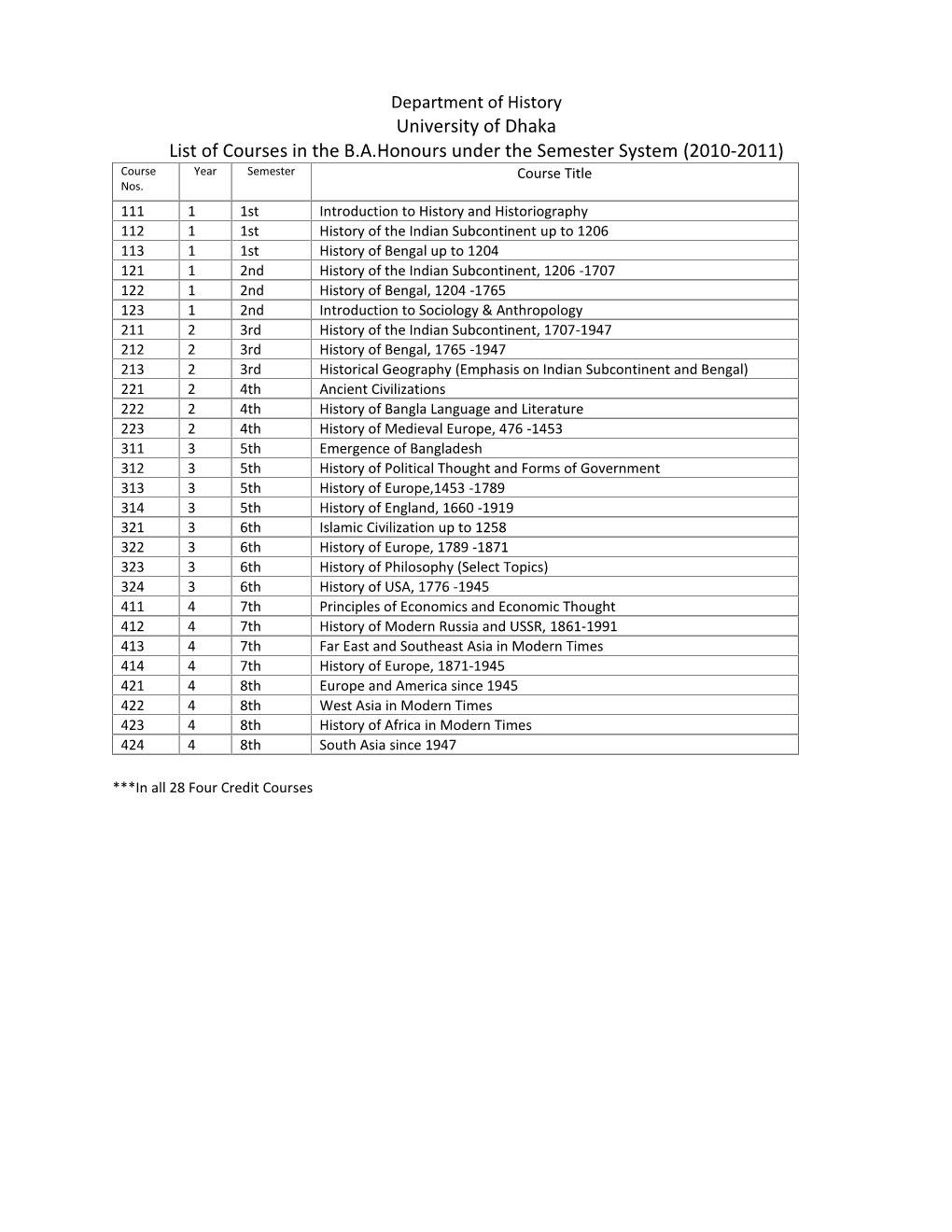
Department of History University of Dhaka List of Courses in the B.A.Honours Under the Semester System (2010-2011) Course Year Semester Course Title Nos
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Come Take a Ride in Tito's Time Machine
Come take a Ride in Tito’s Time Machine A Collection of Essays By Risto Stefov 1 Come take a Ride in Tito’s Time Machine A Collection of Essays Published by: Risto Stefov Publications [email protected] Toronto, Canada All rights reserved. No part of this book may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic or mechanical, including photocopying, recording or by any information storage and retrieval system without written consent from the author, except for the inclusion of brief and documented quotations in a review. Copyright 2012 by Risto Stefov e-book edition Many thanks to TrueMacedonian for providing the source material for these essays. 2 Index Index ............................................................................................. 3 Preface .......................................................................................... 4 Introduction................................................................................... 5 Essay 1 – According to Kristina X ............................................. 10 Essay 2 – Show of Patriotism ..................................................... 16 Essay 3 – Greek betrays Delchev ............................................... 21 Essay 4 – Mischief is my middle name ...................................... 26 Essay 5 – In the Balkans............................................................. 30 Essay 6 – Macedonia is for Republic ......................................... 35 Essay 7 – GREECE: MADE IN GERMANY ............................ 42 Essay 8 -

