Neural Development
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Homocysteine Intensifies Embryonic LIM3 Expression in Migratory Neural Crest Cells: a Quantitative Confocal Microscope Study
University of Northern Iowa UNI ScholarWorks Dissertations and Theses @ UNI Student Work 2014 Homocysteine intensifies embryonic LIM3 expression in migratory neural crest cells: A quantitative confocal microscope study Jordan Naumann University of Northern Iowa Let us know how access to this document benefits ouy Copyright ©2014 Jordan Naumann Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.uni.edu/etd Part of the Biology Commons Recommended Citation Naumann, Jordan, "Homocysteine intensifies embryonic LIM3 expression in migratory neural crest cells: A quantitative confocal microscope study" (2014). Dissertations and Theses @ UNI. 89. https://scholarworks.uni.edu/etd/89 This Open Access Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Student Work at UNI ScholarWorks. It has been accepted for inclusion in Dissertations and Theses @ UNI by an authorized administrator of UNI ScholarWorks. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Copyright by JORDAN NAUMANN 2014 All Rights Reserved HOMOCYSTEINE INTENSIFIES EMBRYONIC LIM3 EXPRESSION IN MIGRATORY NEURAL CREST CELLS – A QUANTITATIVE CONFOCAL MICROSCOPE STUDY An Abstract of a Thesis Submitted in Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree Master of Science Jordan Naumann University of Northern Iowa May 2014 ABSTRACT Elevated levels of homocysteine in maternal blood and amniotic fluid are associated with cardiovascular, renal, skeletal, and endocrine diseases and also with embryonic malformations related to neural crest cells. Neural crest cells are necessary for the formation of tissues and organs throughout the body of vertebrate animals. The migration of neural crest cells is essential for proper development of the target tissues. When migration is disrupted, abnormalities may occur. -

Differentiation of the Cerebellum 2463
Development 128, 2461-2469 (2001) 2461 Printed in Great Britain © The Company of Biologists Limited 2001 DEV1660 Inductive signal and tissue responsiveness defining the tectum and the cerebellum Tatsuya Sato, Isato Araki‡ and Harukazu Nakamura* Department of Molecular Neurobiology, Institute of Development, Aging and Cancer, Seiryo-machi 4-1, Aoba-ku, Sendai 980- 8575, Japan ‡Present address: Department of Neurobiology, University of Heidelberg, Im Neuenheimer Feld 364, D-69120 Heidelberg, Germany *Author for correspondence (e-mail: [email protected]) Accepted 11 April 2001 SUMMARY The mes/metencephalic boundary (isthmus) has an Fgf8b repressed Otx2 expression, but upregulated Gbx2 and organizing activity for mesencephalon and metencephalon. Irx2 expression in the mesencephalon. As a result, Fgf8b The candidate signaling molecule is Fgf8 whose mRNA is completely changed the fate of the mesencephalic alar plate localized in the region where the cerebellum differentiates. to cerebellum. Quantitative analysis showed that Fgf8b Responding to this signal, the cerebellum differentiates in signal is 100 times stronger than Fgf8a signal. Co- the metencephalon and the tectum differentiates in the transfection of Fgf8b with Otx2 indicates that Otx2 is a key mesencephalon. Based on the assumption that strong Fgf8 molecule in mesencephalic generation. We have shown by signal induces the cerebellum and that the Fgf8b signal is RT-PCR that both Fgf8a and Fgf8b are expressed, Fgf8b stronger than that of Fgf8a, we carried out experiments to expression prevailing in the isthmic region. The results all misexpress Fgf8b and Fgf8a in chick embryos. Fgf8a did not support our working hypothesis that the strong Fgf8 signal affect the expression pattern of Otx2, Gbx2 or Irx2. -

