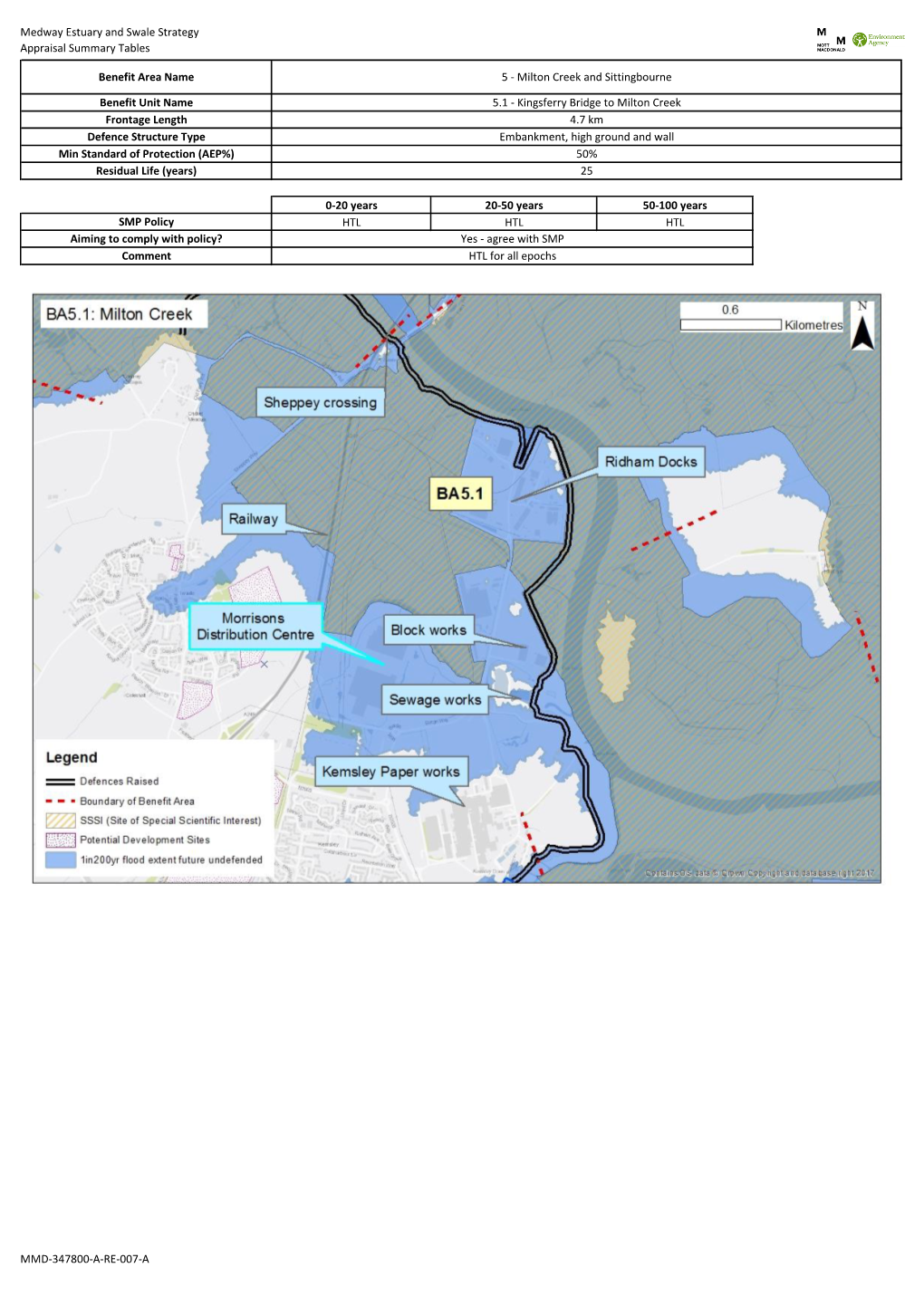
Medway Estuary and Swale Strategy Appraisal Summary Tables 0-20
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Swale’S Coast
The Kent Coast Coastal Access Report This document is part of a larger document produced by Kent Area of the Ramblers’ Association and should not be read or interpreted except as part of that larger document. In particular every part of the document should be read in conjunction with the notes in the Introduction. In no circumstances may any part of this document be downloaded or distributed without all the other parts. Swale’s Coast 4.4 Swale’s Coast 4.4.1 Description 4.4.1.1 Sw ale’s coast starts at TQ828671 at Otterham Quay. It extends for 115 km to TR056650 on Graveney Marshes to the w est of The Sportsman pub. It takes in the Isle of Sheppey w hich is connected to the mainland by tw o bridges at Sw ale. It is the longest coastline in Kent. 4.4.1.2 Approximately 55 km is on PRoWs, 27 km is de facto access (though some is difficult walking) and 33 km is inaccessible to w alkers. The majority of the 27 km of inaccessible coast does not appear to be excepted land. From the Coastal Access aspect it is the most complicated coastline in Kent. Part of the mainland route is along the Saxon Shore Way. 4.4.1.3 The view to seaw ard at the start is over the Medw ay estuary. There are extensive saltings and several uninhabited islands. The route then follows the River Sw ale to Sheppey and back to the Medw ay Estuary. The north and east coasts of Sheppey look out to the Thames Estuary. -