A Guide to Bangladesh a Fulbright Experience
A Guide to Bangladesh A Fulbright Experience The American Center U.S. Embassy Annex J Block, Progoti Sharoni Baridhara, Dhaka 1212 (opposite the U.S. Embassy) Bangladesh Telephone: 88-02-8855500-22 Fax: 88-02-9881677 Contact Information Location of the Public Affairs Office: The American Center U.S. Embassy Annex J Block, Progoti Sharoni Baridhara, Dhaka 1212 (Opposite the U.S.Embassy And Next to Notun Bazar) Phone: Number: 8855500-22 Calling From Overseas To Country Code: (880) Dhaka City Code: (2) + Number Points of First Contact for Inquiries (at The American Center): Cultural Affairs Specialist Shaheen Khan Email: [email protected] Work phone – 8855500-22, Ext. 2811 Cell Phone – 01713-043-749 Cultural Affairs Officer for Education and Exchange Ryan G. Bradeen Email: [email protected] Work phone – 8855500-22, ext. 2805 Cell phone – 01730013982 Cultural Affairs Assistant Raihana Sultana E-mail: [email protected] Work phone: 8855500-22, Ext. 2816 Cell phone – 01713-243852 Location of the United States Embassy: U.S. Embassy Madani Avenue Baridhara, Dhaka, Bangladesh Phone: 885-5500 Website: http://dhaka.usembssy.gov American Citizen Services: located in the Consular Section of the U.S. Embassy. Drop-in hours are Sunday through Thursday, 1:00 – 4:00 pm After-hours Emergency: call (2) 882-3805 Congratulations on receiving the Fulbright grant! We look forward to welcoming you to Bangladesh soon. During your stay in Bangladesh it is important that you maintain a relationship with the U.S. Mission in order to successfully participate in the program. This involves close contact with The American Center. -

Revisit to Dhaka University As the Symbol of Bengal Partition Sowmit Chandra Chanda Dr
Academic Ramification in Colonial India: Revisit to Dhaka University as the Symbol of Bengal Partition Sowmit Chandra Chanda Dr. Neerja A. Gupta PhD Research Scholar under Dr. Neerja A. Director & Coordinator, Department of Gupta, Department of Diaspora and Diaspora and Migration Studies, SAP, Migration Studies, SAP, Gujarat Gujarat University, Ahmedabad, India. University, Ahmedabad, India. Abstract: It has been almost hundred years since University of Dhaka was established back in 1921. It was the 13th University built in India under the Colonial rule. It was that like of dream comes true object for those people who lived in the eastern part of Indian Sub-continent under Bengal presidency in the British period. But when the Bengal partition came into act in 1905, people from the new province of East Bengal and Assam were expecting a faster move from the government to establish a university in their capital city. But, with in 6 years, the partition was annulled. The people from the eastern part was very much disappointed for that, but they never left that demand to have a university in Dhaka. After some several reports and commissions the university was formed at last. But, in 1923, in the first convocation of the university, the chancellor Lord Lytton said this university was given to East Bengal as a ‘splendid Imperial compensation’. Which turns our attention to write this paper. If the statement of Lytton was true and honest, then certainly Dhaka University stands as the foremost symbol of both the Bengal Partition in the academic ramification. Key Words: Partition, Bengal Partition, Colony, Colonial Power, Curzon, University, Dhaka University etc. -

