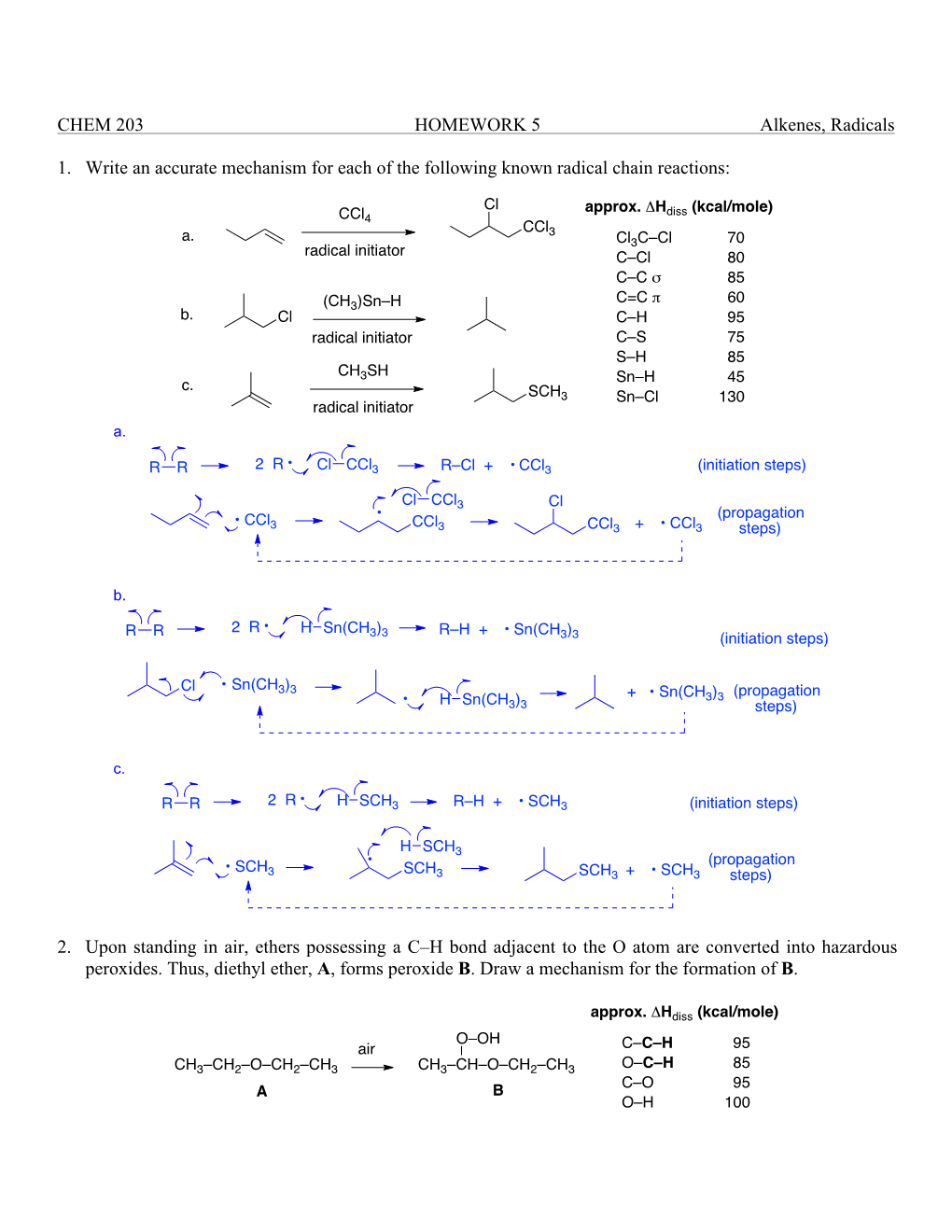
CHEM 203 HOMEWORK 5 Alkenes, Radicals 1. Write an Accurate
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

The Chemistry of Radical Polymerization
THE CHEMISTRY OF RADICAL POLYMERIZATION THE CHEMISTRY OF RADICAL POLYMERIZATION GRAEME MOAD CSIRO Molecular and Health Technologies Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168, AUSTRALIA and DAVID H. SOLOMON Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. University of Melbourne, Victoria 3010, AUSTRALIA Dr Graeme Moad CSIRO Molecular and Health Technologies Bayview Ave, Clayton, Victoria 3168 AUSTRALIA Email: [email protected] Prof David H. Solomon Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering. University of Melbourne Victoria 3010 AUSTRALIA Email: [email protected] Contents Contents............................................................................................................................ v Index to Tables.............................................................................................................xvi Index to Figures ............................................................................................................ xx Preface to the First Edition .....................................................................................xxiii Preface to the Second Edition..................................................................................xxv Acknowledgments......................................................................................................xxvi 1 INTRODUCTION.................................................................................................. 1 1.1 References ........................................................................................................... -

Aim: to Prepare Block Copolymers of Methyl Methacrylate (MMA) and Styrene
Conducting A Reversible-Deactivation Radical Polymerization (RDRP) Aim: To Prepare Block Copolymers of Methyl Methacrylate (MMA) and Styrene. Polymers are ubiquitous in the modern world. They provide tremendous value because the chemical and physical properties of these materials are determined by the monomers that are used to put them together. One of the most powerful methods to construct polymers is radical-chain polymerization and this method is used in the commercial synthesis of polymers everyday. Methyl methacrylate is polymerized to form poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) which is also known as acrylic glass or Plexiglas (about 2 billion pounds per year in the US). This material is lightweight, strong and durable. The polymer chains are rigid due to the tetrasubstituted carbon atom in the polymer backbone and they have excellent optical clarity. As a consequence, these materials are used in aircraft windows, glasses, skylights, signs and displays. Polystyrene (PS), which can also be synthesized from radical chain polymerization, has found extensive use as a material (also approximately 2 billion pounds per year in the US). One of the forms of PS, Styrofoam, is used extensively to make disposable cups, thermal insulation, and cushion for packaging. Scheme 1. Radical polymerization of methyl methacrylate or styrene. While there are extensive uses for these polymers, when synthesizing any material using a free-radical polymerization, samples are obtained with limited control over molecular weight and molecular weight distribution. New methods have been developed directly at Carnegie Mellon (https://www.cmu.edu/maty/) which lead to improved control in this process. This new method is a reversible-deactivation of the polymerization reaction where highly reactive radicals toggle back and forth between an active state, where the polymer chain is growing, and a dormant state, where the polymer chain is capped (Scheme 2). -

TEST - Alkenes, Alkadienes and Alkynes
Seminar_2 1. Nomenclature of unsaturated hydrocarbons 2. Polymerization 3. Reactions of the alkenes (table) 4. Reactions of the alkynes (table) TEST - Alkenes, alkadienes and alkynes. Polymerization • Give the names • Write the structural formula • Write all isomeric compounds • The processes explanation 1. NOMENCLATURE OF UNSATURATED HYDROCARBONS ALKENE NOMENCLATURE We give alkenes IUPAC names by replacing the -ane ending of the corresponding alkane with -ene . The two simplest alkenes are ethene and propene. Both are also well known by their common names ethylene and propylene. Ethylene is an acceptable synonym for ethene in the IUPAC system. Propylene, isobutylene, and other common names ending in -ylene are not acceptable IUPAC names. 1. The longest continuous chain that includes the double bond forms the base name of the alkene. 2. Chain is numbered in the direction that gives the doubly bonded carbons their lower numbers. 3. The locant (or numerical position) of only one of the doubly bonded carbons is specified in the name; it is understood that the other doubly bonded carbon must follow in sequence. 4. Carbon-carbon double bonds take precedence over alkyl groups and halogens in determining the main carbon chain and the direction in which it is numbered. 5. The common names of certain frequently encountered alkyl groups, such as isopropyl and tert-butyl, are acceptable in the IUPAC system. Three alkenyl groups--vinyl, allyl, and isopropenyl--are treated the same way: 6. When a CH 2 group is doubly bonded to a ring, the prefix methylene is added to the name of the ring: 7. Cycloalkenes and their derivatives are named by adapting cycloalkane terminology to the principles of alkene nomenclature: No locants are needed in the absence of substituents; it is understood that the double bond connects C-1 and C 2. -
![Controlled Free Radical Polymerization of Styrene Initiated by a [BPO-Polystyrene-(4-Acetamido-TEMPO)] Macroinitiator](https://docslib.b-cdn.net/cover/7216/controlled-free-radical-polymerization-of-styrene-initiated-by-a-bpo-polystyrene-4-acetamido-tempo-macroinitiator-1287216.webp)
Controlled Free Radical Polymerization of Styrene Initiated by a [BPO-Polystyrene-(4-Acetamido-TEMPO)] Macroinitiator
Die Angewandte Makromolekulare Chemie 265 (1999) 69–74 (Nr. 4630) 69 Controlled free radical polymerization of styrene initiated by a [BPO-polystyrene-(4-acetamido-TEMPO)] macroinitiator Chang Hun Han, So¨ren Butz, Gudrun Schmidt-Naake* Institut fu¨r Technische Chemie, TU Clausthal, Erzstr. 18, 38678 Clausthal-Zellerfeld, Germany (Received 15 October 1998) SUMMARY: The bulk polymerization of styrene at 1258C was studied using a [BPO-polystyrene-(4-acet- amido-TEMPO)] macroinitiator synthesized by a styrene polymerization in the presence of 4-acetamido- 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-N-oxyl (4-acetamido-TEMPO) and benzoyl peroxide (BPO). The rates of poly- merization were independent of the initial macroinitiator concentration and they were very similar to that for the thermal autopolymerization of styrene. Additionally, different types of N-oxyls did not have any effect on the polymerization rate. The number-average molecular weights (Mn) of the obtained polymers agreed very well with theoretical predictions, deviations were observed only at low macroinitiator concentrations. Increasing macroinitiator concentrations resulted in lower magnitudes of the growing molecular weights and reduced polydispersities (Mw/Mn) at the initial stage of the polymerization. The concentration of the polymer chains was calculated, and it was recognized that the concentration of polymer chains increased during the polymerization as a result of an additional radical formation due to the thermal self-initiation of styrene. This thermal self-initiation could be proved qualitatively by the addition of N-oxyl to a macroinitiator polymeriza- tion system. ZUSAMMENFASSUNG: Ausgehend von [BPO-Polystyrol-(4-Acetamido-TEMPO)]-Makroinitiatoren wurde die Substanzpolymerisation von Styrol bei 1258C untersucht. Die Polymerisationsgeschwindigkeit war unabha¨ngig von der eingesetzten Makroinitiator-Konzentration und stimmte im Rahmen der Meß- genauigkeit mit der der thermisch initiierten Autopolymerisation von Styrol u¨berein. -

Azo Polymerization Initiators Comprehensive Catalog
Azo Polymerization Initiators Comprehensive Catalog FUJIFILM Wako Pure Chemical Corporation 4-1 Nihonbashi Honcho 2-Chome, Japan Chuo-Ku, Tokyo 103-0023, Japan TEL+81-3-3244-0305 FUJIFILM Wako Chemicals U.S.A. Corporation 1600 Bellwood Road Richmond, USA VA 23237, U.S.A. TEL+1-804-271-7677 FUJIFILM Wako Chemicals Europe GmbH Fuggerstrasse 12 D-41468 Neuss GERMANY Germany TEL+49-2131-311-0 Wako Chemicals (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. C1-C2, 26F, Junyao International Plaza, China 789 Zhaojiabang Road, Shanghai 200032, China TEL+86-21-6407-0511 Specialty Chemicals Web Site http://www.wako-chem.co.jp/kaseihin_en/ 180401 K2 SI 01 Introduction/What is Radical Polymerization? What is Azo Polymerization Initiator? Radical Formation Mechanism 01 INDEX 01 Introduction/What is Radical Polymerization? P1 07 Detailed Explanations 1. Azo Nitrile P11-14 What are Azo Polymerization Initiator? What are Azo Polymerization Initiator? Radical Formation Mechanism P2 2. Azo Ester P15-16 An azo polymerization initiator is a compound having an azo group (R-N=N-R’), which decomposes with heat 3. Azo Amide P17-18 Characteristics of Azo Polymerization Initiators and Comparison with Peroxides P3 02 4. Azo Imidazoline P19-20 and/or light, and forms carbon radical. The formed carbon radical is excellent in reactivity, and progresses polym- Examples of radical reactions using Azo Polymerization Initiators P4 5. Azo Amidine P21-22 erization and halogenation reactions of different types of vinyl monomers. 03 Selection Guide P5-6 6. Macro Azo Initiator P23-26 04 Decomposition -

