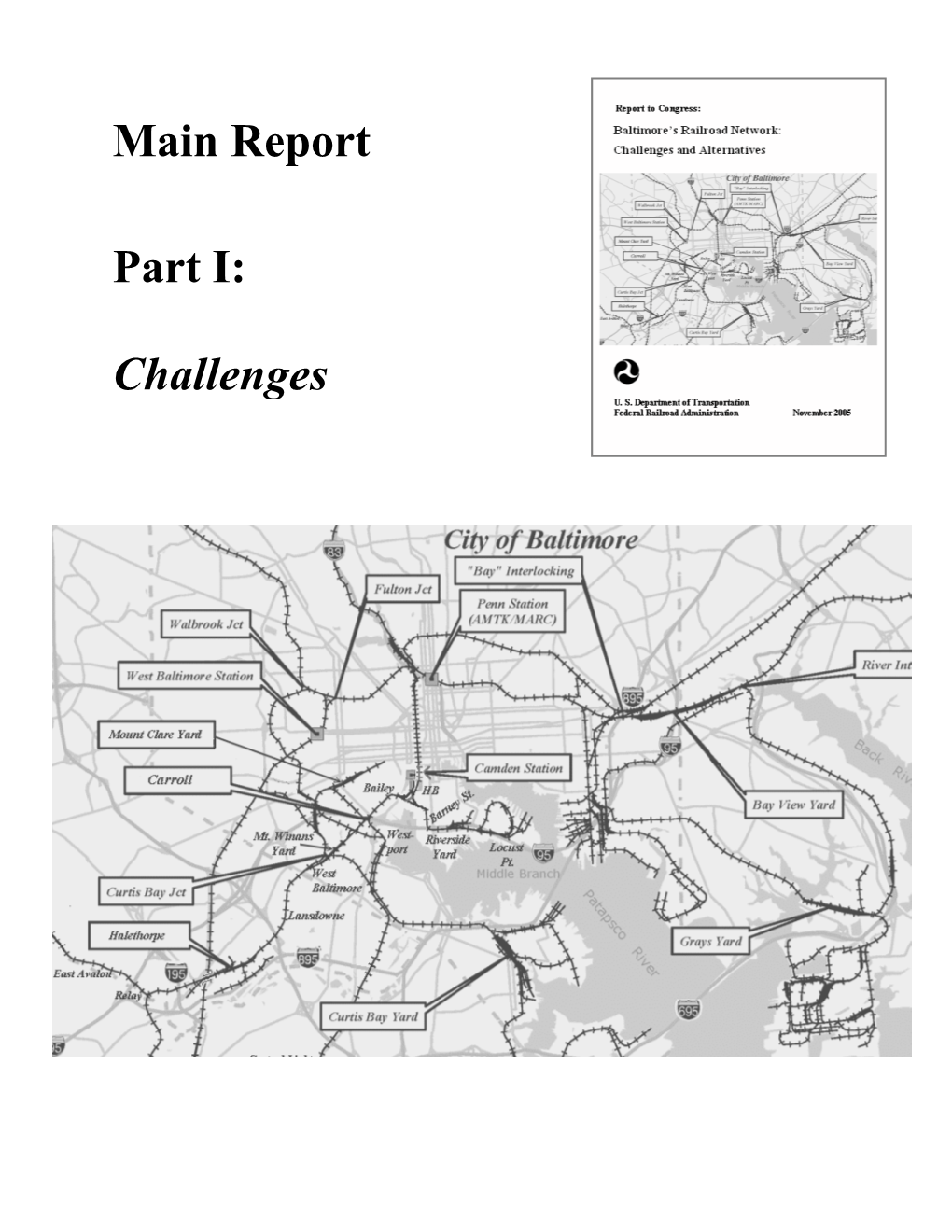
Report Part I (“Challenges”) Traces the Development, Current Condition, and Utilization Levels of Baltimore’S Rail Network
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

