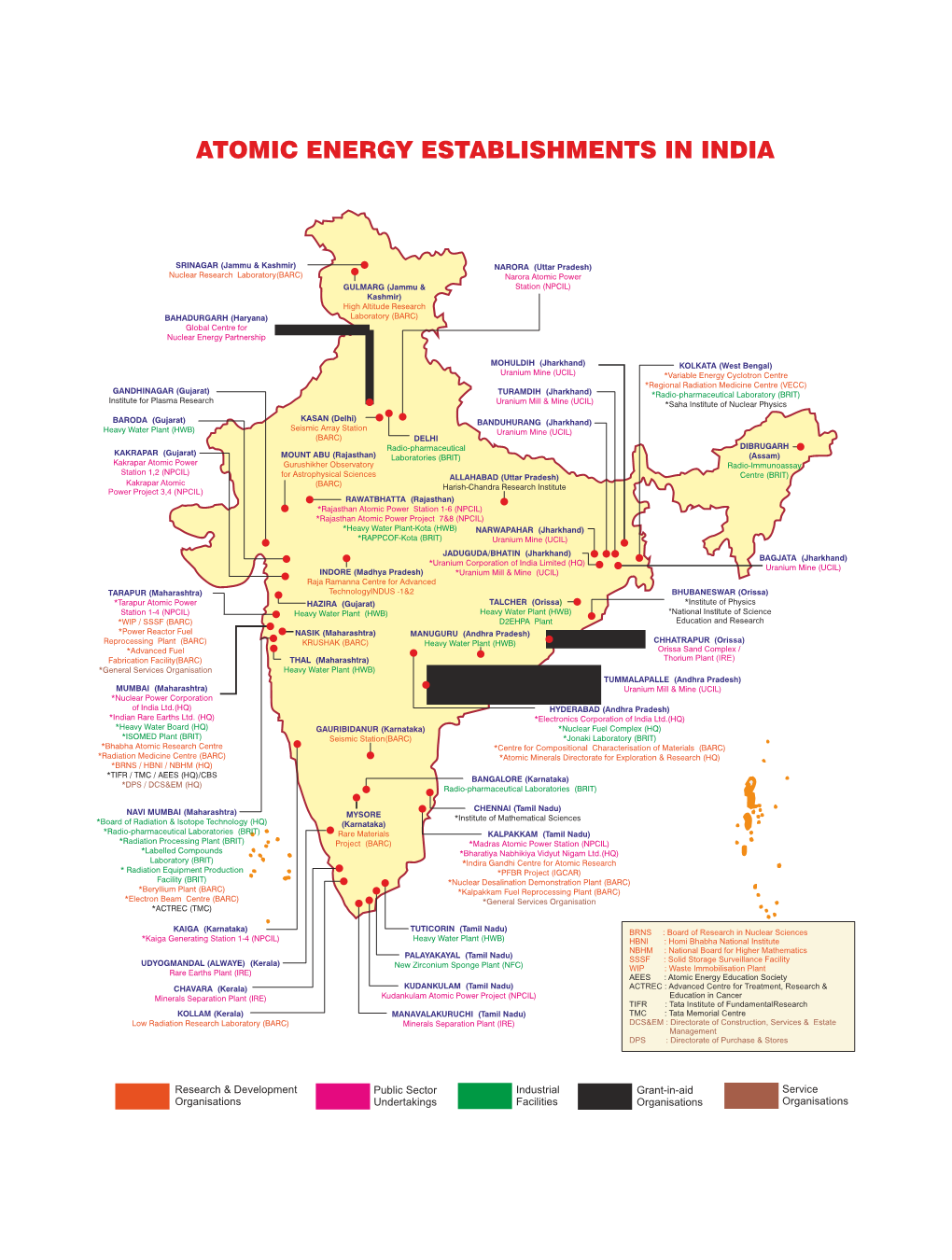
Nuclear Facilities in India
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Annual Report 1991-92
ANNUAL REPORT 1991-92 GOVERNMENT OF INDIA ATOMIC ENERGY REGULATORY BOARD BOMBAY ATOMIC ENERGY REGULATORY BOARD Shri S.D. Soman ... Chairman Dr. R.D. Lele ... Member Consultant Physician and Director of Nuclear Medicine, Jaslok Hospital & Research Centre, Bombay. Dr. S.S. Ramaswamy ... Member Retd. Director General, Factory Advice Service & Labour Institute Bombay. Dr. A. Ciopalakrishnan ... Member Director, Central Mechanical Engineering Research Institute Durgapur S.Vasant Kumar ... Ex-officio Chairman, Member Safety Review Committee for Operating Plants (SARCOP), Bombay Dr. K.S. Parthasarathy ... Secretary Dy. Director, AERB Atomic Energy Regulatory Board, Vikram Sarabhai Bhavari, Anushakti Nagar, Bombay-400 094. ATOMIC ENERGY REGULATORY BOARD The Atomic Energy Regulatory Board was constituted on November 15. 1983 by the President of India by exercising the powers conferred by Section 27 of the Atomic Energy Act 1962 (33 of 1962) to cany out certain regulatory and safety functions under the Act The regulatory authority (Annexure-I) of AERB is derived from rules and notifications promulgated under the Atomic Energy Act 1962 and Environmental Protection Act 1986 The mission of the Beard is to ensure that the use of ionizing radiation and nuclear energy in India does not cause undue risk to health safety and the environment The Board consists of a full time Chairman, an ex-officio Member, three part time Members and a Secretary The bio-data of its members is given in Annexure-ll AERB is supported by th? Advisory Committees for Proiect Salety Review (ACPSRs one for the nuclear power projects and the other for heavy water projects) Ihe Safely Review Committee for Operating Plants (SARCOP) and Salety Review Committee for Applications ol Radiation (SARCARt The memberships of these committees are given in Annexure-lll The ACPSR recommends to the AERB. -

