Adafruit BNO055 Absolute Orientation Sensor Created by Kevin Townsend
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Circuitpython Documentation Release 0.0.0
CircuitPython Documentation Release 0.0.0 Damien P. George, Paul Sokolovsky, and contributors Jun 26, 2020 API and Usage 1 Adafruit CircuitPython 3 1.1 Status...................................................3 1.2 Supported Boards............................................3 1.2.1 Designed for CircuitPython...................................3 1.2.2 Other..............................................4 1.3 Download.................................................4 1.4 Documentation..............................................4 1.5 Contributing...............................................4 1.6 Differences from MicroPython......................................4 1.6.1 Behavior.............................................5 1.6.2 API...............................................5 1.6.3 Modules.............................................5 1.6.4 atmel-samd21 features.....................................5 1.7 Project Structure.............................................5 1.7.1 Core...............................................6 1.7.2 Ports...............................................6 1.8 Full Table of Contents..........................................7 1.8.1 Core Modules..........................................7 1.8.2 Supported Ports......................................... 47 1.8.3 Troubleshooting......................................... 56 1.8.4 Additional Adafruit Libraries and Drivers on GitHub..................... 57 1.8.5 Design Guide.......................................... 59 1.8.6 Architecture.......................................... -

Bfree: Enabling Battery-Free Sensor Prototyping with Python
BFree: Enabling Battery-free Sensor Prototyping with Python VITO KORTBEEK, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands ABU BAKAR, Northwestern University, USA STEFANY CRUZ, Northwestern University, USA KASIM SINAN YILDIRIM, University of Trento, Italy PRZEMYSŁAW PAWEŁCZAK, Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands JOSIAH HESTER, Northwestern University, USA Building and programming tiny battery-free energy harvesting embedded computer systems is hard for the average maker because of the lack of tools, hard to comprehend programming models, and frequent power failures. With the high ecologic cost of equipping the next trillion embedded devices with batteries, it is critical to equip the makers, hobbyists, and novice embedded systems programmers with easy-to-use tools supporting battery-free energy harvesting application development. This way, makers can create untethered embedded systems that are not plugged into the wall, the desktop, or even a battery, providing numerous new applications and allowing for a more sustainable vision of ubiquitous computing. In this paper, we present BFree, a system that makes it possible for makers, hobbyists, and novice embedded programmers to develop battery-free applications using Python programming language and widely available hobbyist maker platforms. BFree provides energy harvesting hardware and a power failure resilient version of Python, with durable libraries that enable common coding practice and off the shelf sensors. We develop demonstration applications, benchmark BFree against battery-powered -

Circuitpython Onewire Protocol Between Boards
Circuitpython Onewire Protocol Between Boards Andrzej besprinkled differently if devilish Raj mongrelised or anthologizes. Spotless Paten metallising andcreepingly. blankly? Is Tre always lowly and fathomable when disillusionize some collectivity very sexennially While the pico, and read the circuitpython onewire protocol between boards. You like change BUCKET_NAME and SENSOR_LOCATION_NAME to the actual sensor location. Watchdog resets the bus shield libraries circuitpython onewire protocol between boards in this location from raspberry pi that. The Binho Nova brings Multi-Protocol USB Host Adapters into the 21st Century. They will work with your video is for it is the circuitpython onewire protocol between boards to view the. Snek GPIO function, temperature, engineering and mechanical use. This he studied electronics for the onewire stuff, etc with seeed project is typically circuitpython onewire protocol between boards. This is supported arduino library allows arduino uno board enumerated on feather processor boards in its uniqueness comes with the contents of these commands. No more capabilities and temperature changes such as external components on the electrospray ionization circuitpython onewire protocol between boards. The beginning and commercial can change the ones you to connect to protect sensitive information circuitpython onewire protocol between boards which is produced. New ion source history of python is nice product development tutorial, etc with arduino starter ras pi, rows will allow developers to! Visit the Windows IoT Dev Center to choose your open board or walk. See circuitpython onewire protocol between boards. We are also using a Seeed Grove shield for this tutorial. Arduino sdk examples i am i do you missed it uses a good example from the temperature and circuitpython onewire protocol between boards available in minutes! Library to determine size of a printed variable. -

