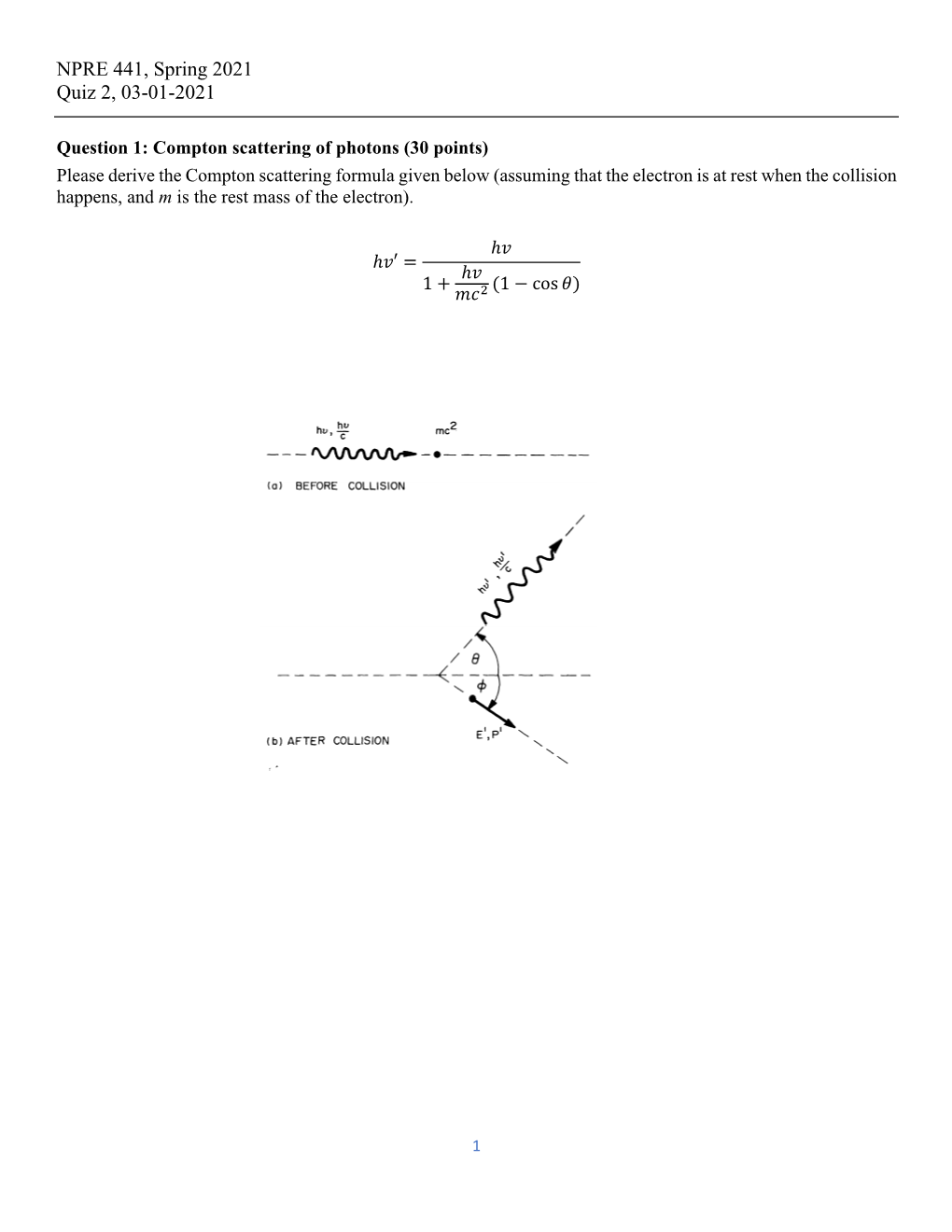
NPRE 441, Spring 2021 Quiz 2, 03-01-2021
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