Fate of the Mammalian Cardiac Neural Crest
Development 127, 1607-1616 (2000) 1607 Printed in Great Britain © The Company of Biologists Limited 2000 DEV4300 Fate of the mammalian cardiac neural crest Xiaobing Jiang1,3, David H. Rowitch4,*, Philippe Soriano5, Andrew P. McMahon4 and Henry M. Sucov2,3,‡ Departments of 1Biological Sciences and 2Cell & Neurobiology, 3Institute for Genetic Medicine, Keck School of Medicine, University of Southern California, 2250 Alcazar St., IGM 240, Los Angeles, CA 90033, USA 4Department of Molecular and Cell Biology, Harvard University, 16 Divinity Ave., Cambridge, MA 02138, USA 5Program in Developmental Biology, Division of Basic Sciences, A2-025, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, 1100 Fairview Avenue North, PO Box 19024, Seattle, WA 98109, USA *Present address: Department of Pediatric Oncology, Dana Farber Cancer Institute, 44 Binney St., Boston, MA 02115, USA ‡Author for correspondence (e-mail: [email protected]) Accepted 26 January; published on WWW 21 March 2000 SUMMARY A subpopulation of neural crest termed the cardiac neural of these vessels. Labeled cells populate the crest is required in avian embryos to initiate reorganization aorticopulmonary septum and conotruncal cushions prior of the outflow tract of the developing cardiovascular to and during overt septation of the outflow tract, and system. In mammalian embryos, it has not been previously surround the thymus and thyroid as these organs form. experimentally possible to study the long-term fate of this Neural-crest-derived mesenchymal cells are abundantly population, although there is strong inference that a similar distributed in midgestation (E9.5-12.5), and adult population exists and is perturbed in a number of genetic derivatives of the third, fourth and sixth pharyngeal arch and teratogenic contexts. -

