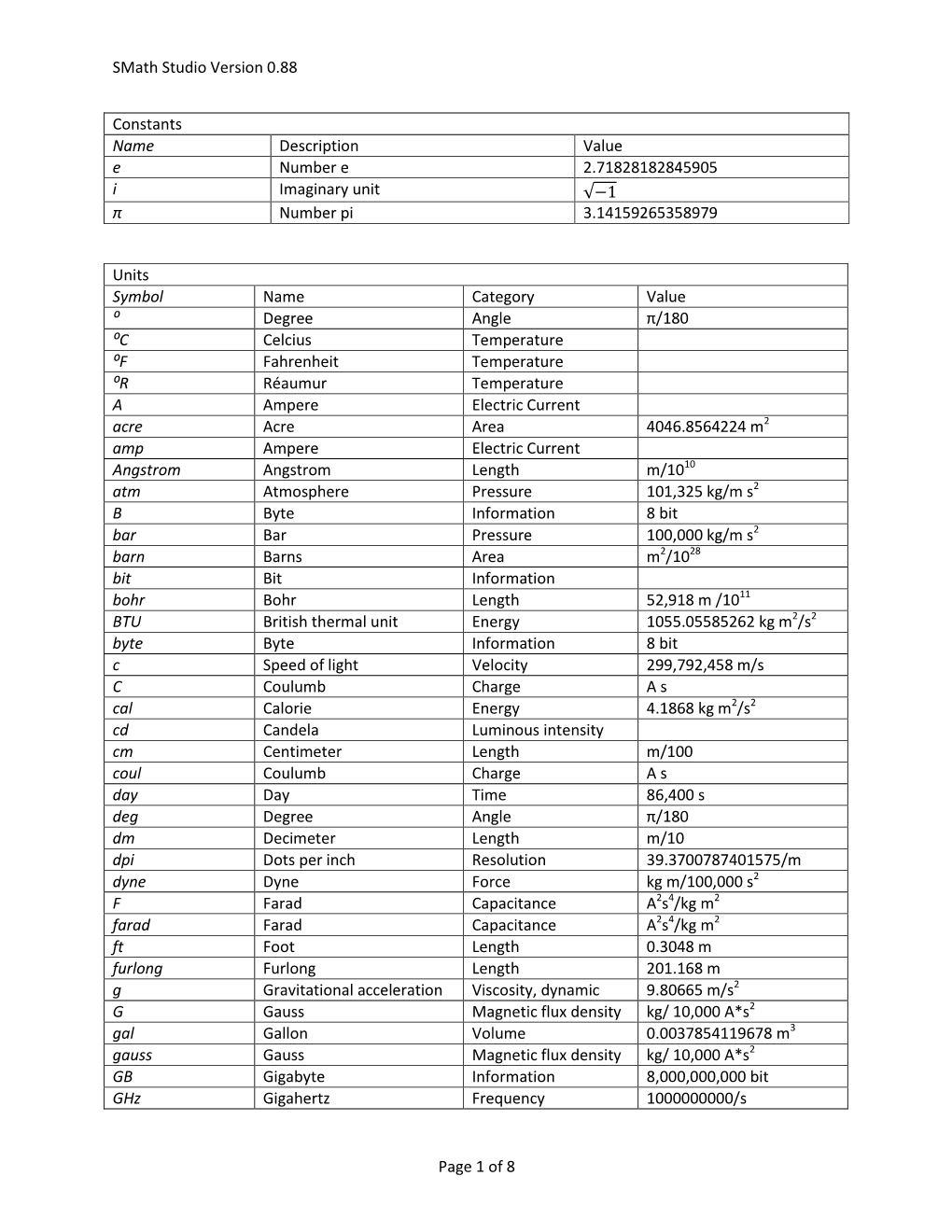
Smath Studio Version 0.88 Page 1 of 8 Constants Name Description
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI)
Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) m kg s cd SI mol K A NIST Special Publication 811 2008 Edition Ambler Thompson and Barry N. Taylor NIST Special Publication 811 2008 Edition Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) Ambler Thompson Technology Services and Barry N. Taylor Physics Laboratory National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, MD 20899 (Supersedes NIST Special Publication 811, 1995 Edition, April 1995) March 2008 U.S. Department of Commerce Carlos M. Gutierrez, Secretary National Institute of Standards and Technology James M. Turner, Acting Director National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 811, 2008 Edition (Supersedes NIST Special Publication 811, April 1995 Edition) Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. Spec. Publ. 811, 2008 Ed., 85 pages (March 2008; 2nd printing November 2008) CODEN: NSPUE3 Note on 2nd printing: This 2nd printing dated November 2008 of NIST SP811 corrects a number of minor typographical errors present in the 1st printing dated March 2008. Guide for the Use of the International System of Units (SI) Preface The International System of Units, universally abbreviated SI (from the French Le Système International d’Unités), is the modern metric system of measurement. Long the dominant measurement system used in science, the SI is becoming the dominant measurement system used in international commerce. The Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of August 1988 [Public Law (PL) 100-418] changed the name of the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and gave to NIST the added task of helping U.S. -