10. Collisions • Use Conservation of Momentum and Energy and The
10. Collisions • Use conservation of momentum and energy and the center of mass to understand collisions between two objects. • During a collision, two or more objects exert a force on one another for a short time: -F(t) F(t) Before During After • It is not necessary for the objects to touch during a collision, e.g. an asteroid flied by the earth is considered a collision because its path is changed due to the gravitational attraction of the earth. One can still use conservation of momentum and energy to analyze the collision. Impulse: During a collision, the objects exert a force on one another. This force may be complicated and change with time. However, from Newton's 3rd Law, the two objects must exert an equal and opposite force on one another. F(t) t ti tf Dt From Newton'sr 2nd Law: dp r = F (t) dt r r dp = F (t)dt r r r r tf p f - pi = Dp = ò F (t)dt ti The change in the momentum is defined as the impulse of the collision. • Impulse is a vector quantity. Impulse-Linear Momentum Theorem: In a collision, the impulse on an object is equal to the change in momentum: r r J = Dp Conservation of Linear Momentum: In a system of two or more particles that are colliding, the forces that these objects exert on one another are internal forces. These internal forces cannot change the momentum of the system. Only an external force can change the momentum. The linear momentum of a closed isolated system is conserved during a collision of objects within the system. -

12. Elastic Collisions A) Overview B) Elastic Collisions V
12. Elastic Collisions A) Overview In this unit, our focus will be on elastic collisions, namely those collisions in which the only forces that act during the collision are conservative forces. In these collisions, the sum of the kinetic energies of the objects is conserved. We will find that the description of these collisions is significantly simplified in the center of mass frame of the colliding objects. In particular, we will discover that, in this frame, the speed of each object after the collision is the same as its speed before the collision. B) Elastic Collisions In the last unit, we discussed the important topic of momentum conservation. In particular, we found that when the sum of the external forces acting on a system of particles is zero, then the total momentum of the system, defined as the vector sum of the individual momenta, will be conserved. We also determined that the kinetic energy of the system, defined to be the sum of the individual kinetic energies, is not necessarily conserved in collisions. Whether or not this energy is conserved is determined by the details of the forces that the components of the system exert on each other. In the last unit, our focus was on inelastic collisions, those collisions in which the kinetic energy of the system was not conserved. In particular non-conservative work was done by the forces that the individual objects exerted on each other during the collision. In this unit, we will look at examples in which the only forces that act during the collision are conservative forces. -

Collisions in Classical Mechanics in Terms of Mass-Momentum “Vectors” with Galilean Transformations
World Journal of Mechanics, 2020, 10, 154-165 https://www.scirp.org/journal/wjm ISSN Online: 2160-0503 ISSN Print: 2160-049X Collisions in Classical Mechanics in Terms of Mass-Momentum “Vectors” with Galilean Transformations Akihiro Ogura Laboratory of Physics, Nihon University, Matsudo, Japan How to cite this paper: Ogura, A. (2020) Abstract Collisions in Classical Mechanics in Terms of Mass-Momentum “Vectors” with Galilean We present the usefulness of mass-momentum “vectors” to analyze the colli- Transformations. World Journal of Mechan- sion problems in classical mechanics for both one and two dimensions with ics, 10, 154-165. Galilean transformations. The Galilean transformations connect the mass- https://doi.org/10.4236/wjm.2020.1010011 momentum “vectors” in the center-of-mass and the laboratory systems. We Received: August 28, 2020 show that just moving the two systems to and fro, we obtain the final states in Accepted: October 9, 2020 the laboratory systems. This gives a simple way of obtaining them, in contrast Published: October 12, 2020 with the usual way in which we have to solve the simultaneous equations. For Copyright © 2020 by author(s) and one dimensional collision, the coefficient of restitution is introduced in the Scientific Research Publishing Inc. center-of-mass system. This clearly shows the meaning of the coefficient of This work is licensed under the Creative restitution. For two dimensional collisions, we only discuss the elastic colli- Commons Attribution International sion case. We also discuss the case of which the target particle is at rest before License (CC BY 4.0). http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ the collision. -