NERVOUS SYSTEM هذا الملف لالستزادة واثراء المعلومات Neuropsychiatry Block
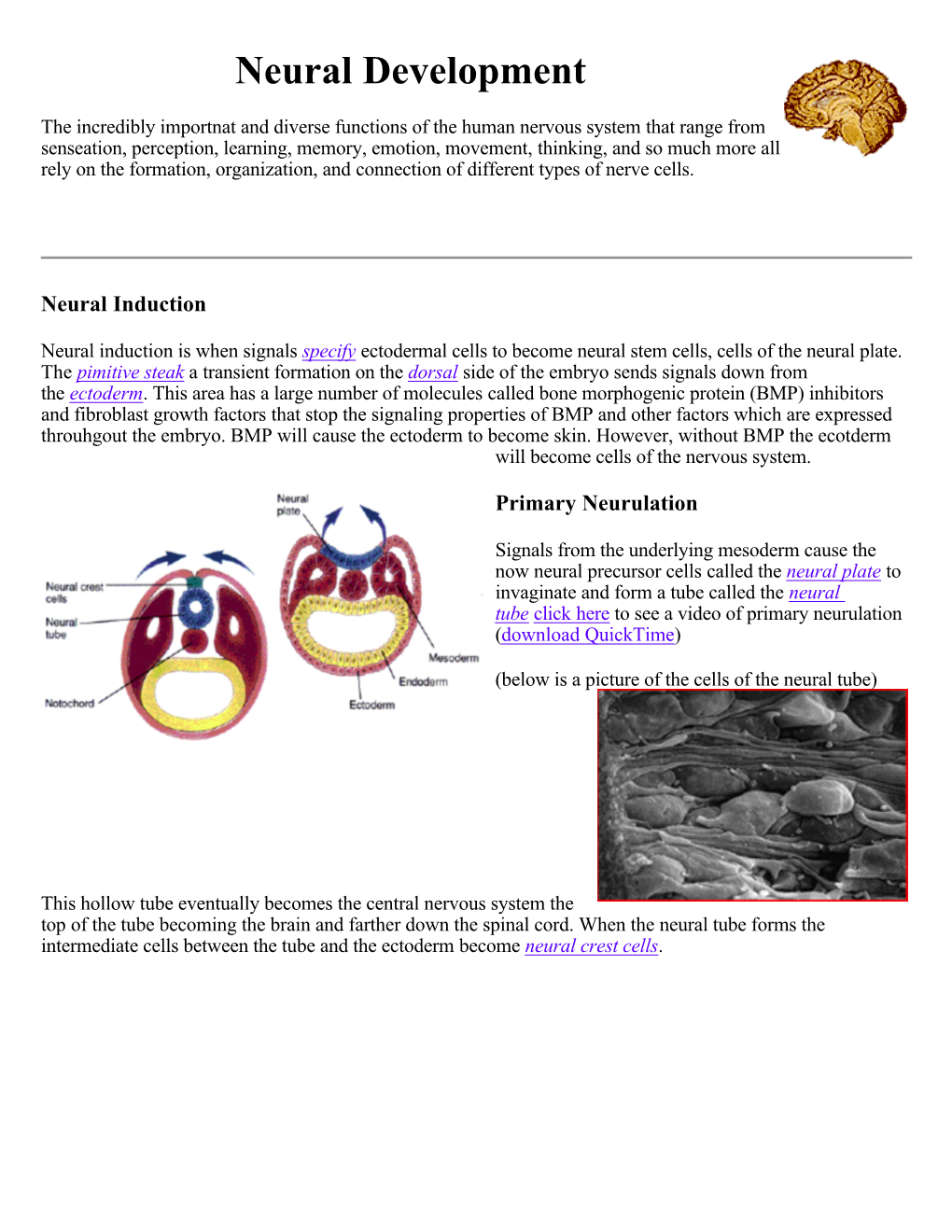
NERVOUS SYSTEM هذا الملف لﻻستزادة واثراء المعلومات Neuropsychiatry block. قال تعالى: ) َو َل َق د َخ َل قنَا ا ِْلن َسا َن ِمن ُس ََل َل ة ِ من ِطي ن }12{ ثُ م َجعَ لنَاه ُ نُ ط َفة فِي َق َرا ر م ِكي ن }13{ ثُ م َخ َل قنَا ال ُّن ط َفة َ َع َل َقة َف َخ َل قنَا ا لعَ َل َقة َ ُم ضغَة َف َخ َل قنَا ا ل ُم ضغَة َ ِع َظا ما َف َك َس ونَا ا ل ِع َظا َم َل ح ما ثُ م أَن َشأنَاه ُ َخ ل قا آ َخ َر َفتَبَا َر َك ّللا ُ أَ ح َس ُن ا ل َخا ِل ِقي َن }14{( Resources BRS Embryology Book. Pathoma Book ( IN DEVELOPMENTAL ANOMALIES PART ). [email protected] 1 OVERVIEW A- Central nervous system (CNS) is formed in week 3 of development, during which time the neural plate develops. The neural plate, consisting of neuroectoderm, becomes the neural tube, which gives rise to the brain and spinal cord. B- Peripheral nervous system (PNS) is derived from three sources: 1. Neural crest cells 2. Neural tube, which gives rise to all preganglionic autonomic nerves (sympathetic and parasympathetic) and all nerves (-motoneurons and -motoneurons) that innervate skeletal muscles 3. Mesoderm, which gives rise to the dura mater and to connective tissue investments of peripheral nerve fibers (endoneurium, perineurium, and epineurium) DEVELOPMENT OF THE NEURAL TUBE Neurulation refers to the formation and closure of the neural tube. BMP-4 (bone morphogenetic protein), noggin (an inductor protein), chordin (an inductor protein), FGF-8 (fibroblast growth factor), and N-CAM (neural cell adhesion molecule) appear to play a role in neurulation. -

Neuroanatomy
Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Neuroanatomy W. Jeffrey Wilson Fall 2012 \Without education we are in a horrible and deadly danger of taking educated people seriously." { Gilbert Keith Chesterton [LATEX in use { a Microsoft- & PowerPoint-free presentation] Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Blood-Brain Barrier Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Peripheral Nervous System • Somatic N.S.: skeletal muscles, skin, joints • Autonomic N.S.: internal organs, glands • Sympathetic N.S.: rapid expenditure of energy • Parasympathetic N.S.: restoration of energy Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Spinal Cord Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Brain | Ventricles Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Brain Midline Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Brain Midline Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Hindbrain Myelencephalon & Metencephalon Outline Protection Peripheral Nervous System Overview of Brain Hindbrain Midbrain Forebrain Reticular -

