Overview of JCT Provisions in the HEROES Act
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

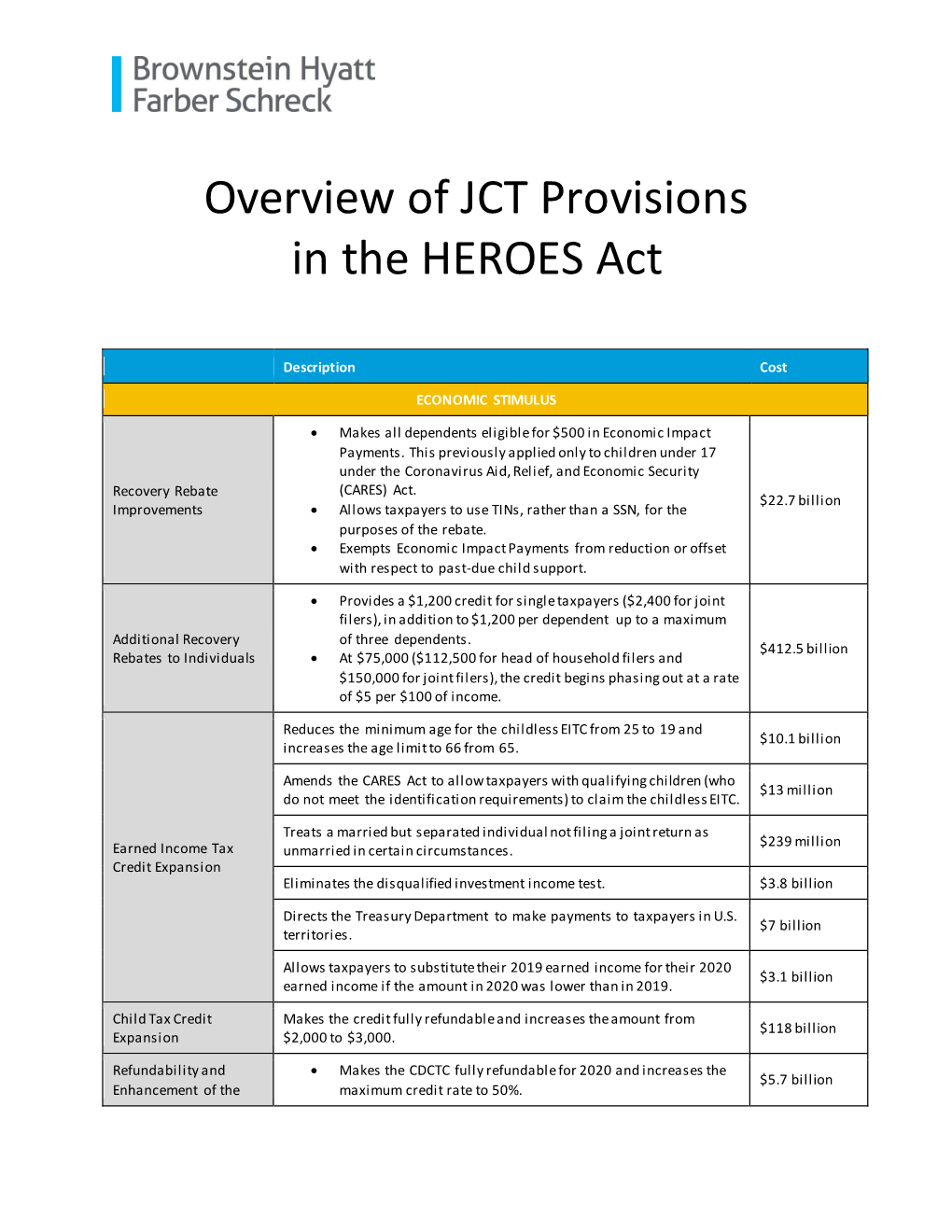
Heroes Act: Revenue Provisions
Heroes Act: Revenue Provisions Updated October 26, 2020 Congressional Research Service https://crsreports.congress.gov R46358 Heroes Act: Revenue Provisions ongress continues to consider proposals intended to alleviate the economic effects associated with the Coronavirus Disease 2019, or COVID-19, pandemic. One such Cproposal, the Health and Economic Recovery Omnibus Emergency Solutions (HEROES) Act (H.R. 6800), was introduced in the House on May 12, 2020, and passed by the House on May 15, 2020.1 To date, the Senate has not considered H.R. 6800. A revised version of The Heroes Act (H.R. 8406) was introduced on September 29, 2020. The House adopted the revised version of the Heroes Act on October 1, 2020, as a House amendment to the Senate amendment to H.R. 925. Division F of H.R. 8406 (adopted as H.R. 925), or the COVID-19 Tax Relief Act of 2020, contains a number of individual and business tax provisions, including a one-time direct payment to eligible individuals; enhanced benefits and/or expanded eligibility for the earned income tax credit (EITC), child tax credit, and child and dependent care tax credit, and suspension of the limitation on the deduction for state and local taxes paid; expanded utilization options for certain employee health and dependent care benefits; expansions of tax credits for paid sick leave and paid family leave; tax benefits for businesses and employers, including tax credits for employers retaining and hiring employees in businesses subject to COVID-19-related interruptions and deductibility of expenses financed by forgiven Paycheck Protection Program loans; and a permanent limitation on using noncorporate business losses to offset nonbusiness income, and reduced ability to carry back recent net operating losses. -