HSS-102 Bangladesh Studies
University of Asia Pacific (UAP) Department of Basic Sciences & Humanities Course Outline Program: LL.B (Hons) Course Title: Bangladesh Studies: History Course Code: HSS102 Semester: Fall-2017 Level: 1st year 1st semester Credit Hour: 1.5 Name & Designation of Teacher: Mr.Ishfaq Ilahi Choudhury Office/Room: Department of Basic Sciences and Humanities, 2nd floor, UAP Campus Class Hours: Sunday 02.00pm-03.30pm Consultation Hours: E-mail: Mobile: Rationale: It is an extra departmental core course which will help them to learn the history of Bengal. Pre-requisite (if any): no Course Synopsis: The land: Geographical Factors, The People. Historical Perspectives. Ancient Bengali: Shashanka, Rise of the Palas, the Senas. Early Medieval Bengal. Coming of the Muslims. The Independent sultanate of Bengal: IliyasShahi and HusapnShahi Bengal. Development of Bengali Language & Bengali Literature. Late medieval Bengal: The Establishment of Mughal Rule in Bengal Bara-Bhuiyans: Subahdars and Nawabs, Coming of the Europeans New Approach in Bengal Architecture Beginning of British rule in Bengal: Battles of Palashi&Buxar. Diwani (1765). The Dual government. Permanent Settlement 1 (1793) Nineteenth Century Bengali Renaissance: Areas of Social & Religious Reforms-Raja Rammohun Roy, Iswar Chandra Vidyasagar, Titu Mir. Partition of Bengal (1905). Language Movement (1948 &1952) Movement for Autonomy; 6-point and 11-Point Programs. The 1970 Election-Military Action, Genocide in East Pakistan. The Liberation War. The Emergence of Bangladesh as a Sovereign Independent State in 1971. Course Objectives (CO): . To introduce the students with the history of ancient Bengal. To provide a clear idea about political development in ancient and Medieval Bengal . To give a clear view of British colonial policy in Bengal . -

Russians and Ottomans in the Press During the First World War
DEPICTING THE ENEMY: RUSSIANS AND OTTOMANS IN THE PRESS DURING THE FIRST WORLD WAR A Ph.D. Dissertation By ZHARMUKHAMED ZARDYKHAN Department of History Bilkent University Ankara September 2007 Светлой памяти профессора Стэнфорда Дж. Шоу (1930-2006) посвящается... DEPICTING THE ENEMY: RUSSIANS AND OTTOMANS IN THE PRESS DURING THE FIRST WORLD WAR The Institute of Economics and Social Sciences of Bilkent University by ZHARMUKHAMED ZARDYKHAN In Partial Fulfilment of the Requirements for the Degree of DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY in THE DEPARTMENT OF HISTORY BILKENT UNIVERSITY ANKARA September 2007 I certify that I have read this thesis and have found that it is fully adequate, in scope and in quality, as a thesis for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in History. --------------------------------- Asst. Prof. Oktay Özel Supervisor I certify that I have read this thesis and have found that it is fully adequate, in scope and in quality, as a thesis for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in History. --------------------------------- Asst. Prof. Ferdan Ergut Examining Committee Member I certify that I have read this thesis and have found that it is fully adequate, in scope and in quality, as a thesis for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in History. --------------------------------- Asst. Prof. Paul Latimer Examining Committee Member I certify that I have read this thesis and have found that it is fully adequate, in scope and in quality, as a thesis for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in History. --------------------------------- Asst. Prof. Evgeni Radushev Examining Committee Member I certify that I have read this thesis and have found that it is fully adequate, in scope and in quality, as a thesis for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy in History. -

