Surface Areas of Prisms and Cylinders 609
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Hydraulic Cylinder Replacement for Cylinders with 3/8” Hydraulic Hose Instructions
HYDRAULIC CYLINDER REPLACEMENT FOR CYLINDERS WITH 3/8” HYDRAULIC HOSE INSTRUCTIONS INSTALLATION TOOLS: INCLUDED HARDWARE: • Knife or Scizzors A. (1) Hydraulic Cylinder • 5/8” Wrench B. (1) Zip-Tie • 1/2” Wrench • 1/2” Socket & Ratchet IMPORTANT: Pressure MUST be relieved from hydraulic system before proceeding. PRESSURE RELIEF STEP 1: Lower the Power-Pole Anchor® down so the Everflex™ spike is touching the ground. WARNING: Do not touch spike with bare hands. STEP 2: Manually push the anchor into closed position, relieving pressure. Manually lower anchor back to the ground. REMOVAL STEP 1: Remove the Cylinder Bottom from the Upper U-Channel using a 1/2” socket & wrench. FIG 1 or 2 NOTE: For Blade models, push bottom of cylinder up into U-Channel and slide it forward past the Ram Spacers to remove it. Upper U-Channel Upper U-Channel Cylinder Bottom 1/2” Tools 1/2” Tools Ram 1/2” Tools Spacers Cylinder Bottom If Ram-Spacers fall out Older models have (1) long & (1) during removal, push short Ram Spacer. Ram Spacers 1/2” Tools bushings in to hold MUST be installed on the same side Figure 1 Figure 2 them in place. they were removed. Blade Models Pro/Spn Models Need help? Contact our Customer Service Team at 1 + 813.689.9932 Option 2 HYDRAULIC CYLINDER REPLACEMENT FOR CYLINDERS WITH 3/8” HYDRAULIC HOSE INSTRUCTIONS STEP 2: Remove the Cylinder Top from the Lower U-Channel using a 1/2” socket & wrench. FIG 3 or 4 Lower U-Channel Lower U-Channel 1/2” Tools 1/2” Tools Cylinder Top Cylinder Top Figure 3 Figure 4 Blade Models Pro/SPN Models STEP 3: Disconnect the UP Hose from the Hydraulic Cylinder Fitting by holding the 1/2” Wrench 5/8” Wrench Cylinder Fitting Base with a 1/2” wrench and turning the Hydraulic Hose Fitting Cylinder Fitting counter-clockwise with a 5/8” wrench. -

An Introduction to Topology the Classification Theorem for Surfaces by E
An Introduction to Topology An Introduction to Topology The Classification theorem for Surfaces By E. C. Zeeman Introduction. The classification theorem is a beautiful example of geometric topology. Although it was discovered in the last century*, yet it manages to convey the spirit of present day research. The proof that we give here is elementary, and its is hoped more intuitive than that found in most textbooks, but in none the less rigorous. It is designed for readers who have never done any topology before. It is the sort of mathematics that could be taught in schools both to foster geometric intuition, and to counteract the present day alarming tendency to drop geometry. It is profound, and yet preserves a sense of fun. In Appendix 1 we explain how a deeper result can be proved if one has available the more sophisticated tools of analytic topology and algebraic topology. Examples. Before starting the theorem let us look at a few examples of surfaces. In any branch of mathematics it is always a good thing to start with examples, because they are the source of our intuition. All the following pictures are of surfaces in 3-dimensions. In example 1 by the word “sphere” we mean just the surface of the sphere, and not the inside. In fact in all the examples we mean just the surface and not the solid inside. 1. Sphere. 2. Torus (or inner tube). 3. Knotted torus. 4. Sphere with knotted torus bored through it. * Zeeman wrote this article in the mid-twentieth century. 1 An Introduction to Topology 5. -