Isle of Sheppey Road Crossing: Come Ashore on the Mainland Side and Leysdown Walk Craft Sideways Under the Harty Ferry Road Sheppey Crossing Inner Span of Bridge
Garrison Point INFO KEY The point at which the Swale, the Medway and Thames Club phone 01795 663052 Hazard Estuary tides meet giving rise IOS Round the Island Race to a tidal back eddy. The Cheyney Rock The course is a clockwise circumnavigation of the island, High water 14.35 BST @ 5.87m Recovery point cardinal buoy marks a disused IOS Sailing Club race• • • outfall & posts (keep outside). 'L' shaped area of sand stones starting and finishing at IOS Sailing Club. Low water 08.28 BST @ 0.85m Please note: the Club cannot be held and rocks that dries several responsible for recovering boats retiring at feet high at low water. these points. Any boat that does retire must Start times & class flags phone the clubhouse on 01795 663052. West Cant 10.30 Monohulls PY1120 and over / Sailboards Grain Hard Event car parking Isle of Outfall Start line 11.00 Monohulls PY1031 to 1119 inc. Tripod Post Grain Mid Cant 11.30 Monohulls PY1030 & under Spectator point 12.00 Multihulls Port of Mean low water Finish line Sheerness Minster boom Starboard nav. buoy Marine Parade A wartime submarine trap Greyed area = mean low water Catamaran YC consisting of a line of Spile CYC Compound submerged barges and Port navigation buoy Sheerness wooden posts. Cardinal mark North Kent QB Dolphins Advised route by road to South Kent Marks of old pier remain River Medway at Queenborough. the sailing club on race day The Broadway Minster Queenborough Spit Bosun’s Store A small chandlery B2008 A250 Shallow water S1 B2007 Barton Hill Dr Large sand bank from S2 Leysdown to Shellness - risk of grounding. -

Sittingbourne's Steam Railway Press Release
Sittingbourne's Steam Railway Registered charity number: 105 7079 Press Release Release date: 14th March 2019 2019 Season – 50th Anniversary of Handover Fifty years ago, this October, paper manufacturer Bowaters, handed over a section of its narrow gauge railway system to the Locomotive Club of Great Britain, and so, over the following few years, the Sittingbourne & Kemsley Light Railway was set up to continue the legacy. Next year, will be the 50th anniversary of public trains and 2022 will be the 50th anniversary of the Sittingbourne & Kemsley Light Railway as a company. Following a time and motion study, Bowaters Paper Co. decided to transition from rail to road operations throughout Sittingbourne and Kemsley Paper Mills and Ridham Dock. The management did not want to see its railway lost forever so it sought to pass on the mantle for operating the ‘main line’ to preservationists. 1 In October 1969, operation of the line between Sittingbourne and Kemsley Paper Mills was handed over to the Locomotive Club of Great Britain, which later set up the Sittingbourne & Kemsley Light Railway. Operating original locomotives, coaches and wagons over the original line is rare in preservation. The paper mill network consisted of 10 miles of sidings and three miles of main line – the two miles from Sittingbourne Exchange Sidings to Kemsley Paper Mill are all that remains of the original main line. Coincidentally, roadworks within Kemsley Paper Mill will see the occasional lorry movement across the site at Kemsley Down, a stark reminder of the industrial history of the Railway. Due to the late Easter, trains will start running on Mothering Sunday, 31st March, with trains running every Sunday and Bank Holiday Monday until the end of September. -

