Introduction
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Angkor Land Explorer 4 Days & 3 Nights
Angkor land explorer 4 days & 3 nights Day 1: Siem Reap arrival Upon arrival at Siem Reap airport, meet and transfers directly for the tour to small circuit including Prasat Ravan, Banteay Kdei, Srah Srang, Ta Prohm, Takeo, Thommanon, and Chau Say Tevoda. Afternoon visit to the World Seventh Wonder of the Magical Temple city of Angkor Wat until view sunset at Phnom Bakheng. Day 2: Siem Reap (B/L/D) Breakfast at the hotel. In the morning visit South Gate of Angkor Thom, Bayon, Baphoun, Terrace of the Elephants, Terrace of the Leper King. Afternoon, visit Grand Circuit including Pre Rup, East Mebon, Ta Som, Neak Pean, Preah Khan, Baksei Chamkrong and South Gate of Angkor Thom. Dinner and enjoy Khmer Traditional Dance Show at local restaurant. Overnight at your proposed hotel in Siem Reap. Day 3: Siem Reap (B/L) Breakfast at the hotel. Touring to floating villages on Tonle Sap Lake where they will enjoy the boat ride to see the floating houses, schools, hospitals, churches and restaurant. Have lunch at local restaurant. In the afternoon, drive out from Siem Reap to see the most beautiful temples of Banteay Srey and Banteay Samre, located 35 kms from Siem Reap. Return to Siem reap. Dinner on your own. Overnight at the proposed hotel in Siem Reap. Day 4: Siem Reap – departure (B) Breakfast at your hotel. Free at leisure until transfer to the airport for boarding departure flight. End trip. Price: $USD/person 8- Hotels 2pax 3-4pax 5-7pax 10pax 11-15pax SGL - Sup Borei Angkor Resort 5* Local (Deluxe Room) 384 358 333 329 323 203 Somadevi Angkor Hotel 4* (Superior Room) 264 238 213 209 203 83 Angkor Holiday Hotel 3* (Superior Room) 249 223 198 194 188 68 (Seasonal prices apply and will be confirmed when booking! All rates are quoted in US$) Tour prices included: A/c car/van/bus pick up, transfer & sightseeing as per program. -

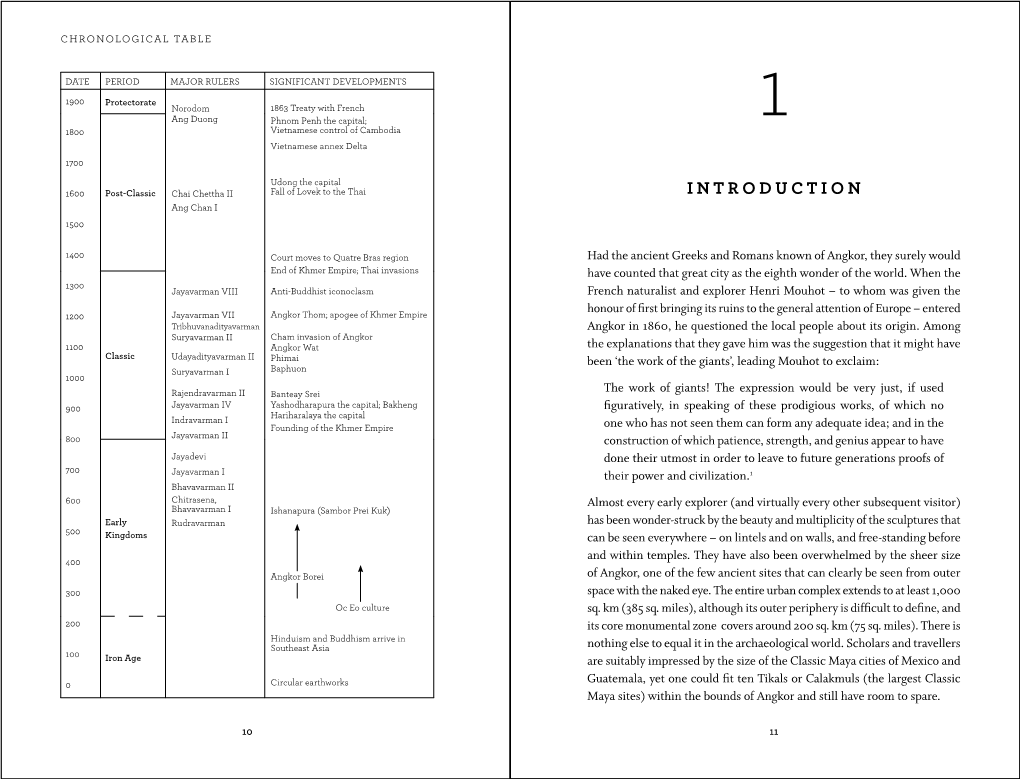
Henri Mouhot (1826-1861) Was a French Naturalist and Explorer Born
Henri Mouhot (1826-1861) was a French naturalist and explorer born into a Protestant family on 25 May 1826 in Franche-Comté, who is renowned for his popularisation of Angkor, Cambodia. He married Ann Park, a descendant (probably a granddaughter) explorer Mungo Park, at St Marylebone in 1854 or 1855, before settling in 1856 in the island of Jersey. Mouhot spent ten years in Russia,working as a language tutor at the St Petersburg Military Academy. He travelled widely in Europe and studied photography before turning to Natural Science as the age of thirty. After a year Mouhot decided to travel to Indochina to collect new zoological specimens and eventually received the financial support of the Royal Geographical Society and the Zoological Society of London after being turned down by the French government. He sailed to Bangkok and then made several trips to Cambodia where he came across Angkor, a place consisting of sites such as ancient terraces, pools, moated cities, palaces and temples. Mouhot is often mistakenly credited with "discovering" Angkor when in fact the site had been visited by several westerners since the sixteenth century. What he did was popularize Angkor in the West as he wrote more evocatively than any previous explorers (through his illustrated journals "Voyage dans les Royaumes de Siam, de Cambodge, de Laos et Autres Parties Centrales de l'Indo-Chine" published in 1868). Although Mouhot made known his insights into this area of Cambodia, he did initially make a grave error in his dating of its formation. Because the explorer saw the Khmer inhabitants as barbaric he made the assumption that they could not have been the original settlers and so dated Angkor back over two millennia, to around the same era as Rome. -