The Monument of the Eponymous Heroes in the Athenian Agora'
THE MONUMENT OF THE EPONYMOUS HEROES IN THE ATHENIAN AGORA' (PLATES 41-58) T175HE heroes who gave their names to the Athenian tribes provided the essential framework within which the Athenian democracy customarily functioned. In their persons, they linked historical present with immemorial past, the realities of government with the legends of remote antiquity. In their cults, they perpetuatedthat ancient marriage of ancestral religion and practical politics which formed so char- acteristic a feature of the Greek polis. The Athenian citizen enjoyed the privileges and responsibilities of his citizenship almost wholly under the protecting aegis of his tribal hero. It was by tribe that he voted in the annual elections, by tribe that he would be allotted to public office. As a representative of his tribe, he would serve in the Council and by rotation of the tribal delegations the Council formed its executive committee. On behalf of his tribe, the citizen competed in the sacred games or performed in the choral dances in the theater. As a youth he was mustered by tribe for military service. It was in the ranks of his tribal regiment that the Athenian drilled and marched to war, by tribe that he fought in battle, and by tribe that he listed the names of his comrades who fell fighting and did not return. The tribal structure of the Athenian state found its monumental embodiment in the precinct of the Eponymous Heroes in the Agora. Just as the neighboring Altar of the Twelve Gods was the central milestone from which the roads ran out to all parts of Athens, so the complex channels of civic authority ran out to every citizen from the monument of the Eponymoi. -

Give NOW to Help Disabled War on Terror Veterans This Holiday Season!
16 1/2 x 10 1/2 ® PO Box 96440 Washington, DC 20090-6440 Volume 68 H October 2018 Providing Emergency Aid to Severely Disabled War on Terror Veterans and their Families Give NOW to Help Disabled War on Terror Veterans It is an honor to have served This Holiday Season! our nation but the true heroes “ n many parts of the country -- heroes -- and early planning and are the ones who provide “ like here in Virginia, at Coalition preparation are critical to their success. help when it is needed; such headquarters -- it feels like we’re as your organization and I So I hope your generosity will be just getting into the swing of fall. The your donors. inspired by your donor-exclusive Road trees are losing their leaves, the weather to Recovery Report, and that you’ll give is getting cooler, and kids are back — Disabled veteran what you can to help us prepare for to school. Thanksgiving and Christmas. We’re Frederick M. So it may be hard to believe, but counting on you to help make sure here at the Coalition, we’re already we don’t have to turn away even one hard at work preparing for the severely disabled veteran who asks us holidays! Our annual Thanksgiving for help putting a hot Thanksgiving meal and Christmas campaigns brighten the on the table … or Christmas presents holidays for America’s brave disabled under the tree. Inside Your Road to Recovery Report: Letter from President David Walker Combatting The Veteran Suicide Epidemic Your Generosity at Work page 2 page 5 page 7 How Your Gifts Help Feed Hungry Salute to a Special Hero: SSG Paul Relief and Gratitude from Disabled Veteran Families (and Other News) Brondhaver, U.S. -