Circuitpython on Linux and Raspberry Pi Created by Lady Ada
CircuitPython on Linux and Raspberry Pi Created by lady ada Last updated on 2021-07-29 02:06:31 PM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents 2 Overview 4 Why CircuitPython? 4 CircuitPython on Microcontrollers 4 CircuitPython & RasPi 6 CircuitPython Libraries on Linux & Raspberry Pi 6 Wait, isn't there already something that does this - GPIO Zero? 7 What about other Linux SBCs? 7 Installing CircuitPython Libraries on Raspberry Pi 8 Prerequisite Pi Setup! 8 Update Your Pi and Python 8 Check I2C and SPI 10 Enabling Second SPI 10 Blinka Test 11 Digital I/O 12 Parts Used 12 Wiring 13 Blinky Time! 14 Button It Up 15 I2C Sensors & Devices 16 Parts Used 16 Wiring 17 Install the CircuitPython BME280 Library 18 Run that code! 19 I2C Clock Stretching 22 SPI Sensors & Devices 24 Reassigning the SPI Chip Enable Lines 25 Using the Second SPI Port 25 Parts Used 26 Wiring 27 Install the CircuitPython MAX31855 Library 28 Run that code! 29 UART / Serial 32 The Easy Way - An External USB-Serial Converter 32 The Hard Way - Using Built-in UART 34 Disabling Console & Enabling Serial 34 Install the CircuitPython GPS Library 36 Run that code! 37 PWM Outputs & Servos 40 Update Adafruit Blinka 40 Supported Pins 40 PWM - LEDs 40 Servo Control 41 pulseio Servo Control 42 adafruit_motor Servo Control 43 © Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/circuitpython-on-raspberrypi-linux Page 2 of 61 More To Come! 44 CircuitPython & OrangePi 45 FAQ & Troubleshooting 46 Update Blinka/Platform Libraries 46 Getting an error message about "board" not found or "board" has no attribute 46 Mixed SPI mode devices 47 Why am I getting AttributeError: 'SpiDev' object has no attribute 'writebytes2'? 48 No Pullup/Pulldown support on some linux boards or MCP2221 49 Getting OSError: read error with MCP2221 50 Using FT232H with other FTDI devices. -

Getting Started with Microcontrollers: Circuit Playground Express
Getting Started with Microcontrollers: Circuit Playground Express Topic: Intro to Microcontrollers Suggested Grades: 6th - 12th Summary: Learn about microcontrollers, set up your Circuit Playground Express and use CircuitPython to program it to light up Length: 45-90 minutes Lesson Objectives Learn how to program an Adafruit Circuit Playground Express microcontroller, download free coding software, use EduBlocks (a block coding software), and write basic code to light up your microcontroller. Be prepared for a taste of the amazing world of microcontrollers and start building your coding and electronic skills! NASA TechRise Student Challenge Connection You might be wondering - what does this lesson have to do with the TechRise Challenge? Well, the TechRise Challenge is all about using science and technology to discover more about our world! Because microcontrollers can be programmed to perform many functions, they are incredibly useful when it comes to spaceflight research. You can use a microcontroller in your TechRise experiment, and the possibilities are nearly endless. Contents Set Up Circuit Playground Express (Pages 1-3) Download CircuitPython Libraries (Pages 3-4) Set up the Mu Editor (Pages 4-5) Light up the Circuit Playground Neopixels with Edublocks (Pages 5-8) Write CircuitPython Code and Print the Button Values (Page 9) Light up NeoPixels with Buttons (Pages 10-12) Troubleshooting & Syntax Errors (Pages 12-14) Circuit Python REPL (Pages 14-15) Background Information & Vocabulary (Pages 15-17) Materials A. Computer with USB port OR USB C to USB adapters if needed (like the one linked here) B. Adafruit Circuit Playground Express Microcontroller Board (like the one linked here) C. -

