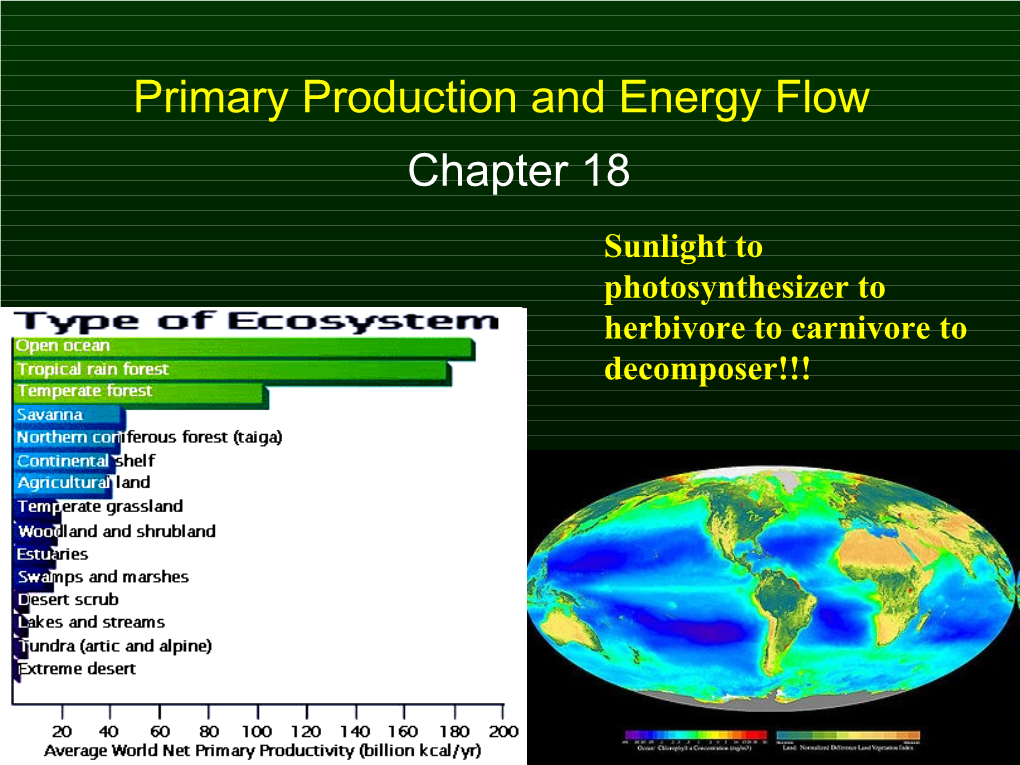
Primary Production and Energy Flow Chapter 18
Total Page:16
File Type:pdf, Size:1020Kb
Load more
Recommended publications
-

Ecosystem Structure and Function. Dr
TOPIC: - ECOSYSTEM STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION. DR. ABHAY KRISHNA SINGH PAPER NAME: - ENVIRONMENTAL GEOGRAPHY SUBJECT: - GEOGRAPHY SEMESTER: - M.A. –IV PAPER CODE: - (GEOG. 403) UNIVERSITY DEPARTMENT OF GEOGRAPHY, DR. SHYMA PRASAD MUKHERJEE UNIVERSITY, RANCHI. Environmental Sciences INTRODUCTION: - All organisms need energy to perform the essential functions such as maintenance, growth, repair, movement, locomotion and reproduction; all of these processes require energy expenditure. The ultimate source of energy for all ecological systems is Sun. The solar energy is captured by the green plants (primary producers or autotrophs) and transformed into chemical energy and bound in glucose as potential energy during the process of photosynthesis. In this stored form, other organisms take the energy and pass it on further to other organisms. During this process, a reasonable proportion of energy is lost out of the living system. The whole process is called flow of energy in the ecosystem. It is the amount of energy that is received and transferred from organism to organism in an ecosystem that modulates the ecosystem structure. Without autotrophs, there would be no energy available to all other organisms that lack the capability of fixing light energy. A fraction i.e. about 1/50 millionth of the total solar radiation reaches the earth’s atmosphere. About 34% of the sunlight reaching the earth’s atmosphere is reflected back into the atmosphere, 10% is held by ozone layer, water vapors and other atmospheric gases. The remaining 56% sunlight reaches the earth’s surface. Only a fraction of this energy reaching the earth’s surface (1 to 5%) is used by green plants for photosynthesis and the rest is absorbed as heat by ground vegetation or water. -