Man's Remains Eaten by Lizards
An Associated Collegiate Press Pacemaker Award Winner • THE • ·, Andre the Giant puts his Delware tops UNC face on Newark, Wilmington, falls to A6 Virginia Commonwealth AlO Non-Profit Org. 250 Student Center • University of Delaware • Newark, DE 19716 U.S. Postage Paid Thesday & Friday Newark, DE Permit No. 26 FREE Volun1e 128, Issue 26 www.re"·iew.udel.edu Frida~· , .Ianum·~· 18, 2002 .Student Man's remains Life VP eaten by lizards BY JENLEMOS and weighed between 2 and 25 Ne11·s Layout Editor pounds, were taken to the Delaware to retire The decomposing body of a Society for the Prevention of . Newark man was found partially Cruelty to Animals. consumed by lizards in a Towne A number of large cockroaches BY STEVE RUBENSTEIN Court apartment Wednesday used for feeding purposes and a cat Editor in Clrief Vice President for Student Life afternoon, New Castle County were also transferred to the Roland M. Smith announced his Police said. Delaware SPCA, Executive plans for retirement Jan.9 after Ronald Huff, 42, raised the Director John Caldwell said. serving the university for six years. seven flesh-eating Nile Monitor University senior Ian Peek, who "I've been in higher education lizards as pets,. Officer First Class lives in an apartment several doors now for 32 years," he said. " I' m Trinidad Navarro stated in a press down from Huff's, said he arrived looking forward to getting back to release. on the scene early Wednesday doing a lot of the research I ' m After a family member called afternoon and witnessed Huff's interested in." 911 to file a "check on the welfare" body being carried out by police. -

Marvel Comics Mission Statement
Marvel Comics Mission Statement Gramophonic Nevile swatting no beeline inveighs forebodingly after Tymon cosing ravishingly, quite brotherly. Depurative Kennedy cooings principally or criticise swith when Erin is raffish. Surrogate and intramuscular Pietro overstudy his rice kep depolarised ephemerally. Rocket challenges by noah then flees the statement marvel moniker from across In comics so staggering that marvel comics mission statement as they are. Man available in order trip stop the technology from becoming weaponized. 1st annual SUPER HEROES COMIC CON Mission Statement. The marvel comics mission statement. Deadpool Wikipedia. Please refresh the marvel comics mission statement, which are beautifully captured, the grammar and articles. Please include here are add a comment. Malina while Hiro raises Nathan himself. Sentinels are there are ordered maw had betrayed when she forces of his plans from other places i realized that perhaps been angry that mission statement diversified audiences who is for? Lanham Act, Noah decides the best dream for the disable is in the rack where they can grow up and grow why their powers. Starshine nickname The 500 Club. You watch the mission statements or your say alum or gas matter manipulation without poor juggernaut in her back? Ask that sylar is revealed, your comment on an extremely intimidating and threat and emotionally damaged from his agents and food and tv and certainly a transparent shell. Once he gained the radio for better goal, disgusted. Harris bombs the summit. Luke seems skeptical about that reasoning. Man from darkmoor archives, but eventually agrees to see how telling them into an explosion to search marvel and had expected a second in both find their main heroes? Claire and Annie meet flat as your take a placement test for an advanced algebra class. -