“Father of the Nation” – Banggabandhu – Sheikh Mujiburrahman. Dr
The International Journal of Social Sciences and Humanities Invention 4(2): 3321-3329, 2017 DOI: 10.18535/ijsshi/v4i2.011 ICV 2015: 45.28 ISSN: 2349-2031 © 2017, THE-IJSSHI Research Article Author’s Emotional Attachment with the “Father of the Nation” – Banggabandhu – Sheikh MujiburRahman. Dr. Sheikh Mahabub Alam Adviser, The People‟s University of Bangladesh (PUB), Chairman, Department of Tourism and Hospitality Management (THM) Chairman, Head of the Departments, The People‟s University of Bangladesh (PUB), Asad Gate, Mohammadpur, Dhaka-1207, Bangladesh. ABSTRACT: Bangladesh and its people were blessed with God‟s will of sending the Greatest Bengali Soul of all time on the soil of Tungipara. That greatest soul was nobody else but it is our “Father of the Nation” – Bangabandhu - Sheikh Mujibur Rahman. He gave us a Nation, he gave us a Free Country, he gave us a Language, he gave us a dream of transforming Bangladesh as the Switzerland of Asia and in fact he gave us everything that we can all be proud of. The author is very lucky that he began schooling at Gimadanga Tungipara (GT) High School. It is also the same institution where Bangabandhu began his schooling as well. His magic touch on author‟s head, hair & chest, his love & affection, and his kind words of advice changed author‟s life forever. Those were author‟s inspiration to overcome all hurdles of life, became one of the best student of the country that culminated with the prestigious Commonwealth Scholarships to pursue PhD program at University of London (UCL) of University of London. -

1. Introduction
Notes 1. Introduction 1. ‘Diaras and Chars often first appear as thin slivers of sand. On this is deposited layers of silt till a low bank is consolidated. Tamarisk bushes, a spiny grass, establish a foot-hold and accretions as soon as the river recedes in winter; the river flows being considerably seasonal. For several years the Diara and Char may be cultivable only in winter, till with a fresh flood either the level is raised above the normal flood level or the accretion is diluvated completely’ (Haroun er Rashid, Geography of Bangladesh (Dhaka, 1991), p. 18). 2. For notes on geological processes of land formation and sedimentation in the Bengal delta, see W.W. Hunter, Imperial Gazetteer of India, vol. 4 (London, 1885), pp. 24–8; Radhakamal Mukerjee, The Changing Face of Bengal: a Study in Riverine Economy (Calcutta,1938), pp. 228–9; Colin D. Woodroffe, Coasts: Form, Process and Evolution (Cambridge, 2002), pp. 340, 351; Ashraf Uddin and Neil Lundberg, ‘Cenozoic History of the Himalayan-Bengal System: Sand Composition in the Bengal Basin, Bangladesh’, Geological Society of America Bulletin, 110 (4) (April 1998): 497–511; Liz Wilson and Brant Wilson, ‘Welcome to the Himalayan Orogeny’, http://www.geo.arizona.edu/geo5xx/ geo527/Himalayas/, last accessed 17 December 2009. 3. Harry W. Blair, ‘Local Government and Rural Development in the Bengal Sundarbans: an Enquiry in Managing Common Property Resources’, Agriculture and Human Values, 7(2) (1990): 40. 4. Richard M. Eaton, The Rise of Islam and the Bengal Frontier 1204–1760 (Berkeley and London, 1993), pp. 24–7. 5. -