Power and Pragmatism in the Political Economy of Angkor
THESIS FOR THE AWARD OF DOCTOR OF PHILOSOPHY IN ARTS _________ DEPARTMENT OF ARCHAEOLOGY, UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY ____________ POWER AND PRAGMATISM IN THE POLITICAL ECONOMY OF ANGKOR EILEEN LUSTIG _________ UNIVERSITY OF SYDNEY 2009 Figure 1 Location map 1 Abstract The relationship between the Angkorian Empire and its capital is important for understanding how this state was sustained. The empire’s political economy is studied by analysing data from Pre-Angkorian and Angkorian period inscriptions in aggregated form, in contrast to previous studies which relied mainly on detailed reading of the texts. The study is necessarily broad to overcome the constraints of having relatively few inscriptions which relate to a selected range of topics, and are partial in viewpoint. The success of the pre-modern Khmer state depended on: its long-established communication and trade links; mutual support of rulers and regional elites; decentralised administration through regional centres; its ability to produce or acquire a surplus of resources; and a network of temples as an ideological vehicle for state integration. The claim that there was a centrally controlled command economy or significant redistribution of resources, as for archaic, moneyless societies is difficult to justify. The mode of control varied between the core area and peripheral areas. Even though Angkor did not have money, it used a unit of account. Despite being an inland agrarian polity, the Khmer actively pursued foreign trade. There are indications of a structure, perhaps hierarchical, of linked deities and religious foundations helping to disseminate the state’s ideology. The establishment of these foundations was encouraged by gifts and privileges granted to elite supporters of the rulers. -

Cambodia-10-Contents.Pdf
©Lonely Planet Publications Pty Ltd Cambodia Temples of Angkor p129 ^# ^# Siem Reap p93 Northwestern Eastern Cambodia Cambodia p270 p228 #_ Phnom Penh p36 South Coast p172 THIS EDITION WRITTEN AND RESEARCHED BY Nick Ray, Jessica Lee PLAN YOUR TRIP ON THE ROAD Welcome to Cambodia . 4 PHNOM PENH . 36 TEMPLES OF Cambodia Map . 6 Sights . 40 ANGKOR . 129 Cambodia’s Top 10 . 8 Activities . 50 Angkor Wat . 144 Need to Know . 14 Courses . 55 Angkor Thom . 148 Bayon 149 If You Like… . 16 Tours . 55 .. Sleeping . 56 Baphuon 154 Month by Month . 18 . Eating . 62 Royal Enclosure & Itineraries . 20 Drinking & Nightlife . 73 Phimeanakas . 154 Off the Beaten Track . 26 Entertainment . 76 Preah Palilay . 154 Outdoor Adventures . 28 Shopping . 78 Tep Pranam . 155 Preah Pithu 155 Regions at a Glance . 33 Around Phnom Penh . 88 . Koh Dach 88 Terrace of the . Leper King 155 Udong 88 . Terrace of Elephants 155 Tonlé Bati 90 . .. Kleangs & Prasat Phnom Tamao Wildlife Suor Prat 155 Rescue Centre . 90 . Around Angkor Thom . 156 Phnom Chisor 91 . Baksei Chamkrong 156 . CHRISTOPHER GROENHOUT / GETTY IMAGES © IMAGES GETTY / GROENHOUT CHRISTOPHER Kirirom National Park . 91 Phnom Bakheng. 156 SIEM REAP . 93 Chau Say Tevoda . 157 Thommanon 157 Sights . 95 . Spean Thmor 157 Activities . 99 .. Ta Keo 158 Courses . 101 . Ta Nei 158 Tours . 102 . Ta Prohm 158 Sleeping . 103 . Banteay Kdei Eating . 107 & Sra Srang . 159 Drinking & Nightlife . 115 Prasat Kravan . 159 PSAR THMEI P79, Entertainment . 117. Preah Khan 160 PHNOM PENH . Shopping . 118 Preah Neak Poan . 161 Around Siem Reap . 124 Ta Som 162 . TIM HUGHES / GETTY IMAGES © IMAGES GETTY / HUGHES TIM Banteay Srei District . -