HIGHLIGHTS Special Topics: Technical Insights: News Throughout the Region: NEWS INDIA& MIDDLE EAST
OCTOBER / NOVEMBER HIGHLIGHTS 2020 - ISSUE 11 Special Topics: SPOTLIGHT ON Johan Sverdrup: a Norwegian megaproject 7 JD Jones poised for explosive Regional Focus: Karnataka 11 growth Interview: IMI Regional President Mr Tarak Chhaya 15 With strong leadership, a clear strategy, and the ability to quickly adapt to changing circumstances, JD Jones Technical Insights: is a real force in the manufacture Compliant valve stem seals reduce emissions 13 and supply of fluid sealing products. The product range – including gland Could hydrogen be the ideal green fuel? 17 packings, seals, compression packings, PFTE products, etc – finds widespread Automation upgrade for Assam’s tea gardens 22 use in a diverse mix of industries around the world. The company has INDIA & MIDDLE EAST News throughout the Region: also forged win-win partnerships with many leading valvemakers, as Valve 2, 6, 9, 10, 12, 16, 18, 20, 24 World India & Middle East discovered when speaking recently to CEO The insiders guide to flow control in India, Iran, Bahrain, Egypt, Kuwait, Oman, Azerbaijan, Jordan, Kazakhstan, Qatar, Saudi Arabia, Sri Lanka, UAE, Bangladesh Mr. Ashish Bajoria. “When Covid-19 struck India in February we of course complied fully Specialist in : with the lockdown. But we did not Multiport allow ourselves to be cowed down by the situation, far from it. We continued Ball Valves to support our clients to the very best Distributors of our ability. Moreover, we used this Wanted period as the ideal opportunity to brainstorm about new markets. I am therefore delighted to say that since Available at February 2020 we have in fact opened JD CONTROLS up four new product verticals.” www.multiportballvalves.com Continued on page 4 NEWS NFC’s plans for a new facility at Kota by 2022 RIL - 1st Indian company to hit $200bn mcap A new facility of the city-based dles, which will be produced at Read more on page 2. -