The International System of Units (SI)
NAT'L INST. OF STAND & TECH NIST National Institute of Standards and Technology Technology Administration, U.S. Department of Commerce NIST Special Publication 330 2001 Edition The International System of Units (SI) 4. Barry N. Taylor, Editor r A o o L57 330 2oOI rhe National Institute of Standards and Technology was established in 1988 by Congress to "assist industry in the development of technology . needed to improve product quality, to modernize manufacturing processes, to ensure product reliability . and to facilitate rapid commercialization ... of products based on new scientific discoveries." NIST, originally founded as the National Bureau of Standards in 1901, works to strengthen U.S. industry's competitiveness; advance science and engineering; and improve public health, safety, and the environment. One of the agency's basic functions is to develop, maintain, and retain custody of the national standards of measurement, and provide the means and methods for comparing standards used in science, engineering, manufacturing, commerce, industry, and education with the standards adopted or recognized by the Federal Government. As an agency of the U.S. Commerce Department's Technology Administration, NIST conducts basic and applied research in the physical sciences and engineering, and develops measurement techniques, test methods, standards, and related services. The Institute does generic and precompetitive work on new and advanced technologies. NIST's research facilities are located at Gaithersburg, MD 20899, and at Boulder, CO 80303. -

Commission Services Working Document
COMMISSION OF THE EUROPEAN COMMUNITIES Brussels, 22 December 2006 COMMISSION STAFF WORKING DOCUMENT on units of measurement (Directive 80/181/EEC) EN EN TABLE OF CONTENTS 1. Introduction.................................................................................................................. 3 2. Extension of the international SI-system ..................................................................... 3 3. Multiple indication of SI units ..................................................................................... 4 4. So-called Arbitrary units (U) ....................................................................................... 4 5. Ratios (not expressed in units) ..................................................................................... 5 6. Non-SI Units required by International Treaties in transport ...................................... 5 7. Non-SI Units used in Traditional industries and in new markets ................................ 5 8. Date of Supplementary indications in non-SI units ..................................................... 6 9. Scope of the directive................................................................................................... 7 10. Stakeholder Consultation ............................................................................................. 8 EN 2 EN 1. INTRODUCTION The use of units of measurement is prescribed in the European Union by means of COUNCIL DIRECTIVE 80/181/EEC of 20 December 1979 on the approximation of the laws of the Member States -

The International System of Units (SI)
The International System of Units (SI) m kg s cd SI mol K A NIST Special Publication 330 2008 Edition Barry N. Taylor and Ambler Thompson, Editors NIST SPECIAL PUBLICATION 330 2008 EDITION THE INTERNATIONAL SYSTEM OF UNITS (SI) Editors: Barry N. Taylor Physics Laboratory Ambler Thompson Technology Services National Institute of Standards and Technology Gaithersburg, MD 20899 United States version of the English text of the eighth edition (2006) of the International Bureau of Weights and Measures publication Le Système International d’ Unités (SI) (Supersedes NIST Special Publication 330, 2001 Edition) Issued March 2008 U.S. DEPARTMENT OF COMMERCE, Carlos M. Gutierrez, Secretary NATIONAL INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND TECHNOLOGY, James Turner, Acting Director National Institute of Standards and Technology Special Publication 330, 2008 Edition Natl. Inst. Stand. Technol. Spec. Pub. 330, 2008 Ed., 96 pages (March 2008) CODEN: NSPUE2 WASHINGTON 2008 Foreword The International System of Units, universally abbreviated SI (from the French Le Système International d’Unités), is the modern metric system of measurement. Long the dominant system used in science, the SI is rapidly becoming the dominant measurement system used in international commerce. In recognition of this fact and the increasing global nature of the marketplace, the Omnibus Trade and Competitiveness Act of 1988, which changed the name of the National Bureau of Standards (NBS) to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) and gave to NIST the added task of helping U.S. industry increase its competitiveness, designates “the metric system of measurement as the preferred system of weights and measures for United States trade and commerce.” The definitive international reference on the SI is a booklet published by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM, Bureau International des Poids et Mesures) and often referred to as the BIPM SI Brochure. -