1) Brainstem and Cerebellum
Lecture Title: BRAIN STEM AND CEREBELLUM (CNS Block, Radiology) Lecture Objectives.. Students at the end of the lecture will be able to: • Identify radiological anatomy of brain stem and cerebellum. • Compares CT and MRI imaging of brain stem and cerebellum. • Recognize the imaging findings in common diseases involving brain stem and cerebellum. Brain Divisions.. • There are three major divisions of the brain: I Prosencephalon – Forebrain Diencephalon thalamus, hypothalamus Telencephalon cerebrum II Mesencephalon – Midbrain III Rhombencephalon - Hindbrain Metencephalon pons and cerebellum Myelencephalon medulla oblongata Brain Divisions.. Brain Stem.. • Three parts from superior to inferior: 1 midbrain 2 pons 3 medulla oblongata 1 2 • Connects cerebral 3 hemisphere with spinal cord Midbrain.. Radiological Features: CT+ • At the level of circle of willis • Anteriorly two cerebral peduncles separated by interpeduncular fossa • Posteriorly four rounded prominences (superior and inferior colliculi) MRI T2WI Midbrain.. MRI Sagittal T1WI MRI axial T2WI 1 4 3 2 2 1 1 superior colliculus 2 inferior colliculus 3 cerebral peduncle 4 interpeduncular cistern Midbrain.. Internal features: substantia nigra separates crus cerebri ventrally from tegmentum posteriorly. Red nuclei are dorsal to substantia nigra at the level of superior colliculi Pons.. Radiological Features: CT+ • The bulbous anterior part consists mainly of fibres continuous on each side with middle cerebellar peduncle • Basilar artery lies in groove anteriorly Petrous bone • Posterior surface of the pons forms the upper part of the floor of the 4th ventricle. • Bony anterior relation: clivus centrally and petrous temporal bones laterally Basilar artery Pons.. MRI axial T2WI MRI Sagittal T1WI 2 p p 1 3 1 P pons 1 4th ventricle 2 basilar artery 3 middle cerebellar peduncle Medulla oblongata. -

Early Regulative Ability of the Neuroepithelium to Form Cardiac Neural Crest
NIH Public Access Author Manuscript Dev Biol. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2012 January 15. NIH-PA Author ManuscriptPublished NIH-PA Author Manuscript in final edited NIH-PA Author Manuscript form as: Dev Biol. 2011 January 15; 349(2): 238±249. doi:10.1016/j.ydbio.2010.10.032. Early regulative ability of the neuroepithelium to form cardiac neural crest Akouavi M. Ezin, John W. Sechrist, Angela Zah, Marianne Bronner, and Scott E. Fraser Division of Biology, Biological Imaging Center, Beckman Institute (139-74), California Institute of Technology, Pasadena, CA 91125, USA Abstract The cardiac neural crest (arising from the level of hindbrain rhombomeres 6–8) contributes to the septation of the cardiac outflow tract and the formation of aortic arches. Removal of this population after neural tube closure results in severe septation defects in the chick, reminiscent of human birth defects. Because neural crest cells from other axial levels have regenerative capacity, we asked whether the cardiac neural crest might also regenerate at early stages in a manner that declines with time. Accordingly, we find that ablation of presumptive cardiac crest at stage 7, as the neural folds elevate, results in reformation of migrating cardiac neural crest by stage 13. Fate mapping reveals that the new population derives largely from the neuroepithelium ventral and rostral to the ablation. The stage of ablation dictates the competence of residual tissue to regulate and regenerate, as this capacity is lost by stage 9, consistent with previous reports. These findings suggest that there is a temporal window during which the presumptive cardiac neural crest has the capacity to regulate and regenerate, but this regenerative ability is lost earlier than in other neural crest populations. -

Cardiac Neural Crest Is Dispensable for Outflow Tract Septation in Xenopus Young-Hoon Lee1,2 and Jean-Pierre Saint-Jeannet2,*
RESEARCH ARTICLE 2025 Development 138, 2025-2034 (2011) doi:10.1242/dev.061614 © 2011. Published by The Company of Biologists Ltd Cardiac neural crest is dispensable for outflow tract septation in Xenopus Young-Hoon Lee1,2 and Jean-Pierre Saint-Jeannet2,* SUMMARY In vertebrate embryos, cardiac precursor cells of the primary heart field are specified in the lateral mesoderm. These cells converge at the ventral midline to form the linear heart tube, and give rise to the atria and the left ventricle. The right ventricle and the outflow tract are derived from an adjacent population of precursors known as the second heart field. In addition, the cardiac neural crest contributes cells to the septum of the outflow tract to separate the systemic and the pulmonary circulations. The amphibian heart has a single ventricle and an outflow tract with an incomplete spiral septum; however, it is unknown whether the cardiac neural crest is also involved in outflow tract septation, as in amniotes. Using a combination of tissue transplantations and molecular analyses in Xenopus we show that the amphibian outflow tract is derived from a second heart field equivalent to that described in birds and mammals. However, in contrast to what we see in amniotes, it is the second heart field and not the cardiac neural crest that forms the septum of the amphibian outflow tract. In Xenopus, cardiac neural crest cells remain confined to the aortic sac and arch arteries and never populate the outflow tract cushions. This significant difference suggests that cardiac neural crest cell migration into the cardiac cushions is an amniote-specific characteristic, presumably acquired to increase the mass of the outflow tract septum with the evolutionary need for a fully divided circulation. -