7.014 Handout PRODUCTIVITY: the “METABOLISM” of ECOSYSTEMS
7.014 Handout PRODUCTIVITY: THE “METABOLISM” OF ECOSYSTEMS Ecologists use the term “productivity” to refer to the process through which an assemblage of organisms (e.g. a trophic level or ecosystem assimilates carbon. Primary producers (autotrophs) do this through photosynthesis; Secondary producers (heterotrophs) do it through the assimilation of the organic carbon in their food. Remember that all organic carbon in the food web is ultimately derived from primary production. DEFINITIONS Primary Productivity: Rate of conversion of CO2 to organic carbon (photosynthesis) per unit surface area of the earth, expressed either in terns of weight of carbon, or the equivalent calories e.g., g C m-2 year-1 Kcal m-2 year-1 Primary Production: Same as primary productivity, but usually expressed for a whole ecosystem e.g., tons year-1 for a lake, cornfield, forest, etc. NET vs. GROSS: For plants: Some of the organic carbon generated in plants through photosynthesis (using solar energy) is oxidized back to CO2 (releasing energy) through the respiration of the plants – RA. Gross Primary Production: (GPP) = Total amount of CO2 reduced to organic carbon by the plants per unit time Autotrophic Respiration: (RA) = Total amount of organic carbon that is respired (oxidized to CO2) by plants per unit time Net Primary Production (NPP) = GPP – RA The amount of organic carbon produced by plants that is not consumed by their own respiration. It is the increase in the plant biomass in the absence of herbivores. For an entire ecosystem: Some of the NPP of the plants is consumed (and respired) by herbivores and decomposers and oxidized back to CO2 (RH). -

Bacterial Production and Respiration
Organic matter production % 0 Dissolved Particulate 5 > Organic Organic Matter Matter Heterotrophic Bacterial Grazing Growth ~1-10% of net organic DOM does not matter What happens to the 90-99% of sink, but can be production is physically exported to organic matter production that does deep sea not get exported as particles? transported Export •Labile DOC turnover over time scales of hours to days. •Semi-labile DOC turnover on time scales of weeks to months. •Refractory DOC cycles over on time scales ranging from decadal to multi- decadal…perhaps longer •So what consumes labile and semi-labile DOC? How much carbon passes through the microbial loop? Phytoplankton Heterotrophic bacteria ?? Dissolved organic Herbivores ?? matter Higher trophic levels Protozoa (zooplankton, fish, etc.) ?? • Very difficult to directly measure the flux of carbon from primary producers into the microbial loop. – The microbial loop is mostly run on labile (recently produced organic matter) - - very low concentrations (nM) turning over rapidly against a high background pool (µM). – Unclear exactly which types of organic compounds support bacterial growth. Bacterial Production •Step 1: Determine how much carbon is consumed by bacteria for production of new biomass. •Bacterial production (BP) is the rate that bacterial biomass is created. It represents the amount of Heterotrophic material that is transformed from a nonliving pool bacteria (DOC) to a living pool (bacterial biomass). •Mathematically P = µB ?? µ = specific growth rate (time-1) B = bacterial biomass (mg C L-1) P= bacterial production (mg C L-1 d-1) Dissolved organic •Note that µ = P/B matter •Thus, P has units of mg C L-1 d-1 Bacterial production provides one measurement of carbon flow into the microbial loop How doe we measure bacterial production? Production (∆ biomass/time) (mg C L-1 d-1) • 3H-thymidine • 3H or 14C-leucine Note: these are NOT direct measures of biomass production (i.e. -

GLOBAL PRIMARY PRODUCTION and EVAPOTRANSPIRATION by Steven W
15 GLOBAL PRIMARY PRODUCTION AND EVAPOTRANSPIRATION by Steven W. Running and Maosheng Zhao DATA PRODUCTS Moderate Resolution Imaging Spectroradiometer Terrestrial primary production provides the energy to (MODIS) sensor, these variables are calculated maintain the structure and functions of ecosystems, every eight days in near real time at 1 km resolution. and supplies goods (e.g. food, fuel, wood and fi bre) MODIS GPP, NPP and ET data are available at the for human society. Gross primary production (GPP) EOS data gateway (see link below). is the amount of carbon fi xed by photosynthesis, To correct for contamination in the global and net primary production (NPP) is the amount of refl ectance data due to severe cloudiness or aerosols carbon converted into biomass after subtracting in the near real time products, these datasets are the cost of plant respiration. The water loss through reprocessed at the end of each year to build more exchange of trace gas CO2 by leaf stomata during stable, permanent datasets. These end-of-year photosynthesis plus evaporation from soil and versions of MODIS GPP, NPP and ET are available at plants is evapotranspiration (ET). ET computes the NTSG, University of Montana (see link below). water lost by a land surface, so it is consequently a component of the water balance in a region, and RESULTS FOR 2000–2006 is therefore relevant for drought monitoring and Figure 1 shows the seven-year average MODIS water management, providing an assessment of NPP for vegetated land on earth at 1 km spatial the water potentially available for human society. -

Lesson Overview from There Depends on Who Eats Whom! 3.3 Energy Flow in Ecosystems
THINK ABOUT IT What happens to energy stored in body tissues when one organism eats another? Energy moves from the “eaten” to the “eater.” Where it goes Lesson Overview from there depends on who eats whom! 3.3 Energy Flow in Ecosystems Food Chains A food chain is a series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten. Food chains can vary in length. An example from the Everglades is shown. Food Chains Food Chains In some aquatic food chains, such as the example shown, Larger fishes, like the largemouth bass, eat the small fishes. primary producers are a mixture of floating algae called The bass are preyed upon by large wading birds, such as the phytoplankton and attached algae. These producers are anhinga, which may ultimately be eaten by an alligator. eaten by small fishes, such as flagfish. Food Chains Food Webs There are four steps in this food chain. In most ecosystems, feeding relationships are much more The top carnivore is four steps removed from the primary complicated than the relationships described in a single, simple producer. chain because many animals eat more than one kind of food. Ecologists call this network of feeding interactions a food web. An example of a food web in the Everglades is shown. Food Chains Within Food Webs Decomposers & Detritivores in Food Webs Each path through a food web is a food chain. Most producers die without being eaten. In the detritus A food web, like the one shown, links all of the food chains in an pathway, decomposers convert that dead material to detritus, ecosystem together. -

Trophic Levels
Trophic Levels Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. Jean Brainard, Ph.D. Say Thanks to the Authors Click http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (No sign in required) AUTHORS Douglas Wilkin, Ph.D. To access a customizable version of this book, as well as other Jean Brainard, Ph.D. interactive content, visit www.ck12.org CK-12 Foundation is a non-profit organization with a mission to reduce the cost of textbook materials for the K-12 market both in the U.S. and worldwide. Using an open-content, web-based collaborative model termed the FlexBook®, CK-12 intends to pioneer the generation and distribution of high-quality educational content that will serve both as core text as well as provide an adaptive environment for learning, powered through the FlexBook Platform®. Copyright © 2015 CK-12 Foundation, www.ck12.org The names “CK-12” and “CK12” and associated logos and the terms “FlexBook®” and “FlexBook Platform®” (collectively “CK-12 Marks”) are trademarks and service marks of CK-12 Foundation and are protected by federal, state, and international laws. Any form of reproduction of this book in any format or medium, in whole or in sections must include the referral attribution link http://www.ck12.org/saythanks (placed in a visible location) in addition to the following terms. Except as otherwise noted, all CK-12 Content (including CK-12 Curriculum Material) is made available to Users in accordance with the Creative Commons Attribution-Non-Commercial 3.0 Unported (CC BY-NC 3.0) License (http://creativecommons.org/ licenses/by-nc/3.0/), as amended and updated by Creative Com- mons from time to time (the “CC License”), which is incorporated herein by this reference. -

Phytoplankton As Key Mediators of the Biological Carbon Pump: Their Responses to a Changing Climate
sustainability Review Phytoplankton as Key Mediators of the Biological Carbon Pump: Their Responses to a Changing Climate Samarpita Basu * ID and Katherine R. M. Mackey Earth System Science, University of California Irvine, Irvine, CA 92697, USA; [email protected] * Correspondence: [email protected] Received: 7 January 2018; Accepted: 12 March 2018; Published: 19 March 2018 Abstract: The world’s oceans are a major sink for atmospheric carbon dioxide (CO2). The biological carbon pump plays a vital role in the net transfer of CO2 from the atmosphere to the oceans and then to the sediments, subsequently maintaining atmospheric CO2 at significantly lower levels than would be the case if it did not exist. The efficiency of the biological pump is a function of phytoplankton physiology and community structure, which are in turn governed by the physical and chemical conditions of the ocean. However, only a few studies have focused on the importance of phytoplankton community structure to the biological pump. Because global change is expected to influence carbon and nutrient availability, temperature and light (via stratification), an improved understanding of how phytoplankton community size structure will respond in the future is required to gain insight into the biological pump and the ability of the ocean to act as a long-term sink for atmospheric CO2. This review article aims to explore the potential impacts of predicted changes in global temperature and the carbonate system on phytoplankton cell size, species and elemental composition, so as to shed light on the ability of the biological pump to sequester carbon in the future ocean. -

Model-Based Analysis of the Energy Fluxes and Trophic Structure of a Portunus Trituberculatus Polyculture Ecosystem
Vol. 9: 479–490, 2017 AQUACULTURE ENVIRONMENT INTERACTIONS Published December 5 https://doi.org/10.3354/aei00247 Aquacult Environ Interact OPENPEN ACCESSCCESS Model-based analysis of the energy fluxes and trophic structure of a Portunus trituberculatus polyculture ecosystem Jie Feng1, Xiang-Li Tian1,*, Shuang-Lin Dong1, Rui-Peng He1, Kai Zhang1, Dong-Xu Zhang1, Qing-Qi Zhang2 1The Key Laboratory of Mariculture, Ministry of Education, Fisheries College, Ocean University of China, Qingdao 266003, PR China 2Marine Fishery Technology Guiding Office of Ganyu, Lianyungang 222100, PR China ABSTRACT: We constructed a quantitative Ecopath model of a trophic network to evaluate the energy flow and properties in a polyculture ecosystem containing 4 species (swimming crab Por- tunus trituberculatus, white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei, short-necked clam Ruditapes philip- pinarum, and redlip mullet Liza haematochila) over a 90 d experimental period. The model con- tained 10 consumers, 4 detritus groups, and 4 primary producers. Ecotrophic efficiency values indicated that the system had high energy utilization efficiency. However, benthic bacteria con- verted the largest amount of energy back to the detritus groups, which had the lowest ecotrophic efficiency (0.01). When aggregating the network to discrete trophic levels (TLs), most of the throughput and biomass of the system were distributed on the first 2 TLs; consequently, there was high energy transfer efficiency between TL I and II (81.98%). The trophic flow of this ecosystem was dominated by energy that originated from the detritus groups (73.77%). Imported artificial food was particularly important for the trophic flow of the total ecosystem, contributing 31.02% to total system consumption. -

Structure of Tropical River Food Webs Revealed by Stable Isotope Ratios
OIKOS 96: 46–55, 2002 Structure of tropical river food webs revealed by stable isotope ratios David B. Jepsen and Kirk O. Winemiller Jepsen, D. B. and Winemiller, K. O. 2002. Structure of tropical river food webs revealed by stable isotope ratios. – Oikos 96: 46–55. Fish assemblages in tropical river food webs are characterized by high taxonomic diversity, diverse foraging modes, omnivory, and an abundance of detritivores. Feeding links are complex and modified by hydrologic seasonality and system productivity. These properties make it difficult to generalize about feeding relation- ships and to identify dominant linkages of energy flow. We analyzed the stable carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios of 276 fishes and other food web components living in four Venezuelan rivers that differed in basal food resources to determine 1) whether fish trophic guilds integrated food resources in a predictable fashion, thereby providing similar trophic resolution as individual species, 2) whether food chain length differed with system productivity, and 3) how omnivory and detritivory influenced trophic structure within these food webs. Fishes were grouped into four trophic guilds (herbivores, detritivores/algivores, omnivores, piscivores) based on literature reports and external morphological characteristics. Results of discriminant function analyses showed that isotope data were effective at reclassifying individual fish into their pre-identified trophic category. Nutrient-poor, black-water rivers showed greater compartmentalization in isotope values than more productive rivers, leading to greater reclassification success. In three out of four food webs, omnivores were more often misclassified than other trophic groups, reflecting the diverse food sources they assimilated. When fish d15N values were used to estimate species position in the trophic hierarchy, top piscivores in nutrient-poor rivers had higher trophic positions than those in more productive rivers. -

