Gene Section Review
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Expression and Cell Cycle Progression by an Endogenous Antisense RNA
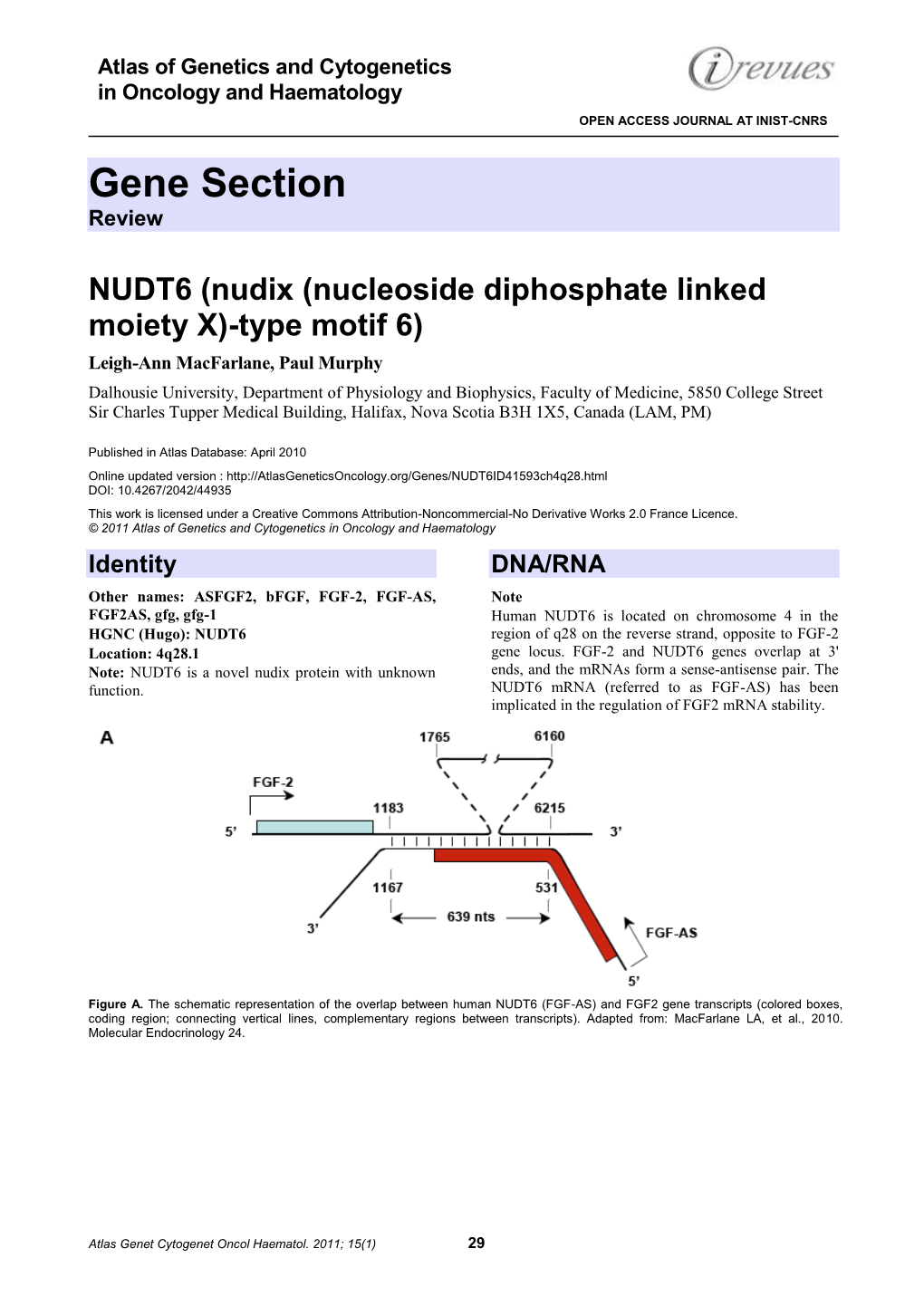
Genes 2012, 3, 505-520; doi:10.3390/genes3030505 OPEN ACCESS genes ISSN 2073-4425 www.mdpi.com/journal/genes Article Regulation of Fibroblast Growth Factor-2 Expression and Cell Cycle Progression by an Endogenous Antisense RNA Mark Baguma-Nibasheka, Leigh Ann MacFarlane and Paul R. Murphy * Department of Physiology and Biophysics, Faculty of Medicine, Dalhousie University, 5850 College Street, Halifax, NS B3H 4R2, Canada; E-Mails: [email protected] (M.B.-N.); [email protected] (L.A.M.) * Author to whom correspondence should be addressed; E-Mail: [email protected]; Tel.: +1-902-494-1579; Fax: +1-902-494-2050. Received: 27 June 2012; in revised form: 31 July 2012 / Accepted: 15 August 2012 / Published: 16 August 2012 Abstract: Basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF2) is a potent wide-spectrum mitogen whose overexpression is associated with immortalization and unregulated cell proliferation in many tumors. The FGF2 gene locus is bi-directionally transcribed to produce FGF2 P51$IURPWKH³VHQVH´VWUDQGDQGDcis-antisense RNA (NUDT6) from the NUDT6 gene RQWKH³DQWLVHQVH´VWUDQG7KH18'7JHQHHQFRGHVDQXGL[PRWLISURWHLQRIXQNQRZQ function, while its mRNA has been implicated in the post-transcriptional regulation of FGF2 expression. FGF2 and NUDT6 are co-expressed in rat C6 glioma cells, and ectopic overexpression of NUDT6 suppresses cellular FGF2 accumulation and cell cycle progression. However, the role of the endogenous antisense RNA in regulation of FGF2 is unclear. In the present study, we employed siRNA-mediated gene knockdown to examine the role of the endogenous NUDT6 RNA in regulation of FGF2 expression and cell cycle progression. Knockdown of either FGF2 or NUDT6 mRNA was accompanied by a significant (>3 fold) increase in the complementary partner RNA. -

The Landscape of Human Mutually Exclusive Splicing
bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/133215; this version posted May 2, 2017. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. It is made available under aCC-BY-ND 4.0 International license. The landscape of human mutually exclusive splicing Klas Hatje1,2,#,*, Ramon O. Vidal2,*, Raza-Ur Rahman2, Dominic Simm1,3, Björn Hammesfahr1,$, Orr Shomroni2, Stefan Bonn2§ & Martin Kollmar1§ 1 Group of Systems Biology of Motor Proteins, Department of NMR-based Structural Biology, Max-Planck-Institute for Biophysical Chemistry, Göttingen, Germany 2 Group of Computational Systems Biology, German Center for Neurodegenerative Diseases, Göttingen, Germany 3 Theoretical Computer Science and Algorithmic Methods, Institute of Computer Science, Georg-August-University Göttingen, Germany § Corresponding authors # Current address: Roche Pharmaceutical Research and Early Development, Pharmaceutical Sciences, Roche Innovation Center Basel, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd., Basel, Switzerland $ Current address: Research and Development - Data Management (RD-DM), KWS SAAT SE, Einbeck, Germany * These authors contributed equally E-mail addresses: KH: [email protected], RV: [email protected], RR: [email protected], DS: [email protected], BH: [email protected], OS: [email protected], SB: [email protected], MK: [email protected] - 1 - bioRxiv preprint doi: https://doi.org/10.1101/133215; this version posted May 2, 2017. The copyright holder for this preprint (which was not certified by peer review) is the author/funder, who has granted bioRxiv a license to display the preprint in perpetuity. -

Towards Personalized Medicine in Psychiatry: Focus on Suicide
TOWARDS PERSONALIZED MEDICINE IN PSYCHIATRY: FOCUS ON SUICIDE Daniel F. Levey Submitted to the faculty of the University Graduate School in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree Doctor of Philosophy in the Program of Medical Neuroscience, Indiana University April 2017 ii Accepted by the Graduate Faculty, Indiana University, in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy. Andrew J. Saykin, Psy. D. - Chair ___________________________ Alan F. Breier, M.D. Doctoral Committee Gerry S. Oxford, Ph.D. December 13, 2016 Anantha Shekhar, M.D., Ph.D. Alexander B. Niculescu III, M.D., Ph.D. iii Dedication This work is dedicated to all those who suffer, whether their pain is physical or psychological. iv Acknowledgements The work I have done over the last several years would not have been possible without the contributions of many people. I first need to thank my terrific mentor and PI, Dr. Alexander Niculescu. He has continuously given me advice and opportunities over the years even as he has suffered through my many mistakes, and I greatly appreciate his patience. The incredible passion he brings to his work every single day has been inspirational. It has been an at times painful but often exhilarating 5 years. I need to thank Helen Le-Niculescu for being a wonderful colleague and mentor. I learned a lot about organization and presentation working alongside her, and her tireless work ethic was an excellent example for a new graduate student. I had the pleasure of working with a number of great people over the years. Mikias Ayalew showed me the ropes of the lab and began my understanding of the power of algorithms. -

Development of Novel Analysis and Data Integration Systems to Understand Human Gene Regulation
Development of novel analysis and data integration systems to understand human gene regulation Dissertation zur Erlangung des Doktorgrades Dr. rer. nat. der Fakult¨atf¨urMathematik und Informatik der Georg-August-Universit¨atG¨ottingen im PhD Programme in Computer Science (PCS) der Georg-August University School of Science (GAUSS) vorgelegt von Raza-Ur Rahman aus Pakistan G¨ottingen,April 2018 Prof. Dr. Stefan Bonn, Zentrum f¨urMolekulare Neurobiologie (ZMNH), Betreuungsausschuss: Institut f¨urMedizinische Systembiologie, Hamburg Prof. Dr. Tim Beißbarth, Institut f¨urMedizinische Statistik, Universit¨atsmedizin, Georg-August Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Prof. Dr. Burkhard Morgenstern, Institut f¨urMikrobiologie und Genetik Abtl. Bioinformatik, Georg-August Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Pr¨ufungskommission: Prof. Dr. Stefan Bonn, Zentrum f¨urMolekulare Neurobiologie (ZMNH), Referent: Institut f¨urMedizinische Systembiologie, Hamburg Prof. Dr. Tim Beißbarth, Institut f¨urMedizinische Statistik, Universit¨atsmedizin, Korreferent: Georg-August Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Prof. Dr. Burkhard Morgenstern, Weitere Mitglieder Institut f¨urMikrobiologie und Genetik Abtl. Bioinformatik, der Pr¨ufungskommission: Georg-August Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Prof. Dr. Carsten Damm, Institut f¨urInformatik, Georg-August Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Prof. Dr. Florentin W¨org¨otter, Physikalisches Institut Biophysik, Georg-August-Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Prof. Dr. Stephan Waack, Institut f¨urInformatik, Georg-August Universit¨at,G¨ottingen Tag der m¨undlichen Pr¨ufung: der 30. M¨arz2018 -

Replication Timing Alterations in Leukemia Affect Clinically Relevant Chromosome Domains
REGULAR ARTICLE Replication timing alterations in leukemia affect clinically relevant chromosome domains Juan Carlos Rivera-Mulia,1 Takayo Sasaki,2 Claudia Trevilla-Garcia,1 Naoto Nakamichi,3 David J. H. F. Knapp,3 Colin A. Hammond,3 Bill H. Chang,4 Jeffrey W. Tyner,5,6 Meenakshi Devidas,7 Jared Zimmerman,2 Kyle N. Klein,2 Vivek Somasundaram,2 Brian J. Druker,4 Tanja A. Gruber,8 Amnon Koren,9 Connie J. Eaves,3 and David M. Gilbert2,10 1Department of Biochemistry, Molecular Biology and Biophysics, University of Minnesota Medical School, Minneapolis, MN; 2Department of Biological Science, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL; 3Terry Fox Laboratory, British Columbia Cancer Agency, Vancouver, BC, Canada; 4Division of Pediatric Hematology and Oncology, Department of Pediatrics, 5Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Medicine, Oregon Health & Science University Knight Cancer Institute, and 6Department of Cell, Developmental and Cancer Biology, Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, OR; 7Department of Biostatistics, College of Medicine, College of Public Health and Health Professions, University of Florida, Gainesville, FL; 8Department of Oncology, St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, TN; 9Department of Molecular Biology and Genetics, Cornell University, Ithaca, NY; and 10Center for Genomics and Personalized Medicine, Florida State University, Tallahassee, FL Human B-cell precursor acute lymphoid leukemias (BCP-ALLs) comprise a group of Key Points genetically and clinically distinct disease entities with features of differentiation arrest at • DNA replication timing known stages of normal B-lineage differentiation. We previously showed that BCP-ALL cells . of 100 pediatric display unique and clonally heritable, stable DNA replication timing (RT) programs (ie, leukemic samples iden- programs describing the variable order of replication and subnuclear 3D architecture of tified BCP-ALL megabase-scale chromosomal units of DNA in different cell types). -

Investigation of Genetic Factors Underlying Typical Orofacial Clefts: Mutational Screening and Copy Number Variation
Journal of Human Genetics (2015) 60, 17–25 & 2015 The Japan Society of Human Genetics All rights reserved 1434-5161/15 www.nature.com/jhg ORIGINAL ARTICLE Investigation of genetic factors underlying typical orofacial clefts: mutational screening and copy number variation Milena Simioni1, Tânia Kawasaki Araujo1, Isabella Lopes Monlleo2, Cláudia Vianna Maurer-Morelli1 and Vera Lúcia Gil-da-Silva-Lopes1 Typical orofacial clefts (OFCs) comprise cleft lip, cleft palate and cleft lip and palate. The complex etiology has been postulated to involve chromosome rearrangements, gene mutations and environmental factors. A group of genes including IRF6, FOXE1, GLI2, MSX2, SKI, SATB2, MSX1 and FGF has been implicated in the etiology of OFCs. Recently, the role of the copy number variations (CNVs) has been studied in genetic defects and diseases. CNVs act by modifying gene expression, disrupting gene sequence or altering gene dosage. The aims of this study were to screen the above-mentioned genes and to investigate CNVs in patients with OFCs. The sample was composed of 23 unrelated individuals who were grouped according to phenotype (associated with other anomalies or isolated) and familial recurrence. New sequence variants in GLI2, MSX1 and FGF8 were detected in patients, but not in their parents, as well as in 200 control chromosomes, indicating that these were rare variants. CNV screening identified new genes that can influence OFC pathogenesis, particularly highlighting TCEB3 and KIF7, that could be further analyzed. The findings of the present study suggest that the mechanism underlying CNV associated with sequence variants may play a role in the etiology of OFC. Journal of Human Genetics (2015) 60, 17–25; doi:10.1038/jhg.2014.96; published online 13 November 2014 INTRODUCTION understand OFC etiology, the molecular mechanisms underlying cleft Orofacial clefts (OFCs) comprise any cleft (that is, a break or gap) in development have not been fully characterized. -

Enriched Alternative Splicing in Islets of Diabetes-Susceptible Mice
International Journal of Molecular Sciences Article Enriched Alternative Splicing in Islets of Diabetes-Susceptible Mice Ilka Wilhelmi 1,2, Alexander Neumann 3 , Markus Jähnert 1,2 , Meriem Ouni 1,2,† and Annette Schürmann 1,2,4,5,*,† 1 Department of Experimental Diabetology, German Institute of Human Nutrition (DIfE), 14558 Potsdam, Germany; [email protected] (I.W.); [email protected] (M.J.); [email protected] (M.O.) 2 German Center for Diabetes Research (DZD), 85764 Munich, Germany 3 Omiqa Bioinformatics, 14195 Berlin, Germany; [email protected] 4 Institute of Nutritional Sciences, University of Potsdam, 14558 Nuthetal, Germany 5 Faculty of Health Sciences, Joint Faculty of the Brandenburg University of Technology Cottbus-Senftenberg, The Brandenburg Medical School Theodor Fontane and The University of Potsdam, 14469 Potsdam, Germany * Correspondence: [email protected] † These authors contributed equally to this work. Abstract: Dysfunctional islets of Langerhans are a hallmark of type 2 diabetes (T2D). We hypoth- esize that differences in islet gene expression alternative splicing which can contribute to altered protein function also participate in islet dysfunction. RNA sequencing (RNAseq) data from islets of obese diabetes-resistant and diabetes-susceptible mice were analyzed for alternative splicing and its putative genetic and epigenetic modulators. We focused on the expression levels of chromatin modifiers and SNPs in regulatory sequences. We identified alternative splicing events in islets of diabetes-susceptible mice amongst others in genes linked to insulin secretion, endocytosis or Citation: Wilhelmi, I.; Neumann, A.; ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis pathways. The expression pattern of 54 histones and chromatin Jähnert, M.; Ouni, M.; Schürmann, A. -

UC San Diego Electronic Theses and Dissertations
UC San Diego UC San Diego Electronic Theses and Dissertations Title Cardiac Stretch-Induced Transcriptomic Changes are Axis-Dependent Permalink https://escholarship.org/uc/item/7m04f0b0 Author Buchholz, Kyle Stephen Publication Date 2016 Peer reviewed|Thesis/dissertation eScholarship.org Powered by the California Digital Library University of California UNIVERSITY OF CALIFORNIA, SAN DIEGO Cardiac Stretch-Induced Transcriptomic Changes are Axis-Dependent A dissertation submitted in partial satisfaction of the requirements for the degree Doctor of Philosophy in Bioengineering by Kyle Stephen Buchholz Committee in Charge: Professor Jeffrey Omens, Chair Professor Andrew McCulloch, Co-Chair Professor Ju Chen Professor Karen Christman Professor Robert Ross Professor Alexander Zambon 2016 Copyright Kyle Stephen Buchholz, 2016 All rights reserved Signature Page The Dissertation of Kyle Stephen Buchholz is approved and it is acceptable in quality and form for publication on microfilm and electronically: Co-Chair Chair University of California, San Diego 2016 iii Dedication To my beautiful wife, Rhia. iv Table of Contents Signature Page ................................................................................................................... iii Dedication .......................................................................................................................... iv Table of Contents ................................................................................................................ v List of Figures ................................................................................................................... -

(FGF-2) Overexpression Is a Risk Factor for Esophageal Cancer
Human Cancer Biology Basic Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF-2) Overexpression Is a Risk Factor for Esophageal Cancer Recurrence and Reduced Survival, which Is Ameliorated by Coexpression oftheFGF-2AntisenseGene Christie Barclay,1Audrey W. Li,1Laurette Geldenhuys,2 Mark Baguma-Nibasheka,1Geoffrey A. Porter,3 Paul J.Veugelers,4 Paul R. Murphy,1and Alan G. Casson2,3 Abstract Purpose:The basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF-2) gene is bidirectionally transcribed to gener- ate overlapping sense and antisense (FGF-AS) mRNAs. FGF-AS has been implicated in the post- transcriptional regulation ofFGF-2 expression. The aim ofthis study was to characterize FGF-2 and FGF-AS in esophageal cancer and to correlate their expression with clinicopathologicfindings and outcome. Experimental Design: Reverse transcription-PCR was used to study FGF-2 and FGF-AS mRNA expression (normalized to glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase) in 48 esophageal can- cers relative to matched histologically normal esophageal epithelia (internal control). We used Cox proportional hazards analysis to calculate hazard ratios for recurrence and survival of patients with underexpression relative to the overexpression ofFGF-2 and/or FGF-AS. Results: Overexpression ofFGF-2 mRNA, by comparison with tumors underexpressing FGF-2, was associated with significantly increased risk for tumor recurrence (hazard ratio, 3.80; 95% confidence interval, 1.64-8.76) and reduced overall survival (hazard ratio, 2.11;95% confidence interval, 1.0-4.58).When the effects of FGF-2 and FGF-AS were considered simultaneously, the association ofFGF-2 mRNA overexpression with recurrence and mortality was even more pronounced, whereas FGF-AS mRNA overexpression was associated with reduced risk for recurrence and improved survival. -

New Genetic Loci Link Adipose and Insulin Biology to Body Fat Distribution
Europe PMC Funders Group Author Manuscript Nature. Author manuscript; available in PMC 2015 August 12. Published in final edited form as: Nature. 2015 February 12; 518(7538): 187–196. doi:10.1038/nature14132. Europe PMC Funders Author Manuscripts New genetic loci link adipose and insulin biology to body fat distribution A full list of authors and affiliations appears at the end of the article. # These authors contributed equally to this work. Abstract Body fat distribution is a heritable trait and a well-established predictor of adverse metabolic outcomes, independent of overall adiposity. To increase our understanding of the genetic basis of body fat distribution and its molecular links to cardiometabolic traits, we conducted genome-wide association meta-analyses of waist and hip circumference-related traits in up to 224,459 individuals. We identified 49 loci (33 new) associated with waist-to-hip ratio adjusted for body mass index (WHRadjBMI) and an additional 19 loci newly associated with related waist and hip circumference measures (P<5×10−8). Twenty of the 49 WHRadjBMI loci showed significant sexual dimorphism, 19 of which displayed a stronger effect in women. The identified loci were enriched for genes expressed in adipose tissue and for putative regulatory elements in adipocytes. Pathway analyses implicated adipogenesis, angiogenesis, transcriptional regulation, and insulin resistance as processes affecting fat distribution, providing insight into potential pathophysiological mechanisms. Europe PMC Funders Author Manuscripts Depot-specific accumulation of fat, particularly in the central abdomen, confers an elevated risk of metabolic and cardiovascular diseases and mortality1. An easily accessible measure of body fat distribution is waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), a comparison of waist and hip circumferences. -

Genetic-Linkage Mapping of Complex Hereditary Disorders to a Whole-Genome Molecular-Interaction Network
Downloaded from genome.cshlp.org on September 29, 2021 - Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press Methods Genetic-linkage mapping of complex hereditary disorders to a whole-genome molecular-interaction network Ivan Iossifov,1 Tian Zheng,2 Miron Baron,3 T. Conrad Gilliam,4 and Andrey Rzhetsky4,5,6 1Department of Biomedical Informatics, Center for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, Columbia University, New York, New York 10032, USA; 2Department of Statistics, Columbia University, New York, New York 10027, USA; 3Department of Psychiatry, Columbia University, New York, New York 10032, USA; 4Department of Human Genetics, University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637, USA; 5Department of Medicine, Institute for Genomics & Systems Biology, Computation Institute, University of Chicago, Chicago, Illinois 60637, USA Common hereditary neurodevelopmental disorders such as autism, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia are most likely both genetically multifactorial and heterogeneous. Because of these characteristics traditional methods for genetic analysis fail when applied to such diseases. To address the problem we propose a novel probabilistic framework that combines the standard genetic linkage formalism with whole-genome molecular-interaction data to predict pathways or networks of interacting genes that contribute to common heritable disorders. We apply the model to three large genotype–phenotype data sets, identify a small number of significant candidate genes for autism (24), bipolar disorder (21), and schizophrenia (25), and -
A Unified Framework of Overlapping Genes
Genomics 100 (2012) 231–239 Contents lists available at SciVerse ScienceDirect Genomics journal homepage: www.elsevier.com/locate/ygeno A unified framework of overlapping genes: Towards the origination and endogenic regulation Meng-Ru Ho a, Kuo-Wang Tsai b, Wen-chang Lin c,⁎ a Biodiversity Research Center, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan b Department of Medical Education and Research, Kaohsiung Veterans General Hospital, Kaohsiung 813, Taiwan c Institute of Biomedical Sciences, Academia Sinica, Taipei 115, Taiwan article info abstract Article history: Overlapping genes are pairs of adjacent genes whose genomic regions partially overlap. They are notable by Received 27 January 2012 their potential intricate regulation, such as cis-regulation of nested gene-promoter configurations, and Accepted 25 June 2012 post-transcriptional regulation of natural antisense transcripts. The originations and consequent detailed reg- Available online 2 July 2012 ulation remain obscure. Herein, we propose a unified framework comprising biological classification rules followed by extensive analyses, namely, exon-sharing analysis, a human–mouse conservation study, and Keywords: transcriptome analysis of hundreds of microarrays and transcriptome sequencing data (mRNA-Seq). We Overlapping gene Natural antisense transcript (NAT) demonstrate that the tail-to-tail architecture would result from sharing functional elements in Gene regulation 3′-untranslated regions (3′-UTRs) of pre-existing genes. Dissimilarly, we illustrate that the other gene over- Cis-regulatory element laps would originate from a new gene arising in a pre-existing gene locus. Interestingly, these types of Promoter coupled overlapping genes may influence each other synergistically or competitively during transcription, Local chromatin status depending on the promoter configurations. This framework discloses distinctive characteristics of over- lapping genes to be a foundation for a further comprehensive understanding of them.