The Isle of Sheppey Brochure.Pdf
Sheerness Dockyard Sheerness Elmley Bird Reserve Bird Elmley i Towns & Villages of Sheppey of Villages & Towns Your Guide to the to Guide Your www.rspb.org.uk/reserves call 01795 665969/01634 222480 or log on to the website: the to on log or 222480 665969/01634 01795 call members. Parking and toilets are available. For more information more For available. are toilets and Parking members. RSPB members are free but there is a small charge for non for charge small a is there but free are members RSPB distance from the bus and train stations train and bus the from distance worth a visit. a worth paddling pool are situated by the beach and within easy walking easy within and beach the by situated are pool paddling birds of prey and aquatic plants, plus much more and certainly and more much plus plants, aquatic and prey of birds companies. The leisure centre and swimming pool, sand pit and pit sand pool, swimming and centre leisure The companies. inhabited by many breeding wetland birds, marsh frogs, insects, frogs, marsh birds, wetland breeding many by inhabited The High Street has may local shops as well as several national several as well as shops local may has Street High The Marshes! The RSPB Reserve has windswept salt marshes that are that marshes salt windswept has Reserve RSPB The Marshes! wilderness left in the south east, come and have a look at Elmley at look a have and come east, south the in left wilderness blow to the town. the to blow Harvest and Flower festival. -

K4 Kemsley Site Condition Report & Baseline Assessment – Epr/Bj3951g
K4 KEMSLEY SITE CONDITION REPORT & BASELINE ASSESSMENT – EPR/BJ3951G E.ON CHP Limited JER1679 K4 Kemsley Site Condition Report & Baseline Assessment Final 25 April 2019 rpsgroup.com REPORT Document status Review Version Purpose of document Authored by Reviewed by Approved by date Site Condition report and Final VO/TC JS/GM JS 25/04/19 Baseline Assessment Approval for issue Jennifer Stringer 25 April 2019 © Copyright RPS Group Plc. All rights reserved. The report has been prepared for the exclusive use of our client and unless otherwise agreed in writing by RPS Group Plc, any of its subsidiaries, or a related entity (collectively 'RPS'), no other party may use, make use of, or rely on the contents of this report. The report has been compiled using the resources agreed with the client and in accordance with the scope of work agreed with the client. No liability is accepted by RPS for any use of this report, other than the purpose for which it was prepared. The report does not account for any changes relating to the subject matter of the report, or any legislative or regulatory changes that have occurred since the report was produced and that may affect the report. RPS does not accept any responsibility or liability for loss whatsoever to any third party caused by, related to or arising out of any use or reliance on the report. RPS accepts no responsibility for any documents or information supplied to RPS by others and no legal liability arising from the use by others of opinions or data contained in this report. -

15 January 2008 Swale Borough Council List of Current Applications
15 January 2008 Swale Borough Council List of current applications received by Swale Borough Council for determination which are available for inspection at the Planning Services, East Street, Sittingbourne, Kent. Copies of applications are also available for inspection at the appropriate District Office (Please see notes). You may also view planning applications via our partnership with the UK Planning website (www.ukplanning.com/swale), but this may take up to 7 days to be completed. You may submit any observations on any application via the website. Please note that any observations that you wish to make on applications should be received either in writing (at the above address) or via e-mail to [email protected] within three weeks of the date of this list (please quote the full application reference in any correspondence or e-mail). In the interests of economy an acknowledgement will not be sent. If you do write to express an interest in an application, you will be informed of the decision in due course. On certain applications it may be some time before a decision is reached. Minster Application Ref SW/07/0798 RDM Case No. 15950 Case Officer Ross McCardle Location Joville,45 Scocles Road,Minster,Sheppey,Kent,ME12 3SD Proposal Replace existing shed with small storage barn (retrospective). Create a 40m x 20m sand menage. Applicants Name Mr & Mrs Snow Applicant Mr & Mrs Snow, Joville, 45 Scocles Road, Minster, Sheppey, Kent, ME12 3SD Sittingbourne Application Ref SW/07/1086 RB Case No. 22900 Case Officer Rob Bailey Location 54 Ridham Avenue,Kemsley,Sittingbourne,Kent,ME10 2SF Proposal Outbuilding containing games room & multi sensory room, Certificate of Lawful Proposed Development. -