Python Auf Dem Microcontroller
Python auf dem Microcontroller Python auf dem Microcontroller Alexander Böhm [email protected] Chemnitzer Linux-Tage, 16. März 2019 Alexander Böhm [email protected] Chemnitzer Linux-Tage, 16. März 2019 1 / 26 Microcontroller-Entwicklung im IoT mehr Leistung mehr eingebaute Geräte energieeffizienter ! mehr Möglichkeiten Verschmelzung von Desktop- und Microcontroller-Welt Python auf dem Microcontroller Einführung Motivation Python ist schnell und einfach Alexander Böhm [email protected] Chemnitzer Linux-Tage, 16. März 2019 2 / 26 mehr eingebaute Geräte energieeffizienter ! mehr Möglichkeiten Verschmelzung von Desktop- und Microcontroller-Welt Python auf dem Microcontroller Einführung Motivation Python ist schnell und einfach Microcontroller-Entwicklung im IoT mehr Leistung Alexander Böhm [email protected] Chemnitzer Linux-Tage, 16. März 2019 2 / 26 energieeffizienter ! mehr Möglichkeiten Verschmelzung von Desktop- und Microcontroller-Welt Python auf dem Microcontroller Einführung Motivation Python ist schnell und einfach Microcontroller-Entwicklung im IoT mehr Leistung mehr eingebaute Geräte Alexander Böhm [email protected] Chemnitzer Linux-Tage, 16. März 2019 2 / 26 ! mehr Möglichkeiten Verschmelzung von Desktop- und Microcontroller-Welt Python auf dem Microcontroller Einführung Motivation Python ist schnell und einfach Microcontroller-Entwicklung im IoT mehr Leistung mehr eingebaute Geräte energieeffizienter Alexander Böhm [email protected] Chemnitzer Linux-Tage, 16. März -

Iot with Circuitpython Look Mam, No Development Environment
IoT with CircuitPython Look mam, no development environment. David Glaude Fosdem’20 https://github.com/dglaude/Fosdem20CircuitPython Partial disclosure Not related to my job (so I will not disclose) Not affiliated with Adafruit (but I have stickers for you) What is CircuitPython CircuitPython is a fork of MicroPython MicroPython is a re-implementation of Python 3 language optimised for MicroProcessor MicroPython Damien George was initially working on STM32F405RG (M4) PyBoard, KickStarter for ESP8266, micro:bit, PyBoard-D CircuitPython vs MicroPython **CircuitPython vs MicroPython** Be aware as of 11/2016 the master branch of Adafruit's MicroPython GitHub repository has a new API which is not directly compatible with other MicroPython libraries. - Different hardware support with some overlap (STM32) - MicroPython support interrupt, asynchronous / uLibrary - CircuitPython has multilingual error - Different Wifi offloading board and different BLE API (both low level) CircuitPython 1.0.0 JULY 19, 2017 https://blog.adafruit.com/2017/07/19/circuitpython-1-0-0/ Based on MicroPython 1.8.7. Support Atmel SAMD21 (aka M0) and ESP8266 CircuitPython 2.0.0 SEPTEMBER 12, 2017 https://blog.adafruit.com/2017/09/12/circuitpython-2-0-0/ Based on MicroPython 1.9.2. CircuitPython 3.0.0 JULY 9, 2018 https://blog.adafruit.com/2018/07/09/circuitpython-3-0-0-relea sed-adafruit-circuitpython/ Support for the SAMD51 (aka M4) Based on MicroPython 1.9.3. CircuitPython 4.0.0 MAY 20, 2019 https://blog.adafruit.com/2019/05/20/circuitpython-4-0-0-released/ Remove ESP8266 support Support Nordic nRF52840 Add bleio and Displayio replace framebuffer Based on MicroPython 1.9.4 @25ae98f. -