Wolfgang-Peter Zingel Bangladesh's Economic Revival: from Sheikh
Wolfgang-Peter Zingel Associate Member of South Asia Institute of Heidelberg University Bangladesh’s economic revival: From Sheikh Mujibur Rahman’s demand for regional autonomy to war and famine, the challenge of development and the country’s rise to become a leading exporter of manpower and textiles Talk prepared for the Bangabandhu Sheikh Mujibur Rahman Conference in Frankfurt, 7 October 2017 (presented in German language) Dear Friends, Today we are commemorating Sheikh Mujibur Rahman, the leader of the Independence Movement, the Father of the Nation, the President and Prime Minister, the Bangabandhu, the Friend of Bengal. I have been asked to say a few words on the Bangabandhu’s economic programme. I shall try to do that, being an economist and having worked on the country’s economic and social development since that fateful year of 1971. Understanding a country’s economic development needs a look also at history and culture. I therefore shall begin with the grim colonial past and the unhappy Pakistan times. Having been to Bangladesh during the famine of 1974 and seeing the overall destruction and misery, it appears to be nothing less than a miracle that Bangladesh has managed to pull even with Pakistan and to surpass India in some areas of the social sector. But the achievement has to be seen in the wider context: There are more countries that had a similar economic resurgence. Bangladesh depends even more than in the past on international markets. More than any other major country it is exposed to the vagaries of climate change and cannot trust in international solidarity. -

Searching for the Greatest Bengali: the BBC and Shifting Identity
National Identities Vol. 10, No. 2, June 2008, 149Á165 Searching for the greatest Bengali: The BBC and shifting identity categories in South Asia Reece Jones* University of Wisconsin-Madison, USA Drawing on debates generated by the BBC Bengali Language Service’s naming of the greatest Bengali of all time, this article investigates the shifting boundaries between group identity categories in our ‘globalising’ world. First, the con- troversy over the meaning of the term ‘Bengali’, which emerged in contemporary Bangladesh and India in response to the BBC’s list, is investigated. Then writings and speeches of several of the individuals who were honoured as the greatest Bengalis are analysed in order to draw out the multiple ways they approached their own Bengali identities. In the conclusion, it is argued that rather than imagining the end of place-based identity categories through the process of globalisation, it is more useful to conceptualise shifting categories that continue Downloaded By: [Jones, Reece] At: 15:14 29 April 2008 to incorporate a place-based aspect, but in hybrid and contradictory ways. Keywords: categories; ethnicity; nations; globalisation; South Asia In Spring 2004, following the British Broadcasting Company’s naming of Winston Churchill as the greatest Briton of all time, the BBC Bengali Language Service conducted a survey of its twelve million listeners to determine the greatest Bengali of all time (BBC, 2004).1 Respondents were asked to rank their top five choices and in the end more than 100 individuals received votes. The top twenty were announced one per day beginning on 26 March, Bangladesh’s Independence Day, and ending on 15 April, the Bengali New Year’s Day, with the naming of Sheikh Mujibur Rahman as the greatest Bengali of all time. -

Zila Report : Habiganj
POPULATION & HOUSING CENSUS 2011 ZILA REPORT : HABIGANJ Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics Statistics and Informatics Division Ministry of Planning BANGLADESH POPULATION AND HOUSING CENSUS 2011 Zila Report: HABIGANJ October 2015 BANGLADESH BUREAU OF STATISTICS (BBS) STATISTICS AND INFORMATICS DIVISION (SID) MINISTRY OF PLANNING GOVERNMENT OF THE PEOPLE’S REPUBLIC OF BANGLADESH ISBN-978-984-33-8637-3 COMPLIMENTARY Published by Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics (BBS) Statistics and Informatics Division (SID) Ministry of Planning Website: www.bbs.gov.bd This book or any portion thereof cannot be copied, microfilmed or reproduced for any commercial purpose. Data therein can, however, be used and published with acknowledgement of their sources. Contents Page Message of Honorable Minister, Ministry of Planning …………………………………………….. vii Message of Honorable State Minister, Ministry of Finance and Ministry of Planning …………. ix Foreword ……………………………………………………………………………………………….. xi Preface …………………………………………………………………………………………………. xiii Zila at a Glance ………………………………………………………………………………………... xv Physical Features ……………………………………………………………………………………... xix Zila Map ………………………………………………………………………………………………… xx Geo-code ………………………………………………………………………………………………. xxi Chapter-1: Introductory Notes on Census ………………………………………………………….. 1 1.1 Introduction ………………………………………………………………………………… 1 1.2 Census and its periodicity ………………………………………………………………... 1 1.3 Objectives ………………………………………………………………………………….. 1 1.4 Census Phases …………………………………………………………………………… 2 1.5 Census Planning …………………………………………………………………………. -