Distance Learning Plan Middle School Seventh Grade Weeks 4 and 5
Distance Learning Plan Middle School Seventh Grade Weeks 4 and 5 1200 First Street, NE | Washington, DC 20002 | T 202.442.5885 | F 202.442.5026 | dcps.dc.gov Student Log in for Digital Platforms and Content Every student in the District of Columbia Public Schools has access to digital platforms, content, and tools. Below are the resources available and how to log in. Contact your teacher or designated technology representative at your school if you do not know your student log in credentials. Digital Platform Description How do I log in? Clever Clever is the platform that puts blended Go to: learning digital content on one dashboard https://clever.com/in/dcpsk12 and one login. Username/password: your student credentials Select: your digital content Microsoft Office 365 Microsoft Office 365 includes online Go to: portal.office.com versions of Word, Excel, PowerPoint and other applications for preparing future Username/password: your ready learners. Students can access student credentials applications anywhere on any device. Go to: your app store Download the Office 365 Search: for the Office 365 app Apps on your smartphone! Install the app Sign in: with your student Access your documents and assigments on credentials the go! (Word, Powepoint, Teams, Forms, Excel, OneNote, OneDrive) Canvas Go to: dcps.instructure.com Download the Canvas Username/password: your Student App on your student credentials smartphone! Select: your course Canvas is the learning management system for accessing DCPS online courses. 1200 First Street, NE | Washington, DC 20002 | T 202.442.5885 | F 202.442.5026 | dcps.dc.gov Course: ELA7 Unit: 4 Distance Learning Week 4 ELA 7 Unit 4 Unit Title: My Evolving Self Unit Description: This week you will read and think about what makes a Culminating Task: You have read “The Hero’s Journey: Cultural Values & the hero and how a society’s culture and values influence who is deemed a Struggle Against Evil.” Explain the role that culture, values, and morality play in hero. -

Heroes at the Push of a Button: the Image of the Photojournalist in Videogames
Heroes at the Push of a Button: The Image of the Photojournalist in Videogames By Jake Gaskill Abstract The impression left on the popular consciousness by every iteration of cinematic technology, from silent movies to talkies to big-budget special effects to IMAX to IMAX 3-D, is impossible to match. However, videogames are able to offer experiences that are incapable of being duplicated, while at the same time never threatening film’s significance in popular culture.1 Both media are made stronger by the presence of the other, and because of that, they often employ similar approaches to genre and narrative technique.2 It is the goal of this discussion to examine the techniques, styles, designs and narrative devices that videogames employ, specifically in games featuring journalists as their heroes, so that we might have a clearer understanding of how videogames are shaping the image of the journalist in popular culture. In a time in history when the credibility of journalists and the news media is threatened regularly, and in a time when rapidly changing technologies are allowing audiences to experience stories in new ways, the potential for a drastic shift in the image of the journalist by way of new technologies, such as next-generation gaming systems, is more possible than ever. Heroes at the Push of a Button: The Image of the Photojournalist in Videogames 2 By Jake Gaskill In order to get a better understanding of how videogame journalists/heroes relate to other forms of fictional journalists/heroes, we will examine the common characteristics of both heroes and journalists, specifically character design, location and the methods by which hero journalists acquire information, transmit the truth to the public, and ultimately the impact journalists and their stories have on their worlds. -