Volumes of Prisms and Cylinders 625
11-4 11-4 Volumes of Prisms and 11-4 Cylinders 1. Plan Objectives What You’ll Learn Check Skills You’ll Need GO for Help Lessons 1-9 and 10-1 1 To find the volume of a prism 2 To find the volume of • To find the volume of a Find the area of each figure. For answers that are not whole numbers, round to prism a cylinder the nearest tenth. • To find the volume of a 2 Examples cylinder 1. a square with side length 7 cm 49 cm 1 Finding Volume of a 2. a circle with diameter 15 in. 176.7 in.2 . And Why Rectangular Prism 3. a circle with radius 10 mm 314.2 mm2 2 Finding Volume of a To estimate the volume of a 4. a rectangle with length 3 ft and width 1 ft 3 ft2 Triangular Prism backpack, as in Example 4 2 3 Finding Volume of a Cylinder 5. a rectangle with base 14 in. and height 11 in. 154 in. 4 Finding Volume of a 6. a triangle with base 11 cm and height 5 cm 27.5 cm2 Composite Figure 7. an equilateral triangle that is 8 in. on each side 27.7 in.2 New Vocabulary • volume • composite space figure Math Background Integral calculus considers the area under a curve, which leads to computation of volumes of 1 Finding Volume of a Prism solids of revolution. Cavalieri’s Principle is a forerunner of ideas formalized by Newton and Leibniz in calculus. Hands-On Activity: Finding Volume Explore the volume of a prism with unit cubes. -

Quick Reference Guide - Ansi Z80.1-2015
QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE - ANSI Z80.1-2015 1. Tolerance on Distance Refractive Power (Single Vision & Multifocal Lenses) Cylinder Cylinder Sphere Meridian Power Tolerance on Sphere Cylinder Meridian Power ≥ 0.00 D > - 2.00 D (minus cylinder convention) > -4.50 D (minus cylinder convention) ≤ -2.00 D ≤ -4.50 D From - 6.50 D to + 6.50 D ± 0.13 D ± 0.13 D ± 0.15 D ± 4% Stronger than ± 6.50 D ± 2% ± 0.13 D ± 0.15 D ± 4% 2. Tolerance on Distance Refractive Power (Progressive Addition Lenses) Cylinder Cylinder Sphere Meridian Power Tolerance on Sphere Cylinder Meridian Power ≥ 0.00 D > - 2.00 D (minus cylinder convention) > -3.50 D (minus cylinder convention) ≤ -2.00 D ≤ -3.50 D From -8.00 D to +8.00 D ± 0.16 D ± 0.16 D ± 0.18 D ± 5% Stronger than ±8.00 D ± 2% ± 0.16 D ± 0.18 D ± 5% 3. Tolerance on the direction of cylinder axis Nominal value of the ≥ 0.12 D > 0.25 D > 0.50 D > 0.75 D < 0.12 D > 1.50 D cylinder power (D) ≤ 0.25 D ≤ 0.50 D ≤ 0.75 D ≤ 1.50 D Tolerance of the axis Not Defined ° ° ° ° ° (degrees) ± 14 ± 7 ± 5 ± 3 ± 2 4. Tolerance on addition power for multifocal and progressive addition lenses Nominal value of addition power (D) ≤ 4.00 D > 4.00 D Nominal value of the tolerance on the addition power (D) ± 0.12 D ± 0.18 D 5. Tolerance on Prism Reference Point Location and Prismatic Power • The prismatic power measured at the prism reference point shall not exceed 0.33Δ or the prism reference point shall not be more than 1.0 mm away from its specified position in any direction. -

