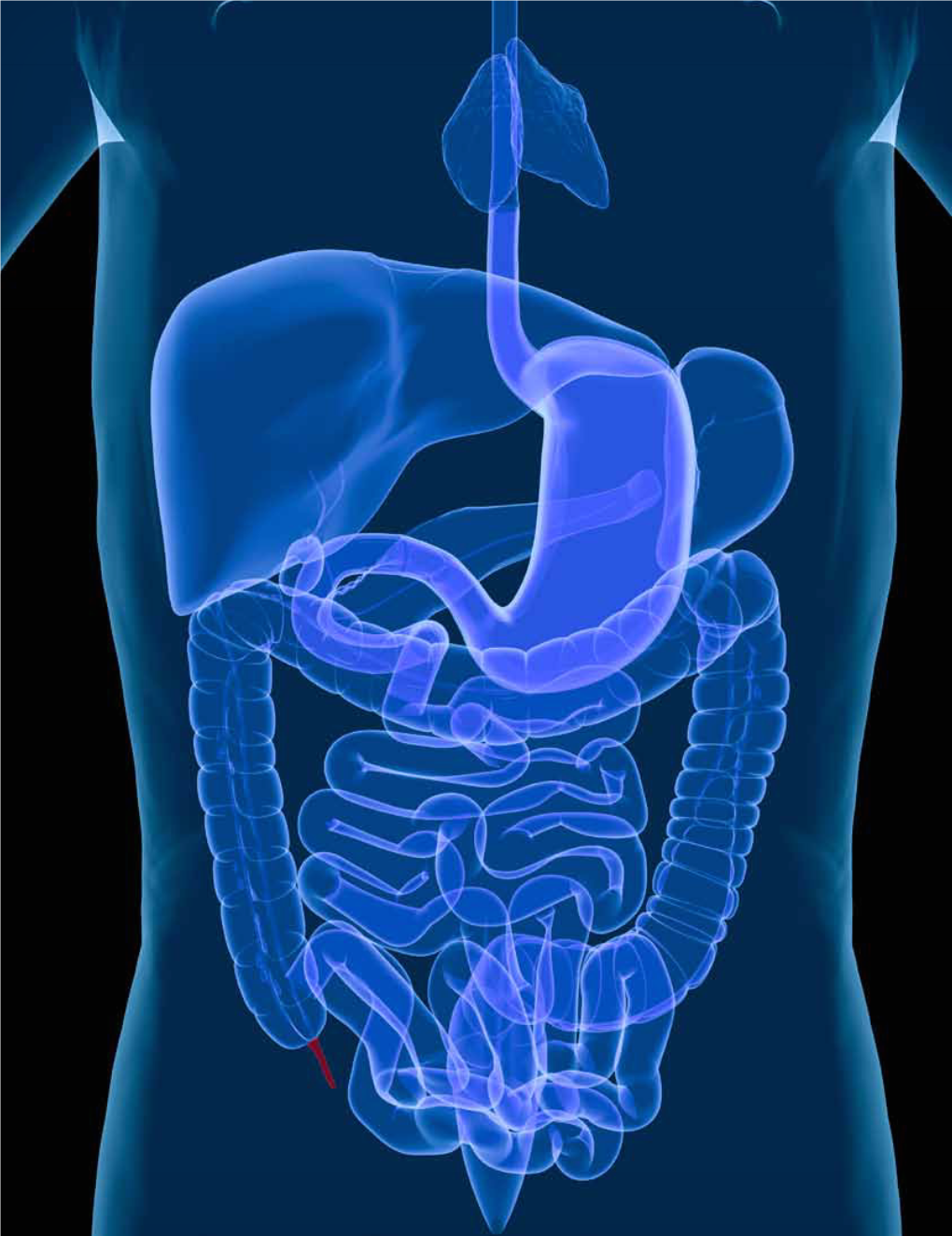
342: Adenocarcinoma of the Appendix
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons' Clinical Practice
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons’ Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Constipation Ian M. Paquette, M.D. • Madhulika Varma, M.D. • Charles Ternent, M.D. Genevieve Melton-Meaux, M.D. • Janice F. Rafferty, M.D. • Daniel Feingold, M.D. Scott R. Steele, M.D. he American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons for functional constipation include at least 2 of the fol- is dedicated to assuring high-quality patient care lowing symptoms during ≥25% of defecations: straining, Tby advancing the science, prevention, and manage- lumpy or hard stools, sensation of incomplete evacuation, ment of disorders and diseases of the colon, rectum, and sensation of anorectal obstruction or blockage, relying on anus. The Clinical Practice Guidelines Committee is com- manual maneuvers to promote defecation, and having less posed of Society members who are chosen because they than 3 unassisted bowel movements per week.7,8 These cri- XXX have demonstrated expertise in the specialty of colon and teria include constipation related to the 3 common sub- rectal surgery. This committee was created to lead inter- types: colonic inertia or slow transit constipation, normal national efforts in defining quality care for conditions re- transit constipation, and pelvic floor or defecation dys- lated to the colon, rectum, and anus. This is accompanied function. However, in reality, many patients demonstrate by developing Clinical Practice Guidelines based on the symptoms attributable to more than 1 constipation sub- best available evidence. These guidelines are inclusive and type and to constipation-predominant IBS, as well. The not prescriptive. -