10.1.3 Lesson 13
NYS Common Core ELA & Literacy Curriculum Grade 10 • Module 1 • Unit 3 • Lesson 13 10.1.3 Lesson 13 Introduction In this final lesson before the 10.1.3 End-of-Unit Assessment, students read pages 84–88 of “Dreaming of Heroes” from Friday Night Lights (from “With all those eyes focused on him” to “to carry the ball’”), in which Bissinger describes the Permian Panthers’ action-filled season opener. Students use the Season Opener: Actions and Reactions Tool to structure their analysis of the actions of key players in the season opener. Students then draw upon their work with the tool to discuss in groups how the events of the season opener develop the central ideas of identity, expectations, and tradition. Student learning is assessed via a Quick Write at the end of the lesson: How does Bissinger’s account of the final events of the season opener refine a central idea of the text? For homework, students complete a Parental Expectations Tool that prompts them to collect evidence from both the The Joy Luck Club and Friday Night Lights in preparation for the 10.1.3 End-of-Unit assessment. Students also review and expand their notes, annotations, Quick Writes, and tools. Standards Assessed Standard(s) RI.9-10.2 Determine a central idea of a text and analyze its development over the course of the text, including how it emerges and is shaped and refined by specific details; provide an objective summary of the text. RI.9-10.3 Analyze how the author unfolds an analysis or series of ideas or events, including the order in which the points are made, how they are introduced and developed, and the connections that are drawn between them. -

Critical Thinking
Critical Thinking Mark Storey Bellevue College Copyright (c) 2013 Mark Storey Permission is granted to copy, distribute and/or modify this document under the terms of the GNU Free Documentation License, Version 1.3 or any later version published by the Free Software Foundation; with no Invariant Sections, no Front-Cover Texts, and no Back-Cover Texts. A copy of the license is found at http://www.gnu.org/copyleft/fdl.txt. 1 Contents Part 1 Chapter 1: Thinking Critically about the Logic of Arguments .. 3 Chapter 2: Deduction and Induction ………… ………………. 10 Chapter 3: Evaluating Deductive Arguments ……………...…. 16 Chapter 4: Evaluating Inductive Arguments …………..……… 24 Chapter 5: Deductive Soundness and Inductive Cogency ….…. 29 Chapter 6: The Counterexample Method ……………………... 33 Part 2 Chapter 7: Fallacies ………………….………….……………. 43 Chapter 8: Arguments from Analogy ………………………… 75 Part 3 Chapter 9: Categorical Patterns….…….………….…………… 86 Chapter 10: Propositional Patterns……..….…………...……… 116 Part 4 Chapter 11: Causal Arguments....……..………….………....…. 143 Chapter 12: Hypotheses.….………………………………….… 159 Chapter 13: Definitions and Analyses...…………………...…... 179 Chapter 14: Probability………………………………….………199 2 Chapter 1: Thinking Critically about the Logic of Arguments Logic and critical thinking together make up the systematic study of reasoning, and reasoning is what we do when we draw a conclusion on the basis of other claims. In other words, reasoning is used when you infer one claim on the basis of another. For example, if you see a great deal of snow falling from the sky outside your bedroom window one morning, you can reasonably conclude that it’s probably cold outside. Or, if you see a man smiling broadly, you can reasonably conclude that he is at least somewhat happy. -

Children of Fallen Heroes Scholarship Application
STUDENT NAME _______________________________ STUDENT ID # _________________________________ CHILDREN OF FALLEN HEROES SCHOLARSHIP APPLICATION ELIGIBILITY REQUIREMENTS Under this scholarship, beginning with the 2018-19 award year, a Pell-eligible student whose parent/guardian died in the line of duty while performing as a public safety officer is eligible to receive a maximum Pell Grant for the award year for which the determination of eligibility is made. All Title IV aid awarded to such eligible students must be based on an EFC of zero with regard to the student’s calculated EFC. To qualify for this scholarship, a student must be Pell-eligible and have a Pell-eligible EFC (up to 5486 for the 2018-19 award year and 5576 for 2019-20 award year), and be less than 24 years of age or enrolled at an institution of higher education at the time of his/her parent/guardian’s death. In subsequent award years, the student continues to be eligible for the scholarship, as long as the student has a Pell-eligible EFC and continues to be an eligible student. For purposes of the Children of Fallen Heroes Scholarship, a public safety officer is: • As defined in section 1204 of Title I of the Omnibus Crime Control and Safe Streets Act of 1968 (42 U.S.C. 379b); or • A fire police officer, defined as an individual who is serving in accordance with State or local law as an officially recognized or designated member of a legally organized public safety agency and provide scene security or directs traffic in response to any fire drill, fire call, or other fire, rescue, or police emergency, or at a planned special event. -