Ecology (Pyramids, Biomagnification, & Succession
ENERGY PYRAMIDS & Freshmen Biology FOOD CHAINS/FOOD WEBS May 4 – May 8 Lecture ENERGY FLOW •Energy → powers life’s processes •Energy = ATP! •Flow of energy determines the system’s ability to sustain life FEEDING RELATIONSHIPS • Energy flows through an ecosystem in one direction • Sun → autotrophs (producers) → heterotrophs (consumers) FOOD CHAIN VS. FOOD WEB FOOD CHAINS • Energy stored by producers → passed through an ecosystem by a food chain • Food chain = series of steps in which organisms transfer energy by eating and being eaten FOOD WEBS •Feeding relationships are more complex than can be shown in a food chain •Food Web = network of complex interactions •Food webs link all the food chains in an ecosystem together ECOLOGICAL PYRAMIDS • Used to show the relationships in Ecosystems • There are different types: • Energy Pyramid • Biomass Pyramid • Pyramid of numbers ENERGY PYRAMID • Only part of the energy that is stored in one trophic level can be passed on to the next level • Much of the energy that is consumed is used for the basic functions of life (breathing, moving, reproducing) • Only 10% is used to produce more biomass (10 % moves on) • This is what can be obtained from the next trophic level • All of the other energy is lost 10% RULE • Only 10% of energy (from organisms) at one trophic level → the next level • EX: only 10% of energy/calories from grasses is available to cows • WHY? • Energy used for bodily processes (growth/development and repair) • Energy given off as heat • Energy used for daily functioning/movement • Only 10% of energy you take in should be going to your actual biomass/weight which another organism could eat BIOMASS PYRAMID • Total amount of living tissue within a given trophic level = biomass • Represents the amount of potential food available for each trophic level in an ecosystem PYRAMID OF NUMBERS •Based on the number of individuals at each trophic level. -

Determination of Trophic Relationships Within a High Arctic Marine Food Web Using 613C and 615~ Analysis *
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Published July 23 Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. Determination of trophic relationships within a high Arctic marine food web using 613c and 615~ analysis * Keith A. ~obson'.2, Harold E. welch2 ' Department of Biology. University of Saskatchewan, Saskatoon, Saskatchewan. Canada S7N OWO Department of Fisheries and Oceans, Freshwater Institute, 501 University Crescent, Winnipeg, Manitoba, Canada R3T 2N6 ABSTRACT: We measured stable-carbon (13C/12~)and/or nitrogen (l5N/l4N)isotope ratios in 322 tissue samples (minus lipids) representing 43 species from primary producers through polar bears Ursus maritimus in the Barrow Strait-Lancaster Sound marine food web during July-August, 1988 to 1990. 613C ranged from -21.6 f 0.3%0for particulate organic matter (POM) to -15.0 f 0.7%0for the predatory amphipod Stegocephalus inflatus. 615~was least enriched for POM (5.4 +. O.8%0), most enriched for polar bears (21.1 f 0.6%0), and showed a step-wise enrichment with trophic level of +3.8%0.We used this enrichment value to construct a simple isotopic food-web model to establish trophic relationships within thls marine ecosystem. This model confirms a food web consisting primanly of 5 trophic levels. b13C showed no discernible pattern of enrichment after the first 2 trophic levels, an effect that could not be attributed to differential lipid concentrations in food-web components. Although Arctic cod Boreogadus saida is an important link between primary producers and higher trophic-level vertebrates during late summer, our isotopic model generally predicts closer links between lower trophic-level invertebrates and several species of seabirds and marine mammals than previously established. -

Phytoplankton Primary Production and Its Utilization by the Pelagic Community in the Coastal Zone of the Gulf of Gdahsk (Southern Baltic)
MARINE ECOLOGY PROGRESS SERIES Vol. 148: 169-186. 1997 Published March 20 Mar Ecol Prog Ser l Phytoplankton primary production and its utilization by the pelagic community in the coastal zone of the Gulf of Gdahsk (southern Baltic) Zbigniew Witekl-*,Stanislaw Ochockil, Modesta ~aciejowska~, Marianna Pastuszakl, Jan ~akonieczny',Beata podgorska2, Janina M. ~ownacka', Tomasz Mackiewiczl, Magdalena Wrzesinska-Kwiecieh' 'Sea Fisheries Institute, ul. Koltqtaja 1, 81-332 Gdynia, Poland 'Marine Biology Center, Polish Academy of Sciences, ul. SW. Wojciecha S,81-347 Gdynia, Poland ABSTRACT In th~sstudy we estimated the amount and fate of phytoplankton primary product~onin the coastal zone of the Gulf of Gdansk, Poland, an area exposed to nutnent enrichment from the Vis- tuld R~verand nearby inunlcipal agglomeration The ~nvestigat~onswere carned out at 2 sites dur~ng 5 months in 1993 (February, April, May, August and October). A prolonged bloom pei-iod occurred in the coastal zone, as compared to the open Gulf and the open sea waters. From Aprll until October most values of gross primary production in the near-surface layer were in the range 100 to 500 mgC m-'' d1 Phytoplankton net exudate release constituted on average 5% of the gross prlmai-y production, total exudate release was estimated to be about 2 times h~gher.Bacterial production in the growth season was relatively low (the mean value ly~ngbetween 5 and 9%of gloss primary production), nevertheless, the microbial community (bactena and protozoans) ut~l~zeda large proportion of primary production (from about 50% in April and May to 16'%, in October).