Definitions and Concepts for AQA Physics a Level
Definitions and Concepts for AQA Physics A Level Topic 4: Mechanics and Materials Breaking Stress: The maximum stress that an object can withstand before failure occurs. Brittle: A brittle object will show very little strain before reaching its breaking stress. Centre of Mass: The single point through which all the mass of an object can be said to act. Conservation of Energy: Energy cannot be created or destroyed - it can only be transferred into different forms. Conservation of Momentum: The total momentum of a system before an event, must be equal to the total momentum of the system after the event, assuming no external forces act. Couple: Two equal and opposite parallel forces that act on an object through different lines of action. It has the effect of causing a rotation without translation. Density: The mass per unit volume of a material. Efficiency: The ratio of useful output to total input for a given system. Elastic Behaviour: If a material deforms with elastic behaviour, it will return to its original shape when the deforming forces are removed. The object will not be permanently deformed. Elastic Collision: A collision in which the total kinetic energy of the system before the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision. Elastic Limit: The force beyond which an object will no longer deform elastically, and instead deform plastically. Beyond the elastic limit, when the deforming forces are removed, the object will not return to its original shape. Elastic Strain Energy: The energy stored in an object when it is stretched. -

Bibliography of Low Energy Electron
Bibliography of Low Energy Electron Collision Cross Section Data United States Department of Commerce National Bureau of Standards Miscellaneous Publication 289 — THE NATIONAL BUREAU OF STANDARDS The National Bureau of Standards 1 provides measurement and technical information services essential to the efficiency and effectiveness of the work of the Nation's scientists and engineers. The Bureau serves also as a focal point in the Federal Government for assuring maximum application of the physical and engineering sciences to the advancement of technology in industry and commerce. To accomplish this mission, the Bureau is organized into three institutes covering broad program areas of research and services: THE INSTITUTE FOR BASIC STANDARDS . provides the central basis within the United States for a complete and consistent system of physical measurements, coordinates that system with the measurement systems of other nations, and furnishes essential services leading to accurate and uniform physical measurements throughout the Nation's scientific community, industry, and commerce. This Institute comprises a series of divisions, each serving a classical subject matter area: —Applied Mathematics—Electricity—Metrology—Mechanics—Heat—Atomic Physics—Physical Chemistry—Radiation Physics—Laboratory Astrophysics 2—Radio Standards Laboratory, 2 which includes Radio Standards Physics and Radio Standards Engineering—Office of Standard Refer- ence Data. THE INSTITUTE FOR MATERIALS RESEARCH . conducts materials research and provides associated materials services including mainly reference materials and data on the properties of ma- terials. Beyond its direct interest to the Nation's scientists and engineers, this Institute yields services which are essential to the advancement of technology in industry and commerce. This Institute is or- ganized primarily by technical fields: —Analytical Chemistry—Metallurgy—Reactor Radiations—Polymers—Inorganic Materials—Cry- ogenics 2—Materials Evaluation Laboratory-— Office of Standard Reference Materials. -

The Effects of Elastic Scattering in Neutral Atom Transport D
The effects of elastic scattering in neutral atom transport D. N. Ruzic Citation: Phys. Fluids B 5, 3140 (1993); doi: 10.1063/1.860651 View online: http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.860651 View Table of Contents: http://pop.aip.org/resource/1/PFBPEI/v5/i9 Published by the American Institute of Physics. Related Articles Dissociation mechanisms of excited CH3X (X = Cl, Br, and I) formed via high-energy electron transfer using alkali metal targets J. Chem. Phys. 137, 184308 (2012) Efficient method for quantum calculations of molecule-molecule scattering properties in a magnetic field J. Chem. Phys. 137, 024103 (2012) Scattering resonances in slow NH3–He collisions J. Chem. Phys. 136, 074301 (2012) Accurate time dependent wave packet calculations for the N + OH reaction J. Chem. Phys. 135, 104307 (2011) The k-j-j′ vector correlation in inelastic and reactive scattering J. Chem. Phys. 135, 084305 (2011) Additional information on Phys. Fluids B Journal Homepage: http://pop.aip.org/ Journal Information: http://pop.aip.org/about/about_the_journal Top downloads: http://pop.aip.org/features/most_downloaded Information for Authors: http://pop.aip.org/authors Downloaded 23 Dec 2012 to 192.17.144.173. Redistribution subject to AIP license or copyright; see http://pop.aip.org/about/rights_and_permissions The effects of elastic scattering in neutral atom transport D. N. Ruzic University of Illinois, 103South Goodwin Avenue, Urbana Illinois 61801 (Received 14 December 1992; accepted21 May 1993) Neutral atom elastic collisions are one of the dominant interactions in the edge of a high recycling diverted plasma. Starting from the quantum interatomic potentials, the scattering functions are derived for H on H ‘, H on Hz, and He on Hz in the energy range of 0. -