No-Discharge Zones for Vessel Sewage in Maryland and Virginia
This document is scheduled to be published in the Federal Register on 05/11/2021 and available online at federalregister.gov/d/2021-09957, and on govinfo.gov 6560-50-P ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY [FRL 10021-74-Region 3] Clean Water Act: No-Discharge Zones for Vessel Sewage in Maryland and Virginia AGENCY: Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). ACTION: Notice–final determination. SUMMARY: On behalf of the State of Maryland, the Secretary of the Maryland Department of Natural Resources requested that the Regional Administrator, U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Region 3 approve a no-discharge zone for thirteen water bodies in Anne Arundel County, Maryland pursuant to the Clean Water Act. After review of Maryland’s application, EPA determined that adequate facilities for the safe and sanitary removal and treatment of sewage from all vessels are reasonable available for all thirteen waterbodies within Anne Arundel County. The application is available upon request from EPA (at the email address below). DATES: This approval is effective upon the date of publication in the Federal Register on [INSTERT DATE OF PUBLICATION IN THE FEDERAL REGISTER]. FOR FURTHER INFORMATION CONTACT: Ferry Akbar Buchanan, U. S. Environmental Protection Agency – Region III. Telephone: (215) 814-2570; email address: [email protected]. SUPPLEMENTARY INFORMATION: Pursuant to Clean Water Act section 312(f)(3), if any state determines that the protection and enhancement of the quality of some or all of the state’s waters require greater environmental protection, the state may designate the waters as a vessel sewage no-discharge zone. However, the state may not establish the no-discharge zone until EPA has determined that adequate pumpout facilities for the safe and sanitary removal and treatment of sewage from all vessels are reasonably available for the proposed waters. -

Virginia Railway Express Strategic Plan 2004-2025
VRE STRATEGIC PLAN Contents EXECUTIVE SUMMARY .......................................................................................................................V Current State of the Railroad ..............................................................................................................v The Strategic Planning Process..........................................................................................................vi The VRE Ridership Market................................................................................................................vii Strategic Plan Scenarios and Recommendations .............................................................................viii Core Network Needs...........................................................................................................................ix Potential Network Expansion ..............................................................................................................x Phased Service Improvement and Capital Investment Plan ..............................................................xii Financial, Institutional and Organizational Issues ..........................................................................xiii VRE Moving Forward ......................................................................................................................xiv 1. CURRENT STATE OF THE RAILROAD..........................................................................................1 VRE SYSTEM OVERVIEW .........................................................................................................................1 -

I-95 Fort Mchenry Tunnel: Moravia Road to Tunnel Improvements
Maryland Transportation Authority 2020 - 2023 Transportation Improvement Program Highway Capacity National Highway System I-95 Fort McHenry Tunnel: Moravia Road to Tunnel Improvements TIP ID 22-1601-41 Year of Operation 2018 Agency Maryland Transportation Authority Project Type Roadway widening Project Category Highway Capacity Functional Class Interstate Conformity Status Not Exempt Physical Data 3.7 miles, 6 to 8 lanes CIP or CTP ID(s) MdTA-12 Est. Total Cost $73,807,000 Description: This project will reconfigure I-95 to provide four continuous mainline lanes in each direction. The specific limits are from north of the Fort McHenry Toll Plaza to the I-95 Express Toll Lanes (ETLs) in the northbound direction, and from north of the Fort McHenry Toll Plaza to north of O’Donnell Street in the southbound direction. The total work within the limits extends for 3.7 miles in the northbound direction and 1.1 miles in the southbound direction. The project involves restriping I-95 to provide one additional lane of traffic including reconstruction of at-grade shoulders, replacement of at-grade median concrete traffic barriers, and reconstruction of portions of existing bridge decks and all concrete bridge parapets. Construction continues, but the project opened to traffic for beneficial use in 2018. The project is funded with MDTA toll revenues. Justification: This project will provide lane continuity and additional capacity along I-95 between the Fort McHenry Tunnel and the I-95 ETLs. This is needed to address existing congestion and to accommodate diverted traffic from I-895 that will result from MDTA’s Canton Viaduct Project. -