Virtual Sambor Prei Kuk: an Interactive Learning Tool
Virtual Sambor Prei Kuk: An Interactive Learning Tool Daniel MICHON Religious Studies, Claremont McKenna College Claremont, CA 91711 and Yehuda KALAY Faculty of Architecture and Town Planning The Technion - Israel Institute of Technology Haifa 32000, Israel ABSTRACT along the trade routes from its Indic origins into Southeast Asia—one of the great cultural assimilations in human history. MUVEs (Multi-User Virtual Environments) are a new media for researching the genesis and evolution of sites of cultural Much of this important work has, so far, remained the exclusive significance. MUVEs are able to model both the tangible and province of researchers, hidden from the general public who intangible heritage of a site, allowing the user to obtain a more might find it justifiably interesting. Further, the advent of dynamic understanding of the culture. This paper illustrates a immersive, interactive, Web-enabled, Multi-User Virtual cultural heritage project which captures and communicates the Environments (MUVEs) has provided us with the opportunity interplay of context (geography), content (architecture and to tell the story of Sambor Prei Kuk in a way that can help artifacts) and temporal activity (rituals and everyday life) visitors experience this remarkable cultural heritage as it might leading to a unique digital archive of the tangible and intangible have been in the seventh-eighth century CE. MUVEs are a new heritage of the temple complex at Sambor Prei Kuk, Cambodia, media vehicle that has the ability to communicate cultural circa seventh-eighth century CE. The MUVE is used to provide heritage experience in a way that is a cross between a platform which enables the experience of weaved tangible and filmmaking, video games, and architectural design. -

Temples Tour Final Lite
explore the ancient city of angkor Visiting the Angkor temples is of course a must. Whether you choose a Grand Circle tour or a lessdemanding visit, you will be treated to an unforgettable opportunity to witness the wonders of ancient Cambodian art and culture and to ponder the reasons for the rise and fall of this great Southeast Asian civili- zation. We have carefully created twelve itinearies to explore the wonders of Siem Reap Province including the must-do and also less famous but yet fascinating monuments and sites. + See the interactive map online : http://angkor.com.kh/ interactive-map/ 1. small circuit TOUR The “small tour” is a circuit to see the major tem- ples of the Ancient City of Angkor such as Angkor Wat, Ta Prohm and Bayon. We recommend you to be escorted by a tour guide to discover the story of this mysterious and fascinating civilization. For the most courageous, you can wake up early (depar- ture at 4:45am from the hotel) to see the sunrise. (It worth it!) Monuments & sites to visit MORNING: Prasats Kravan, Banteay Kdei, Ta Prohm, Takeo AFTERNOON: Prasats Elephant and Leper King Ter- race, Baphuon, Bayon, Angkor Thom South Gate, Angkor Wat Angkor Wat Banteay Srei 2. Grand circuit TOUR 3. phnom kulen The “grand tour” is also a circuit in the main Angkor The Phnom Kulen mountain range is located 48 km area but you will see further temples like Preah northwards from Angkor Wat. Its name means Khan, Preah Neak Pean to the Eastern Mebon and ‘mountain of the lychees’. -

JSS 027 1G Reviewofbooks
115 1'1EVIEWS OF BOOKS. JEAN YvEs CLAEYS, Me.mbre de !'Ecole Fmnc;a,iHe d'Extreme Orient, Inspecteur du Service Archeulogiqne de 1'Indochiue L'.A.?·eheolO[JI:o d1L Siam; Hano'i, 1931, in-8, 88 pages; with numerous photogntphs, sketches, phms a,ucl ouc mtLp of Si111u. 'rhe author of the above vet·y interesting book is a young French architect and archreologist ·who, t[Uite recently, on the retirement of Monsieur Henri Parmentier, the Nestor of Indochinese archreo logists, took over the important position of Im>poctor of the Archreological Service in the iive countt-ies whiel1 constitute the French Indochinese Union. l\1. OlaeyH modestly calls his book a rapid survey o.E the archreological sites of Siam f'rom Nakhon Sri 'rhammarat in the south to Ohiengsaen in the extreme north. We think, however, that his survey contains more tha,n the rudiments of that complete and all embracing archu,eological Hnrvey of the kingdom o£ Siam which some day surely must be made if science is only given the necessu.ry means to carry it out. Monsieur Claeys' "book moreover reads easily, due to his clear style, his up-to-da~e information and the intelligent manner in which he treats hi,; Rubjcct aml an·ives at his conclusions. His book has made Siamese 11rchreology richer and better known to the world outside this country, for ·which all students of things Siamese will thank him. In his introduction, the author praises with good reasons the admirable pioneer work done by His Royal .Highness P?'l>nce Damrong, "un vrai erudit ",who by his indefatigable interest in his country's past history has also powerfully stimulated others to work for the cause of archaeology. -

Views of Angkor in French Colonial Cambodia (1863-1954)
“DISCOVERING” CAMBODIA: VIEWS OF ANGKOR IN FRENCH COLONIAL CAMBODIA (1863-1954) A Dissertation Presented to the Faculty of the Graduate School of Cornell University In Partial Fulfillment of the Requirements for the Degree of Doctor of Philosophy by Jennifer Lee Foley January 2006 © 2006 Jennifer Lee Foley “DISCOVERING” CAMBODIA: VIEWS OF ANGKOR IN FRENCH COLONIAL CAMBODIA (1863-1954) Jennifer Lee Foley, Ph. D Cornell University 2006 This dissertation is an examination of descriptions, writings, and photographic and architectural reproductions of Angkor in Europe and the United States during Cambodia’s colonial period, which began in 1863 and lasted until 1953. Using the work of Mary Louise Pratt on colonial era narratives and Mieke Bal on the construction of narratives in museum exhibitions, this examination focuses on the narrative that came to represent Cambodia in Europe and the United States, and is conducted with an eye on what these works expose about their Western, and predominately French, producers. Angkor captured the imagination of readers in France even before the colonial period in Cambodia had officially begun. The posthumously published journals of the naturalist Henri Mouhot brought to the minds of many visions of lost civilizations disintegrating in the jungle. This initial view of Angkor proved to be surprisingly resilient, surviving not only throughout the colonial period, but even to the present day. This dissertation seeks to follow the evolution of the conflation of Cambodia and Angkor in the French “narrative” of Cambodia, from the initial exposures, such as Mouhot’s writing, through the close of colonial period. In addition, this dissertation will examine the resilience of this vision of Cambodia in the continued production of this narrative, to the exclusion of the numerous changes that were taking place in the country. -

Mai Tho Truyen
C n o n p P G o ử n N m C n M ọ uyền --- o0o --- Nguồn www.chuaxaloi.vn Chuyển sang ebook 18-08-2016 Người thực hiện : Nguyễn Ngọc Thảo - [email protected] Tuyết Nhung - [email protected] Dũng Trần - [email protected] Nam Thiên - [email protected] Link Audio Tại Website http://www.phapthihoi.org Mục Lục LỜI NÓI ẦU PHẬ GI O Ử ÔNG NAM CHƢƠNG I - SỰ MỞ RỘNG CỦA PHẬT GIÁO CHƢƠNG II - NGHI VẤN VỀ SUVARNABHUMI LỊCH Ử PHẬ GI O MIẾN IỆN LỜI NÓI ĐẦU THỜI KỲ THỨ NHẤT THỜI KỲ THỨ HAI KẾT LUẬN LỊCH Ử PHẬ GI O NAM DƢƠNG LỜI NÓI ĐẦU CHƢƠNG I - PHẬT GIÁO Ở NAM DƢƠNG TỪ ĐẦU TỚI THẾ KỶ THỨ VIII TÂY LỊCH CHƢƠNG II - PHẬT GIÁO Ở NAM DƢƠNG, TỪ THẾ KỶ THỨ IX TỚI NGÀY NAY CHƢƠNG III - NGHỆ THUẬT VÀ VĂN CHƢƠNG PHẬT GIÁO NAM DƢƠNG KẾT LUẬN LỊCH SỬ PHẬ GI O CAM BỐ CHƢƠNG I - MỘT ÍT TÀI LIỆU LỊCH SỬ CHƢƠNG II - THỜI KỲ DU NHẬP HAY THỜI KỲ FOU-NAN CHƢƠNG III - THỜI KỲ TCHEN LA (CHƠN LẠP) (Thế kỷ VI-IX) LỊCH Ử PHẬ GI O AI LAO CHƢƠNG I - QUỐC GIA VÀ DÂN TỘC LÀO CHƢƠNG II - PHẬT GIÁO DU NHẬP CHƢƠNG III - ẢNH HƢỞNG PHẬT GIÁO TRONG ĐỜI SỐNG DÂN TỘC LÀO, HIỆN TÌNH PHẬT GIÁO LỊCH Ử PHẬ GI O H I LAN CHƢƠNG I - MỘT ÍT LỊCH SỬ CHƢƠNG II - DU NHẬP VÀ CÁC THỜI KỲ TIẾN BỘ CHƢƠNG III - TÌNH HÌNH PHẬT GIÁO HIỆN NAY LỊCH Ử PHẬ GI O CHIÊM THÀNH CHƢƠNG I - MỘT ÍT LỊCH SỬ CHƢƠNG II - VĂN HÓA VÀ TÔN GIÁO LỊCH Ử PHẬ GI O ÍCH LAN CHƢƠNG I - MỘT ÍT LỊCH SỬ CHƢƠNG II - PHẬT GIÁO DU NHẬP TÍCH LAN CHƢƠNG III - PHẬT GIÁO TÍCH LAN TỪ 200 TỚI 20 TRƢỚC CN CHƢƠNG IV - TỪ ĐẦU TÂY LỊCH CHO ĐẾN HIỆN NAY ---o0o--- CH NH RÍ MAI HỌ RUYỀN (1905-1973) ---o0o--- LỜI NÓI ẦU Với mục đích kế thừa tôn chỉ học Phật và phổ biến giáo lý, tri thức đến mọi tầng lớp cư sĩ, Phật tử được hiểu đúng chánh pháp và hành trì lợi lạc. -
![Bibliography [PDF] (97.67Kb)](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/4717/bibliography-pdf-97-67kb-824717.webp)
Bibliography [PDF] (97.67Kb)
WORKS CITED Atlas Colonial illustré Paris: Librarie Larousse, 1905. Bal, Mieke. Double Exposures The Subject of Cultural Analysis. New York: Routledge, 1996. Benjamin, Walter. “The Task of the Translator,” Illuminations Essays and Reflections New York: Schocken Books, 1969. Benoit, Pierre. Le Roi Lépreux. Paris: Kailash Éditions, 2000. Bingham, Robert. Lightening on the Sun. New York: Doubleday, 2000. Black, Jeremy. The British Abroad the Grand Tour in the Eighteenth Century. New York: St. Martin's Press, 1992. Bouillevaux, C. E. Ma visite aux ruines cambodgiennes en 1850 Sanit-Quentin: Imprimerie J. Monceau, 1874. ———. Voyage Dans L'indo-Chine 1848-1856. Paris: Librarie de Victor Palmé, 1858. Carné, Louis de. Travels on the Mekong : Cambodia, Laos and Yunnan, the Political and Trade Report of the Mekong Exploration Commission (June 1866-June 1868). Bangkok: White Lotus, 2000. David Chandler, “An Anti-Vietnamese Rebellion in Early Nineteenth Century Cambodia”, Facing the Cambodian Past, Bangkok, Silkworm Books, 1996b. ———. "Assassination of Résident Bardez." In Facing the Cambodian Past: Selected Essays 1971-1994. Chiang Mai: Silkworm, 1996b. ———. "Cambodian Royal Chronicles (Rajabangsavatar), 1927-1949: Kingship and Historiography at the End of the Colonial Era." In Facing the Cambodian Past : Selected Essays 1971-1994, vi, [1], 331. Chiang Mai: Silkworn Books, 1996b. ———. A History of Cambodia. Second ed. Chiang Mai: Silkworm Books, 1996a. ———. "Seeing Red: Perceptions of Cambodian History in Democratic Kampuchea." In Facing the Cambodian Past Selected Essays 1971-1994. Chiang mai: Silkworm Books, 1996b. 216 217 ———. "Transformation in Cambodia." In Facing the Cambodian Past Selected Essays 1971-1994. Chiang Mai: Silkworm Books, 1996b. Chimprabha, Marisa. "Anti-Thai Feelings Flare up in Cambodia." The Nation, May 10 2004. -