SITTINGBOURNE £1.25 (0.68 Acre) Kent ME9 8SR Per Sqft
Secure Concrete Yard To Let CORE COMMERCIAL Ridham Dock Rent just 30,000 sqft Ridham Dock Road SITTINGBOURNE £1.25 (0.68 acre) Kent ME9 8SR per sqft Location Sittingbourne is in North Kent at the junction of M2 motorway and A249 about 50 miles East of London. Ridham Dock is about 3 miles north of Sittingbourne adjoining Kemsley Mill and Knauf. The property forms part of the Ridham Dock Complex adjoining European Metal Recycling. Description An open storage yard with paling fencing and gate. Power and water supply. Accommodation Secure yard 30,000 sqft (0.68 acre) Terms To let on a new flexible lease at a rent of £37,500 per annum (1.25 per sqft) plus VAT. Rates payable Suitable recycling uses £11,431 2016/17 (Rateable Value £23,000). Produced and copyright by Core Commercial Sittingbourne A249 RIDHAM IWADE PRODUCED & COPYRIGHT Knauf BY CORE COMMERCIAL Kemsley Barge Ridham Dock Road Way SITTINGBOURNE David Marriott [email protected] CORE Neil Mason COMMERCIAL [email protected] 01892 834483 Stephen Smith [email protected] www.CoreCommercial.co.uk IMPORTANT NOTICE The agents give notice to anyone who may read these particulars as follows: 1.These particulars are prepared for the guidance only of prospective purchasers. They are intended to give a fair overall description of the property but are not intended to constitute part of an offer or contract. 2. Any information contained herein (whether in the text, plans or photographs) is given in good faith but should not be relied upon as being a statement or representation of fact. -

Item C2 SW/10/774 SW/10/774 – the Proposed Construction and Operation of the Proposed Construction and Operation of a Biomass
Item C2 SW/10/774 ––– The proposed construction and operation of a Biomass Combined Heat and Power plant including external and covered waste wood storage area, associated weighbridweighbridge,ge, parking and underground pipework to pumping station at Ridham Dock, Iwade, Nr Sittingbourne. A report by Head of Planning Applications Group to Planning Applications Committee on 14 June 2011 This application has been submitted by SLR Consulting on behalf of Biomass Power Plant Ridham Ltd for the proposed development of a combined heat and power plant including the external provision of a waste wood storage area, weighbridge, parking and ancillary piping works for the pumping station, Ridham Dock, Iwade. Recommendation: Subject to provision of suitable reed bed compensation area, permission be granted subject to conditions and subject to a legal agreement. Local Member: Mr. M. Whiting and Mr. A. Willicombe Unrestricted Site Description 1. The application site is located on Ridham Dock, which is a well established commercial and industrial wharf situated adjacent to the river Swale. The dock is also surrounded by sensitive site designations including the Swale Special Protection Area (SPA), Ramsar site and a Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI). The Elmley National Nature Reserve is located east of the site, on the other side of the river. 2. The River Swale straddles the eastern and northern boundary of the dock and flows into the Thames estuary. The inlet point for the dock is located at the point the river sweeps across the northern boundary. The dock site is protected from flooding by the Ridham Dock wall flood defence (see Fig 2: Site Location Plan) which is located along the eastern and northern boundary. -

Ferry Road to Swale Station Via Kingsferry Bridge
www.gov.uk/englandcoastpath England Coast Path Stretch: Isle of Sheppey Report IOS 10: Ferry Road to Swale Station via Kingsferry Bridge Part 10.1: Introduction Start Point: Ferry Road (Grid reference 591640 169303) End Point: Swale Station (Grid reference 591302 169241) Relevant Maps: IOS 10a 10.1.1 This is one of a series of linked but legally separate reports published by Natural England under section 51 of the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949, which make proposals to the Secretary of State for improved public access along this stretch of coast of the Isle of Sheppey, Kent. 10.1.2 This report covers length IOS 10 of the stretch, which is between Ferry Road, on the south coast of the Isle of Sheppey and Swale Station, on the north Kent mainland. It makes free-standing statutory proposals for this part of the stretch and seeks approval for them by the Secretary of State in their own right under section 52 of the National Parks and Access to the Countryside Act 1949. 10.1.3 The report explains how we propose to implement the England Coast Path (“the trail”) on this part of the stretch and details the likely consequences in terms of the wider ‘Coastal Margin’ that will be created if our proposals are approved by the Secretary of State. Our report also sets out: any proposals we think are necessary for restricting or excluding coastal access rights to address particular issues, in line with the powers in the legislation; and any proposed powers for the trail to be capable of being relocated on particular sections (“roll- back”), if this proves necessary in the future because of coastal change. -

