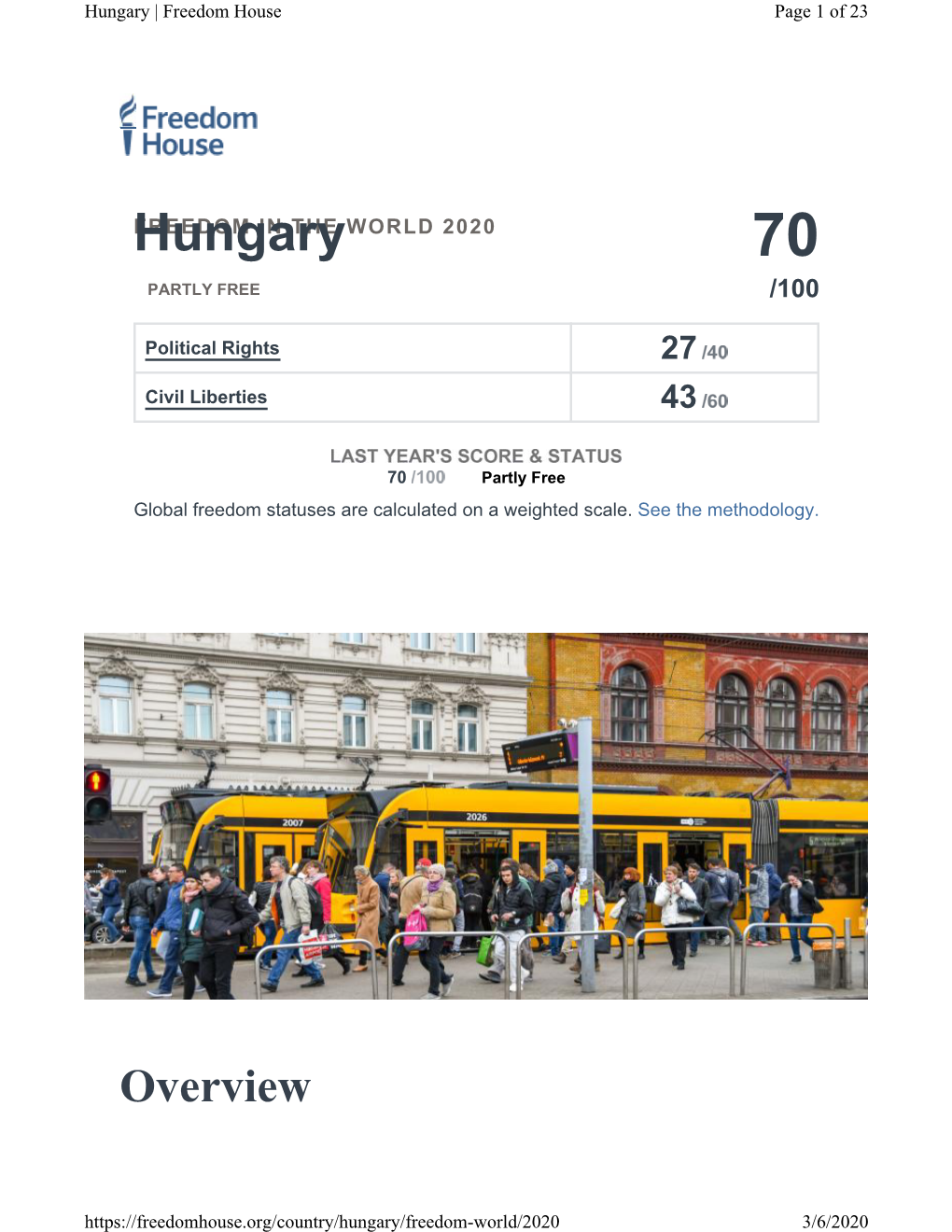
Freedom in the World Report 2020
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Electorate, 1990-1998 by Gergely Karácsony and Gábor Tóka
1 The Electorate, 1990-1998 by Gergely Karácsony and Gábor Tóka Published in Hungary: Government and Politics 1848-2000, ed. by Mária Ormos and Béla K. Király. Highland Lakes, NJ: Atlantic Research and Publications, Inc. and Boulder, CO: Social Science Monographs, pp. 495-518. In this chapter we review the voters' behavior in the parliamentary elections of 1990, 1994, and 1998.1 As the reader will recall, these were not the only competitive elections in Hungarian history in which a large majority of citizens could vote. However, unlike, for instance, the elections of 1920, 1938, 1945 or 1947, the electoral contests of the 1990's took place in a political context characterized by widespread consensus on fundamental democratic values among the relevant political parties. For the first time ever, no relevant political player was intimidated or barred from participating in the elections, and citizens could reasonably expect both that the votes were to be counted fairly and that the democratic game was to continue indefinitely after the election. The lawful revolution of 1988-1990 produced an unexpectedly stable institutional framework. The rules regarding executive-legislative relations, the checks and balances provided in the constitution, the electoral system, and the number and name of the major party alternatives remained largely unchanged throughout the 1990s. Despite disagreements about various details of the institutional framework, every relevant political camp retained a basic loyalty to the rules of the game as defined in the process of democratic transition. This comprehensive elite consensus was manufactured at a price, though, which introduced a large dose of unpredictability into the new political system. -