Equipment Roster
Location 3400 NE Grand Blvd. Oklahoma City, OK 73111 (405) 424-8222 Conveniently located just a half mile west of Interstate 35 off Exit 131 (NE 36th Street), on historic Grand Boulevard. - Half-mile east of Martin Luther King Boulevard - Just south of Lincoln Park Golf Course - 1 mile south of the Oklahoma City Zoo Oklahoma Railway Museum 3400 NE Grand Blvd. Oklahoma City, OK 73111 (405) 424-8222 www.oklahomarailwaymuseum.org EQUIPMENT ROSTER 40 1 Oklahoma Railway Museum The Oklahoma Railway Museum, Ltd. Bridge Logos (ORM) offers 35-minute excursion trains on the first and third Saturdays of each month for the public from 10 am until 4 pm starting the first Saturday in April. The trains leave the historic Oakwood Depot at 9:15, 11:15, 1:15 and 3:15 The Museum itself is open Thursday - Saturday from 9 am to 4 pm and there is no admission charge to tour the grounds. Train rides are free for children under the age of 3, $5 for children 3 years to 12 years, and These Frisco and Rock Island Railroad $12 for those 13 years and older. In heralds were displayed for almost 80 years addition to the train ride, railroad (1931-2010) on Oklahoma City’s South equipment, including motor cars, Robinson Street Bridge. The bridge was locomotives and passenger cars, are on located approximately a half mile east of display. A display car contains permanent Union Station and allowed both railroads to exhibits of railroad memorabilia. pass above Robinson to access to the station. The bridge was torn down to make Oakwood Station way for a new bridge with the rerouting of the I-40 crosstown expressway. -

Records Relating to Railroads in the Cartographic Section of the National Archives
REFERENCE INFORMATION PAPER 116 Records Relating to Railroads in the Cartographic Section of the national archives 1 Records Relating to Railroads in the Cartographic Section of the National Archives REFERENCE INFORMATION PAPER 116 National Archives and Records Administration, Washington, DC Compiled by Peter F. Brauer 2010 United States. National Archives and Records Administration. Records relating to railroads in the cartographic section of the National Archives / compiled by Peter F. Brauer.— Washington, DC : National Archives and Records Administration, 2010. p. ; cm.— (Reference information paper ; no 116) includes index. 1. United States. National Archives and Records Administration. Cartographic and Architectural Branch — Catalogs. 2. Railroads — United States — Armed Forces — History —Sources. 3. United States — Maps — Bibliography — Catalogs. I. Brauer, Peter F. II. Title. Cover: A section of a topographic quadrangle map produced by the U.S. Geological Survey showing the Union Pacific Railroad’s Bailey Yard in North Platte, Nebraska, 1983. The Bailey Yard is the largest railroad classification yard in the world. Maps like this one are useful in identifying the locations and names of railroads throughout the United States from the late 19th into the 21st century. (Topographic Quadrangle Maps—1:24,000, NE-North Platte West, 1983, Record Group 57) table of contents Preface vii PART I INTRODUCTION ix Origins of Railroad Records ix Selection Criteria xii Using This Guide xiii Researching the Records xiii Guides to Records xiv Related -

Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA)
Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA) I-95 Major Deck and Superstructure Rehabilitation South of the Fort McHenry Tunnel Northeast Bridge Preservation Partnership Conference September 20, 2016 David A. LaBella, P.E., Maryland Transportation Authority Agenda • About MDTA • History of FMT • Project Development • Project Design Elements • Project Construction • Q&A 2 Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA) 2 3 Maryland Transportation Authority (MDTA) • William Preston Lane Jr. Memorial (Bay) Bridge (US 50/301) – 4.3 miles • Francis Scott Key Bridge (I-695) – 11.0 miles (1.9 miles bridge) • Baltimore Harbor Tunnel (I-895) – 18.25 miles (1.4 miles tunnel) • Fort McHenry Tunnel (I-95/I-395) – 13.2 miles (1.5 miles tunnel) • John F. Kennedy Memorial Highway (I-95) – 51.6 miles (1.0 mile Millard E. Tydings Memorial Bridge) • Thomas J. Hatem Memorial Bridge (US 40) – 1.9 miles • Governor Harry W. Nice Memorial Bridge (US 301) – 2.1 miles • Intercounty Connector (MD 200) – 17.5 miles 4 Project Limits Southern Caton Tunnel Portal Avenue 4 I-95, South of Fort McHenry Tunnel to Caton Avenue Work in Both NB and SB Directions 5 Project Overview • Located in Baltimore City on I-95, South of the Fort McHenry Tunnel to Caton Avenue • Project Length 4.4 miles • Mainline I-95 and Ramp Bridges Serving I-95 Expansion Joint Replacements Riding Surface Replacement • Work Began in 2014 and Completed in 2016 (Deck Work - Two Construction Seasons) 6 Fort McHenry Tunnel Facility • I-95: Construction Dates of Bridges Varied; North of Tunnel Primarily in Early -

Smith, AICP Project Manager Office of Freight and Multimodalism Maryland Department of Transportation 410-865-1097 [email protected]
Presentation to the Pennsylvania Rail Seminar May 22, 2014 Maryland’s Freight Rail Efforts Overview of Maryland DOT Maryland Department of Transportation Maryland Transportation Authority Maryland State Maryland Maryland Maryland Transit Maryland Port Highway Aviation Motor Vehicle Administration Administration Administration Administration Administration Maryland Freight Rail • Class I • Short Lines o CSX o Canton Railroad o Norfolk Southern o Bay Coast Railroad o Maryland and Delaware Railroad o Maryland Midland Railway o Baltimore Industrial Railroad Maryland Class I Rail Map Maryland Freight Rail Projects o MDOT is working to progress several freight rail projects throughout the State o CSX • National Gateway o Norfolk Southern • Northeast Corridor projects o Short Lines • Canton Railroad Kane Street Yard Canton Railroad Company • MDOT is working with Canton Railroad Company on the development of the Kane Street Yard • Canton Railroad Company • Class III operator serving Port of Baltimore • Operates approximately 20 miles of track • Direct access to CSX and Norfolk Southern Canton Railroad Map Kane Street Yard Canton Kane Street Yard • 10-Acre Storage and Switching Yard in eastern Baltimore City • Once constructed, the project will increase capacity for Canton Railroad and provide quality of life improvements for area residents • Reduces horn blowing and blocking of grade crossings • Canton Railroad has wanted to construct Kane Street Yard for more than a decade but has lacked funds to complete the project Kane Street Yard – MDOT’s -

MD Rail Plan
Maryland State Rail Plan Project Update Presented to: Baltimore Regional Transportation Board Freight Movement Task Force Presented by: Harry Romano, MDOT OFM Date: March 25, 2021 Agenda » Introduction » Background, Plan Outline, Schedule » Vision and Goals » Review Project Types » Coordination and Outreach » Next Steps 2 Real-Time Feedback Using Poll Everywhere 3 Poll Everywhere #1: In one word, what do you see as the greatest opportunity for rail in Maryland? Poll Everywhere #2: In one word, what concept should not be left out of the Maryland State Rail Plan? 5 6 Background, Plan Outline, and Schedule 7 Why Is Maryland Updating the State Rail Plan? » Federal requirement per the 2008 Passenger Rail Investment and Improvement Act (PRIIA), affirmed in federal surface transportation bills, 4-year update per the FAST Act » Positions the state and rail stakeholders for federal funding » Outlines public and private investments and policies needed to ensure the efficient, safe, and sustainable movement of freight and passenger by rail 8 What Does a State Rail Plan Cover? Commuter Rail Freight Rail Intercity Passenger Rail 9 Background – Maryland’s Freight Rail Network Total Miles Operated Miles Owned, Miles Owned, Not Railroad Miles Leased (Except Trackage Rights Operated Operated Trackage Rights) Class I Railroads CSX Transportation 5 455 7 460 86 Norfolk Southern Railway 59 42 59 200 Total Class I Railroads 5 514 49 519 286 Class II Railroads Wheeling and Lake Erie Railroad 25 Class III Railroads Canton Railroad 16 16 Georges Creek Railway -