OT Resource for K9 Overview of Surgical Procedures
OT Resource for K9 Overview of surgical procedures Prepared by: Hannah Woolley Stage Level 1 2 Gynecology/Oncology Surgeries Lymphadenectomy (lymph node dissection) Surgical removal of lymph nodes Radical: most/all of the lymph nodes in tumour area are removed Regional: some of the lymph nodes in the tumour area are removed Omentectomy Surgical procedure to remove the omentum (thin abdominal tissue that encases the stomach, large intestine and other abdominal organs) Indications for omenectomy: Ovarian cancer Sometimes performed in combination with TAH/BSO Posterior Pelvic Exenteration Surgical removal of rectum, anus, portion of the large intestine, ovaries, fallopian tubes and uterus (partial or total removal of the vagina may also be indicated) Indications for pelvic exenteration Gastrointestinal cancer (bowel, colon, rectal) Gynecological cancer (cervical, vaginal, ovarian, vulvar) Radical Cystectomy Surgical removal of the whole bladder and proximal lymph nodes In men, prostate gland is also removed In women, ovaries and uterus may also be removed Following surgery: Urostomy (directs urine through a stoma on the abdomen) Recto sigmoid pouch/Mainz II pouch (segment of the rectum and sigmoid colon used to provide anal urinary diversion) 3 Radical Vulvectomy Surgical removal of entire vulva (labia, clitoris, vestibule, introitus, urethral meatus, glands/ducts) and surrounding lymph nodes Indication for radical vulvectomy Treatment of vulvar cancer (most common) Sentinel Lymph Node Dissection (SLND) Exploratory procedure where the sentinel lymph node is removed and examined to determine if there is lymph node involvement in patients diagnosed with cancer (commonly breast cancer) Total abdominal hysterectomy/bilateral saplingo-oophorectomy (TAH/BSO) Surgical removal of the uterus (including cervix), both fallopian tubes and ovaries Indications for TAH/BSO: Uterine fibroids: benign growths in the muscle of the uterus Endometriosis: condition where uterine tissue grows on structures outside the uterus (i.e. -

Information for Patients Having a Sigmoid Colectomy
Patient information – Pre-operative Assessment Clinic Information for patients having a sigmoid colectomy This leaflet will explain what will happen when you come to the hospital for your operation. It is important that you understand what to expect and feel able to take an active role in your treatment. Your surgeon will have already discussed your treatment with you and will give advice about what to do when you get home. What is a sigmoid colectomy? This operation involves removing the sigmoid colon, which lies on the left side of your abdominal cavity (tummy). We would then normally join the remaining left colon to the top of the rectum (the ‘storage’ organ of the bowel). The lines on the attached diagram show the piece of bowel being removed. This operation is done with you asleep (general anaesthetic). The operation not only removes the bowel containing the tumour but also removes the draining lymph glands from this part of the bowel. This is sent to the pathologists who will then analyse each bit of the bowel and the lymph glands in detail under the microscope. This operation can often be completed in a ‘keyhole’ manner, which means less trauma to the abdominal muscles, as the biggest wound is the one to remove the bowel from the abdomen. Sometimes, this is not possible, in which case the same operation is done through a bigger incision in the abdominal wall – this is called an ‘open’ operation. It does take longer to recover with an open operation but, if it is necessary, it is the safest thing to do. -