Energy Considerations in Collisions How It Works
L-8 (M-7) I. Collisions II. Work and Energy • Momentum: an object of mass m, moving with velocity v has a momentum p = m v. • Momentum is an important and useful concept that is used to analyze collisions – The colliding objects exert strong forces on each other over relatively short time intervals – Details of the forces are usually not known, but the forces acting on the objects are equal in magnitude and opposite in direction (3rd law) – The law of conservation of momentum which follows from Newton’s 2nd and 3rd laws, allows us to predict what happens in collisions 1 2 I. Physics of collisions: Law of Conservation of Momentum conservation of momentum • A consequence of Newton’s Newton’s Cradle 3rd law is that if we add the • The concept of momentum is very useful momentum of both objects when discussing how 2 objects interact. before a collision, it is the same as the momentum of • Suppose two objects are on a collision the two objects immediately course. AB after the collision. • We know their masses and speeds before • The law of conservation of momentum and the law of they collide conservation of energy are During the short time of • The momentum concept helps us to two of the fundamental laws of nature. the collision, the effect of predict what will happen after they collide. gravity is not important. 3 4 Momentum conservation in a two-body collision, Energy considerations in collisions How it works. v • Objects that are in motion have kinetic energy: v B, before A, before KE = ½ m v2 (Note that KE does not depend on before B collision A the direction of the object’s motion) more on this . -

Collisions and Momentum
1 Collisions and Momentum Introduction: The important vector quantities in physics are the momentum and force. Force is defined as the time rate of change of the momentum. The momentum (p) of an object is given by the product of its mass (a scalar) and its velocity (a vector): p = m v Since the force is the rate of change of the momentum, we would expect that if the force is zero, then the momentum would remain constant. This is the basis for Newton’s first law of motion. We also find that in the case of a collision between two objects of different momenta, the total momentum, which is the vector sum of the momenta of the two individual objects, will not change as a result of the collision if no external force is acting on the objects. If you have ever played billiards, you probably made good use of this rule. This is the rule of conservation of momentum. Another quantity in physics is the kinetic energy (K.E.), a scalar quantity defined as: 1 2 K.E. = 2 mv The kinetic energy is one half the mass multiplied by the velocity squared. An elastic collision is a collision where the total kinetic energy (the sum of the energies of the colliding objects) is conserved (the same both before and after the collision). An inelastic collision is one where the kinetic energy is not conserved. (It is important to remember that in both kinds of collisions the total energy of the colliding objects is conserved.) In this experiment we will study the collision of two steel balls to test the law of conservation of momentum and to test the elasticity of such a collision by comparing the kinetic energies of the balls before and after the collision. -