Ectoderm: Neurulation, Neural Tube, Neural Crest
4. ECTODERM: NEURULATION, NEURAL TUBE, NEURAL CREST Dr. Taube P. Rothman P&S 12-520 [email protected] 212-305-7930 Recommended Reading: Larsen Human Embryology, 3rd Edition, pp. 85-102, 126-130 Summary: In this lecture, we will first consider the induction of the neural plate and the formation of the neural tube, the rudiment of the central nervous system (CNS). The anterior portion of the neural tube gives rise to the brain, the more caudal portion gives rise to the spinal cord. We will see how the requisite numbers of neural progenitors are generated in the CNS and when these cells become post mitotic. The molecular signals required for their survival and further development will also be discussed. We will then turn our attention to the neural crest, a transient structure that develops at the site where the neural tube and future epidermis meet. After delaminating from the neuraxis, the crest cells migrate via specific pathways to distant targets in an embryo where they express appropriate target-related phenotypes. The progressive restriction of the developmental potential of crest-derived cells will then be considered. Additional topics include formation of the fundamental subdivisions of the CNS and PNS, as well as molecular factors that regulate neural induction and regional distinctions in the nervous system. Learning Objectives: At the conclusion of the lecture you should be able to: 1. Discuss the tissue, cellular, and molecular basis for neural induction and neural tube formation. Be able to provide some examples of neural tube defects caused by perturbation of neural tube closure. -

The Ectoderm: Neurulation, Neural Tube, Neural Crest
Events that remove cells Progressive restriction from the epidermal of developmental lineage potential The ectoderm: neurulation, neural tube, neural crest Taube P. Rothman [email protected] Neural Shaping the neural plate induction 18 days PRIMARY NEURULATION Neural induction, Wnt Wnt formation of the neural plate Dorsal and Wnt Wnt ventral Formation of of the neural signaling in the groove and neural folds spinal cord Closure of neural Neural crest folds, formation of neural tube and neural crest Initially, the neural tube is composed of a single layer of neuroepithelial cells 1 Dorsal view: Neurulating embryos Dorsal view: Neurulating embryos REGIONS OF NEURAL TUBE CLOSURE Days 21-22 Day 23 cranioschisis meningomyecele REGIONALIZATION OF THE CNS PRIMARY AND SECONDARY VESICLES AND FLEXURES Cephalic Rhombomere flexure Cervical flexure NEUROGENESIS IN THE NEUROEPITHELIUM How are billions of CNS cells (neurons and glia) generated? lumen Cerebral cortex lumen Post mitotic daughter cell Lumen Nuclei (but not cells) migrate during the cell The plane of division of progenitor cells in the cycle ventricular zone influences their fate The neuroepithelium is a single layer of rapidly dividing stem cells 2 At least half the neurons that are generated undergo apoptosis and die. Neuronal survival depends upon recognition of target related trophic signals. Ectomesenchyme The neural crest Neural crest cells are guided through permissive Wnt BMP environments to RhoB reach their targets slug Ephrin proteins inhibit neural crest migration THE REGION OF THE NEURAXIS FROM WHICH A CREST CELL MIGRATES DETERMINES THE TARGET REACHED BY ITS DERIVATIVES cranial circumpharyngeal neural crest truncal cardiac vagal truncal sacral 3 Genetic potential, developmental restriction and differentiation •Some neural crest cells appear to be pluripotent. -