Women's and Gender History in Central Eastern Europe, 18Th to 20Th Centuries
Forthcoming in: Irina Livezeanu, Arpad von Klimo (eds), The Routledge History of East Central Europe since 1700 (Routledge 2015) Women‘s and Gender History1 Krassimira Daskalova and Susan Zimmermann Since the 1980s, historians working on East Central Europe, as on other parts of the world, have shown that historical experience has been deeply gendered. This chapter focuses on the modern history of women, and on gender as a category of analysis which helps to make visible and critically interrogate ―the social organization of sexual difference‖2. The new history of women and gender has established, as we hope to demonstrate in this contribution, a number of key insights. First, gender relations are intimately related to power relations. Gender, alongside dominant and non-dominant sexualities, has been invoked persistently to produce or justify asymmetrical and hierarchical arrangements in society and culture as a whole, to restrict the access of women and people identifying with non-normative sexualities to material and cultural goods, and to devalue and marginalize their ways of life. Second, throughout history both equality and difference between women and men have typically resulted in disadvantage for women. Men and women have generally engaged in different socio-cultural, political and economic activities, and this gender-based division of labor, which has itself been subject to historical change, has tended to put women in an inferior position. Even when women and men appeared as equals in one sphere of life, this perceived equality often resulted in drawbacks or an increased burden for women in another area and women‘s contribution was still devalued as compared to men‘s. -

ESS9 Appendix A3 Political Parties Ed
APPENDIX A3 POLITICAL PARTIES, ESS9 - 2018 ed. 3.0 Austria 2 Belgium 4 Bulgaria 7 Croatia 8 Cyprus 10 Czechia 12 Denmark 14 Estonia 15 Finland 17 France 19 Germany 20 Hungary 21 Iceland 23 Ireland 25 Italy 26 Latvia 28 Lithuania 31 Montenegro 34 Netherlands 36 Norway 38 Poland 40 Portugal 44 Serbia 47 Slovakia 52 Slovenia 53 Spain 54 Sweden 57 Switzerland 58 United Kingdom 61 Version Notes, ESS9 Appendix A3 POLITICAL PARTIES ESS9 edition 3.0 (published 10.12.20): Changes from previous edition: Additional countries: Denmark, Iceland. ESS9 edition 2.0 (published 15.06.20): Changes from previous edition: Additional countries: Croatia, Latvia, Lithuania, Montenegro, Portugal, Slovakia, Spain, Sweden. Austria 1. Political parties Language used in data file: German Year of last election: 2017 Official party names, English 1. Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs (SPÖ) - Social Democratic Party of Austria - 26.9 % names/translation, and size in last 2. Österreichische Volkspartei (ÖVP) - Austrian People's Party - 31.5 % election: 3. Freiheitliche Partei Österreichs (FPÖ) - Freedom Party of Austria - 26.0 % 4. Liste Peter Pilz (PILZ) - PILZ - 4.4 % 5. Die Grünen – Die Grüne Alternative (Grüne) - The Greens – The Green Alternative - 3.8 % 6. Kommunistische Partei Österreichs (KPÖ) - Communist Party of Austria - 0.8 % 7. NEOS – Das Neue Österreich und Liberales Forum (NEOS) - NEOS – The New Austria and Liberal Forum - 5.3 % 8. G!LT - Verein zur Förderung der Offenen Demokratie (GILT) - My Vote Counts! - 1.0 % Description of political parties listed 1. The Social Democratic Party (Sozialdemokratische Partei Österreichs, or SPÖ) is a social above democratic/center-left political party that was founded in 1888 as the Social Democratic Worker's Party (Sozialdemokratische Arbeiterpartei, or SDAP), when Victor Adler managed to unite the various opposing factions. -

RSCAS 2017/37 Rebuilding the Hungarian Right Through Civil
RSCAS 2017/37 Robert Schuman Centre for Advanced Studies Rebuilding the Hungarian Right through Civil Organization and Contention: The Civic Circles Movement Béla Greskovits European University Institute Robert Schuman Centre for Advanced Studies Rebuilding the Hungarian Right through Civil Organization and Contention: The Civic Circles Movement Béla Greskovits EUI Working Paper RSCAS 2017/37 This text may be downloaded only for personal research purposes. Additional reproduction for other purposes, whether in hard copies or electronically, requires the consent of the author(s), editor(s). If cited or quoted, reference should be made to the full name of the author(s), editor(s), the title, the working paper, or other series, the year and the publisher. ISSN 1028-3625 © Béla Greskovits, 2017 Printed in Italy, July 2017 European University Institute Badia Fiesolana I – 50014 San Domenico di Fiesole (FI) Italy www.eui.eu/RSCAS/Publications/ www.eui.eu cadmus.eui.eu Robert Schuman Centre for Advanced Studies The Robert Schuman Centre for Advanced Studies (RSCAS), created in 1992 and directed by Professor Brigid Laffan, aims to develop inter-disciplinary and comparative research and to promote work on the major issues facing the process of integration and European society. The Centre is home to a large post-doctoral programme and hosts major research programmes and projects, and a range of working groups and ad hoc initiatives. The research agenda is organised around a set of core themes and is continuously evolving, reflecting the changing agenda of European integration and the expanding membership of the European Union. Details of the research of the Centre can be found on: http://www.eui.eu/RSCAS/Research/ Research publications take the form of Working Papers, Policy Papers, Policy Briefs, Distinguished Lectures, Research Project Reports and Books. -

Events of 2013
Europe Katalin Halász and Nurçan Kaya Europe Paul Iganski AZERBAIJAN AZER. ARMENIA GEORGIA RUSSIA SEA TURKEY K CYPRUS ICELAND AC BL UKRAINE VA MOLDO BELARUS ATL ANTIC FINLAND BULGARIA TVIA ROMANIA ANEAN SEA LA FINLAND OCEAN ESTONIA NORWAY GREECE LITHUANIA ovo SWEDEN MACEDONIA SERBIA MONTENEGRO AKIA RUSSIA Kos OV POLAND ESTONIA SL ALBANIA Kaliningrad (Rus.) HUNGARY BOSNIA AND HERZE. LATVIA MEDITERR SWEDEN IRELAND DENMARK CROATIA UNITED ITALY CZECH REP. LITHUANIA KINGDOM AUSTRIA AY KaliningradSLOVENIA (Rus.) NORW BELARUS LIECH. NETHERLANDS SAN MARINO GERMANY DENMARK GERMANY POLAND BELGIUM LUXEMBOURG LUXEMBOURG MONACO UKRAINE CZECH REP.SWITZERLAND BELGIUM SLOVAKIA NETHERLANDS LIECH. MOLDOVA FRANCE SWITZERLAND AUSTRIA HUNGARY FRANCE SLOVENIA ANDORRA UNITED ROMANIA KINGDOM CROATIA BOSNIA GEORGIA ANDORRA SAN MARINO SERBIA PORTUGAL AND HERZE. BLACK SEA MONACO MONTENEGRO AZERBAIJAN ICELAND IRELAND Kosovo SPAIN BULGARIA ARMENIA MACEDONIASPAIN ANTIC AZER. ITALY ALBANIA L TURKEY OCEAN GREECE AT PORTUGAL CYPRUS MEDITERRANEAN SEA n November 2013, in her opening speech considerable anti-migrant and generalized anti- at the European Union Fundamental ‘foreigner’ sentiment across the region. I Rights Agency (FRA) conference on The internet and social media have provided Combating Hate Crime in the EU, Cecilia new opportunities for venting such sentiment. Malmström, the Commissioner of the European Individuals from minority communities who step Commission in charge of Home Affairs, into the public eye in politics, media and sport, expressed concern about the ‘mounting wave have provided new targets for hate through social of harassment and violence targeting asylum media. Between 2012 and 2014 the Council of seekers, immigrants, ethnic minorities and Europe is engaged in a major initiative against sexual minorities in many European countries’. -

Hungarian Studies ^Vieiv Vol
HSK Hungarian Studies ^vieiv Vol. XXVI, Nos. 1-2 (Spring-Fall, 1999) Special Volume: Women and Hungary: Reclaiming Images and Histories Edited by Marlene Kadar and Agatha Schwartz Essays in Politics, History, Literary and Art History, and Biography HUNGARIAN STUDIES REVIEW HUNGARIAN STUDIES NATIONAL ASSOCIATION OF CANADA SZECHENYI LIBRARY VOL. 26, NOS. 1-2 (SPRING-FALL 1999) EDITORS GEORGE BISZTRAY N.F. DREISZIGER University of Toronto Royal Military College of Canada GUEST EDITORS FOR 1999 MARLENE KADAR AGATHA SCHWARTZ York University University of Ottawa EDITORIAL ADVISERS OLIVER BOTAR GEZA JESZENSZKY University of Manitoba Budapest and Washington ILONA KOVACS MARIA KRISZTINKOVICH National Szechenyi Library Vancouver, B.C. BARNABAS A. RACZ THOMAS SAKMYSTER Eastern Michigan U. University of Cincinnati THOMAS SPIRA S.B. VARDY U.P.E.I. Duquesne University JOZSEF VEKERDI Budapest SUBSCRIPTIONS MANAGER EVA TOMORY Toronto Correspondence should be addressed to: The Editors, Hungarian Studies Review, University of Toronto, 21 Sussex Ave., Toronto, Ont., Canada M5S 1A1 E-mail: [email protected] Articles appearing in the HSR are indexed in: HISTORICAL ABSTRACTS and, AMERICA: HISTORY AND LIFE. Copyright © (1999) the Hungarian Studies Review. ISSN 0713-8083 (replacing 0317-204X) The Hungarian Studies Review is an interdisciplinary journal devoted to the publication of articles and book reviews relating to Hungary and Hungarians. Since its launching in 1974, the Review has been a forum for the scholarly discussion of issues in Hungarian history, politics and cultural affairs. Subscriptions are $12.00 per annum. Membership in the Hungarian Studies Association of Canada includes a subscription to the journal. For further informa- tion, visit our web-page: http://www.ccsp.sfu.ca/calj.hsr Statements and opinions expressed in the HSR are those of the individual authors and do not necessarily reflect the views of the journal's editors. -

Ageing and Care for the Elderly in Hungary General Survey and Problems
STUDY Budapest Ageing and Care for the Elderly in Hungary General Survey and Problems ANDREA GYARMATI April 2019 The burden of social care in Hungary is constantly increasing. The over-65 age demo- graphic now numbers 1.8 million people, around 1.3 million of whom live with some form of disability. However, care close to the home (home help) is accessible to just 7% of those in this category. Only 3% of elderly people are able to take advantage of specialist care in a nursing home, while those on the ever-lengthening waiting lists already number more than half of those already in care institutions. No new places in state-funded nurs- ing care accommodation have been created in the last eight years. All municipal governments are obliged to provide certain basic social services (catering, home help). Their capacities, however, are unevenly distributed: In some areas as many as 80% of elderly inhabitants are guaranteed care services, while in others the figure is only a few percent. The system is characterised by a lack of available information: only about one third of elderly people are actually aware of what they are entitled to. The Hungarian state currently only spends about 0.4% of GDP on care for the elderly, with a minimal year-on-year increase. Financing is provided through a kind of planned economy: the funds specified in the budgetary law are not earmarked for any actual expenses related to care provision. The care deficit, meanwhile, continues to grow. The number of professional carers is declining, as wages in the social sector are the lowest in the entire national economy, which means that since 2010 the number of unfilled job vacancies has steadily increased. -

Hungary: Democracy Under Threat
Hungary: Democracy under Threat Six Years of Attacks against the Rule of Law November 2016 / N° 684a November Cover photo: Thousands of people gathered outside parliament building in Kossuth Lajos Square call for Prime Minister Viktor Orban’s resignation with slogans of «for a European Hungary» in Budapest, Hungary on February 1, 2015. © Mehmet Yilmaz / ANADOLU AGENCY taBLE OF CONTENts 1. INTRODUCTION 4 1.1 METHODOLOGY 8 2. CHALLENGES TO THE RULE OF LAW : UNDERMINING DEMOCRATIC CHECKS AND BALANCES 10 2.1 ESTABLISHED POWERS 10 2.1.1 Constitutional matters: Reshaping the constitutional framework 10 2.1.2 Reforming the judiciary 15 2.1.3 Electoral laws and other restrictions to the legislative power 21 2.2 NON-ESTABLISHED POWERS 24 2.2.1 Taking control of the media 24 2.2.2 Restricting freedom of information 37 2.2.3 A shrinking space for civil society 44 2.2.4 Churches and religious groups 43 3. CHALLENGES TO THE RULE OF LAW: VIOLATIONS OF THE RIGHTS OF MIGRANTS, ASYLUM SEEKERS AND REFUGEES 51 4.THE HUNGARIAN SITUATION IN THE LIGHT OF INTERNATIONAL STANDARDS ON THE RULE OF LAW 59 5. CONCLUSIONS 70 6. RECOMMENdatiONS 72 ANNEXES 79 ANNEX I. HISTORIC CHRONOLOGY 79 ANNEX II. CHRONOLOGY OF LAWS 80 ANNEX III. EUROPEAN UNION’S INSTITUTIONS’ MAIN REACTIONS TO DEVELOPMENTS IN HUNGARY SINCE 2010 81 1. Introduction Since Prime Minister Viktor Orban took power in 2010 following the country’s general elections that saw its party, conservative Fidesz (the Hungarian Civic Party) and their small coalition partner the Christian Democratic People’s Party (KDNP) win the two-thirds (67,88% or 262 seats) in Parliament, Hungary has undergone a progressive shift away from the principles on which a democratic state is built. -

(Beijing, 1995) Platform for Action in Hungary
HUNGARY Beijing+10 Evaluation of the implementation of the UN World Congress on Women (Beijing, 1995) Platform for Action in Hungary Part I: Review of achievements and obstacles in respect of gender equality and the provision of increased decision-making rights for women Article 66 (1) of the Constitution prohibits discrimination between women and men the Republic of Hungary. Act CXXV of 2003 on equal treatment and promotion of equal opportunities defined the concept of various types of discrimination, including discrimination based on gender, and includes a provision on its prohibition. With this Act the Republic of Hungary harmonised the directives of the European Union concerning equal opportunities for women and men. Although legislation guarantees de jure equality of women and men, i.e., the right of both genders to equal treatment, there are still a lot of things to do before de facto equality is achieved. This requires elimination of numerous forms of open (direct) and hidden (indirect) discrimination, as well as other positive measures that help establishing real equality. The government has agreed to regularly evaluate the implementation of the Beijing Platform for Action and to review the results and make new initiatives in 2005 ten years after the adoption of the Beijing Platform for Action. Results and challenges The Act on “Equal treatment and promotion of equal opportunities” was adopted in 2003. In the Republic of Hungary the Constitution and other legal regulations state the prohibition of discrimination, yet the adoption of the new regulation is of outstanding importance. This Act provides that promotion of equal opportunities is primarily an obligation of the state with a declared purpose of providing effective legal protection to those suffering from discrimination. -

The Analysis of the 2018 Hungarian Parliamentary Elections in the Aspect of the FIDESZ-KDNP
Ádám Bohár (International Business School Budapest-Vienna) tHe analysis of tHe 2018 Hungarian parliamentary electiOns in tHe aspect of tHe FIDESZ-KDNP Keywords: Fidesz, KDNP, Election, 2018, parliament, Hungary, 1990, Jobbik, LMP, DK, Viktor Orbán, Gábor Vona, Bernadett Szél, Ferenc Gyurcsány, polariza- tion, sub-polarization 1.—Introduction In 2018, the 8th parliamentary election will be held in Hungary since the fall of the communist regime in 1989 and the first election in 1990. The election will answer a question that has never been asked in the history of Hungarian politics: will the Fidesz-KDNP coalition win the elections and gain the majority of the votes, and by that, the governing right for the third time in a row. This would be the first occasion that political parties elected and govern the country for such a long period of time in Hunga- ry. Both Fidesz (Fidesz – Hungarian Civic Alliance), and KDNP (Chris- tian Democratic People’s Party) part of the Hungarian political scene since 1990. With the help of articles and books written in the subject, this paper overviews both parties. In order to understand the current scene, I will re- visit the political scene in Hungary from 1990 until 2018, in the aspect of the number of parties whom qualified their selves to the Parliament. With each election, new challenges, and sometimes, new parties arise to compete. I will overview the 2010 election as a milestone in the change of the politi- cal scene, what led to the change, and how the changes affected it. As for the 2018 election, I will cover the main ideas and mottos of the party and 236—Á��������������������������������� — ádám bOHár its campaign and how the party reacted to the opposition and other events throughout the 2017–2018 period. -

Szapor, Judith, Hungarian Women's
Acsády, Judit. “Szapor, Judith, Hungarian Women’s Activism in the Wake of the First World War: From Rights to Revanche. London: Bloomsbury Academic, 2018. 207 pp. Illus.” Hungarian Cultural Studies. e-Journal of the American Hungarian Educators Association, Volume 11 (2018) DOI: 10.5195/ahea.2018.329 Szapor, Judith, Hungarian Women’s Activism in the Wake of the First World War: From Rights to Revanche. London: Bloomsbury Academic, 2018. 207 pp. Illus. Reviewed by Judit Acsády*, Center for Social Sciences, MTA, Budapest Judith Szapor's Hungarian Women’s Activism in the Wake of the First World War: From Rights to Revanche is a new work in the field of the history of Hungarian women’s political activities and social movements in the early twentieth century. The history of feminism having been long silenced in Hungary has recently attracted new interest both there and abroad. Similarly, conservative women’s organizations during and after World War I have also became the focus of recent research projects. Scholars from different backgrounds and countries, including those of the ex-Soviet bloc, joined efforts and produced a number of important works, among them edited volumes by Alison Fell, Ingrid Sharp, and Matthew Stibbe. Judith Szapor, the author of the book under review likewise belongs to this international research network, which was initially started and led by Sharp and Stibbe. Hungarian Women’s Activism is based on Szapor’s newest research supported by Canadian research grants at her Department of History and Classical Studies of McGill University. The book includes five chapters with further subsections and a concluding chapter that summarizes the assumptions and describes the implications and the long-lasting social and historical effects of the ideological constructs of the 1920s discussed in the book. -

Interrogating the Historical Revisionism of the Hungarian Right: the Queer Case of Ceć Ile Tormay Anita Kurimay Bryn Mawr College, [email protected]
Bryn Mawr College Scholarship, Research, and Creative Work at Bryn Mawr College History Faculty Research and Scholarship History 2016 Interrogating the Historical Revisionism of the Hungarian Right: The Queer Case of Ceć ile Tormay Anita Kurimay Bryn Mawr College, [email protected] Let us know how access to this document benefits ouy . Follow this and additional works at: http://repository.brynmawr.edu/history_pubs Part of the History Commons Custom Citation A. Kurimay, "Interrogating the Historical Revisionism of the Hungarian Right: The Queer Case of Ceć ile Tormay." East European Politics and Societies 30 (2016): 10 – 33. This paper is posted at Scholarship, Research, and Creative Work at Bryn Mawr College. http://repository.brynmawr.edu/history_pubs/21 For more information, please contact [email protected]. Anita Kurimay, “Interrogating the Historical Revisionism of the Hungarian Right: The Queer Case of Cécile Tormay.” East European Politics and Societies 30 (2016): 10 – 33. Abstract The article examines the historical processes and the motivations of contemporary Hungarian politicians to officially rehabilitate the memory of Cécile Tormay, the internationally acclaimed writer and founder of Hungary’s conservative women’s movement. Through tracing the politics of remembering Tormay since World War II it demonstrates how Tormay’s recent reemergence as a new national icon was intimately tied to a decisive shift in the direction of Hungarian politics from a pro-Western stance to one that is openly hostile towards Western liberalism. Tormay, part of the ruling elite in the authoritarian interwar Horthy regime, was a fierce anticommunist, antisemite, and staunch nationalist who rallied Hungarians to reclaim territories lost after World War I.