Ultra-Cold Collisions and Evaporative Cooling of Caesium in a Magnetic Trap
Ultra-cold Collisions and Evaporative Cooling of Caesium in a Magnetic Trap Angharad Mair Thomas A thesis submitted in partial fulfilment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy at the University of Oxford Jesus College University of Oxford Hilary Term 2004 Abstract Ultra-cold Collisions and Evaporative Cooling of Caesium in a Magnetic Trap Angharad Mair Thomas, Jesus College, Oxford University DPhil Thesis, Hilary Term 2004 Caesium-133 atoms have been evaporatively cooled in a magnetic trap to tem- peratures as low as 8 nK producing a final phase-space density within a factor of 4 of that required for the onset of Bose-Einstein condensation. At the end of the forced radio-frequency evaporation, 1500 atoms in the F = 3; mF = ¡3 state remain in the magnetic trap. A decrease in the one-dimensional evaporative cool- ing efficiency at very low temperatures is observed as the trapped sample enters the collisionally thick (hydrodynamic) regime. Different evaporation trajectories are experimentally studied leading to a greater understanding of one-dimensional evaporation, inelastic collisions and the hydrodynamic regime. A theoretical sim- ulation accurately reproduces the experimental data and indicates that the reduc- tion in the evaporative cooling efficiency as the cloud enters the hydrodynamic regime is the main obstacle to the realization of Bose-Einstein condensation in the F = 3; mF = ¡3 state. In addition, we report measurements of the two-body inelastic collision rate coefficient for caesium atoms as a function of magnetic field and collision energy. The positions of three previously identified resonances are confirmed, with reduced uncertainties, at magnetic fields of 108.87(6), 118.46(3) and 133.52(3) Gauss. -

Neutron-Proton Collisions
Neutron-Proton Collisions E. Di Grezia INFN, Sezione di Napoli, Complesso Universitario di Monte S. Angelo Via Cintia, Edificio 6, 80126 Napoli, Italy∗ A theoretical model describing neutron-proton scattering developed by Majorana as early as in 1932, is discussed in detail with the experiments that motivated it. Majorana using collisions’ theory, obtained the explicit expression of solutions of wave equation of the neutron-proton system. In this work two different models, the unpublished one of Majorana and the contemporary work of Massey, are studied and compared. PACS numbers: INTRODUCTION In early 1932 a set of experimental phenomena revealed that the neutron plays an important role in the structure of nucleus like the proton, electron and α-particle and can be emitted by artificial disintegration of lighter elements. The discovery of the neutron is one of the important milestones for the advancement of contemporary physics. Its existence as a neutral particle has been suggested for the first time by Rutherford in 1920 [1], because he thought it was necessary to explain the formation of nuclei of heavy elements. This idea was supported by other scientists [2] that sought to verify experimentally its existence. Because of its neutrality it was difficult to detect the neutron and then to demonstrate its existence, hence for many years the research stopped, and eventually, in between 1928-1930, the physics community started talking again about the neutron [3]. For instance in [3] a model was developed in which the neutron was regarded as a particle composed of a combination of proton and electron. At the beginning of 1930 there were experiments on induced radioactivity, which were interpreted as due to neutrons. -

Linear Momentum and Collisions 261
CHAPTER 8 | LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS 261 8 LINEAR MOMENTUM AND COLLISIONS Figure 8.1 Each rugby player has great momentum, which will affect the outcome of their collisions with each other and the ground. (credit: ozzzie, Flickr) Learning Objectives 8.1. Linear Momentum and Force • Define linear momentum. • Explain the relationship between momentum and force. • State Newton’s second law of motion in terms of momentum. • Calculate momentum given mass and velocity. 8.2. Impulse • Define impulse. • Describe effects of impulses in everyday life. • Determine the average effective force using graphical representation. • Calculate average force and impulse given mass, velocity, and time. 8.3. Conservation of Momentum • Describe the principle of conservation of momentum. • Derive an expression for the conservation of momentum. • Explain conservation of momentum with examples. • Explain the principle of conservation of momentum as it relates to atomic and subatomic particles. 8.4. Elastic Collisions in One Dimension • Describe an elastic collision of two objects in one dimension. • Define internal kinetic energy. • Derive an expression for conservation of internal kinetic energy in a one dimensional collision. • Determine the final velocities in an elastic collision given masses and initial velocities. 8.5. Inelastic Collisions in One Dimension • Define inelastic collision. • Explain perfectly inelastic collision. • Apply an understanding of collisions to sports. • Determine recoil velocity and loss in kinetic energy given mass and initial velocity. 8.6. Collisions of Point Masses in Two Dimensions • Discuss two dimensional collisions as an extension of one dimensional analysis. • Define point masses. • Derive an expression for conservation of momentum along x-axis and y-axis. -

The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases
The Kinetic-Molecular Theory of Gases Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the FlexBook®, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2014 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Com- mons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference.