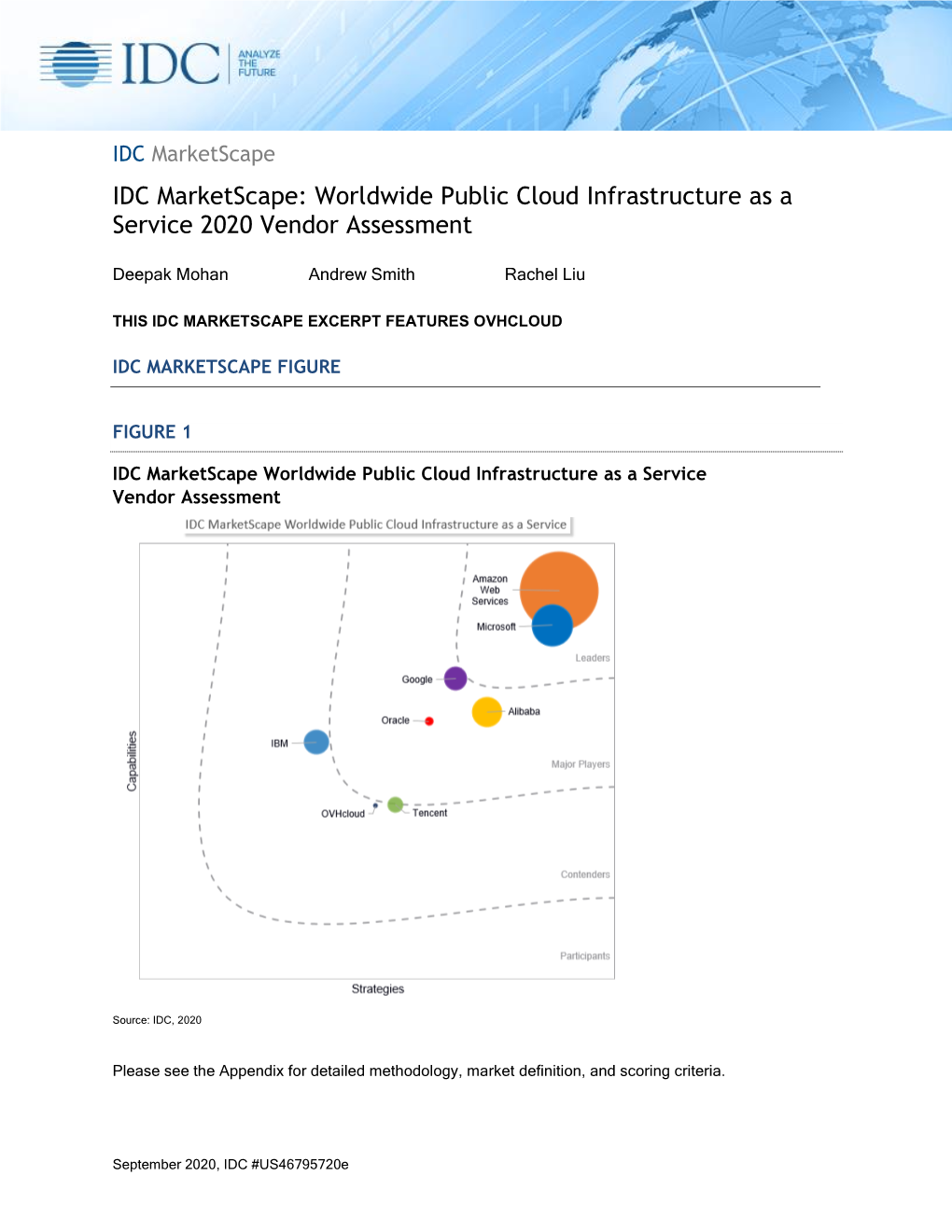
IDC Marketscape: Worldwide Public Cloud Infrastructure As a Service 2020 Vendor Assessment
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Rapport D'information Sur Les Géants Du Numérique
N° 4213 ______ ASSEMBLÉE NATIONALE CONSTITUTION DU 4 OCTOBRE 1958 QUINZIÈME LÉGISLATURE Enregistré à la Présidence de l’Assemblée nationale le 2 juin 2021. RAPPORT D’INFORMATION DÉPOSÉ en application de l’article 145 du Règlement PAR LA COMMISSION DES AFFAIRES ÉTRANGÈRES en conclusion des travaux d’une mission d’information constituée le 20 novembre 2019 sur les géants du numérique ET PRÉSENTÉ PAR M. ALAIN DAVID ET MME MARION LENNE, Députés —— — 3 — SOMMAIRE ___ Pages INTRODUCTION ........................................................................................................... 7 SYNTHÈSE DES RECOMMANDATIONS DES RAPPORTEURS ............ 10 PREMIÈRE PARTIE : LE NUMÉRIQUE, OBJET ET TERRAIN GÉOPOLITIQUE DU XXI ÈME SIÈCLE ................................................................... 13 I. LES GÉANTS AMÉRICAINS DU NUMÉRIQUE, NOUVEAUX CONCURRENTS DES ÉTATS ? ............................................................................... 13 A. LA GENÈSE DES GAFAM : UNE HISTOIRE AMÉRICAINE .......................... 13 B. LES CARACTÉRISTIQUES DES GÉANTS AMÉRICAINS DU NUMÉRIQUE : DES ENTREPRISES HORS NORMES ................................... 17 1. Les cinq « GAFAM » présentent plusieurs caractéristiques communes mais aussi d’importantes spécificités ............................................................................. 17 2. Du numérique aux géants : le développement d’entreprises devenues systémiques, dont les activités se sont largement diversifiées ............................... 18 a. La théorie économique permet d’éclairer -

Technology, Media & Telecom
CLOUD MANAGED SERVICES AND HOSTING SECTOR REVIEW | Q1 2020 Technology, Media & Telecom Cloud Managed Services and Hosting| Q3 2020 TECHNOLOGY, MEDIA & TELECOM PAGE | 0 HW Cloud Managed Services and Hosting Solutions Introduction HARRIS WILLIAMS (“HW”) HW TECHNOLOGY, MEDIA & TELECOM (“TMT”) GROUP • 25+ years and more than 1,000 closed transactions • 35+ dedicated TMT professionals • 350+ professionals across eight office globally • TMT offices include Boston, San Francisco, and London • 170+ closed transactions in the last 24 months • 10 industry groups KEY TMT THEMES ✓SaaS / Cloud ✓Data & Analytics ✓Digital Transformation ✓A.I. / Machine Learning FOCUSED ADVISORY SERVICES HORIZONTAL FOCUS SECTORS VERTICAL FOCUS SECTORS • Mergers and acquisitions (M&A) • Application Software • Architecture, Engineering, and Construction Software • Capital raises • Cloud Managed Services and Hosting Solutions • Education Technology and Services • Corporate divestitures • Compliance Solutions • Energy Technology • CRM and Marketing Automation • Facilities and Real Estate Software • Human Capital Management • Financial Technology and Payments CONSISTENT RECOGNITION FOR QUALITY • Infrastructure and Security Software • Government Technology • IT and Tech-Enabled Services • Healthcare IT • Marketing, Research, and Insights Software • Industrial and Supply Chain Technology • Internet and eCommerce • Retail Technology HW CLOUD MANAGED SERVICES AND HOSTING SOLUTIONS TEAM OTHER TMT GROUP LEADERSHIP Thierry Monjauze Anthony Basmajian Priyanka Naithani Sylvain Noblet -

GAIA-X: Technical Architecture Release – June, 2020 Imprint
GAIA-X: Technical Architecture Release – June, 2020 Imprint Publisher Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) Public Relations Division 11019 Berlin www.bmwi.de Authors DE-CIX Management GmbH Günter Eggers (NTT Global Data Centers EMEA GmbH) Bernd Fondermann (German Edge Cloud GmbH & Co KG) Google Germany GmbH Berthold Maier (T-Systems International GmbH) Klaus Ottradovetz (Atos SE) Dr.-Ing. Julius Pfrommer (Fraunhofer IOSB) Dr. Ronny Reinhardt (Cloud&Heat Technologies GmbH) Hannes Rollin (T-Systems International GmbH) Arne Schmieg (German Edge Cloud GmbH & Co. KG) Sebastian Steinbuß (IDSA e. V.) Dr. Philipp Trinius (T-Systems International GmbH – Telekom Security) Andreas Weiss (EuroCloud Germany) Dr. Christian Weiss (Deutsche Telekom AG) Dr. Sabine Wilfling (Scheer GmbH) Current as at June 2020 Design and production PRpetuum GmbH, 80801 Munich You can obtain this and other brochures from: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy, Public Relations Division Email: [email protected] www.bmwi.de Central ordering service: Tel.: +49 30 182 722 72 Fax: +49 30 181 027 227 21 This brochure is published as part of the public relations work of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy. It is distributed free of charge and is not intended for sale. The distribution of this brochure at campaign events or at information stands run by political parties is prohibited, and political party-related information or advertising shall not be inserted in, printed on, or affixed to this publication. Content 1 -

Cookbook-En.Pdf
L'INFRASTRUCTURE # 1 CASE STUDIES BOOK DISCOVER ORIGINAL INFRASTRUCTURES DEPLOYED AT OVH.COM Online media, applications and business software, collaborative tools, smart music playlists at points of sale, total outsourcing of an urban community’s IT… OVH.com CASE STUDIES BOOK - EDITORIAL 3 “Each year, OVH is able to offer several hundred new services. After listening to you, we have come to realize that launching new services is not enough. We should also assist and guide you in the adoption of these innovations. Often you just need to see some practical use cases. That is the goal of the “Case Studies Book”, to provide you with such examples. And of course, if you need advice, our customer advocates and our Professional Services team are always available. Enjoy your reading!” Octave Klaba, Founder OVH CASE STUDIES BOOK CASE STUDIES BOOK This publication has been edited by the OVH Group, 2 rue Kellermann 59100 Roubaix (FRANCE) - RCS Lille Métropole 424 761 419 00045. Written by: Hugo Bonnaffé in collaboration with: Rémy Vandepoel, Vincent Cassé, Jean-Daniel Bonnetot, Félicien Lainé, Jonathan Guinez, Sylvain Wallez et Alexandre Morel. Translation: Michael Kapus Layout: Marie Delattre Graphic Design: Carl Lambert, Lucille Folens and Élodie Lenin Photographers: Élycia Husse, Frédéric Anne, Alban Gernigon, Stéphane Bureau du Colombier, iStockphoto Printer: Nord'imprim Special thanks is given to each customer that made this project possible by revealing the details of their infrastructures and their willingness to share their expertise with the OVH Community. Congratulations to everyone who took to the stage during the OVH World Tour to present their projects and explain their technical choices. -

Achieving Digital Sustainability
ACHIEVING DIGITAL SUSTAINABILITY RapportProgress report, d’étape, summary synthèseof collaboration of platformthe platform work and 11 Arcepde proposalstravail toand combine proposals increasing de use Arcepof digital technologypour andun reducing numerique its environmental soutenable. footprint — 15 December 2020 INTRODUCTION The impact that electronic communi- cations networks, devices, data centres and ICT use have on the environment is a source of growing concern, and one number of devices, etc.) is cause for con- which an increasing number of stake- cern. According to the Senate task force holders are gradually starting to address. on ICT’s environmental footprint6, digi- The Citizens’ Convention on Climate1 also tal technology’s GHG footprint could notes that while digital technology is a increase substantially if nothing is done crucial lever of the green transition, and to curtail it (+60% by 2040 or 6.7% of the battle against climate change, it must the national GHG footprint). If such an not itself be the source of increased emis- increase were to materialise, it would sions. be counter to the commitments made under the Paris Climate Agreement7 of According to various studies conducted 2015 which aims to contain the increase over the past two years2, digital tech- in global temperature to well below 2°C, nology currently represents 3% to 4% and requires swift and massive efforts from of global greenhouse gas3 4 (GHG) emis- every sector of the economy to reduce sions, and 2% of the carbon footprint in their own carbon footprint8. France5 (including the hardware pro- On top of which, there are other contrib- duction and usage stages). -

GAIA-X: Technical Architecture Release – June, 2020 Imprint
GAIA-X: Technical Architecture Release – June, 2020 Imprint Publisher Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy (BMWi) Public Relations Division 11019 Berlin www.bmwi.de Authors DE-CIX Management GmbH Günter Eggers (NTT Global Data Centers EMEA GmbH) Bernd Fondermann (German Edge Cloud GmbH & Co KG) Google Germany GmbH Berthold Maier (T-Systems International GmbH) Klaus Ottradovetz (Atos SE) Dr.-Ing. Julius Pfrommer (Fraunhofer IOSB) Dr. Ronny Reinhardt (Cloud&Heat Technologies GmbH) Hannes Rollin (T-Systems International GmbH) Arne Schmieg (German Edge Cloud GmbH & Co. KG) Sebastian Steinbuß (IDSA e. V.) Dr. Philipp Trinius (T-Systems International GmbH – Telekom Security) Andreas Weiss (EuroCloud Germany) Dr. Christian Weiss (Deutsche Telekom AG) Dr. Sabine Wilfling (Scheer GmbH) Current as at June 2020 Design and production PRpetuum GmbH, 80801 Munich You can obtain this and other brochures from: Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy, Public Relations Division Email: [email protected] www.bmwi.de Central ordering service: Tel.: +49 30 182 722 72 Fax: +49 30 181 027 227 21 This brochure is published as part of the public relations work of the Federal Ministry for Economic Affairs and Energy. It is distributed free of charge and is not intended for sale. The distribution of this brochure at campaign events or at information stands run by political parties is prohibited, and political party-related information or advertising shall not be inserted in, printed on, or affixed to this publication. Content 1 -

Télécharger Un Extrait
LE RÔLE CENTRAL DES NOMS DE DOMAINE DAVID CHELLY Naming Start-up Référencement Nommage 1 Avant-propos Il est d’usage de démarrer un ouvrage en adressant ses remerciements à ses proches, puis d’inviter une ou plusieurs personnes de référence du secteur à écrire la préface, c’est-à-dire à passer la pommade à l’auteur pour son formidable travail. Cet ouvrage vous épargne ces conventions à l’utilité relative et vous invite dès à présent à un voyage dans l’étonnant monde des noms de domaine. Dans l’écosystème de l’internet, les noms de domaine occupent une place transversale. Ils sont utilisés par une multitude d’acteurs, depuis les webmasters indépendants jusqu’aux informaticiens, juristes et marketeurs dans les entreprises, en passant par les bureaux d’enregistrement, les agences web et les investisseurs en noms de domaine. C’est à l’ensemble de ces professionnels que s’adresse ce livre, avec l’ambition d’offrir une vision globale et transdisciplinaire des possibilités offertes par les noms de domaine. Cette problématique est particulièrement d’actualité, puisque l’on est passé en quelques années de moins de deux cent cinquante extensions de noms de domaine disponibles à plus de mille cinq cents aujourd’hui, ce qui pose une multitude de questions en termes de protection juridique, de référencement et de branding. Les étudiants spécialisés dans l’internet, les chercheurs d’emploi et les personnes en reconversion professionnelle pourront également trouver un intérêt à la lecture de cet ouvrage, dans le sens où les opportunités d’emploi sont considérables dans ce secteur en fort essor, mais peu abordé dans les programmes des formations académiques. -
Premium Domain Sales Report
2020 $320,136 PREMIUM DOMAINS Total premium revenue REPORT Premium Registrar RESULTS $203,884 Premium revenue 155 Premium domains sold $1315 Average price per domain sold Registrar market share per domains sold Alibaba Cloud Computing 18% Namecheap 10% GoDaddy 28% Google 5% Gandi 4% HEXONET 4% OVHcloud Others 3% 28% Registrar market share in terms of revenue HEXONET 18% Namecheap 9% GoDaddy West.cn 37% 7% $ Alibaba Cloud Computing 4% Google 3% Others 22% TOP 5 TOP 5 Premium tiers in terms of revenue Premium tiers in terms of domains sold 1st Tier $2500 1st Tier $100 2nd Tier $4000 2nd Tier $250 3rd Tier $1000 3rd Tier $2500 4th Tier $100 4th Tier $1000 5th Tier $250 5th Tier $500 Premium Brokerage RESULTS TOP 3 brokered premium domains 1st energy.cloud $50,000 $116,252 2nd power.cloud $24,360 Premium domain revenue 3rd simple.cloud $14,825 Why innovative companies choose premium .cloud domains power.cloud Powercloud is the fastest growing billing and CRM system in the energy industry. Therefore it was essential to have a strong brand identity and a domain name that stays in your head. As cloud-natives, we believe the domain power.cloud will support us on our way to becoming the digital leader in the energy industry. “ Marc Pion, Head of Marketing & Communications, powercloud GmbH ” What’s trending with .cloud Companies from all over the world and in all dierent sectors choose .cloud premium domains for their business. Digital Transformation logistics.cloud blue.cloud Consumer Applications ! tldr.cloud golf.cloud Cloud-based Service tera.cloud iam.cloud International Sites jupiter.cloud sigma.cloud All prices indicated in this report are retail prices (tiers excluded) If the registrar markup of EPP premium domains sold is unknown, we apply an estimate of 30% get.cloud Smart domain for modern business Copyright © 2021 - Aruba PEC S.p.A a Socio Unico - P.IVA 01879020517. -

C. Les Bureaux D'enregistrement
1 C. Les bureaux d’enregistrement 1. Qu’est-ce qu’un bureau d’enregistrement ? Un bureau d’enregistrement est une entreprise chargée d’enregistrer des noms de domaine auprès des registres, pour le compte de ses clients, qu’ils soient professionnels ou particuliers. Un bureau d’enregistrement proposant des noms de domaine sous les extensions génériques doit être accrédité par l’ICANN, dans le cadre d’une procédure onéreuse et compliquée. On en compte environ mille à travers le monde 1. Chacun peut toutefois s'improviser bureau d'enregistrement de noms de domaine, en devant revendeur affilié à un bureau d'enregistrement agréé. Les extensions nationales (FR, BE, CH, etc.) sont commercialisées par des bureaux agréés par le registre national, selon des conditions qui diffèrent selon les pays, mais généralement peu contraignantes. 2. Un marché ultra-concurrentiel Le secteur des bureaux d'enregistrement des noms de domaine est très concurrentiel, puisque chaque prestataire propose exactement le même produit. A l’image du leader mondial Godaddy, nombre de bureaux d'enregistrement internationaux proposent des prix très agressifs. Cette situation pèse fortement sur la rentabilité des 1 Au 1er avril 2020, il existait 2453 contrats d’accréditation avec l’ICANN, mais près de la moitié concernent une seule entreprise, HugeDomains, via ses bureaux d’enregistrement Dropcatch. 2 acteurs, d’autant que la multiplication des nouvelles extensions s’est accompagnée d’un grand nombre de reventes entre registres, de changements de prestataires techniques et de modifications de politiques de prix. En pratique, ceci complique la gestion des offres de la part des bureaux d’enregistrement, avec en sus des ventes en deça des niveaux attendus. -
View the Slides
The Hijackers Guide To The Galaxy: Off-path Taking Over Internet Resources Tianxiang Dai, Philipp Jeitner, Haya Shulman, Michael Waidner German National Research Center for Applied Cybersecurity ATHENE Technical University of Darmstadt Fraunhofer Institute for Secure Information Technology SIT National Research Center for Applied Cybersecurity 1 Overview ➢ Digital resources and providers ➢ Taking over resource holders’ accounts ➢ Vulnerable customers ➢ Potential resource manipulations ➢ Vulnerable resources ➢ Countermeasures & Conclusions National Research Center for Applied Cybersecurity 2 Digital resources and providers Provider datasets RIRs AFRINIC APNIC ARIN Customers datasets Digital resource Digital LACNIC RIPE providers resources Registrars Godaddy Namecheap ▪ 75% of customers of Networksolutions enom RIRs (Local ISPs) name.com Alibaba Amazon Gandi Namesilo Google OVH ▪ 100K-top Alexa Cloud Amazon Azure Access to resources (IaaS) Alibaba Google IBM Tencent Oracle via SSO accounts DigitalOcean Linode IONOS Hostwinds OVHCloud Vultr CloudSigma Certificate IdenTrust DigiCert Authorities Sectigo GoDaddy GlobalSign National Research Center for Applied Cybersecurity 3 Attacking providers Taking over accounts from off-path ▪ Take over accounts via password recovery: How to poison cache? ▪ Poison DNS cache for victim domain ▪ On-path lookup interception ▪ Off-path: ▪ Trigger password recovery for victim domain ▪ BGP prefix hijacks ▪ Reset password and take over account ▪ Side channels ▪ IP fragmentation Vulnerable BGP sub- Side- Frag- providers -
![Arxiv:2012.01946V1 [Cs.CR] 3 Dec 2020](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/1136/arxiv-2012-01946v1-cs-cr-3-dec-2020-6421136.webp)
Arxiv:2012.01946V1 [Cs.CR] 3 Dec 2020
Can I Take Your Subdomain? Exploring Related-Domain Attacks in the Modern Web Marco Squarcina1, Mauro Tempesta1, Lorenzo Veronese1, Stefano Calzavara2, Matteo Maffei1 1TU Wien, 2Università Ca’ Foscari Venezia Abstract known to web security experts, yet they do not capture the full spectrum of possible threats to web application security. Related-domain attackers control a sibling domain of their tar- get web application, e.g., as the result of a subdomain takeover. In this paper, we are concerned about a less known attacker, Despite their additional power over traditional web attackers, referred to as related-domain attacker [6]. A related-domain related-domain attackers received only limited attention by attacker is traditionally defined as a web attacker with an extra the research community. In this paper we define and quantify twist, i.e., its malicious website is hosted on a sibling domain for the first time the threats that related-domain attackers pose of the target web application. For instance, when reasoning to web application security. In particular, we first clarify the about the security of www.example.com, one might assume capabilities that related-domain attackers can acquire through that a related-domain attacker controls evil.example.com. different attack vectors, showing that different instances of The privileged position of a related-domain attacker endows it the related-domain attacker concept are worth attention. We for instance with the ability of compromising cookie confiden- then study how these capabilities can be abused to compro- tiality and integrity, because cookies can be shared between mise web application security by focusing on different angles, domains with a common ancestor, reflecting the assumption including: cookies, CSP, CORS, postMessage and domain underlying the original web design that related domains are relaxation. -

Addressing Impediments to Digital Trade Addressing Impediments to Digital Trade CEPR PRESS
Edited by Ingo Borchert and L. Alan Winters Addressing Impediments to Digital Trade Addressing Impediments to Digital Trade CEPR PRESS Centre for Economic Policy Research 33 Great Sutton Street London, EC1V 0DX UK Tel: +44 (0)20 7183 8801 Email: [email protected] Web: www.cepr.org ISBN: 978-1-912179-42-8 Copyright © CEPR Press, 2021. CEPR, which takes no institutional positions on economic policy matters, is delighted to provide a platform for an exchange of views on the topics covered in this eBook. The opinions expressed in the eBook are those of the authors and not those of CEPR, the Department for Digital, Culture, Media & Sport, the UKTPO or any of the institutions with which the authors are affiliated. Adressing Impediments to Digital Trade Edited by Ingo Borchert and L Alan Winters CENTRE FOR ECONOMIC POLICY RESEARCH (CEPR) The Centre for Economic Policy Research (CEPR) is a network of over 1,500 research economists based mostly in European universities. The Centre’s goal is twofold: to promote world-class research, and to get the policy-relevant results into the hands of key decision-makers. CEPR’s guiding principle is ‘Research excellence with policy relevance’. A registered charity since it was founded in 1983, CEPR is independent of all public and private interest groups. It takes no institutional stand on economic policy matters and its core funding comes from its Institutional Members and sales of publications. Because it draws on such a large network of researchers, its output reflects a broad spectrum of individual viewpoints as well as perspectives drawn from civil society.