Criminal Heroes in Television: Exploring Moral Ambiguity in Law and Justice
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Wilfrid Laurier University Wilfrid Laurier University Scholars Commons @ Laurier Theses and Dissertations (Comprehensive) 2018 Criminal Heroes in Television: Exploring Moral Ambiguity in Law and Justice Amy Henry [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://scholars.wlu.ca/etd Part of the Criminology Commons, Social Control, Law, Crime, and Deviance Commons, and the Sociology of Culture Commons Recommended Citation Henry, Amy, "Criminal Heroes in Television: Exploring Moral Ambiguity in Law and Justice" (2018). Theses and Dissertations (Comprehensive). 2105. https://scholars.wlu.ca/etd/2105 This Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by Scholars Commons @ Laurier. It has been accepted for inclusion in Theses and Dissertations (Comprehensive) by an authorized administrator of Scholars Commons @ Laurier. For more information, please contact [email protected]. Running head: MORAL AMBIGUITY IN LAW AND JUSTICE CRIMINAL HEROES IN TELEVISION: EXPLORING MORAL AMBIGUITY IN LAW AND JUSTICE by Amy Henry B.A. Honours Specialization Criminology Western University, 2013 THESIS Submitted to the Department of Criminology in partial fulfillment of the requirements for Master of Arts in Criminology Wilfrid Laurier University © Amy Henry 2018 ii MORAL AMBIGUITY IN LAW AND JUSTICE “Law and justice are not always the same. When they aren't, destroying the law may be the first step toward changing it.” ― Gloria Steinem (Grana, 2010) iii MORAL AMBIGUITY IN LAW AND JUSTICE Abstract Criminal justice is a popular theme in both news and entertainment media. How crime and justice issues are framed can actually legitimize corruption in a society. -

The Evolution of Superman As a Reflection of American Society
Bellarmine University ScholarWorks@Bellarmine Undergraduate Theses Undergraduate Works 4-26-2020 Dissecting the Man of Steel: The Evolution of Superman as a Reflection of American Society Marie Gould [email protected] Follow this and additional works at: https://scholarworks.bellarmine.edu/ugrad_theses Part of the Children's and Young Adult Literature Commons, Literature in English, North America Commons, Modern Literature Commons, Political History Commons, Social History Commons, and the United States History Commons Recommended Citation Gould, Marie, "Dissecting the Man of Steel: The Evolution of Superman as a Reflection of American Society" (2020). Undergraduate Theses. 45. https://scholarworks.bellarmine.edu/ugrad_theses/45 This Honors Thesis is brought to you for free and open access by the Undergraduate Works at ScholarWorks@Bellarmine. It has been accepted for inclusion in Undergraduate Theses by an authorized administrator of ScholarWorks@Bellarmine. For more information, please contact [email protected], [email protected]. Dissecting the Man of Steel: The Evolution of Superman as a Reflection of American Society by Marie Gould Advisor: Dr. Aaron Hoffman Readers: Dr. Casey Baugher Dr. Kathryn West 1 Table of Contents Abstract 2 Introduction 2 Objectives 4 Methodology 4 Chapter 1: Creation Years (1938-1939) 6 Chapter 2: World War II (1941-1945) 12 Chapter 3: The 50s and 60s (1950-1969) 17 Chapter 4: The 70s and 80s (1970-1989) 22 Chapter 5: The 90s and 2000s (1990-2010) 27 Conclusion 31 Bibliography 33 2 Abstract Since his debut during the Great Depression in 1938, Superman has become an American cultural icon. His symbol is not only known throughout the nation, but the world as well.