E-Newsletter Volume 1 Issue 1 November 2019
Volume-1 Issue-1 For Internal Private Circulation only FROM CHAIRMAN’S DESK Dr. U. Kamachi Mudali Chairman IIChE-MRC Indian Institute Of Chemical Engineers is a confluence of streams of professionals from academia, research institute and industry. It was founded by Dr. Hira Lal Roy before Indian Independence in order to cluster stalwarts in Chemical Engineering from various professions to support the chemical industries as well as Institutes by providing a forum for interaction and joint endeavors. IIChE- MRC conducts and supports many events through out the year and feels it prudent to share its achievements with all members. Hence, IIChE-MRC decided to publish this quarterly e- newsletter for the benefit of all members from academia, research institute, industry and student chapters to gain acquaintance with current events, technical articles on Industry and upcoming events of IIChE-MRC. I hope that this e-newsletter proves beneficial to the chemical engineering as well as allied sciences readers and encourage them to take up joint ventures with immense participation towards the Nation building. Dr. U. Kamachi Mudali IIChEMRC Executive Committee Dr. U. Kamachi Mudali, Hon. Chairman Mr. Rajesh Jain Member Dr Anita Kumari Hon. Vice Chairperson Mr. Ravindra Joshi Member Dr. Alpana Mahapatra Member Dr. Bibhash Chakravorty Hon. Secretary Dr. T.L. Prasad Member Mr. Dhawal Saxena Hon. Jt Secretary Mr. V.Y.Sane Member Mr. Mahendra Patel Hon. Treasurer Mr. Joy Shah Member Mr. Shreedhar .M. Chitanvis Member Dr. Aparna M. Tamaskar Member INDIAN INSTITUTE OF CHEMICAL ENGINEERS Mumbai Regional Centre B-18, Vardhman Complex, Gr Floor, Opp Home Town & 247 Park, LBS Marg, Vikhroli (West), Mumbai - 400 083 1 November 2019 IICHE MRC E-NEWSLETTER 1 Volume-1 Issue-1 INDEX From Chairman’s Desk / IICHEMRC Executive Committee Index / Editor’s Corner / Disclaimer Recent Events / Forthcoming Events • Workshop on Solid Waste Management on 24/09/2019 at IITB I by NAE, IITB, IIChE & IEA. -

Nuclear Power Business Executive V P L&T Ltd
11TH NUCLEAR ENERGY CONCLAVE Steering Committee Dr S Banerjee Shri Anil Razdan Dr. R. B. Grover Chairman, Nuclear Energy President, IEF & Member, AEC & Group, IEF, Chancellor, Homi Former Secretary,Power Former Vice Chancellor Bhabha National Institute Homi Bhabha & Former Chairman, AEC & National Institute Secretary, DAE Ms. Minu Singh Shri V.P. Singh Shri P.P. Yadav Shri Anil Parab M.D., Nuvia India Former ED, BHEL ED (Nuclear Power Business Executive V P L&T Ltd. Development), BHEL Dr Harsh Mahajan Shri Amarjit Singh, MBE Shri S.C. Chetal Shri S.M. Mahajan Director, Mahjan Imaging Secretary General, IEF Former Director, IGCAR & Convener, Nuclear Group, Mission Director, AUSC Project IEF, Former ED, BHEL & Consultant (Power Sector) Organiser India Energy Forum: The Forum is a unique, independent, not-for-profit, research organization and represents energy sector as a whole. It is manned by highly qualified and experienced energy professionals committed to evolving a national energy policy. The Forum's mission is the development of a sustainable and competitive energy sector, promoting a favourable regulatory framework, establishing standards for reliable and safety, ensuring an equitable deal for consumers, producers and the utilities, encouraging efficient and eco-friendly development and use of energy and developing new and better technologies to meet the growing energy needs of the society. Its membership includes all the key players of the sector including BHEL, NTPC, NHPC, Power Grid Corporation, Power Finance Corporation, Reliance Energy, Alstom and over 100 highly respected energy experts. It works closely with various chambers and trade associates including Bombay Chamber, Bengal Chamber, Madras Chamber, PHD Chamber, Observer Research Foundation, IRADE, INWEA,Indian Coal Forum, and FIPI. -