Appendix Cancer and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei (PMP) a Guide for People Affected by Cancer
Cancer information fact sheet Understanding Appendix Cancer and Pseudomyxoma Peritonei (PMP) A guide for people affected by cancer This fact sheet has been prepared What is appendix cancer? to help you understand more about Appendix cancer occurs when cells in the appendix appendix cancer and pseudomyxoma become abnormal and keep growing and form a peritonei (PMP). mass or lump called a tumour. Many people look for support after The type of cancer is defined by the particular being diagnosed with a cancer that cells that are affected and can be benign (non- is rare or less common than other cancerous) or malignant (cancerous). Malignant cancer types. This fact sheet includes tumours have the potential to spread to other information about how these cancers parts of the body through the blood stream or are diagnosed and treated, as well as lymph vessels and form another tumour at a where to go for additional information new site. This new tumour is known as secondary and support services. cancer or metastasis. Many people feel shocked and upset when told they have cancer. You may experience strong emotions The abdomen after a cancer diagnosis, especially if your cancer is rare or less common like appendix cancer or PMP. A feeling of being alone is usual with rare cancers, and you might be worried about how much is known about your type of cancer as well as how it will be managed. You may also be concerned about the cancer coming back after treatment. Linking into local support services (see last page) can help overcome feelings of isolation and will give you information that you may find useful. -

Mucocele of the Appendix - Appendectomy Or Colectomy?
Original Article Mucocele of the appendix - appendectomy or colectomy? JANDUÍ GOMES DE ABREU FILHO1, ERIVALDO FERNANDES DE LIRA1 1Service of Coloproctology of Hospital de Base do Distrito Federal (HBDF), Secretariat of Health in Distrito Federal - Brasília (DF), Brazil. FILHO JGDA; LIRA EFD. Mucocele of the appendix - appendectomy or colectomy? Rev bras Coloproct, 2011;31(3): 276-284. ABSTRACT: Mucocele of the appendix is a rare disease. It can be triggered by benign or malignant diseases, which cause the obstruc- tion of the appendix and the consequent accumulation of mucus secretion. The preoperative diagnosis is difficult due to non-specific clinical manifestations of the disease. Imaging tests can suggest the diagnosis. The treatment is always surgical and depends on the integrity and size of the appendix base and on the histological type of the original lesion. The prognosis is good in cases of integrity of the appendix. The perforation of the appendix and subsequent extravasation of its contents into the abdominal cavity may lead to pseudomyxoma peritonei, which has very poor prognosis if not treated properly. Keywords: mucocele; appendix; pseudomyxoma peritonei; treatment. INTRODUCTION first one defends the right colectomy as a treatment9, and the second one recommends only appendecto- The mucocele of the appendix was first de- my10. Despite the different adopted conducts, in both scribed in 1842 by Rokitansky1. This disease is reported cases a cystadenoma was diagnosed in the considered as a rare lesion of the appendix, which appendix; the choice was for elective surgery. is found in 0.2 to 0.3% of the appendectomies2. It The objective of this review is to analyze liter- is characterized by the dilation of the organ lumen ature as to mucocele, especially regarding diagnosis with mucus accumulation, being more frequent and treatment, besides discussing follow-up and prog- among individuals aged 50 years or more3,4. -