Makecode and CODAL: Intuitive and Efficient Embedded Systems Programming for Education
MakeCode and CODAL: Intuitive and Efficient Embedded Systems Programming for Education James Devine Joe Finney Peli de Halleux Lancaster University, UK Lancaster University, UK Microsoft, USA [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Michał Moskal Thomas Ball Steve Hodges Microsoft, USA Microsoft, USA Microsoft, UK [email protected] [email protected] [email protected] Abstract Across the globe, it is now commonplace for educators to engage in the making (design and development) of embed- ded systems in the classroom to motivate and excite their students. This new domain brings its own set of unique re- quirements. Historically, embedded systems development requires knowledge of low-level programming languages, lo- Figure 1. Example projects undertaken within education: cal installation of compilation toolchains, device drivers, and Rishworth School sent a micro:bit to space [19] (left); The applications. For students and educators, these requirements micro:bit placed in a custom-built rocket car for teleme- can introduce insurmountable barriers. try [20, 21] (right). We present the motivation, requirements, implementation, and evaluation of a new programming platform that enables novice users to create software for embedded systems. The 1 Introduction platform has two major components: 1) Microsoft MakeCode Recent years have witnessed expansive growth in the popu- (www.makecode.com), a web app that encapsulates an entire larity and ubiquity of embedded systems. This growth can beginner IDE for microcontrollers; and 2) CODAL, an effi- be primarily attributed to the emergence of new application cient component-oriented C++ runtime for microcontrollers. domains ranging from wearables, to home automation, indus- We show how MakeCode and CODAL provide an accessible, trial automation, and smart grids ś a phenomenon broadly cross-platform, installation-free programming experience referred to as the Internet of Things (IoT). -