Guide .Or Metric Practice
GUIDE OR METRIC PRACTICE Internationally recognized conventions have been established for standard usage of SI units. Robert A. Nelson ROBERT NELSON is the author of the booklet SI: The International System of Units, 2nd ed. (American Association of Physics Teachers, College Park, Maryland, 1982). He is president of Satellite Engineering Research Corporation, a consulting firm in Bethesda, Maryland, and teaches in the department of aerospace engineering at the University of Maryland. he modernized metric system is known as the Système TInternational d’Unités (International System of Table 1. SI base units Units), with the international abbreviation SI. It is found- Quantity Unit ed on seven base units, listed in table 1, that by conven- Name Symbol tion are regarded as dimensionally independent. All other length meter m mass kilogram kg units are derived units, formed coherently by multiplying time second s and dividing units within the system without numerical electric current ampere A factors. Examples of derived units, including some with thermodynamic temperature kelvin K special names, are listed in table 2. The expression of amount of substance mole mol multiples and submultiples of SI units is facilitated luminous intensity candela cd through the use of the prefixes listed in table 3. SI obtains its international authority from the Meter Convention, signed in Paris by the delegates of 17 coun- Table 2. Examples of SI derived units tries, including the United States, on 20 May 1875, and Quantity Unit Special name Symbol Equivalent amended in 1921. Today 49 countries are members. The plane angle radian rad m/m=1 treaty established the Conférence Générale des Poids et solid angle steradian sr m22 /m =1 speed, velocity m/s Mesures (General Conference on Weights and Measures) acceleration m/s2 as the formal diplomatic body responsible for ratification angular velocity rad/s of new proposals related to metric units. -

Mobius Units Help SI/Metric Units (Accept Prefixes)
Mobius Units Help The Unit column of the following tables display all of the units that are recognized by the system. You can use either the units themselves, or combinations of these units, for example kJ/mol, kg*m^2, or m/s/s. The system accepts equivalent answers with different units as long as both units are accepted in the system. That is, if the answer is 120 cm, then 1.2 m or 1200 mm will also be accepted as correct. SI/Metric Units (Accept Prefixes) The units in this section can each be prefixed with one of the accepted SI prefixes below. SI Prefixes Base Units Prefix Factor Name Unit Definition Name Y 10^24 yotta m meter Z 10^21 zetta s second E 10^18 exa kg kilogram P 10^15 peta A amp T 10^12 tera K kelvin G 10^9 giga M 10^6 mega Derived SI Units k 10^3 kilo Unit Definition Name 6.02214199 * h 10^2 hecto mol mole da 10^1 deca 10^23 d 10^-1 deci rad 1 radian c 10^-2 centi sr 1 steradian m 10^-3 milli Hz 1/s hertz u 10^-6 micro N kg m/s^2 newton n 10^-9 nano Pa N/m^2 pascal p 10^-12 pico J N m joule f 10^-15 femto W J/s watt a 10^-18 atto C A s coulomb z 10^-21 zepto V J/C volt y 10^-24 yocto F C/V farad ohm V/A ohm CGS Units S A/V siemens Unit Definition Name Wb V s weber erg 10^-7 J erg T Wb/m^2 tesla dyn 10^-5 N dyne H Wb/A henry P 0.1 Pa*s poise lm cd sr lumen St cm^2/s stokes lx lm/m^2 lux sb cd/cm^2 stilb Bq s^-1 becquerel ph 10^4 lx phot Gy J/kg gray Gal cm/s^2 gal Sv J/kg sievert Mx 10^-8 Wb maxwell kat mol/s katal G 10^-4 T gauss Metric Units oersted Oe (10^3/4/Pi) A/m (rationalized) Unit Definition Name L m^3/1000 liter M mol/L molar eV J*1.602E-19 electron volt SI/Metric Units (No Prefixes) These units, and alternative ways of writing units, do not accept SI prefixes. -