Direct Oral Anticoagulants Use in the Setting of Bariatric Surgery and Feeding Tubes Excellence.Acforum.Org
Rapid Resource Direct Oral Anticoagulants Use in the Setting of Bariatric Surgery and Feeding Tubes excellence.acforum.org ACE Rapid Resources are not informed practice guidelines; they are Anticoagulation Forum, Inc.’s best recommendations based on (DOACs) NOTES current knowledge, and no warranty or guaranty is expressed or implied. The content provided is for informational purposes for medical • DOACs are absorbed at various professionals only and is not intended to be used or relied upon by them as specific medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment, the locations throughout the determination of which remains the responsibility of the medical professionals for their patients. gastrointestinal tract. Bariatric Surgery (See Table 1) • Bariatric surgery results in weight FIGURE 1 – Types of Bariatric Surgery loss by reducing stomach volume (which results in a more alkaline pH) A B C D and/or reducing effective intestinal surface area which results in malabsorption. • There is very little evidence regarding safety and efficacy of DOACs in patients with a history of bariatric surgery or requiring DOAC administration via a feeding tube. A. Adjustable gastric banding (AGB): Adjustable silicone band placed around stomach to create a smaller pouch. • This document was compiled utilizing current literature incorporating case B. Roux-en-Y gastric bypass (RYGB): reports, package inserts, and Stomach stapled to form gastric pouch that connects to distal jejunum, excluding the duodenum and proximal jejunum. pharmacokinetic studies as no current C. Gastrectomy (partial or total): randomized controlled trials are Sleeve gastrectomy results in longitudinal resection of 80% of stomach. available. As always, clinical judgment D. Biliopancreatic diversion with duodenal switch (BPD-DS): and a shared decision making Gastric pouch reattached more distally to terminal ileum resulting in considerable reduction in absorptive surface approach should be utilized. -

Hybrid Procedure Offers a Less Invasive Alternative to Colectomy
The better way to get better Hybrid procedure offers a less invasive alternative to colectomy Insufflation gas provides important advantage The colonoscopy-laparoscopy procedure is made possible through the combined skills of the gastroenterologist and laparoscopic surgeon, and the use of CO2 rather than ambient air for insufflation — the introduction of gas into the colon to improve visibility. CO2 is more quickly absorbed by the gastrointestinal tract and results in less bowel distension, giving the laparoscopic surgeon a better field of vision within the abdominal cavity. © Copyright Olympus. Used with permission. “Some patients who would have required a bowel resection can instead benefit from this A new, minimally invasive procedure that is a hybrid of colonoscopy and less invasive procedure. We’re laparoscopy is proving to be a safe and effective alternative to open colectomy using this combined technique (removal of part of the colon) for patients with benign colon polyps that are as a way for patients to avoid colectomy,” explains James not removable endoscopically. Yoo, M.D., a colorectal surgeon Patients who undergo this hybrid procedure experience less pain and often go at UCLA. “This procedure home after only one or two days. Scarring and wound complications are minimal involves tiny incisions for the as the laparoscopic surgeon makes only small, keyhole incisions in the abdomen laparoscopic instruments and patients stay in the hospital only rather than the long incision characteristic of a traditional colectomy. a day or two.” WWW.UCLAHEALTH.ORG 1-800-UCLA-MD1 (1-800-825-2631) Who can benefit from the procedure? Participating When a routine colonoscopy reveals polyps, they are usually removed at the Physicians time of the procedure as a precaution against their progression to cancer. -

