge. In confined spaces, diffusion distances are shorter, and chemical reactions produce fewer and more regular products. Crowding will occur in the spaces between Muscovite mica sheets, which has many advantages as a site for life’s origins. Keywords Muscovite mica . Molecular crowding . Origin of life . Mechanochemistry. Abiogenesis . Chemical confinement effects . Chirality. Protocells Cells are crowded. Protein molecules in cells are typically so close to each other that there is room for only one protein molecule between them (Phillips, Kondev et al. 2008). This is nothing like a dilute ‘prebiotic soup.’ Therefore, by analogy with living cells, the origins of life were probably also crowded. Molecular Confinement Effects Many chemical reactions are limited by the time needed for reactants to diffuse to each other. Shorter distances speed up these reactions. Molecular complementarity is another principle of life in which pairs or groups of molecules form specific interactions (Root-Bernstein 2012). Current examples are: enzymes & substrates & cofactors; nucleic acid base pairs; antigens & antibodies; nucleic acid - protein interactions. Molecular complementarity is likely to have been involved at life’s origins and also benefits from crowding. Mineral surfaces are a likely place for life’s origins and for formation of polymeric molecules (Orgel 1998). -

Flex'ion Li-Ion Battery System
Flex’ionTM Li-ion Battery System For Mission Critical Applications DATA CENTERS OIL & GAS UTILITY Flex’ion TM main advantages Main benefits versus VRLA lead-acid batteries LIFE TIME LOW MAINTENANCE INSTALLATION SPACE INSTALLATION WEIGHT 20 YEARS CALENDAR LIFE 3X MORE COMPACT 6X LIGHTER 10X MORE CYCLE LIFE LIION LEADACID LIION LEADACID LIION LEADACID REDUCED TCO & IMPROVED SYSTEM AVAILABILITY REDUCED BATTERY ROOM & INFRASTRUCTURE COST From cell to module and system FLEX’IONTM SYSTEM LIION CELL FLEX’IONTM BATTERY MODULE A WIDE RANGE OF COMBINATIONS: From 1 to 500 kWh From 10 kW to 2.3 MW From 110 to 750 Vdc (CE) and 600 Vdc (UL) Flex'ionTM system Battery Module Stores electrical energy ready for use during mains failure Cabinet IP20, non-seismic or seismic BMM Manages safety functions at string level Intelli-Connect™ Allows string to discharge if charging is interrupted MBMM+PLC Manages internal system-level & external communications HMI Touchscreen display providing system information LED Button Controlled system start / stop & battery status Battery-stop Button Opens the main breaker in each string to isolate the battery system DATA REMOTE MONITORING VISUALIZE HMI DATA ON A SMART DEVICE Door Handle Lever design & lockable Flex’ionTM key differentiators Dedicated structure to support your need Local support for engineering, services and after-sales SHORT LEADTIME Short lead-time thanks to US and European production US & EUROPEAN PRODUCTION Established recycling policy for a sustainable approach Modular & scalable battery configuration Optimized -