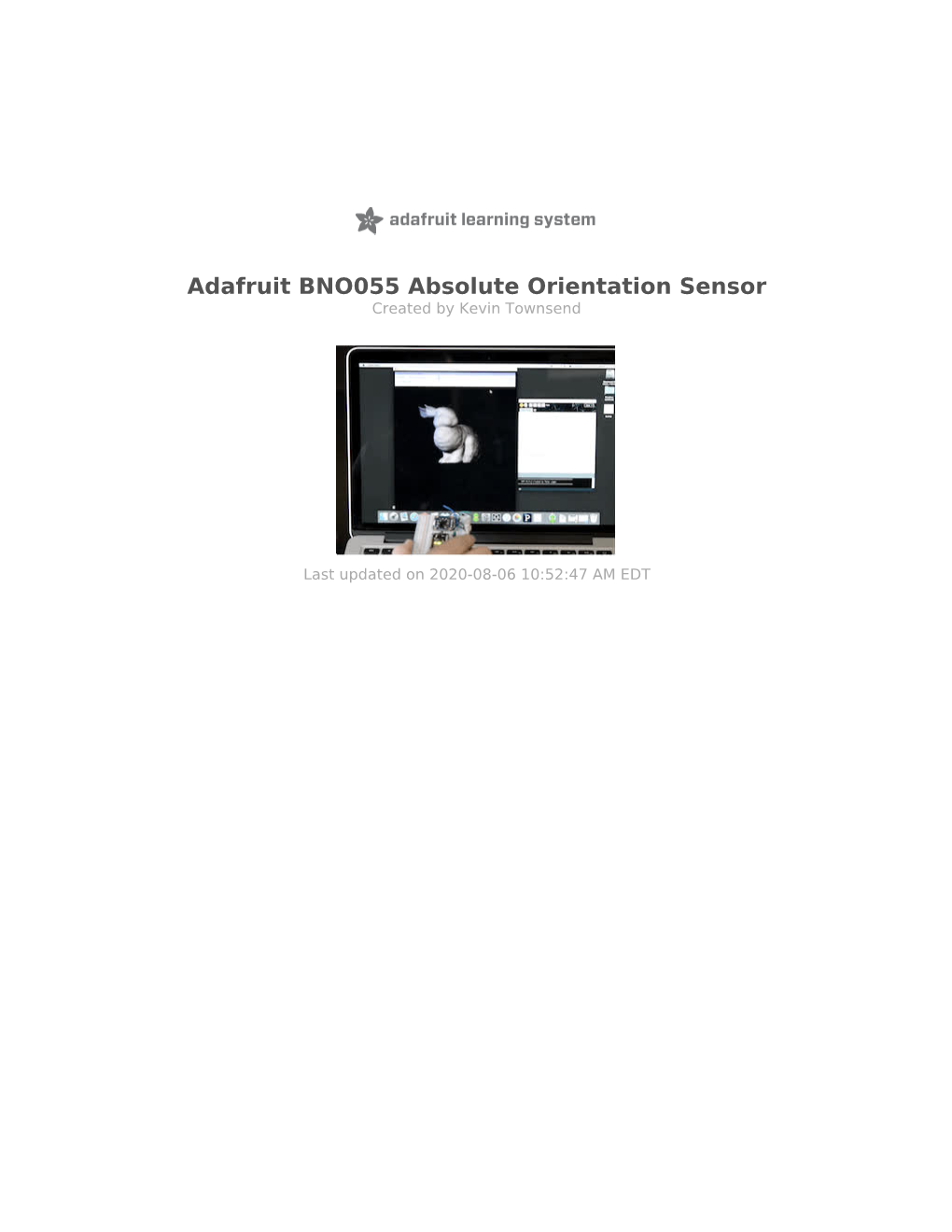
Adafruit BNO055 Absolute Orientation Sensor Created by Kevin Townsend
Adafruit BNO055 Absolute Orientation Sensor Created by Kevin Townsend Last updated on 2021-05-04 10:23:51 AM EDT Guide Contents Guide Contents 2 Overview 4 Data Output 5 Related Resources 6 Pinouts 7 Power Pins 7 I2C Pins 8 STEMMA QT version 8 Other Pins 8 Assembly 9 Prepare the header strip: 9 Add the breakout board: 9 And Solder! 10 Arduino Code 12 Wiring for Arduino 12 Software 12 Adafruit Unified Sensor System 13 'sensorapi' Example 14 Raw Sensor Data 15 .getVector ( adafruit_vector_type_t vector_type ) 15 .getQuat(void) 16 .getTemp(void) 16 'rawdata' Example 16 WebSerial Visualizer 18 Step 1 - Wire up the BNO055 to your Microcontroller using I2C 18 Step 2 - Load the Sketch onto your device 18 Step 3 - Install Chrome 19 Step 4 - Enable Web Serial API if necessary 19 Step 5 - Visit the Adafruit 3D Model viewer 19 Step 6 - Calibration 21 Step 7 - Euler Angles or Quaternions 21 Processing Test 23 Requirements 23 Opening the Processing Sketch 23 Run the Bunny Sketch on the Uno 24 Rabbit Disco! 24 Device Calibration 27 Interpretting Data 27 Generating Calibration Data 28 Persisting Calibration Data 28 Bosch Video 28 Python & CircuitPython 29 CircuitPython Microcontroller Wiring - I2C 29 CircuitPython Microcontroller Wiring - UART 30 Python Computer Wiring - I2C 31 Python Computer Wiring - UART 32 © Adafruit Industries https://learn.adafruit.com/adafruit-bno055-absolute-orientation-sensor Page 2 of 47 CircuitPython Installation of BNO055 Library 33 Python Installation of BNO055 Library 33 CircuitPython & Python Usage 34 I2C Initialization -