Carcinoid Tumor of Appendix: Review of Consecutive 5131 Appendectomy
J Surg Med. 2018;2(2):134-136. Research article DOI: 10.28982/josam.414055 Araştırma makalesi Carcinoid tumor of appendix: Review of consecutive 5131 appendectomy Apendiksin karsinoid tümörü: Ardışık 5131 apendektominin incelemesi İlyas Kudaş 1, Olgun Erdem 2, Ahmet Topçu 2, Abdullah Şişik 2 1 Department of General Surgery, Abstract Tekman State Hospital, Erzurum, Aim: Appendiceal carcinoid tumor (neuroendocrine tumor) is rarely seen, and it is frequently found incidentally Turkey after evaluation of appendectomy specimen. Histopathologically, the appendiceal carcinoid tumor is usually the 2 Department of General Surgery, University of Health Science, Umraniye type of enterochromafine cell and stems from a sub-epithelial cell population that differs from the Education and Research Hospital, neuroendocrine tumor in other regions. Although it is often detected in appendectomy, appendiceal one is the Istanbul, Turkey most common type of primary malignant lesion and is detected in 0.3-0.9% of patients with appendectomy. In this study, it is intended to present an appendix carcinoid tumor series that is diagnosed incidentally after appendectomy. Methods: 5131 appendectomy that was performed between years of 2009 and 2017 constituted the study universe. 35 (0.68%) patients diagnosed with carcinoid tumors were evaluated in the histopathological examination. The patients were recorded in terms of demographic data, clinical status, histopathology and surgical reports. Additional operations and follow-up data were noted. Results: 21 of the 35 patients with appendiceal carcinoid tumors were males, and 14 were women. Male/Female ratio was 1.5. The mean age of the patients was 27.3±11.0. There was no difference in terms of gender and age with other appendectomy patients who diagnosed non-tumor (p=0.476 and p=0.413, respectively). -

Integrated Clinico-Molecular Profiling of Appendiceal Adenocarcinoma
www.nature.com/bjc ARTICLE Molecular Diagnostics Integrated clinico-molecular profiling of appendiceal adenocarcinoma reveals a unique grade-driven entity distinct from colorectal cancer Kanwal Raghav 1, John P. Shen1, Alexandre A. Jácome1, Jennifer L. Guerra1, Christopher P. Scally2, Melissa W. Taggart3, Wai C. Foo3, Aurelio Matamoros4, Kenna R. Shaw5, Keith Fournier2, Michael J. Overman1 and Cathy Eng1 BACKGROUND: Appendiceal adenocarcinoma (AA) is an orphan disease with unique clinical attributes but often treated as colorectal cancer (CRC). Understanding key molecular differences between AA and CRC is critical. METHODS: We performed retrospective analyses of AA patients (N = 266) with tumour and/or blood next-generation sequencing (NGS) (2013–2018) with in-depth clinicopathological annotation. Overall survival (OS) was examined. For comparison, CRC cohorts annotated for sidedness, consensus molecular subtypes (CMS) and mutations (N = 3283) were used. RESULTS: Blood-NGS identified less RAS/GNAS mutations compared to tissue-NGS (4.2% vs. 60.9%, P < 0.0001) and showed poor concordance with tissue for well-/moderately differentiated tumours. RAS (56.2%), GNAS (28.1%) and TP53 (26.9%) were most frequent mutations. Well/moderately differentiated tumours harboured more RAS (69.2%/64.0% vs. 40.5%) and GNAS (48.7%/32.0% vs. 10.1%) while moderate/poorly differentiated tumours had more TP53 (26.0%/27.8% vs. 7.7%) mutations. Appendiceal adenocarcinoma (compared to CRC) harboured significantly fewer APC (9.1% vs. 55.4%) and TP53 (26.9% vs. 67.5%) and more GNAS mutations (28.1% vs. 2.0%) (P < 0.0001). Appendiceal adenocarcinoma mutation profile did not resemble either right-sided CRC or any of the four CMS in CRC. -

Impact of Accreditation in Bariatric Surgery Alana Gebhart, B.A.A, Monica Young, M.D.A, Michael Phelan, Ph.D.B, Ninh T
Surgery for Obesity and Related Diseases 10 (2014) 767–773 Original article Impact of accreditation in bariatric surgery Alana Gebhart, B.A.a, Monica Young, M.D.a, Michael Phelan, Ph.D.b, Ninh T. Nguyen, M.D.a,* aDepartment of Surgery, University of California, Irvine School of Medicine, Irvine, California bDepartment of Statistics, University of California, Irvine School of Medicine, Irvine, California Received October 16, 2013; accepted March 2, 2014 Abstract Background: Several studies have shown improved outcomes associated with accredited bariatric centers. The aim of our study was to examine the outcomes of bariatric surgery performed at accredited versus nonaccredited centers using a nationally representative database. Additionally, we aimed to determine if the presence of bariatric surgery accreditation could lead to improved out- comes for morbidly obese patients undergoing other general laparoscopic operations. Methods: Using the Nationwide Inpatient Sample database, for data between 2008 and 2010, clinical data of morbidly obese patients who underwent bariatric surgery, laparoscopic antireflux surgery, cholecystectomy, and colectomy were analyzed according to the hospital’s bariatric accreditation status. Results: A total of 277,068 bariatric operations were performed during the 3-year period, with 88.4% of cases performed at accredited centers. In-hospital mortality was significantly lower at accredited compared to nonaccredited centers (.08% versus .19%, respectively). Multivariate anal- ysis showed that nonaccredited centers had higher risk-adjusted mortality for bariatric procedures compared to accredited centers (odds ratio [OR] 3.1, P o .01). Post hoc analysis showed improved mortality for patients who underwent gastric bypass and sleeve gastrectomy at accredited centers compared to nonaccredited centers (.09% versus .27%, respectively, P o .01). -