Gas Phase Ion/Molecule Reactions As Studied by Fourier Transform Ion Cyclotron Resonance Mass Spectrometry
INIS-mf—10165 GAS PHASE ION/MOLECULE REACTIONS AS STUDIED BY FOURIER TRANSFORM ION CYCLOTRON RESONANCE MASS SPECTROMETRY STEEN INGEMANN J0RGENSEN GAS PHASE ION/MOLECULE REACTIONS AS STUDIED BY FOURIER TRANSFORM ION CYCLOTRON RESONANCE MASS SPECTROMETRY ACADEMISCH PROEFSCHRIFT ter verkrijging van de graad van doctor in de Wiskunde en Natuurwetenschappen aan de Universiteit van Amsterdam, op gezag van de Rector Magnificus dr. D.W. Bresters, hoogleraar in de Faculteit der Wiskunde en Natuurwetenschappen, in het openbaar te verdedigen in de Aula der Universiteit (tijdelijk in het Wiskundegebouw, Roetersstraat 15) op woensdag 12 juni 1985 te 16.00 uur. door STEEN INGEMANN J0RGENSEN geboren te Kopenhagen 1985 Offsetdrukkerij Kanters B.V., Alblasserdam PROMOTOR: Prof. Dr. N.M.M. Nibbering Part of the work described in this thesis has been accomplished under the auspices of the Netherlands Foundation for Chemical Research (SON) with the financial support from the Netherlands Organization for the Advancement of Pure Research (ZWO). STELLINGEN 1. De door White e.a. getrokken conclusie, dat het cycloheptatrieen anion omlegt tot het benzyl anion in de gasfase, is onvoldoende ondersteund door de experimentele gegevens. R.L. White, CL. Wilkins, J.J. Heitkamp, S.W. Staley, J. Am. Chem. Soc, _105, 4868 (1983). 2. De gegeven experimentele methode voor de lithiëring van endo- en exo- -5-norborneen-2,3-dicarboximide is niet in overeenstemming met de ge- postuleerde vorming van een algemeen dianion van deze verbindingen. P.J. Garratt, F. Hollowood, J. Org. Chem., 47, 68 (1982). 3. De door Barton e.a. gegeven verklaring voor de observaties, dat O-alkyl- -S-alkyl-dithiocarbonaten reageren met N^-dimethylhydrazine onder vor- ming van ^-alkyl-thiocarbamaten en ^-alkyl-thiocarbazaten, terwijl al- koxythiocarbonylimidazolen uitsluitend £-alkyl-thiocarbazaten geven, is hoogst twijfelachtig. -

Metal Ions in Ribozyme Folding and Catalysis Raven Hanna* and Jennifer a Doudna†
Ch4206.qxd 03/15/2000 08:57 Page 166 166 Metal ions in ribozyme folding and catalysis Raven Hanna* and Jennifer A Doudna† Current research is reshaping basic theories regarding the state. This ‘two-metal-ion model’ became the standard to roles of metal ions in ribozyme function. No longer viewed as which subsequent experimental observations were com- strict metalloenzymes, some ribozymes can access alternative pared, and upon which most current theories are based. catalytic mechanisms depending on the identity and availability of metal ions. Similarly, reaction conditions can allow different Catalytic metal ions of the group I intron folding pathways to predominate, with divalent cations Of the large ribozymes, most is known about catalysis by the sometimes playing opposing roles. Tetrahymena thermophila group I intron, which performs a two- step transesterification reaction using a single active site. It is Addresses generally studied in multiple-turnover form, only executing Department of Molecular Biophysics and Biochemistry and †Howard the cleavage portion of the splicing reaction, where the Hughes Medical Institute, Yale University, 266 Whitney Ave, intron catalyzes nucleophilic attack of the 3′ hydroxyl of a New Haven, CT 06520, USA bound guanosine on a specific phosphodiester bond in a *e-mail: [email protected] †e-mail: [email protected] bound oligonucleotide substrate. Its tightly folded catalytic core positions divalent cations around the labile bond to sta- Current Opinion in Chemical Biology 2000, 4:166–170 bilize the transition state. Assembling details about the 1367-5931/00/$ — see front matter chemical environment of the active site is critical for under- © 2000 Elsevier Science Ltd. -

Physical Organic Chemistry
PHYSICAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY Yu-Tai Tao (陶雨台) Tel: (02)27898580 E-mail: [email protected] Website:http://www.sinica.edu.tw/~ytt Textbook: “Perspective on Structure and Mechanism in Organic Chemistry” by F. A. Corroll, 1998, Brooks/Cole Publishing Company References: 1. “Modern Physical Organic Chemistry” by E. V. Anslyn and D. A. Dougherty, 2005, University Science Books. Grading: One midterm (45%) one final exam (45%) and 4 quizzes (10%) homeworks Chap.1 Review of Concepts in Organic Chemistry § Quantum number and atomic orbitals Atomic orbital wavefunctions are associated with four quantum numbers: principle q. n. (n=1,2,3), azimuthal q.n. (m= 0,1,2,3 or s,p,d,f,..magnetic q. n. (for p, -1, 0, 1; for d, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2. electron spin q. n. =1/2, -1/2. § Molecular dimensions Atomic radius ionic radius, ri:size of electron cloud around an ion. covalent radius, rc:half of the distance between two atoms of same element bond to each other. van der Waal radius, rvdw:the effective size of atomic cloud around a covalently bonded atoms. - Cl Cl2 CH3Cl Bond length measures the distance between nucleus (or the local centers of electron density). Bond angle measures the angle between lines connecting different nucleus. Molecular volume and surface area can be the sum of atomic volume (or group volume) and surface area. Principle of additivity (group increment) Physical basis of additivity law: the forces between atoms in the same molecule or different molecules are very “short range”. Theoretical determination of molecular size:depending on the boundary condition. -