Elmley Church and It's History
ELMLEY CHURCH AND IT'S HISTORY By Derek Faulkner The small Elmley church had stood on Elmley since c.1247, when it was confirmed and dedicated to St. James. Later, in the reign of Henry 6th, it was in the hands of the Crown but in 1449 he granted the patronage and advowson of it to All Souls College, Oxford, and they continued as it's patrons until it's eventual demise in the 1950's. From then on there was a yearly pension of 40 shillings, payable from the church to the Abbot of St. Mary Graces near the Tower (of London?). In 1640 the rectory was valued in the King's books at £70 and by 1788 still only £80. In 1816, after more than 200 years of dilapidation, it was fitted up again for Divine Service by a Dr. Percy, which seems quite surprising given that the scattered population of Elmley by 1831 was still only 29 people. However, from 1697 it had still continued to have a continuous line of Rectors, appointed to it, almost always the vicar from nearby Iwade church, who would have the responsibility for services at both churches. Among a long list of Rectors names, the stand out one for me was one Savage Tyndall, rector from 1746-1751 - what a splendid name for a vicar! However from 1850 as a brick-making factory and it's subsequent workers' cottages began to take shape alongside Elmley hill, the need for what the church could offer intensified. But before that could happen the church was in need of repairs, substantially so. -

Kemsley Present and Past
Kemsley Present and Past KEMSLEY TODAY The village of Kemsley is less than 100 years old. According to Wikipedia, at the end of the 19th century, the site on which the village sits, was simply a row of cottages beside a brick works. But in 1924, with expansion impossible at the old Sittingbourne Paper Mills, the owner Edward Lloyd, built the new Kemsley Paper Mill, which served by a creek, allowed the direct importation of raw materials to the site. At the same time he built a garden village to house his employees, the core of which comprises the modern day Kemsley village. Kemsley today, is but a suburb of the rapidly expanding Sittingbourne. The village also has a derelict pub 'The Kemsley Arms' (which was under threat of being developed into flats) but which has become the first building in Swale to be listed as an “asset of community value” under new legislation. THE SITTINGBOURNE AND KEMSLEY LIGHT RAILWAY HISTORY -The line was developed as an industrial railway by paper maker Frank Lloyd in 1904, to transport pulp materials and finished products between Ridham Dock, on the Swale, and the company's paper mill at Sittingbourne, and from the mid-1920s to a second mill at Kemsley. In the late 1960s, the railway faced closure by its then owners Bowater, but the Locomotive Club of Great Britain accepted an offer to operate the railway from 1970. However, the section of line from Kemsley Down to Ridham Dock was abandoned for the redevelopment of the paper mills. Since then the railway has endured a turbulent history with the closure of the paper mills in Sittingbourne and the subsequent redevelopment of the site to become part of the Morrisons chain. -

Sheppey Outdoors Country Break
Outdoors An Outdoors Break in... The Swale The Isle of Sheppey Kent’s Treasure Island This Country Break explores the Isle of Sheppey, one of England’s few true islands, sited at the mouths of the Thames and the Medway and cut off from the rest of Kent by the tidal channel and estuary known as the Swale. At just 36 square miles the island packs a lot in, from the miles of beaches (perfect for lazing on or getting wet from), its acres of low-lying marshes making it one of the best places in UK to see birds of prey, to its renowned fossil beds which provide regular prehistoric finds. Scratch a little beneath the surface and you’ll also discover more history and heritage per square mile than just about anywhere else in the country. Uncover the strong maritime tradition, stand on the same soil as Saxon Queens, Dutch Invaders and famous writers, and for the piece-de-résistance visit the site of the birthplace of UK aviation. So forget what you think you know about Sheppey and come and take a fresh look, you’re sure to find something surprising! Find out more at www.visitsheppey.com 1 The Great Outdoors... Contains Ordnance Survey Data © Crown Copyright and Database Right 2011 With its big skies, rolling landscape and miles of beaches and marsh, Sheppey is a great choice for getting out and about in the great outdoors, and there are no shortage of ways to do so... fortunately we’ve done the hard work, so here are the very best! These are just a few ideas so feel free to mix it up or swap them Getting There around, combine with any events that are on in the area (remember to check local websites and magazines) and in short The Isle of Sheppey is easily make it an experience of your own.