Eldean Bridge NHL Nomination
NPS Form 10-900 USDI/NPS NRHP Registration Form (Rev. 8-86) OMB No. 1024-0018 ELDEAN BRIDGE Page 1 United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service National Register of Historic Places Registration Form 1. NAME OF PROPERTY Historic Name: Eldean Bridge (preferred historic common name) Other Name/Site Number: Allen’s Mill Bridge (original historic name); Marshall Bridge; World Guide #35-55-01; Farver Road Bridge 0.15 2. LOCATION Street Address: Spanning Great Miami River at bypassed section of Eldean Road/CR33 (bypassed section of Eldean Road is now the west part of Farver Road) Not for Publication: City/Town: Troy vicinity, Concord Township-Staunton Township Vicinity: X State: Ohio County: Miami Code: 055 Zip Code: 45373 3. CLASSIFICATION Ownership of Property Category of Property Private: ___ Building(s): ___ Public-Local: X District: ___ Public-State: ___ Site: ___ Public-Federal: ___ Structure: X Object: ___ Number of Resources within Property Contributing Noncontributing buildings buildings sites sites 1 structures structures objects objects 1 Total 0 Total Number of Contributing Resources Previously Listed in the National Register: 1 Name of Related MultipleDRAFT Property Listing: NPS Form 10-900 USDI/NPS NRHP Registration Form (Rev. 8-86) OMB No. 1024-0018 ELDEAN BRIDGE Page 2 United States Department of the Interior, National Park Service National Register of Historic Places Registration Form 4. STATE/FEDERAL AGENCY CERTIFICATION As the designated authority under the National Historic Preservation Act of 1966, as amended, I hereby certify that this ____ nomination ____ request for determination of eligibility meets the documentation standards for registering properties in the National Register of Historic Places and meets the procedural and professional requirements set forth in 36 CFR Part 60. -

Unique Uses for Emissions Inventories in Maryland
Unique Uses for Emissions Inventories in Maryland Roger Thunell, Chief AQ Planning Division, MDE – EPA EI Conference – August 2017 Welcome to Baltimore • During Your Visit • Crab Cakes • Microbrews • Burger Cookies • Camden Yards Focus on Three Topics • Use of CAMD data as a Regulatory Mechanism • Locomotive Survey • Temporal Improvements for Small EGUs in Modeling Inventories 3 CAMD Data as a Regulatory Mechanism • Focused on coal-fired EGUs with SCR or SNCR post-combustion controls • Baseline Starting Point - The year with the lowest recorded NOX emission rate for an entire ozone season • Using Daily CAMD data, compute the 123 30-day rolling averages for that ozone season. – (Ozone Season = 153 Days) 4 CAMD Data as a Regulatory Mechanism • Selected the highest maximum 30-day rolling average from this 123 value dataset. • This max 30-day rolling NOX emission rate represents an “achievable” emission rate for the unit – Some have referred to this as “optimization” of the unit. We would disagree and refer to it as “achievable” – Since the unit has demonstrated that it is capable of hitting this rate over an entire ozone season 5 CAMD Data as a Regulatory Mechanism • What can you do with this unit-specific “achievable” NOX rate – Design/Set permissible NOX rates per Unit • MDE has done this by setting “Indicator Rates” within our latest NOX regulation for coal-fired EGUs • The “Indicator Rates” are not identical to the “Achievable” rates but they are similar • Requires EGU owner/operators to explain why they were unable to meet the “Indicator -