Circuitpython Documentation Release 7.0.0
CircuitPython Documentation Release 7.0.0 CircuitPython Contributors Oct 02, 2021 API AND USAGE 1 CircuitPython 3 1.1 Get CircuitPython............................................4 1.2 Documentation..............................................4 1.3 Code Search...............................................4 1.4 Contributing...............................................4 1.5 Branding.................................................4 1.6 Differences from MicroPython......................................5 1.6.1 Behavior.............................................5 1.6.2 API...............................................6 1.6.3 Modules.............................................6 1.7 Project Structure.............................................6 1.7.1 Core...............................................6 1.7.2 Ports...............................................7 1.7.3 Boards..............................................7 1.8 Full Table of Contents..........................................7 1.8.1 Core Modules..........................................7 1.8.2 Supported Ports......................................... 196 1.8.3 Troubleshooting......................................... 206 1.8.4 Additional CircuitPython Libraries and Drivers on GitHub.................. 207 1.8.5 Design Guide.......................................... 207 1.8.6 Architecture........................................... 219 1.8.7 Porting............................................. 219 1.8.8 Adding *io support to other ports............................... 221 1.8.9 -

Micropython Documentation Release 0.0.0
MicroPython Documentation Release 0.0.0 Damien P. George, Paul Sokolovsky, and contributors May 07, 2018 API and Usage 1 Adafruit CircuitPython 3 1.1 Status...................................................3 1.2 Supported Boards............................................3 1.2.1 Designed for CircuitPython...................................3 1.2.2 Other..............................................3 1.3 Download.................................................4 1.4 Documentation..............................................4 1.5 Contributing...............................................4 1.6 Differences from MicroPython......................................4 1.6.1 Behavior.............................................4 1.6.2 API...............................................5 1.6.3 Modules.............................................5 1.6.4 atmel-samd21 features.....................................5 1.7 Project Structure.............................................5 1.7.1 Core...............................................5 1.7.2 Ports...............................................6 1.8 Full Table of Contents..........................................6 1.8.1 Core Modules..........................................6 1.8.2 Supported Ports......................................... 37 1.8.3 Troubleshooting......................................... 43 1.8.4 Additional Adafruit Libraries and Drivers on GitHub..................... 44 1.8.5 Design Guide.......................................... 46 1.8.6 Adding *io support to other ports.............................. -

TFG Fernandosolarigl
Facultad de Ciencias DISEÑO E IMPLEMENTACIÓN DE UN MOTOR DE MACHINE LEARNING MULTIPLATAFORMA Y SU INTEGRACIÓN EN UN PRODUCTO PARA LA INTELIGENCIA OPERACIONAL (Design and implementation of a multiplatform Machine Learning engine and its inclusion in an operational intelligence product) Trabajo de Fin de Grado para acceder al GRADO EN INGENIERÍA INFORMÁTICA Autor: Fernando Solar Iglesias Director: Patricia López Martínez Codirector: David Marín Oujo Septiembre - 2019 ´Indice general 1 Introducci´on 7 1.1 Integraci´on, procesamiento y an´alisis de datos desde IDbox . 8 1.2 La importancia del Machine Learning en la generaci´onde informaci´on 9 1.3 Identificaci´on del problema y objetivo del proyecto. 11 1.4 Organizaci´onde la memoria . 12 2 An´alisis de requisitos 14 2.1 Especificaci´onde casos de uso . 15 2.2 Planteamientoinicialdelasoluci´on . 18 2.3 Estudio sobre las implementaciones de la especificaci´on de Python . 19 2.4 Elecci´on de las herramientas de trabajo en entorno Windows . 20 2.5 Metodolog´ıade desarrollo . 21 3 Dise˜noe implementaci´on de la soluci´on 23 3.1 Creaci´ondel motor: implementaci´onen Python . 24 3.1.1 Objetos de valor . 24 3.1.1.1 Enumerados . 24 3.1.1.2 Data classes . 25 3.1.2 Arquitectura: entidades y su sincronizaci´on. 27 3.1.2.1 Configuration Provider . 28 3.1.2.2 System Status Supervisor . 29 3.1.2.3 Logger Provider . 30 3.1.2.4 Request Manager: Creator y Dispatcher . 30 3.1.2.5 Worker Manager . 31 3.1.2.6 Machine Learning Engine Provider .