A Three-Dimensional Laguerre Geometry and Its Visualization
A Three-Dimensional Laguerre Geometry and Its Visualization Hans Havlicek and Klaus List, Institut fur¨ Geometrie, TU Wien 3 We describe and visualize the chains of the 3-dimensional chain geometry over the ring R("), " = 0. MSC 2000: 51C05, 53A20. Keywords: chain geometry, Laguerre geometry, affine space, twisted cubic. 1 Introduction The aim of the present paper is to discuss in some detail the Laguerre geometry (cf. [1], [6]) which arises from the 3-dimensional real algebra L := R("), where "3 = 0. This algebra generalizes the algebra of real dual numbers D = R("), where "2 = 0. The Laguerre geometry over D is the geometry on the so-called Blaschke cylinder (Figure 1); the non-degenerate conics on this cylinder are called chains (or cycles, circles). If one generator of the cylinder is removed then the remaining points of the cylinder are in one-one correspon- dence (via a stereographic projection) with the points of the plane of dual numbers, which is an isotropic plane; the chains go over R" to circles and non-isotropic lines. So the point space of the chain geometry over the real dual numbers can be considered as an affine plane with an extra “improper line”. The Laguerre geometry based on L has as point set the projective line P(L) over L. It can be seen as the real affine 3-space on L together with an “improper affine plane”. There is a point model R for this geometry, like the Blaschke cylinder, but it is more compli- cated, and belongs to a 7-dimensional projective space ([6, p. -

Natural Cadmium Is Made up of a Number of Isotopes with Different Abundances: Cd106 (1.25%), Cd110 (12.49%), Cd111 (12.8%), Cd
CLASSROOM Natural cadmium is made up of a number of isotopes with different abundances: Cd106 (1.25%), Cd110 (12.49%), Cd111 (12.8%), Cd 112 (24.13%), Cd113 (12.22%), Cd114(28.73%), Cd116 (7.49%). Of these Cd113 is the main neutron absorber; it has an absorption cross section of 2065 barns for thermal neutrons (a barn is equal to 10–24 sq.cm), and the cross section is a measure of the extent of reaction. When Cd113 absorbs a neutron, it forms Cd114 with a prompt release of γ radiation. There is not much energy release in this reaction. Cd114 can again absorb a neutron to form Cd115, but the cross section for this reaction is very small. Cd115 is a β-emitter C V Sundaram, National (with a half-life of 53hrs) and gets transformed to Indium-115 Institute of Advanced Studies, Indian Institute of Science which is a stable isotope. In none of these cases is there any large Campus, Bangalore 560 012, release of energy, nor is there any release of fresh neutrons to India. propagate any chain reaction. Vishwambhar Pati The Möbius Strip Indian Statistical Institute Bangalore 560059, India The Möbius strip is easy enough to construct. Just take a strip of paper and glue its ends after giving it a twist, as shown in Figure 1a. As you might have gathered from popular accounts, this surface, which we shall call M, has no inside or outside. If you started painting one “side” red and the other “side” blue, you would come to a point where blue and red bump into each other. -