Free Radical Polymerization
Free Radical Polymerization Reference: Aspen Polymers: Unit Operations and Reaction Models, Aspen Technology, Inc., 2013. 1. Introduction The free-radical bulk/solution polymerization model is applicable to bulk and solution polymerization processes. Some examples of applicable polymers are: - General purpose polystyrene - Made by polymerization of styrene monomer with or without solvent fed continuously to reactor. - High impact polystyrene - Made by polymerization of an unsaturated rubber dissolved in styrene in a solution process. Also produced in suspension processes. - Poly(vinyl chloride) - Produced in bulk polymerization using monomer soluble free radical initiators. Most of the homopolymers and copolymers of vinyl chloride, however, are produced by suspension polymerization. - Poly(vinyl acetate) - Produced industrially by the polymerization of vinyl acetate in bulk or solution processes. Also produced in suspension and emulsion processes. Both batch and continuous processes are used. - Poly(methyl methacrylate) - The vast majority of commercially prepared acrylic polymers and methacrylic polymers are copolymers. Commercially they are prepared by solution polymerization. They are also produced by emulsion and suspension polymerization. - Low density polyethylene - Made by high pressure, free radical processes in either a tubular reactor or a stirred autoclave. Typical commercial processes include staged compression, initiator injection, partial conversion of ethylene to polymer, separation of ethylene from polymer, extrusion of molten polymer, and cooling of ethylene. Bulk and solution polymerization processes are characterized by the fact that the reactions proceed in a single phase. Typically, the monomers are fed to a reactor with or without a solvent. A small amount of initiator is also fed. At the reaction temperature, the initiator decomposes to form radicals that initiate the polymerization reactions. -

Radical Polymerizations II Special Cases
Radical Polymerizations II Special Cases Devon A. Shipp Department of Chemistry, & Center for Advanced Materials Processing Clarkson University Potsdam, NY 13699-5810 Tel. (315) 268-2393, Fax (315) 268-6610 [email protected] 46 © Copyright 2016 Devon A. Shipp Living Polymerizations • Objectives • Requirements – Initiation must be fast – Continuous chain • Ri >> Rp growth – Termination must be – No termination eliminated • Or at least reduced to – Well-defined chains insignificance • Chain structure • Chain length • Problems with free • Molecular weight radical polymerization distribution – Initiation is slow • Block copolymer – Radical-radical synthesis termination is fast 47 Reversible-Deactivation Radical Polymerizations (RDRP) • Often called living radical polymerization activation Dormant polymer Active polymer radical + capping group deactivation Monomer (Propagation) t P h o g l i y e Δ[M] Monomer repeat unit Functional terminal d DP = i W s ( ω ) end ("capping") group [In] r 0 p a e l r u s c X i t e y In l n o M Y Y < 1.5 Initiator ( α ) end 48 % Monomer Conversion Features of Living Polymerizations • Linear increase in • Low polydispersity molecular weight – Mw/Mn < 1.5 (often ~ 1.1) – Vs. monomer conversion • First-order monomer • Pre-defined molecular consumption weight – Same as conventional radical polymerization – DPn = Mn/FWM = Δ[M] / [Initiator] 49 Terminology/Tests for Living Polymerization • Controversy over terminology – Controlled, living, pseudo-living, quasi-living, living/controlled, living/controlled, reversible-deactivation,… • IUPAC definition of living polymerization: – Absence of irreversible transfer and termination • Cannot be applied to any radical polymerization! • Some tests for RDRP: – Continued chain growth after addition monomer added – Molecular weight increases linearly with conversion – Active species (i.e. -