Nesting in Chesapeake Bay Regions of Concern
W&M ScholarWorks VIMS Articles Virginia Institute of Marine Science 9-2015 Decadal re-evaluation of contaminant exposure and productivity of ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) nesting in Chesapeake Bay Regions of Concern RS Lazarus BA Rattner PC McGowan Robert Hale Virginia Institute of Marine Science et al Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.wm.edu/vimsarticles Part of the Environmental Sciences Commons Recommended Citation Lazarus, RS; Rattner, BA; McGowan, PC; Hale, Robert; and al, et, "Decadal re-evaluation of contaminant exposure and productivity of ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) nesting in Chesapeake Bay Regions of Concern" (2015). VIMS Articles. 1661. https://scholarworks.wm.edu/vimsarticles/1661 This Article is brought to you for free and open access by the Virginia Institute of Marine Science at W&M ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in VIMS Articles by an authorized administrator of W&M ScholarWorks. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Environmental Pollution 205 (2015) 278e290 Contents lists available at ScienceDirect Environmental Pollution journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/envpol Decadal re-evaluation of contaminant exposure and productivity of ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) nesting in Chesapeake Bay Regions of Concern * Rebecca S. Lazarus a, b, Barnett A. Rattner a, , Peter C. McGowan c, Robert C. Hale d, Sandra L. Schultz a, Natalie K. Karouna-Renier a, Mary Ann Ottinger b, 1 a U.S. Geological Survey, Patuxent Wildlife Research Center, Beltsville, MD 20705, USA b Marine-Estuarine Environmental Sciences Program and Department of Animal and Avian Sciences, University of Maryland, College Park, MD 20742, USA c U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service, Chesapeake Bay Field Office, Annapolis, MD 21401, USA d Virginia Institute of Marine Science, College of William and Mary, Gloucester Point, VA 23062, USA article info abstract Article history: The last large-scale ecotoxicological study of ospreys (Pandion haliaetus) in Chesapeake Bay was con- Received 30 March 2015 ducted in 2000e2001 and focused on U.S. -

THE DISPATCHER Newsletter for Central Oklahoma Railfan Club Ltd
THE DISPATCHER Newsletter for Central Oklahoma Railfan Club Ltd. Affiliated with: February -1936 National Railway Historical Society Editor, Lawrence Gibbs, 623 McFarland, Stillwater, OK 74074 TRA President, David Eads, 3108 Berkshire Way, OKC 73120 Treasurer, Roger Morton, 2424 Northwood Lane, Edmond, OK 73013 ¥ SPECIAL FEED ATSF MILESTONE Lynn reported that despite the Logan County Historical Society On Jan. 17 Santa Fe Railway uncertain future of our location, has acquired the Santa Fe station in marked the 1 millionth auto to be restoration continues, specifically on Guthrie. The railroad operation has shipped on the railroad from the the F unit. Good weather the past been moved to a smaller structure. GM assembly plant in OKC. month has allowed work to be done Jay Hannah of the society said the Since production began in April each Sunday. The brake system has station was completed in February 1979, ATSF has hauled more than been restored to working order and a 1903, so it's appropriate for it to 68,000 tri-level carloads of auto new addition of a Nathan five-chime change hands again in February and mobiles for the facility. horn has given audio to the unit. for that reason, a special feed has E.ail cars* take inbound traffic Morton gave a treasury report of been planned. directly into the plant for immediate some concern. It seems that income Hannah said the society is hosting use in the production process. Since the past two months is the lowest in a bean dinner at $3.50 on Tuesday, 1979, Santa Fe has handled some several years.