Voltage Angle Limit Profile Specification
European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity VOLTAGE ANGLE LIMIT PROFILE SPECIFICATION 2021-04-21 SOC APPROVED VERSION 1.0 ENTSO-E | Rue de Spa, 8 | 1000 Brussels | [email protected] | www.entsoe.eu | @entso_e Voltage Angle Limit Profile Specification v1.0 European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity 1 Copyright notice: 2 Copyright © ENTSO-E. All Rights Reserved. 3 This document and its whole translations may be copied and furnished to others, and derivative 4 works that comment on or otherwise explain it or assist in its implementation may be prepared, 5 copied, published and distributed, in whole or in part, without restriction of any kind, provided 6 that the above copyright notice and this paragraph are included on all such copies and 7 derivative works. However, this document itself may not be modified in any way, except for 8 literal and whole translation into languages other than English and under all circumstances, the 9 copyright notice or references to ENTSO-E may not be removed. 10 This document and the information contained herein is provided on an "as is" basis. 11 ENTSO-E DISCLAIMS ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT 12 LIMITED TO ANY WARRANTY THAT THE USE OF THE INFORMATION HEREIN WILL NOT 13 INFRINGE ANY RIGHTS OR ANY IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR 14 FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. 15 This document is maintained by the ENTSO-E CIM EG. Comments or remarks are to be 16 provided at [email protected] 17 NOTE CONCERNING WORDING USED IN THIS DOCUMENT 18 The force of the following words is modified by the requirement level of the document in which 19 they are used. -

Siunitx – a Comprehensive (Si) Units Package∗
siunitx – A comprehensive (si) units package∗ Joseph Wright† Released 2021-09-22 Contents 1 Introduction 3 2 siunitx for the impatient 3 3 Using the siunitx package 4 3.1 Numbers . 4 3.2 Angles . 5 3.3 Units . 6 3.4 Complex numbers and quantities . 7 3.5 The unit macros . 8 3.6 Unit abbreviations . 10 3.7 Creating new macros . 14 3.8 Tabular material . 15 4 Package control options 17 4.1 The key–value control system . 17 4.2 Printing . 18 4.3 Parsing numbers . 20 4.4 Post-processing numbers . 22 4.5 Printing numbers . 25 4.6 Lists, products and ranges . 28 4.7 Complex numbers . 31 4.8 Angles . 32 4.9 Creating units . 34 4.10 Using units . 35 4.11 Quantities . 38 4.12 Tabular material . 39 4.13 Locale options . 49 4.14 Preamble-only options . 49 5 Upgrading from version 2 49 6 Unit changes made by BIPM 51 ∗This file describes v3.0.31, last revised 2021-09-22. †E-mail: [email protected] 1 7 Localisation 52 8 Compatibility with other packages 52 9 Hints for using siunitx 52 9.1 Adjusting \litre and \liter ........................ 52 9.2 Ensuring text or math output . 53 9.3 Expanding content in tables . 53 9.4 Using siunitx with datatool .......................... 54 9.5 Using units in section headings and bookmarks . 55 9.6 A left-aligned column visually centred under a heading . 56 9.7 Regression tables . 57 9.8 Maximising performance . 58 9.9 Special considerations for the \kWh unit . -

ANABSTR Database Summary Sheet
ANABSTR (Analytical Abstracts) Subject • Applied and industrial analysis Coverage • Chromatography and electrophoresis • Clinical and biochemical analysis • Environment, agriculture, and food • General analytical chemistry • Inorganic and organic analysis • Pharmaceutical analysis • Spectroscopy and radiochemical methods File Type Bibliographic Features Alerts (SDIs) Weekly CAS Registry Page Images Number® Identifiers Keep & Share SLART Learning Database Structures Record • Bibliographic information, abstracts (since 1984), names and CAS Registry Numbers Content of chemical substances, as well as index terms. • With the help of those index terms the identified elements and compounds (Analyte), the analysed media (Matrix) or the applied analytical methods (Concepts) can be searched. File Size More than 507,500 citations (04/2021) Coverage 1980-present Updates Updated weekly Language English Database The Royal Society of Chemistry Producer Thomas Graham House, Milton Road Cambridge CB4 4WF Great Britain Phone: +44 1223 432110 Fax: +44 1223 423429 Email: [email protected] Copyright Holder April 2021 2 ANABSTR Database FIZ Karlsruhe Supplier STN Europe P.O. Box 2465 76012 Karlsruhe Germany Phone: +49-7247-808-555 Fax: +49-7247-808-259 Email: [email protected] Sources • Journals • Technical Reports • Books • Standards • Conference proceedings User Aids • Online Helps (HELP DIRECTORY lists all help messages available) • STNGUIDE Clusters • ALLBIB • AUTHORS • BIOSCIENCE • CHEMISTRY • CORPSOURCE • NPS STN Database Cluster Information: -