Management of the Indian Nuclear Fuel Fabrication Facilities During COVID – 19 Pandemic
Department of Atomic Energy Nuclear Fuel Complex Hyderabad – Pazhayakayal – Kota Online Webinar Management of the Indian Nuclear Fuel Fabrication Facilities during COVID – 19 Pandemic Dr. Dinesh Srivastava Distinguished Scientist Chairman & Chief Executive IAEA Online Webinar: Maintaining Nuclear Safety of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facilities during Pandemic 1 Outline Introduction Fulfillment of NFC commitment Infrastructure development Covid-19 protection plan during production New norm post covid-19 Summary. IAEA Online Webinar: Maintaining Nuclear Safety of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facilities during Pandemic 2 Fuel Bundles Manufactured at NFC 220 MWe PHWR 540 MWe PHWR 160 MWe BWR (RAPS 3&4) (TAPS 3&4) (TAPS 1&2) 19 Element Bundle 37 Element Bundle 6 × 6 BWR Bundle 16.5 kg in Weight 23.8 kg in Weight 203 kg in Weight IAEA Online Webinar: Maintaining Nuclear Safety of Nuclear Fuel Cycle Facilities during Pandemic 3 PHWR Fuel Manufacturing Process MDU / SDU / Washed and Dissolution HTUP / UOC Dried Frit Dissolution Solvent Extraction Solvent Extraction Precipitation Precipitation Drying Filtration Calcination Drying Reduction Calcination Stabilization Grinding Nuclear Grade Nuclear Grade UO2 Powder ZrO2 Powder Blending Precompaction Coking Granulation UO Green 2 Final Compaction Pellets Chlorination Sintering Reduction Centreless Grinding Vacuum Distillation Sponge Handling Washing & Drying Zircaloy Stacking Ingots Compaction End Machining Alloying UO2 Green Appendage Welding Pellets EB Welding Graphite Coating -

Nuclear Energy in India's Energy Security Matrix
Nuclear Energy in India’s Energy Security Matrix: An Appraisal 2 of 55 About the Author Maj Gen AK Chaturvedi, AVSM, VSM was commissioned in Corps of Engineers (Bengal Sappers) during December 1974 and after a distinguished career of 38 years, both within Engineers and the staff, retired in July 2012. He is an alumnus of the College of Military Engineers, Pune; Indian Institute of Technology, Madras; College of Defence Management, Secunderabad; and National Defence College, New Delhi. Post retirement, he is pursuing PhD on ‘India’s Energy Security: 2030’. He is a prolific writer, who has also been quite active in lecture circuit on national security issues. His areas of interests are energy, water and other elements of ‘National Security’. He is based at Lucknow. http://www.vifindia.org © Vivekananda International Foundation Nuclear Energy in India’s Energy Security Matrix: An Appraisal 3 of 55 Abstract Energy is essential for the economic growth of a nation. India, which is in the lower half of the countries as far as the energy consumption per capita is concerned, needs to leap frog from its present position to upper half, commensurate with its growing economic stature, by adopting an approach, where all available sources need to be optimally used in a coordinated manner, to bridge the demand supply gap. A new road map is needed to address the energy security issue in short, medium and long term. Solution should be sustainable, environment friendly and affordable. Nuclear energy, a relatively clean energy, has an advantage that the blueprint for its growth, which was made over half a century earlier, is still valid and though sputtering at times, but is moving steadily as envisaged. -

11. 2"'DST/SERC School on "Isotope Tracer Techniques for Water Resources Development and Management' 23 Dr Bhabhawasmuchmorethanthat
11. 2"'DST/SERC school on "Isotope tracer techniques for water resources development and management' 23 Dr Bhabhawasmuchmorethanthat. Hewasa Recognitionisan importantmotivatingfactor;so brilliantscientistand an outstandingscience are opportunityand rewarding professional administrator.But most of all, he was a avenues.TheScientificAdvisoryCommitteeto pioneeringvisionary, who understoodthe theCabinet- headedbyourPrincipalScientific importanceofindigenousscientificresearchfor Adviser, Dr Chidambaram- has been self-reliantdevelopment. consideringhowto optimisethebenefitstothe Visionarieslike Bhabha have shaped the countryfromitsscientificresearchinstitutions.It shouldalsotacklethechallengeofrecruitingthe scientifictemperofourcountry.Indiaistodayat bestscientifictaientintoourresearchinstitutions the forefrontof the KnowledgeRevolution- whichdrivestheNewEconomy.Forthis,weowe andretainingthemthere.Wehavetonurturean environment,whichencouragestheinnovative a hugedebt to the excellenceofour scientific andtechnicalpersonnel. spiritandwelcomescreativeideas. Muchofthistalentfindsitswayabroad.Fromthe In thiscontext,it is hearteningtosee thatso SiliconValleyto Microsoft,frombiochemistryto manyyoung studentsparticipatedinthe DAE robotics - expatriateIndian scientistsand essaycontest.Theyareourfuturescientistsand. engineers are present in every corporate engineers.Theywill becomeourambassadors, organisationandineveryfieldofresearch. carrying the message of science based development to various partsourcountry. India's atomic energy programmestartedherein -