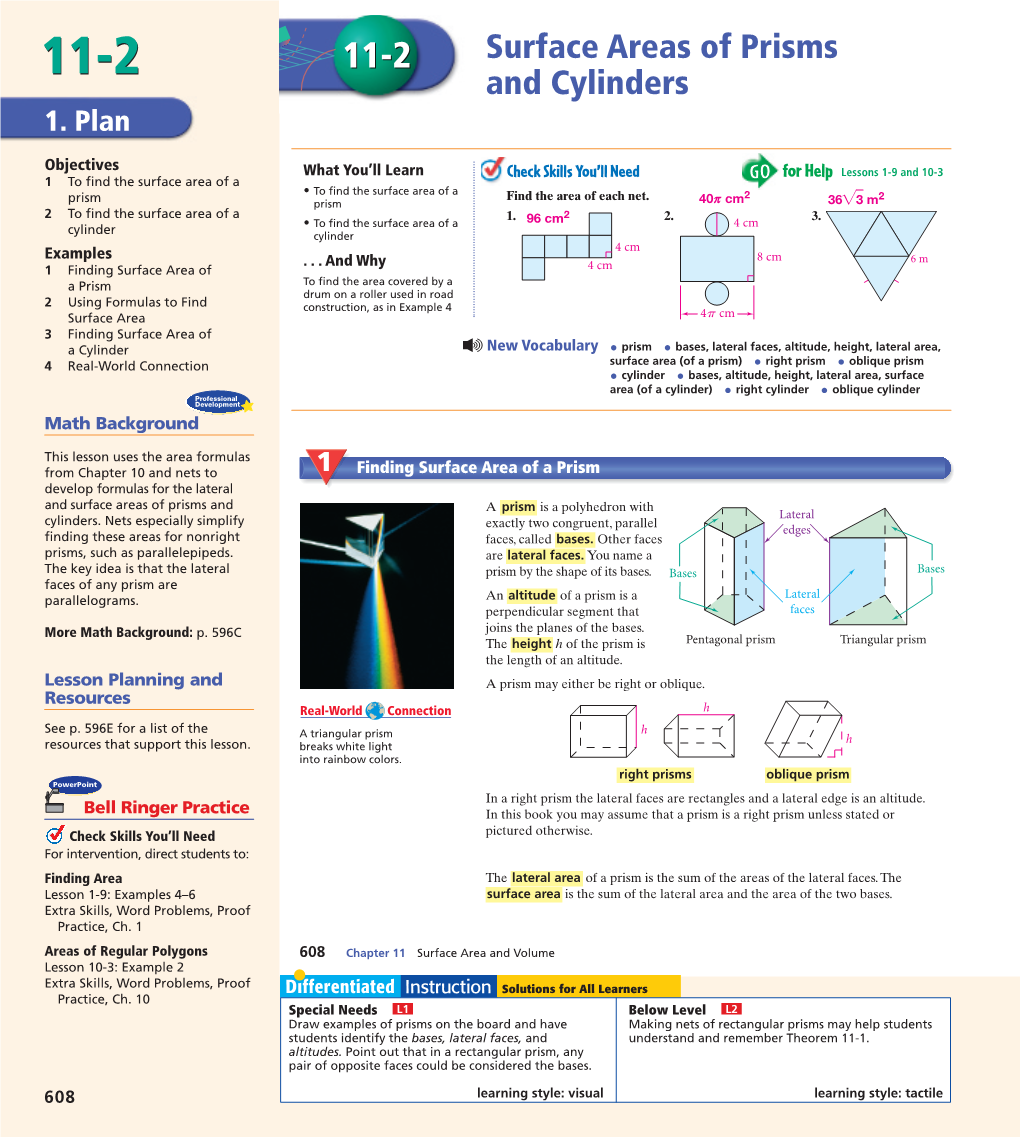
10-4 Surface and Lateral Area of Prism and Cylinders.Pdf
Aim: How do we evaluate and solve problems involving surface area of prisms an cylinders? Objective: Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a prism. Learn and apply the formula for the surface area of a cylinder. Vocabulary: lateral face, lateral edge, right prism, oblique prism, altitude, surface area, lateral surface, axis of a cylinder, right cylinder, oblique cylinder. Prisms and cylinders have 2 congruent parallel bases. A lateral face is not a base. The edges of the base are called base edges. A lateral edge is not an edge of a base. The lateral faces of a right prism are all rectangles. An oblique prism has at least one nonrectangular lateral face. An altitude of a prism or cylinder is a perpendicular segment joining the planes of the bases. The height of a three-dimensional figure is the length of an altitude. Surface area is the total area of all faces and curved surfaces of a three-dimensional figure. The lateral area of a prism is the sum of the areas of the lateral faces. Holt Geometry The net of a right prism can be drawn so that the lateral faces form a rectangle with the same height as the prism. The base of the rectangle is equal to the perimeter of the base of the prism. The surface area of a right rectangular prism with length ℓ, width w, and height h can be written as S = 2ℓw + 2wh + 2ℓh. The surface area formula is only true for right prisms. To find the surface area of an oblique prism, add the areas of the faces. -