Plasma Polymerization of Amine-Rich Films Aimed at Their Bioapplications
qM qMqM qMqM Previous Page | Contents |Zoom in | Zoom out | Front Cover | Search Issue | Next Page Qmags THE WORLD’S NEWSSTAND® Plasma Polymerization of Amine-Rich Films Aimed at Their Bioapplications Lenka Zajíčková, Anton Manakhov, Petr Skládal, Marek Eliáš, David Nečas, Jan Čechal Central European Institute of Technology – CEITEC, Brno, Czech Republic 2014 TechCon Featured Article Best Poster Winner mine coatings are useful for numerous applications including tissue engineering and biosensing. The bio-applications of Aamine thin films, such as a biomolecule immobilization, biosensors or a cell adhesion enhancement require good layer stability in water. However, typically for allylamine or ammonia/ethylene plasma polymerization, increased plasma polymer cross-linking, leading to improved film stability, is achieved at the expense of the amine-group Figure 1. Examples of monomers suitable for the deposition of amine containing plasma polymers: density. Cyclopropylamine (CPA) is a promising non-toxic monomer a) allylamine, b) ethylenediamine, c) cyclopropylamine, d) diaminocyclohexane and e) n-heptylamine. recently used for the deposition of amine-rich thin films. The stability of the CPA plasma polymers depends on power, discharge mode, Plasma Polymerization of Cyclopropylamine monomer flow rate and the discharge configuration. In this paper Although CPA is not toxic and has a high vapor pressure of 32 kPa at it is demonstrated that the deposition of CPA plasma polymers can 25 oC, the investigation of CPA plasma polymerization has been quite be processed on various substrates including sensor electrodes (for limited. It is surprising because very good results have been already biosensing application) and on the nanofibrous meshes (for a tissue obtained concerning the incorporation of NH2 groups in inductively engineering). -

Effect of Chain Transfer to Polymer in Conventional and Living Emulsion Polymerization Process
processes Article Effect of Chain Transfer to Polymer in Conventional and Living Emulsion Polymerization Process Hidetaka Tobita ID Department of Materials Science and Engineering, University of Fukui, 3-9-1 Bunkyo, Fukui 910-8507, Japan; [email protected]; Tel.: +81-776-27-8767 Received: 28 December 2017; Accepted: 5 February 2018; Published: 7 February 2018 Abstract: Emulsion polymerization process provides a unique polymerization locus that has a confined tiny space with a higher polymer concentration, compared with the corresponding bulk polymerization, especially for the ab initio emulsion polymerization. Assuming the ideal polymerization kinetics and a constant polymer/monomer ratio, the effect of such a unique reaction environment is explored for both conventional and living free-radical polymerization (FRP), which involves chain transfer to the polymer, forming polymers with long-chain branches. Monte Carlo simulation is applied to investigate detailed branched polymer architecture, including 2 the mean-square radius of gyration of each polymer molecule, <s >0. The conventional FRP shows a very broad molecular weight distribution (MWD), with the high molecular weight region conforming to the power law distribution. The MWD is much broader than the random branched 2 polymers, having the same primary chain length distribution. The expected <s >0 for a given MW is much smaller than the random branched polymers. On the other hand, the living FRP shows a much narrower MWD compared with the corresponding random branched polymers. Interestingly, 2 the expected <s >0 for a given MW is essentially the same as that for the random branched polymers. Emulsion polymerization process affects branched polymer architecture quite differently for the conventional and living FRP. -

Polymer Chemistry
Produktinformation Seite 1 von 1 Polymer Chemistry Allison Calhoun, Andrew James Peacock Properties and Application ISBN 3-446-22283-9 Leseprobe Weitere Informationen oder Bestellungen unter http://www.hanser.de/3-446-22283-9 sowie im Buchhandel http://www.hanser.de/deckblatt/deckblatt1.asp?isbn=3-446-22283-9&style=Leseprobe 05.05.2006 2 Polymer Chemistry 2.1 Introduction In this chapter, we will see how polymers are manufactured from monomers. We will explore the chemical mechanisms that create polymers as well as how polymerization methods affect the final molecular structure of the polymer. We will look at the effect of the chemical structure of monomers, catalysts, radicals, and solvents on polymeric materials. Finally, we will apply our molecular understanding to the real world problem of producing polymers on a commercial scale. 2.2 Thermoplastics and Thermosets Thermoplastics consist of linear or lightly branched chains that can slide past one another under the influence of temperature and pressure. These polymers flow at high temperatures, allowing us to mold them into useful products. When we heat and/or shear thermoplastic polymers, we can change their shape. For example, polyethylene milk containers can be reprocessed back into the melt stage and then formed into a park bench.We fi nd thermoplastics in a wide variety of commonly used items, such as pantyhose (polyamide), compact disks (polycarbonate), grocery bags (polyethylene), house siding (polyvinyl chloride), gas and water pipes (polyethylene, polyvinyl chloride, and polypropylene), and medical intravenous fluid bags (polyvinyl chloride). Thermosets consist of a network of interconnected chains whose positions are fi xed relative to their neighbors. -