SI Metric Units Vs USA Measures
Modern metric system (SI) units Some of the old pre-metric measures and old metric units still in use in the USA. This not a complete list — there are many others. acre (commercial) (36 000 ft2), acre (US survey) (43 560 ft2), acre (US international foot) (43 560 ft2), acre foot (43 560 ft3), Almost all measurements in your life can be acre foot per day, acre foot per year, acre inch (3630 ft3), agate (1/14 inch), arc second, atmosphere, atmosphere (standard), done with the metric units that will fit on the bag (1/6 US dry bbl), bag (3 UK bushells), barleycorn, barrel (oil), barrel (petroleum), barrel (US cranberry), barrel (US dry), barrel (US federal proof spirits), barrel (US federal), barrel (US liquid), bbl, bbl (US fed), board foot, bottle (spirits), bottle back of a business card: (wine), British thermal unit, British thermal unit (32 °F), British thermal unit (68 °F), British thermal unit (98 °F), British thermal unit (International steam table), British thermal unit (International), British thermal unit (IT), British thermal unit (mean), British thermal unit (thermochemical), BThU, BTU, Btu (International table), Btu (mean), Btu (th), Btu/hour, bushel, bushel (barley) (USDA), bushel (oats) (USDA), bushel (rye) (USDA), bushel (shelled corn) (USDA), bushel (soybeans), bushel (US volume), bushel (wheat), bushel potatoes (USDA), cable (US), cal (15 °C), cal (20 °C), cal (4 °C), cal (IT), cal (mean), cal (th), caliber 1000 grams = 1 kilogram (US), calibre (UK), calorie, Calorie, calorie (16 °C), calorie (20 °C), calorie (4 °C), calorie -

The International System of Units (SI)
NIST Special PublicationUnited 330 States Department of Commerce 2001 Edition National Institute of Standards and Technology The International System of Units (SI) Barry N. Taylor, Editor RN STEM MODE METRIC SYSTEM MOD TEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM M SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODER ERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MOD YSYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM M M MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODEDERN ODODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN MMETRIC SYSTEM MO CSC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEMTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEMSYS EERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRETRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SY MMETRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEMSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METR RRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEMYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRICMETR SYSYSTEM MOMODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERNRN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRM IC SYSTEM MODERNRN METRICME SYSTEM C SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEMTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODEMODERN METRIC SYSSTEM MODERN METRIC SYST ODODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRICTRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEMS MODERNN METRICMET SYSTEM MODERN SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERMODE N METRIC SYSTEMTEM MODERM N METRIC SYSTE TRTRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRMETRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRICETR SYSTEM MODERN M MMETRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERN METRIC SYSTEM MODERRN METRME IC SYSTEMEM MODERN METRIC SYSTE IC SYS -

The International System of Units (SI)
—————————————————————————— Bureau International des Poids et Mesures The International System of Units (SI) 9th edition 2019 ———————————————— v1.08 Copyright statement The SI Brochure is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 IGO (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/igo/), which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license, and indicate if changes were made. The BIPM and the Metre Convention • 117 The BIPM and the Metre Convention The International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) was set up by the Metre As of 20 May 2019 there Convention signed in Paris on 20 May 1875 by seventeen States during the final session of were fifty nine Member States: Argentina, Australia, the diplomatic Conference of the Metre. This Convention was amended in 1921. Austria, Belgium, Brazil, Bulgaria, Canada, Chile, 2 The BIPM has its headquarters near Paris, in the grounds (43 520 m ) of the Pavillon de China, Colombia, Croatia, Breteuil (Parc de Saint-Cloud) placed at its disposal by the French Government; its upkeep Czech Republic, Denmark, Egypt, Finland, France, is financed jointly by the Member States of the Metre Convention. Germany, Greece, Hungary, India, Indonesia, Iran (Islamic The task of the BIPM is to ensure worldwide unification of measurements; its objectives are Rep. of), Iraq, Ireland, Israel, to: Italy, Japan, Kazakhstan, Kenya, Korea (Republic of),