14435: ION Light
® ION™ Light www. .com ENGINEERING COMPANY INC. 51 Winthrop Road Chester, Connecticut 06412-0684 Phone: (860) 526-9504 Sales Email:[email protected] Canadian Sales:[email protected] Customer Service:[email protected] Safety First This document provides necessary information to allow your Whelen product to be properly and safely installed. Before beginning the installation and/or operation of this product, the installation technician and operator must read this manual completely. Important information is contained herein that could prevent serious injury or damage. ! Proper installation of this product requires the installer to have a good understanding of ! Do not attempt to activate or control this device in a hazardous driving situation. automotive electronics, systems and procedures. ! If this product uses a remote device to activate or control this product, make sure that this ! Whelen Engineering requires the use of waterproof butt splices and/or connectors if that control is located in an area that allows both the vehicle and the control to be operated connector could be exposed to moisture. safely in any driving condition. ! Failure to use specified installation parts and/or hardware will void the product warranty! ! This product contains either strobe light(s), halogen light(s), high-intensity LEDs or a combination of these lights. Do not stare directly into these lights. Momentary blindness ! If mounting this product requires drilling holes, the installer MUST be sure that no vehicle and/or eye damage could result.. components or other vital parts could be damaged by the drilling process. Check both sides of the mounting surface before drilling begins. -

Major Ion Chemistry and Quality Assessment of Groundwater in Haripur Area
PINSTECH-222 MAJOR ION CHEMISTRY AND QUALITY ASSESSMENT OF GROUNDWATER IN HARIPUR AREA Waheed Akram Jamil Ahmad Tariq Naveed Iqbal Manzoor Ahmad Isotope Application Division Directorate of Technology Pakistan Institute of Nuclear Science and Technology P. O. Nilore, Islamabad, Pakistan July, 2011 CONTENTS 1. INTRODUCTION 1 2. STUDY AREA 2 2.1 General Description 2 2.2 Geology 2 2.3 Climate 2 3. FIELD SAMPLING 3 4. ANALYSIS 3 5. RESULTS AND DISCUSSION 4 5.1 Physicochemical Parameters 4 5.2 Major Ion Chemistry 4 5.3 Groundwater Types 5 5.4 Geochemical Evolution of Groundwater 6 5.5 Groundwater Quality 8 5.5.1 Drinking use 8 5.5.2 Irrigation use 9 6 CONCLUSIONS 11 ACKNOWLEDGMENTS 11 REFERENCES 12 ABSTRACT Study was conducted for investigating chemical composition of groundwater; identifying the compositional types of groundwater, delineating the processes controlling the groundwater chemistry and assessing the groundwater quality for drinking / irrigation uses. Groundwater samples collected from shallow (hand pumps, open well, motor pumps) and deep (tube wells) aquifers were analyzed 2+ 2+ 2 for major cations (Na\ K*, Ca , Mg ) and anions (HC03\ Cf, S04 '). The data indicated that Ca2+ is the dominant cation in most of the samples followed by Mg2+ whereas HCO3 is the most abundant anion in all samples. Hydrochemisty provides a clear indication of active recharge of shallow and deep aquifers by modern meteoric water. Carbonate dissolution was found to be the prevailing process controlling the groundwater chemistry. Chemical quality was assessed for drinking purpose by comparing with WHO, Indian and national standards, and for irrigation purpose using empirical indices such as SAR and RSC.