Free Ethylene Radical Polymerization Under Mild Conditions
View metadata, citation and similar papers at core.ac.uk brought to you by CORE provided by Archive Ouverte en Sciences de l'Information et de la Communication Free Ethylene Radical Polymerization under Mild Conditions: The Impact of the Solvent Etienne Grau, Jean-Pierre Broyer, Christophe Boisson, Roger Spitz, Vincent Monteil To cite this version: Etienne Grau, Jean-Pierre Broyer, Christophe Boisson, Roger Spitz, Vincent Monteil. Free Ethylene Radical Polymerization under Mild Conditions: The Impact of the Solvent. Macromolecules, American Chemical Society, 2009, 42 (19), pp.7279-7281. 10.1021/ma901622u. hal-00944969 HAL Id: hal-00944969 https://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-00944969 Submitted on 26 Nov 2019 HAL is a multi-disciplinary open access L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est archive for the deposit and dissemination of sci- destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents entific research documents, whether they are pub- scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, lished or not. The documents may come from émanant des établissements d’enseignement et de teaching and research institutions in France or recherche français ou étrangers, des laboratoires abroad, or from public or private research centers. publics ou privés. Free ethylene radical polymerization under mild conditions: the impact of the solvent Etienne Grau, Jean-Pierre Broyer, Christophe Boisson, Roger Spitz, Vincent Monteil* Université de Lyon, Univ. Lyon 1, CPE Lyon, CNRS UMR 5265 Laboratoire de Chimie Catalyse Polymères et Procédés (C2P2), LCPP team Bat 308F, 43 Bd du 11 novembre 1918, F-69616 Villeurbanne, France. *[email protected] ABSTRACT: Ethylene polymerization is performed industrially either by radical polymerization under severe conditions (1000-4000 bar, 200-300°C) or by catalytic mechanism at lower temperatures (usually less than 100°C) and pressures (below 50 bar). -

Living/Controlled Radical Polymerizations in Dispersed Phase Systems
Prog. Polym. Sci. 27 *2002) 1039±1067 www.elsevier.com/locate/ppolysci Living/controlled radical polymerizations in dispersed phase systems Michael F. Cunningham* Department of Chemical Engineering, Queen's University, Kingston, Ont., Canada K7L 3N6 Received 5 November 2001; revised 25 January 2002; accepted 28 January 2002 Abstract Living/controlled radical polymerization provides a route to synthesizing materials with designed microstruc- ture and narrow molecular weight distributions. A variety of living radical systems have been developed in recent years, and are based on either reversible termination *SFRP, ATRP) or reversible transfer mechanisms *RAFT, degenerative transfer). Application of living radical polymerization to heterogeneous systems such as emulsion and miniemulsion polymerization may provide process and economic advantages over the traditional homoge- neous bulk and solution polymerizations. However, adaptation of living radical chemistry to aqueous dispersions poses several challenges relating to maintaining effective control over the growth of living chains. These chal- lenges originate from having two or even three phases in the reaction mixture, which can lead to issues related to phase partitioning of the controlling agent, transport of the controlling agent between phases, the role of aqueous phase kinetics, and the phenomena of particle nucleation and colloidal stability. This review examines recent progress in this area, with an emphasis on unresolved issues and future opportunities. q 2002 Elsevier Science Ltd. All rights reserved. Keywords: Living radical polymerization; Controlled radical polymerization; Stable free radical polymerization; Atom transfer radical polymerization; Reversible addition±fragmentation transfer; Degenerative transfer; Emulsion polymerization; Mini- emulsion polymerization Contents 1. Introduction ..................................................................1040 1.1. Scope of the review ........................................................1040 1.2.