PE940 Colectomy
Patient and Family Education Colectomy Surgical treatment for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) and Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) What is a colectomy? A colectomy is a surgery that removes A colectomy is a surgery that removes the colon, or large intestine. The the colon, or large colectomy and reconstruction of your child’s digestive system may take one, intestine. The two or three surgeries. The colectomy and reconstruction will be done under colectomy and general anesthesia. This means that your child will be given medicine to make reconstruction of the them sleep without pain during the surgery. digestive system may The colectomy can be done laparoscopically or using an “open” surgery. In take one, two or three laparoscopic surgery, the surgeon makes a few small incisions and inserts a surgeries. thin, lighted tube with a camera and the surgical tools. An open surgery uses one larger incision. Your child’s surgeon will discuss with you the benefits of each type of surgery. Stomach Large Small Intestine Intestine (colon) Rectum Anus Appendix Picture 1. The digestive system. The shaded areas are removed during the colectomy. Why does my child need a colectomy? Your child may need a colectomy for Ulcerative Colitis (UC) or Crohns disease if medicines and changes in what they eat and drink don’t control the symptoms. Children with Familial Adenomatous Polyposis (FAP) need a colectomy to remove the chance of getting colon cancer. Children with UC may also have a greater chance of getting cancer later on in life. The rest of this handout will describe surgeries usually used for UC and FAP but not commonly for Crohns. -

Focus Group on Laparoscopic Colectomy Education As Endorsed
Guidelines Focus Group on Laparoscopic Colectomy Education as Endorsed by The American Society of Colon and Rectal Surgeons (ASCRS) and The Society of American Gastrointestinal and Endoscopic Surgeons (SAGES) James Fleshman, M.D.,1 Peter Marcello, M.D.,2 Michael J. Stamos, M.D.,3 Steven D. Wexner, M.D.4 1 Department of Colorectal Surgery, Washington University, St. Louis, Missouri 2 Department of Colorectal Surgery, Lahey Clinic, Burlington, Massachusetts 3 Department of Surgery, Division of Colon and Rectal Surgery, University of California, Irvine, Medical Center, Orange, California 4 Department of Colorectal Surgery, Cleveland Clinic Florida, Weston, Florida INTRODUCTION developing training programs for their members and accrediting courses, which are provided by the mem- A Focus Group on Laparoscopic Colectomy Edu- bers on a local level. This recommendation for train- cation was convened and has developed a guideline ing was developed by a focus group of surgeons for educating trained surgeons in the use of lap- and industry representatives with extensive experi- aroscopic colectomy for colorectal disease. This ence in training fellows in ACGME (Accreditation guideline has been developed to address the increased Council For Graduate Medical Education) – approved interest in laparoscopic colectomy for cancer. The training programs, teaching in a laparoscopic train- group has made recommendations regarding the ing program sponsored by the Association of Pro- content, faculty, and training model for hands-on gram Directors in Colon and Rectal Surgery, and courses in laparoscopic colorectal surgery. This guide- training general surgeons in industry and institution- line is intended to assist societies, course directors, al-sponsored training programs. The group was teaching institutions, and national organizations in convened at Washington University in St.