Year 6 – Wednesday 24Th June 2020 – Maths
1 Year 6 – Wednesday 24th June 2020 – Maths Can I identify 3D shapes that have pairs of parallel or perpendicular edges? Parallel – edges that have the same distance continuously between them – parallel edges never meet. Perpendicular – when two edges or faces meet and create a 90o angle. 1 4. 7. 10. 2 5. 8. 11. 3. 6. 9. 12. C1 – Using the shapes above: 1. Name and sort the shapes into: a. Pyramids b. Prisms 2. Draw a table to identify how many faces, edges and vertices each shape has. 3. Write your own geometric definition: a. Prism b. pyramid 4. Which shape is the odd one out? Explain why. C2 – Using the shapes above; 1. Which of the shapes have pairs of parallel edges in: a. All their faces? b. More than one half of the faces? c. One face only? 2. The following shapes have pairs of perpendicular edges. Identify the faces they are in: 2 a. A cube b. A square based pyramid c. A triangular prism d. A cuboid 3. Which shape with straight edges has no perpendicular edges? 4. Which shape has perpendicular edges in the shape but not in any face? C3 – Using the above shapes: 1. How many faces have pairs of parallel edges in: a. A hexagonal pyramid? b. A decagonal (10-sided) based prism? c. A heptagonal based prism? d. Which shape has no face with parallel edges but has parallel edges in the shape? 2. How many faces have perpendicular edges in: a. A pentagonal pyramid b. A hexagonal pyramid c. -

Unit 6 Visualising Solid Shapes(Final)
• 3D shapes/objects are those which do not lie completely in a plane. • 3D objects have different views from different positions. • A solid is a polyhedron if it is made up of only polygonal faces, the faces meet at edges which are line segments and the edges meet at a point called vertex. • Euler’s formula for any polyhedron is, F + V – E = 2 Where F stands for number of faces, V for number of vertices and E for number of edges. • Types of polyhedrons: (a) Convex polyhedron A convex polyhedron is one in which all faces make it convex. e.g. (1) (2) (3) (4) 12/04/18 (1) and (2) are convex polyhedrons whereas (3) and (4) are non convex polyhedron. (b) Regular polyhedra or platonic solids: A polyhedron is regular if its faces are congruent regular polygons and the same number of faces meet at each vertex. For example, a cube is a platonic solid because all six of its faces are congruent squares. There are five such solids– tetrahedron, cube, octahedron, dodecahedron and icosahedron. e.g. • A prism is a polyhedron whose bottom and top faces (known as bases) are congruent polygons and faces known as lateral faces are parallelograms (when the side faces are rectangles, the shape is known as right prism). • A pyramid is a polyhedron whose base is a polygon and lateral faces are triangles. • A map depicts the location of a particular object/place in relation to other objects/places. The front, top and side of a figure are shown. Use centimetre cubes to build the figure. -

Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs
Uniform Panoploid Tetracombs George Olshevsky TETRACOMB is a four-dimensional tessellation. In any tessellation, the honeycells, which are the n-dimensional polytopes that tessellate the space, Amust by definition adjoin precisely along their facets, that is, their ( n!1)- dimensional elements, so that each facet belongs to exactly two honeycells. In the case of tetracombs, the honeycells are four-dimensional polytopes, or polychora, and their facets are polyhedra. For a tessellation to be uniform, the honeycells must all be uniform polytopes, and the vertices must be transitive on the symmetry group of the tessellation. Loosely speaking, therefore, the vertices must be “surrounded all alike” by the honeycells that meet there. If a tessellation is such that every point of its space not on a boundary between honeycells lies in the interior of exactly one honeycell, then it is panoploid. If one or more points of the space not on a boundary between honeycells lie inside more than one honeycell, the tessellation is polyploid. Tessellations may also be constructed that have “holes,” that is, regions that lie inside none of the honeycells; such tessellations are called holeycombs. It is possible for a polyploid tessellation to also be a holeycomb, but not for a panoploid tessellation, which must fill the entire space exactly once. Polyploid tessellations are also called starcombs or star-tessellations. Holeycombs usually arise when (n!1)-dimensional tessellations are themselves permitted to be honeycells; these take up the otherwise free facets that bound the “holes,” so that all the facets continue to belong to two honeycells. In this essay, as per its title, we are concerned with just the uniform panoploid tetracombs. -