US Nuclear Cooperation with India
U.S. Nuclear Cooperation with India: Issues for Congress Paul K. Kerr Analyst in Nonproliferation June 26, 2012 Congressional Research Service 7-5700 www.crs.gov RL33016 CRS Report for Congress Prepared for Members and Committees of Congress U.S. Nuclear Cooperation with India: Issues for Congress Summary India, which has not signed the Nuclear Nonproliferation Treaty and does not have International Atomic Energy Agency safeguards on all of its nuclear material, exploded a “peaceful” nuclear device in 1974, convincing the world of the need for greater restrictions on nuclear trade. The United States created the Nuclear Suppliers Group (NSG) as a direct response to India’s test, halted nuclear exports to India a few years later, and worked to convince other states to do the same. India tested nuclear weapons again in 1998. However, President Bush announced July 18, 2005, he would “work to achieve full civil nuclear energy cooperation with India” and would “also seek agreement from Congress to adjust U.S. laws and policies,” in the context of a broader partnership with India. U.S. nuclear cooperation with other countries is governed by the Atomic Energy Act (AEA) of 1954 (P.L. 95-242). However, P.L. 109-401, which President Bush signed into law on December 18, 2006, allows the President to waive several provisions of the AEA. On September 10, 2008, President Bush submitted to Congress, in addition to other required documents, a written determination that P.L. 109-401’s requirements for U.S. nuclear cooperation with India to proceed had been met. President Bush signed P.L. -

Industrial Visit to Nuclear Fuel Complex, Hyderabad on 27Th
INDUSTRIAL VISIT VISITED INDUSTRY:NFC(NUCLEAR FUEL COMPLEX) LOCATION OF THE INDUSTRY:NFC INDUSTRY, ECIL, Moula ali, Hyderabad, Telangana :500062 DATE OF INDUSTRY VISIT:13-02-2019 DEPARTMENT:CHEMICAL ENGINEERING YEAR:ENGINEERING 3rd YEAR CONTENTS: Introduction History Principle of production Flowchart How energy is generated Making of nuclear fuel Oath of thanks INTRODUCTION: The nuclear fuel complex(NFC) was established in 1971 as a major industrial unit of Indian’s department of atomic energy,for the supply of nuclear fuel bundles and reactor core components. It is a unique facility where natural and enriched fuel, zirconium alloy cladding and reactor core components are manufactured under one roof. HISTORY: NFC is a unit of department of atomic energy,Government of India. The complex is responsible for the supply of nuclear bundles and reactor core components for all the nuclear power reactors in India. It is a unique facility where the natural and enriched uranium fuel, zirconium alloy cladding and reactor core components are manufactured under one roof starting from the raw materials. PRINCIPLE OF PRODUCTION: As the power generated is low,then the per capita energy consumption is becoming low. There is insufficient power supply for all the people. Power generated Per capita energy consumption= Total population. since power generated by coal,thermal,tidal,solar energy is very less and it is inadequate for human usage. So by using nuclear energy they have been manufacturing uranium bundles which are used in generating electricity. PRODUCT: Uranium Bundles RAW MATERIALS: Magnesium di- uranate(MDU) Sand containing Zirconium FLOW CHART: FILTERATION DISSOLUTION SLURRY EXTRACTION PRECIPITATION COMPACTION STABILIZATION REDUCTION CALCINATION DRYING PELLET GRINDING PELLET READING SINTERING ENDCAP-WELDING NUCLEAR REACTOR INSPECTION END PLATE WELDING BUNDLE ASSEMBLY These are steps involved in the manufacturing of uranium rods which are used for the electricity generation. -

Governing Uranium in India
A Service of Leibniz-Informationszentrum econstor Wirtschaft Leibniz Information Centre Make Your Publications Visible. zbw for Economics Nayan, Rajiv Research Report Governing uranium in India DIIS Report, No. 2015:02 Provided in Cooperation with: Danish Institute for International Studies (DIIS), Copenhagen Suggested Citation: Nayan, Rajiv (2015) : Governing uranium in India, DIIS Report, No. 2015:02, ISBN 978-87-7605-736-7, Danish Institute for International Studies (DIIS), Copenhagen This Version is available at: http://hdl.handle.net/10419/120395 Standard-Nutzungsbedingungen: Terms of use: Die Dokumente auf EconStor dürfen zu eigenen wissenschaftlichen Documents in EconStor may be saved and copied for your Zwecken und zum Privatgebrauch gespeichert und kopiert werden. personal and scholarly purposes. Sie dürfen die Dokumente nicht für öffentliche oder kommerzielle You are not to copy documents for public or commercial Zwecke vervielfältigen, öffentlich ausstellen, öffentlich zugänglich purposes, to exhibit the documents publicly, to make them machen, vertreiben oder anderweitig nutzen. publicly available on the internet, or to distribute or otherwise use the documents in public. Sofern die Verfasser die Dokumente unter Open-Content-Lizenzen (insbesondere CC-Lizenzen) zur Verfügung gestellt haben sollten, If the documents have been made available under an Open gelten abweichend von diesen Nutzungsbedingungen die in der dort Content Licence (especially Creative Commons Licences), you genannten Lizenz gewährten Nutzungsrechte. may exercise -

E-Newsletter Volume 2 Issue 1 April 2020
Volume-2 Issue-1 For Internal Private Circulation only FROM CHAIRMAN’S DESK Dr. U. Kamachi Mudali Chairman IIChE-MRC Around the world, all eyes are on the spread of the COVID-19. The pandemic is challenging families, health care systems, and governments. The pandemic is also challenging our organization and staff in unprecedented ways. The challenge, however, is prompting necessary action, while avoiding over-reaction. India has stood up to the coronavirus crisis as Industry, R&D, academia and media are supporting government to kick out the menace. People are following key advices on hand washing, coughing etiquette, not touching face, physical distance and staying at home. With this type of support and discipline, I have no doubt that together we will win soon. Indian Institute of Chemical Engineers (IIChE) is the premier professional organization furthering the development of chemical, petrochemical and allied industries with respect to R&D, design and engineering, educational programmes and consultancy. It also provides a platform for interacting with other disciplines of science and engineering. Apart from its tremendous academic and professional value, IIChE happens to be the most opportune ground for our members and other participants to network with fellow professionals, which is undeniably an important prerequisite for professional growth today. IIChE-MRC, being the largest among regional centres of IIChE, continues to conduct and support many events throughout the year. It also prudent to share achievements with members through this triannual E-Newsletter for the benefit of members. There has been inspiring feedback on last issue of the E-Newsletter across the board which was circulated among many regional centers, HQ, social networks, former EC members etc. -

Pre-Qualification Document
GOVERNMENT OF INDIA DEPARTMENT OF ATOMIC ENERGY NUCLEAR FUEL COMPLEX CIVIL ENGINEERING DIVISION HYDERABAD – 500 062 PH: 040-27184099/040-27184725 & Fax: 040-27122532 WORKS: CIVIL, PH AND STRUCTURAL STEEL AND OTHER ALLIED WORKS FOR ATMF PLANT AT NFC, HYD. PROJECT: ADVANCED TUBE MANUFACTURING FACILITY (ATMF) PQ NIT NOTICE NO.: C/ 1186/2018 PRE-QUALIFICATION DOCUMENT P a g e | 1 CONTENTS SECTION TITLE PAGE NIT Notice inviting tenders for Pre-qualification 4-22 Part : I Brief particulars of the work 23-24 Part : II Information & instructions for applicants 25-31 1. General 25 2. Definitions 26 3. Method of application 27 4. Final decision making Authority 27 5. Particulars provisional 27 6. Site visit 27 7. Initial criteria of eligibility 28 8. Evaluation criteria 29 9. Financial information 30 10.Experience in similar works 30 11.Organisation information 30 12.Construction plant & equipment 30 13. Preference for Green Building Norms 30 14.Letter of transmittal 30 15.Short listing the agencies 31 16.Award criteria 31 Part : III Information regarding eligibility 32-49 1. Letter of Transmittal 32-33 2. Form “A‟- Financial information 34 3. Form “B‟- Solvency certificate from Applicant’s Bankers 35 4.Form “C‟- Details of all works of similar class completed during 36- the last seven years. 37 5.Form “D‟- Projects under execution or awarded 38 6.Form “E‟- Performance report of works referred to in form “C” & 39 “D” 7.Form “F‟- Structure & organisation 40 8.Form “G‟- Details of technical & administrative personnel to be 41 employed for the work 9.Form “H‟- Details of construction plant & equipment likely to be 42- used in carrying out th e work 45 10.