Angkor Highlight (04 Nights / 05 Days)
(Approved By Ministry of Tourism, Govt. of India) Angkor Highlight (04 Nights / 05 Days) Routing: Arrival Siem Reap - Rolous Group – Small Circuit – Angkor Wat – Grand Circuit - Banteay Srei – Tonle Sap Lake - Siem Reap Day 01 : Arrival Siem Reap (D) Welcome to Siem Reap, Cambodia! Upon arrival at Siem Reap Airport, greeting by our friendly tour guide, then you will be transferred direct to check in at hotel (room may ready at noon). This afternoon, we drive to visit the Angkor National Museum, learn about “the Legend Revealed” and see how the Khmer Empire has been established during the golden period. Continue to visit the Killing Fields at Wat Thmey, get to know some information about Khmer Rouge Regime or called the year of Zero (1975 – 1979) where over 2 million of Khmer people has been killed. Next visit to Preah Ang Check Preah Angkor, the secret place where local people go praying for good luck or safe journey. Day 02 : Rolous Group – Small Circuit (B, L) In the morning – we drive to explore the Roluos group. The Roluos group lies 15km(10 miles) southwest of Siem Reap and includes three temples - Bakong, Prah Ko and Lolei - dating from the late 9th century and corresponding to the ancient capital of Hariharalaya, from which the name of Lolei is derived. Remains include 3 well-preserved early temples that venerated the Hindu gods. The bas-reliefs are some of the earliest surviving examples of Khmer art. Modern-day villages surround the temples. In the afternoon, we visit small circuit including the unique brick sculptures of Prasat Kravan, the jungle intertwined Ta Prohm, made famous in Angelina Jolie’s Tomb Raider movie. -

Post/Colonial Discourses on the Cambodian Court Dance
Kyoto University Southeast Asian Studies, Vol. 42, No. 4, 東南アジア研究 March 2005 42巻 4 号 Post/colonial Discourses on the Cambodian Court Dance SASAGAWA Hideo* Abstract Under the reign of King Ang Duong in the middle of nineteenth century, Cambodia was under the influence of Siamese culture. Although Cambodia was colonized by France in 1863, the royal troupe of the dance still performed Siamese repertoires. It was not until the cession of the Angkor monuments from Siam in 1907 that Angkor began to play a central role in French colonial discourse. George Groslier’s works inter alia were instrumental in historicizing the court dance as a “tradition” handed down from the Angkorean era. Groslier appealed to the colonial authorities for the protection of this “tradition” which had allegedly been on the “decline” owing to the influence of French culture. In the latter half of the 1920s the Résident Supérieur au Cambodge temporarily succeeded in transferring the royal troupe to Groslier’s control. In the 1930s members of the royal family set out to reconstruct the troupe, and the Minister of Palace named Thiounn wrote a book in which he described the court dance as Angkorean “tradition.” His book can be considered to be an attempt to appropriate colonial discourse and to construct a new narrative for the Khmers. After independence in 1953 French colonial discourse on Angkor was incorporated into Cam- bodian nationalism. While new repertoires such as Apsara Dance, modeled on the relief of the monuments, were created, the Buddhist Institute in Phnom Penh reprinted Thiounn’s book. Though the civil war was prolonged for 20 years and the Pol Pot regime rejected Cambodian cul- ture with the exception of the Angkor monuments, French colonial discourse is still alive in Cam- bodia today.