Plus Cylinder Lensometry Tara L Bragg, CO August 2015
Mark E Wilkinson, OD Plus Cylinder Lensometry Tara L Bragg, CO August 2015 Lensometry A lensometer is an optical bench consisting of an illuminated moveable target, a powerful fixed lens, and a telescopic eyepiece focused at infinity. The key element is the field lens that is fixed in place so that its focal point is on the back surface of the lens being analyzed. The lensometer measures the back vertex power of the spectacle lens. The vertex power is the reciprocal of the distance between the back surface of the lens and its secondary focal point. This is also known as the back focal length. For this reason, a lensometer does not really measure the true focal length of a lens, which is measured from the principal planes, not from the lens surface. The lensometer works on the Badal principle with the addition of an astronomical telescope for precise detection of parallel rays at neutralization. The Badel principle is Knapp’s law applied to lensometers. Performing Manual Lensometry Focusing the Eyepiece The focus of the lensometer eyepiece must be verified each time the instrument is used, to avoid erroneous readings. 1. With no lens or a plano lens in place on the lensometer, look through the eyepiece of the instrument. Turn the power drum until the mires (the perpendicular cross lines), viewed through the eyepiece, are grossly out of focus. 2. Turn the eyepiece in the plus direction to fog (blur) the target seen through the eyepiece. 3. Slowly turn the eyepiece in the opposite direction until the target is clear, then stop turning. -

2D and 3D Shapes.Pdf
& • Anchor 2 - D Charts • Flash Cards 3 - D • Shape Books • Practice Pages rd Shapesfor 3 Grade by Carrie Lutz T hank you for purchasing!!! Check out my store: http://www.teacherspayteachers.com/Store/Carrie-Lutz-6 Follow me for notifications of freebies, sales and new arrivals! Visit my BLOG for more Free Stuff! Read My Blog Post about Teaching 3 Dimensional Figures Correctly Credits: Carrie Lutz©2016 2D Shape Bank 3D Shape Bank 3 Sided 5 Sided Prisms triangular prism cube rectangular prism triangle pentagon 4 Sided rectangle square pentagonal prism hexagonal prism octagonal prism Pyramids rhombus trapezoid 6 Sided 8 Sided rectangular square triangular pyramid pyramid pyramid Carrie LutzCarrie CarrieLutz pentagonal hexagonal © hexagon octagon © 2016 pyramid pyramid 2016 Curved Shapes CURVED SOLIDS oval circle sphere cone cylinder Carrie Lutz©2016 Carrie Lutz©2016 Name _____________________ Side Sort Date _____________________ Cut out the shapes below and glue them in the correct column. More than 4 Less than 4 Exactly 4 Carrie Lutz©2016 Name _____________________ Name the Shapes Date _____________________ 1. Name the Shape. 2. Name the Shape. 3. Name the Shape. ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ 4. Name the Shape. 5. Name the Shape. 6. Name the Shape. ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ 4. Name the Shape. 5. Name the Shape. 6. Name the Shape. ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ octagon circle square rhombus triangle hexagon pentagon rectangle trapezoid Carrie Lutz©2016 Faces, Edges, Vertices Name _____________________ and Date _____________________ 1. Name the Shape. 2. Name the Shape. 3. Name the Shape. ____________________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ _____ faces _____ faces _____ faces _____Edges _____Edges _____Edges _____Vertices _____Vertices _____Vertices 4.