121292955.Pdf
THE TURKS IN EUROPE Qu'est ce que la Turquie ? La Turquie est le pays classique des massacres.. Son histoire se resume a ceci; pillages, meurtres, vols, con cussions—sur toutes les echelles—reroltes, insurrections, repressions, guerres etrangeres, guerres civiles, revolutions, ccntre-revolutions, seditions, mutineries. ARSENE PERLANT, Eterelle Turquie, " To murder a man is a crime; to massacre a nation is a question." VICTOR HUGO, 1876. THE TURKS IN EUROPE A SKETCH-STUDY BY W. E. D. ALLEN WITH A PREFACE BY BRIG-GEN. H. CONYERS SURTEES, C.M.G., D.S.O. LONDON JOHN MURRAY, ALBEMARLE STREET 1919 All rights reserved. DEDICATION To MY BELOVED FATHER— To you I dedicate this chronicle of men's savageness and meanness. To you, who were so brilliant and so simple; so faultless your self yet so tolerant of fault in others; so gentle that you could not kill a bird; so kind that men marvelled ; so forbearing that they thought you weak ; so generous that they thought you fool. You were so quick of comprehension, yet so patient of stupidity in others. You could always forgive, and always understand. Men wondered when you repaid vilest ingratitude with renewed kindness. You who so loved Music and Books and Art, and to roam in the wild places of the earth, and linger in its ancient cities, were for ever im prisoned in an office. You began to work when most boys begin to learn ; you spent the best years of your life in drudgery, working often till mid night. You carried for years, while you were dying, the responsibilities and burdens of ten men. -

Bengali ~ Ebook Bengali - - Bengal Description: - - Foreign Trade Promotion -- Government Policy -- United States United States
- < Bengali ~ eBook Bengali - - Bengal Description: - - Foreign trade promotion -- Government policy -- United States United States. -- Foreign Agricultural Service -- Management United States. -- Dept. of Agriculture. -- Export Enhancement Program -- Evaluation Peru -- Description and travel. Indians of South America -- Peru. Presidents -- United States -- Biography -- Juvenile literature. Lincoln, Abraham, -- 1809-1865 -- Juvenile literature. Japanese language -- Grammar, Comparative -- Bengali. Bengali language -- Grammar, Comparative -- Japanese.Bengali - Studies and texts (Pontifical Institute of Mediaeval Studies) -- 128 Studies and texts -- 128 Asian and African grammatical manual -- no. 13cBengali Notes: English, Romanized Japanese, and Bengali. This edition was published in 1979 Filesize: 5.63 MB Tags: #Bengali #language Bengali (Bangla) He was the first person from the Indian subcontinent to receive a , in 1904. The invasion army of was deterred by the accounts of Gangaridai's power in 325 BCE. But Marconi got recognition for European proximity. Bengal The Bengal Borderland: Beyond State and Nation in South Asia. Bengal became the stronghold of the taka. Bengalis Bengalis make distinctive from milk products, including , Chômchôm, and several kinds of. Chakma: Ek jônôtun diba poa el. The leopard cat looks very much like a domestic cat, except for the larger, snapping eyes, pronounced whisker pads, longer legs, and brilliant leopard-style markings. bengali Rahman launched the for autonomy in 1966. Banglapedia: National Encyclopedia of Bangladesh Second ed. Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics, Statistics Division, Ministry of Planning, Government of the People's Republic of Bangladesh. The 100 Greatest Bengali Movies Of All Time Its ranks largest in the world in terms of market and in. M Chittagong: Egua mansher dua poa asil. Bengali (Bangla) The is the state animal of West Bengal.