26 April 2010 TE Prepublication Page 1 Nomina Generalia General Terms
26 April 2010 TE PrePublication Page 1 Nomina generalia General terms E1.0.0.0.0.0.1 Modus reproductionis Reproductive mode E1.0.0.0.0.0.2 Reproductio sexualis Sexual reproduction E1.0.0.0.0.0.3 Viviparitas Viviparity E1.0.0.0.0.0.4 Heterogamia Heterogamy E1.0.0.0.0.0.5 Endogamia Endogamy E1.0.0.0.0.0.6 Sequentia reproductionis Reproductive sequence E1.0.0.0.0.0.7 Ovulatio Ovulation E1.0.0.0.0.0.8 Erectio Erection E1.0.0.0.0.0.9 Coitus Coitus; Sexual intercourse E1.0.0.0.0.0.10 Ejaculatio1 Ejaculation E1.0.0.0.0.0.11 Emissio Emission E1.0.0.0.0.0.12 Ejaculatio vera Ejaculation proper E1.0.0.0.0.0.13 Semen Semen; Ejaculate E1.0.0.0.0.0.14 Inseminatio Insemination E1.0.0.0.0.0.15 Fertilisatio Fertilization E1.0.0.0.0.0.16 Fecundatio Fecundation; Impregnation E1.0.0.0.0.0.17 Superfecundatio Superfecundation E1.0.0.0.0.0.18 Superimpregnatio Superimpregnation E1.0.0.0.0.0.19 Superfetatio Superfetation E1.0.0.0.0.0.20 Ontogenesis Ontogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.21 Ontogenesis praenatalis Prenatal ontogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.22 Tempus praenatale; Tempus gestationis Prenatal period; Gestation period E1.0.0.0.0.0.23 Vita praenatalis Prenatal life E1.0.0.0.0.0.24 Vita intrauterina Intra-uterine life E1.0.0.0.0.0.25 Embryogenesis2 Embryogenesis; Embryogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.26 Fetogenesis3 Fetogenesis E1.0.0.0.0.0.27 Tempus natale Birth period E1.0.0.0.0.0.28 Ontogenesis postnatalis Postnatal ontogeny E1.0.0.0.0.0.29 Vita postnatalis Postnatal life E1.0.1.0.0.0.1 Mensurae embryonicae et fetales4 Embryonic and fetal measurements E1.0.1.0.0.0.2 Aetas a fecundatione5 Fertilization -

Embryology Team
Embryology team Development of cerebrum and cerebellum Team members 1- Lama Alhwairikh 1-Nawaf Modahi 2- Norah AlRefayi 2- Abdulrahman Ahmed Al-Kadhaib 3- Sara Alkhelb 3- Khalid Al-Own 4-Abdulrahman Al-Khelaif Student Guide: 1- The notes, which are written by the team, are in Blue . 2- Everything written in Red is important. • By the beginning of the 3rd week of development, three germ cell layers become established, 1 ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm. • During the middle of the 3rd week, the dorsal midline ectoderm undergoes thickening to form the 2 neural plate. • The margins of the plate become elevated, forming 3 neural folds. • A longitudinal, midline depression, called the 4 neural groove is formed. • The 2 neural folds then fuse together, to form 5 the neural tube. • Formation of the neural tube is completed by 6 the middle of the fourth week of development. The brain vesicle grows and gives 3 dilatations named as: • Prosencephalon • Mesencephalon • Rhombencephalon Telencephalon cerebral hemispheres Forebrain prosencephalon Diencephalon Thalami Midbrain mesencephalon Mesencephalon Midbrain Metencephalon Pones & cerebellum Hindbrain rhombencephalon Myelencephalon Medulla By the end of 4th week the 3 primary vesicles develop (3 vesicles stage) By the 5th week 5 secondary vesicles develop (5 vesicles stage) By 4th week: By the 4th week: The neural tube grows rapidly and bends ventrally with the head fold, producing two flexures: Midbrain (cephalic) flexure: In the region of midbrain. Cervical flexure: between the hind brain & the spinal cord. Later Pontine flexure appears in the hindbrain, in the opposite direction of the cephalic & cervical flexures, resulting in stretching and thinning of the roof of the hindbrain.